Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review of Cloud Computing Environment
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views6 pagesInternational Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March – April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Original Title
IJETTCS-2014-04-04-061
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInternational Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March – April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views6 pagesReview of Cloud Computing Environment
International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March – April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
International Journal of EmergingTrends & Technology in Computer Science(IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Volume 3, Issue 2 March April 2014 Page 75
Abstract: This paper present a review on cloud
computing. Cloud computing is becoming the hottest
issue in IT world. Cloud computing is the Internet
based computing where essential shared servers provide
software, infrastructure, platform, devices and other
resources and offering to customers on a pay-as-you-
use basis. It is often said that the cloud computing is a
type of computing where scalable, flexible, and supple
IT abilities are provided as a service to multiple
customers. The overall objective of this work is to
evaluate the gaps in earlier work in cloud computing
and finding the suitable solution for the same.
Keywords: XaaS, Cloud computing, Pay as you use, On-
demand.
1. INTRODUCTION
Cloud computing is one of the fieriest, evolving
technology in the IT world. The term cloud is parallel to
the Internet. But in actual cloud computing model, this
means having all the software and data held on a server
or a group of servers, and accessing them through the
internet. In some cases the client is simply a device
furnished with a nominal OS and running a web browser.
Users can use these services available on the cloud
without knowing how the managing of the resources is
done. Thus the users can only focus on their processing
rather than wasting time and attaining knowledge on the
resources needed to cope up their processes. To view
cloud computing is to think of the email account. To
access the account, open the browser, go to the email
client and simply log-in and the important part is to have
the Internet access. The email account is not housed i.e.
the whole of the Yahoo or Gmail software is not installed
on the computer instead it is accessed by the Internet
connection.
Figure 1: Cloud computing
2. CLOUD COMPUTING CHARACTERISTICS
2.1 On-Demand
A basic idea of the cloud computing is to deliver the
resources whenever there is need. From the users point
of view the available computing resources are nearly
unlimited i.e., the customer does not care about the set of
servers located at one site thus it is the duty of the cloud
computing provider to have adequate resources to fulfil
the requests of all their customers. Employing computing
resources on-demand is one of the most preferred abilities
for a large number of enterprises because it removes the
need for planning forward, acquiring, and fixing the
resources they may require at some point in the future.
This allows the customer to prevent making a needless
investment in servers.
2.2 Pay-per-use
In case of cloud computing the customer pays only on the
basis of the usage whereas in the case of the traditional
computing there is a need to locate the resources
physically on the customer side. The cloud computing
provides the facility of paying the service provider
depending only on the use of the customer.
Figure 2: Cloud computing working
2.3 Rapid elasticity
The cloud provider scales up or down the resources
depending upon the specific of a service level agreement
that are provided for the changing customer needs. This
service defines the time for the cloud provider to response
back. Such an contract is required by the cloud provider,
because the cloud provider does not in fact have countless
resources, so depending upon the service level agreement
the provider has to discover a set of distributions of
resources that fulfil the demands of their users otherwise
the service level agreement require a penalty that the
provider has to pay to each customer for not meeting the
agreement.
2.4 Maintenance and upgrading
The provider maintains the computing resource rather
than the user. Thus the provider preserves and updates
Review of Cloud Computing Environment
Amandeep Kaur
1
, Jasjit Kaur
2
1&2
Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, Guru Nanak Dev
University Amritsar, Punjab, 143001, India
International Journal of EmergingTrends & Technology in Computer Science(IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Volume 3, Issue 2 March April 2014 Page 76
the resources. Thus all improvement of the resources are
hidden from the users view, but this might be true in the
ideal case. Sometimes due to some of the reasons the
customer is shifted from one platform to the other, in that
case the customer may be provided with any resource.
3. CLOUD COMPUTING V/S GRID COMPUTING
Cloud computing and grid computing are often
considered to be same but they are quite different. Cloud
computing comes from grid computing and provides on-
demand resource to the user on the usage basis. If the
users are systems managers and integrators, they do care
how things are maintained in the cloud. However if the
users are consumers, they do not. They are only
concerned about the usage but not of the management of
the cloud. Grid computing requires the use of software
that can split and allocate fragments of a program as one
large system copy to several thousand computers.
The grids are homogeneous. The Grid are
characteristically dispersed by its nature over a LAN,
MAN or WAN. Grid computing is applicable on the
resources of the computer to solve a single problem. The
example of grid computing is SETI i.e. Search for Extra-
terrestrial Intelligence @ Home project. With the help of
SETI the unused cycles of the computers are used to
search the signs of intelligence in the specified time.
Another example of Grid Computing is Berkeley Open
Infrastructure for Network Computing (BOINC). In this
project the idle cycles of the CPU are used to do protein
finding experiments.
4. CLOUD COMPUTING TYPES
The clouds are of mainly four types.
4.1 Private Cloud
The cloud infrastructure has been arranged, and is
preserved and functioned for a specific organization.
They are used by that group. A pure private cloud is built
for the private use of one customer, who keeps and fully
controls this cloud. The distinguishing feature of any
private cloud is that the fact that the cloud is used by a
specific customer. A private cloud might be maintained
by the client, but built, fixed, and accomplished by a third
party rather than the client. The physical servers might be
situated at the customers sites. The substitute to a private
cloud is a virtual private cloud. In such a virtual private
cloud a customer is assigned a private cloud within the
physical setup of a public cloud. Due to the sharing of
definite resources within the cloud the customer can be
guaranteed that their data stored on and processing is
done only on devoted servers.
4.2 Public Cloud
The cloud infrastructure is accessible to the public by a
cloud service provider with the Internet connection. This
allows a customer to use a service in the cloud with pay-
as-you-go basis instead of purchasing the whole cloud.
Community Cloud: The cloud infrastructure is shared
between a large number of organizations with like
interests and needs. This help in reducing the capital
expenditure costs as the expenses are united among the
organizations.
Figure 3: Deployment Models
4.3 Hybrid Cloud
Figure 4: Hybrid Cloud
The cloud infrastructure comprises of a number of clouds
of any type, but the clouds have the capability through
their interfaces to be transferred from one cloud to
another. This can be a blend of private and public clouds
that support the requirement to hold some data in an
organization, and also the need to offer facilities in the
cloud.
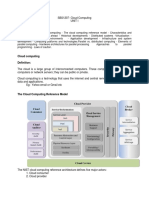
5. SERVICES
Every service provider provides a specific function
allowing user to have less or more control on the cloud
depending on the type i.e. private, public, hybrid or
community. The cloud need vary depending on how the
cloud will be used i.e. the space and the resources related
with the cloud. Cloud computing can be classified by the
model of service it offers into many different groups.
These are defined using the XaaS taxonomy, where X
can be Software, Platform, or Infrastructure, and the final
"S" is for Service.
In addition to above some professionals list the following
building blocks of cloud computing:
1. Storage-as-a-Service
2. Database-as-a-Service
International Journal of EmergingTrends & Technology in Computer Science(IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Volume 3, Issue 2 March April 2014 Page 77
3. Information-as-a-Service
4. Process-as-a-Service
5. Application-as-a-Service
6. Integration-as-a-Service
7. Security-as-a-Service
8. Management/Governance-as-a-Service
9. Testing-as-a-Service
5.1 Software as a Service (SaaS)
A SaaS provider gives subscribed or pay-as-you-use user
access to both resources and services. SaaS makes it
preventable to have a physical copy of software to install
on the devices. SaaS makes easier to have the same
software on all of your devices at once by accessing it on
the cloud. In a SaaS agreement, one have the least control
over the cloud. An example of SaaS is Google Docs. It is
a group that is free for everyone to use. Creating accounts
is free. By login-in access to the word processor,
spreadsheet is given. These various online services
provided by google are accomplished from the thin client
i.e. web browser and requires no installation.
5.2 Platform as a Service (PaaS)
A PaaS system is above the Software as a Service
arrangement. A PaaS provider gives subscribers
admission to the components that they require to grow
and function applications over the internet. One of the
common example of PaaS is Facebook. Designers and
developers can generate any application for the Facebook
platform using APIs and make that app available to the
users.
5.3 Infrastructure as a Service
An IaaS system deals mainly with computational
infrastructure. It offers the subscriber to completely
outsource the storage and resources that they want for
computation. An example of IaaS is Amazon EC2. From
the small to full-blown sites, it provided the cloud
infrastructure facility to run them all.
Figure 5: Cloud Computing service Model
5.4 Software as a Service
Software as a Service (SaaS) is the model in which an
application is held as a service which is provided to
customers who can have access to it via the Internet.
When the software is presented off site, the customers
dont have to uphold it or care for it. On the other hand, it
is not in the customers hands when the hosting service
decides to change it. The idea is to use the software as it
is and it is not essential to make a lot of changes or
require incorporation to other system. The provider does
all the repairing and advancements as well as keeping the
infrastructure running.
The cost for using the software is the on-going process
i.e. the user pay for the service as much it is being used.
Instead of paying it once, it is like the more the service is
being used, the more it be billed. There are many types of
software that offer themselves to the SaaS model.
Customers who are not liable to perform software
development but need applications, they use SaaS.
The most important benefit of SaaS is none other than
costing less money rather than purchasing the whole
application. Some of the benefits of SaaS are:
Figure 3: SaaS service provider
A. Familiarity with the World Wide Web: Almost
everyone have access to the computer and knows how to
use Internet. Thus helping the customers to use the
services. Smaller Staff: IT systems generally requires
small staff because of the overhead associated with the
salaries and other benefits. The ability to host the
applications reduces the need of such huge IT staff.
B. Customization: SaaS applications are easily
customizable as compared to the older ones.
Better Marketing: With the SaaS the applications are
open to all the customers which was earlier difficult
because the developer who has marketed the small
application may have had a problem marketing the huge
application.
C. Security: The Secure socket layer (SSL) is used. This
allows the customers to reach their applications securely
without having to hire complex back end configuration.
More Bandwidth: As the bandwidth is increasing, this
allows the users to access the applications with low
latencies and good speeds.
D. Difficulties of SaaS: Like everything, SaaS also have
some difficulties in its employment and use. It may be
possible that an organization which has a specific need
International Journal of EmergingTrends & Technology in Computer Science(IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Volume 3, Issue 2 March April 2014 Page 78
may not available through SaaS. In that case they may
have to buy the software as a whole and install on the
specified machine. It may also be possible that the
customer have paid for the application but later they are
not able to port that application to the new vendor.
6. RELATED WORK
Dong et al. (2013) [1] has studied that as with the
progress of cloud computing, many applications have
been reinforced to offer in the cloud computing, which in
turn increase the availability. As the resources are
generally dispersed, active and heterogeneous so first, a
monitoring model of cloud computing resources
availability is created and then, according to the dynamic
process of the cloud computing service, the availability of
cloud computing resources is investigated from QoS of a
single cloud resource node which is defined by mutual
attribution and special attribution to QoS of some cloud
resources which are connected by series model, parallel
model and mix model to provide service. According to the
analysis of the each cloud service resource, the
availability of cloud computing service is monitored.
Meng et al. (2013) [2] has analysed the cloud computing
security in digital library. The cloud computing approach
of library digital resources is defined, then a gatherings of
databases and network resources is adopted to provide
their service, then these resources and facilities are placed
in the cloud. And then the cloud key distribution scheme
to opt to library applications is done. The better
traditional PKI, the PKI-based cloud computing
communication and secrecy protection mechanisms for
library are introduced.
Chalse et al. (2013) [3] has analysed the cloud security
problem, the various issues in a cloud computing system
and their effect upon the different cloud users. As the
cloud computing environment is constructed based on
open Architecture and interface so the various computing
system and their outcome upon the system, upon
organizations and also upon different cloud operators are
analysed. A view of activities that can be taken to deal
with the cloud security problem and prevention that must
be taken into account by any organization and cloud users
seeking investment in cloud computing are also
presented.
Jaber et al. (2013) [4] has demonstrated that the cloud
computing i.e. the cloud computing is gaining popularity
in every field. Also the cloud computing initiated from a
commercial enterprise notion, and established into a
healthy IT creation. In fact the cloud computing is ahead
but, customers remain hesitant to organise their
commercial enterprise into the cloud which is due to the
lack of protection. The main reason is the complexity
which is involved in managing the information on the
cloud. So the different cryptography aspects that cause a
threat to the cloud computing environment should be
known to the user.
Guan et al. (2013) [5] has discussed the gaining
popularity of cloud computing and the various problems
associated with the hardware and software faults and the
various factors such as environmental. To identify strange
cloud behaviours, the cloud execution is monitored and
runtime performance data is collected. The collected data
consists of performance metrics for different types of
failures, which display different correlations with the
performance metrics. This paper has proposed the
mechanism that discovers the components of different
failure types in cloud computing infrastructures. It also
discussed the performance metric by examining the
techniques to attain efficient identification.
Zhang et al. (2013) [6] has discussed that the Cloud
computing as typical Internet-based applications is
lacking in carrier-grade signalling control mechanism
and cannot guarantee Quality of Service (QoS), which is
in turn a barrier for telecom operator. On the other side,
as the core signalling architecture of Next Generation
Networking (NGN), IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) is
facing the difficulty of the absence of innovative value-
added services. This paper has proposed an architecture
to provision cloud computing services over IMS. The
cloud services are considered as the common IMS
applications and then cloud customers are allowed to
access cloud services under the control of Session
Initiation Protocol (SIP) signalling and QoS mechanism
of IMS.
Guan et al. (2012) [7] has discussed the gaining
popularity of cloud computing and the various problems
associated with the hardware and software faults and the
various factors such as environmental. Dependability
guarantee is critical for constructing justifiable cloud
computing services. As the virtualization is an enabling
technology for the cloud, it is important to explore the
effect of virtualization on the cloud dependability. The
cloud dependability analysis (CDA) framework with
methods to describe failure behaviour in cloud computing
infrastructures is proposed. The failure-metric DAGs
(directed a cyclic graph) to examine the relationship of
several performance metrics with failure actions in
virtualized and non-virtualized systems is also proposed.
The generated DAGs in the two environments are
compared to examine the impact of virtualization on the
cloud dependability.
Liu, W. (2012) [8] has studied the cloud computing. The
cloud computing is related to the other computings such
as grid computing, distributed computing, parallel
computing and so on. As the cloud computing is related
to the data storage, reliability and services so the security
is the main concern of the cloud computing. The security
can avert the speedy growth of cloud computing. This
International Journal of EmergingTrends & Technology in Computer Science(IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Volume 3, Issue 2 March April 2014 Page 79
paper discusses the few cloud computing systems and
investigates cloud computing security issues and its
policies according to the cloud computing concepts and
characters. As the single security method cannot resolve
the cloud computing security issue so many traditional
and new technologies and strategies should be used in a
collective manner for protecting the total cloud
computing system.
Zhao, Wei, et al. (2012) [9] has discussed that the cloud
computing delivers computing resources as a service over
a web. As it is the emerging technology, it becomes
essential to evaluate the performance and security issues
that cloud computing meets. Currently, demonstrating
and imitation technology has become an influential tool
in cloud computing research group to handle these issues.
This paper states that there are two types of cloud
computing simulators, that is, simulators just based on
software and simulators based on both software and
hardware.
Xin et al. (2012) [10] has studied the concept of cloud
computing and stated that it is considered to be the next
generation of information technology framework. It can
deliver dynamic resource pools, virtualization and high
obtainability. The new development comes with lots of
new challenges also.as a result a secure computing
environment should be built. The method to make secure
cloud computing is the multi-dimension architecture. It is
a three layer model .at the first the user authentication is
essential to confirm that user data cannot be tampered.
Mollah et al. (2012) [11] has studied the cloud computing
which is one of the evolving topic in the field of
information technology. It focus on all computation
resources and manage mechanically through the software
without interference. As there are different layers present
in the cloud computing architecture, service types etc. as
a result the architecture, advantages, platforms, issues
and challenges, etc. are studied. The four generations of
computing such as mainframe based computing, personal
computing, client server based computing and web server
based computing respectively has its own pros and cons.
Thus the cloud computing is the next generation of the
computing services.
Sim and Mong (2012) [12] examined the Agent-based
cloud computing which is related with the design and
development of software agents for enhancing cloud
service discovery, service etc. An agent-based model for
constructing software tools and test beds for cloud
resource management. Agent-based cloud computing
introduces the developing of Cloudle: an agent-based
search engine for cloud service detection, showing that
agent-based co-operation mechanisms can be efficiently
accepted for boosting cloud service co-operation and
cloud business, and presenting that agent-based
cooperative problem-solving techniques can be effectively
adopted for automating cloud service composition. For
the cloud business, this developed a multifaceted cloud
negotiation mechanism that supports parallel negotiation
activities in interrelated markets: a cloud service market
between consumer agents and dealer agents, and multiple
cloud resource markets between broker agents and
provider agents.
7. GAPS IN EARLIER WORK
The survey has shown that the most of the existing
researchers has neglected at least one of the followings:-
a. The use of scalability in software has been
neglected by many researchers.
b. The scalability of the number of cloud user has also
been neglected.
c. The effect of the response time has also been
neglected.
8. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
The survey has shown that the most of the existing
researchers has neglected the scalability of cloud users in
cloud computing environment. The response time of the
users has also found to be a critical issue in cloud
computing. So in near future we will extend this work to
overcome the scalability issue of cloud computing either
in SaaS or in the number of users.
References
[1] Dong, Wang En, Wu Nan, and Li Xu. "QoS-Oriented
Monitoring Model of Cloud Computing Resources
Availability." Computational and Information
Sciences (ICCIS), 2013 Fifth International
Conference on. IEEE, 2013.
[2] Meng, Qingjie, and Changqing Gong. "Research of
cloud computing security in digital
library." Information Management, Innovation
Management and Industrial Engineering (ICIII),
2013 6th International Conference on. Vol. 2. IEEE,
2013.
[3] Chalse, Rajkumar, Ashwin Selokar, and Arun
Katara. "A New Technique of Data Integrity for
Analysis of the Cloud Computing
Security." Computational Intelligence and
Communication Networks (CICN), 2013 5th
International Conference on. IEEE, 2013.
[4] Jaber, Aws Naser, and Mohamad Fadli Bin Zolkipli.
"Use of cryptography in cloud computing." Control
System, Computing and Engineering (ICCSCE),
2013 IEEE International Conference on. IEEE, 2013.
[5] Guan, Qiang, and Song Fu. "Adaptive Anomaly
Identification by Exploring Metric Subspace in Cloud
Computing Infrastructures." Reliable Distributed
Systems (SRDS), 2013 IEEE 32nd International
Symposium on. IEEE, 2013.
[6] Zhang, W., Lei, W., Chen, X., & Liu, S. (2013,
June). Architecture and Key Issues of IMS-Based
Cloud Computing. In Cloud Computing (CLOUD),
International Journal of EmergingTrends & Technology in Computer Science(IJETTCS)
Web Site: www.ijettcs.org Email: editor@ijettcs.org, editorijettcs@gmail.com
Volume 3, Issue 2, March April 2014 ISSN 2278-6856
Volume 3, Issue 2 March April 2014 Page 80
2013 IEEE Sixth International Conference on (pp.
629-635). IEEE.
[7] Guan, Qiang, Chi-Chen Chiu, and Song Fu. "CDA:
A Cloud Dependability Analysis Framework for
Characterizing System Dependability in Cloud
Computing Infrastructures." Dependable Computing
(PRDC), 2012 IEEE 18th Pacific Rim International
Symposium on. IEEE, 2012.
[8] Liu, Wentao. "Research on cloud computing security
problem and strategy."Consumer Electronics,
Communications and Networks (CECNet), 2012 2nd
International Conference on. IEEE, 2012.
[9] Zhao, Wei, et al. "Modeling and simulation of cloud
computing: A review." Cloud Computing Congress
(APCloudCC), 2012 IEEE Asia Pacific. IEEE, 2012.
[10] Xin, Zhang, Lai Song-qing, and Liu Nai-wen.
"Research on cloud computing data security model
based on multi-dimension." Information Technology
in Medicine and Education (ITME), 2012
International Symposium on. Vol. 2. IEEE, 2012.
[11] Mollah, Muhammad Baqer, Kazi Reazul Islam, and
Sikder Sunbeam Islam. "Next generation of
computing through cloud computing
technology." Electrical & Computer Engineering
(CCECE), 2012 25th IEEE Canadian Conference on.
IEEE, 2012.
[12] Sim, Kwang Mong. "Agent-based cloud
computing." Services Computing, IEEE Transactions
on 5.4 (2012): 564-577.
AUTHORS
Amandeep Kaur is an assistant professor in the
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Guru
Nanak Dev University, Amritsar Punjab India. She has
done B.Tech from Beant College of engineering and
technology and M.Tech from Guru Nanak Dev
University, Amritsar in 2011. Her research interests
include Cloud Computing.
Jasjit Kaur is a student of Department in Computer
Science and Engineering, Guru Nanak Dev University,
Amritsar Punjab India. She completed her B.Tech in
Information Technology in 2012 from Global Institutes of
Management and Emerging Technologies. Now she is
M.Tech student. Her research interests include Cloud
Computing.
You might also like
- Cloud Computing: An Overview: Charandeep Singh Bedi, Rajan SachdevaDocument10 pagesCloud Computing: An Overview: Charandeep Singh Bedi, Rajan SachdevaCharndeep BediNo ratings yet
- Job Scheduling in Cloud Computing: A Review of Selected TechniquesDocument5 pagesJob Scheduling in Cloud Computing: A Review of Selected TechniquesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Cloud Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument14 pagesUnit 1 - Cloud Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inMr. HolaNo ratings yet
- Ijet V4i3p33 PDFDocument10 pagesIjet V4i3p33 PDFInternational Journal of Engineering and TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Mini Project Work Entiled OnDocument24 pagesCloud Computing: Mini Project Work Entiled OnZeanav KhanNo ratings yet
- 2015 Green Cloud Live MigrationDocument6 pages2015 Green Cloud Live MigrationPradheeba Smirithi PNo ratings yet
- Axioms of Cloud Computing: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)Document4 pagesAxioms of Cloud Computing: International Journal of Emerging Trends & Technology in Computer Science (IJETTCS)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Review of Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesReview of Cloud ComputingijsretNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report On Cloud Computing.Document25 pagesSeminar Report On Cloud Computing.Rahul Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing An IntroductionDocument39 pagesCloud Computing An Introductionsrishtityagi2020No ratings yet
- Unit-1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument14 pagesUnit-1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingmadhavNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - Question BankDocument54 pagesCloud Computing - Question BankNishtha SinghNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Student's Name:: Abdirahman Said Dhore B1EN27Document9 pagesCloud Computing Student's Name:: Abdirahman Said Dhore B1EN27Abdirahman DhooreNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesCloud ComputingGHOST 007No ratings yet
- Five Characteristics of Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesFive Characteristics of Cloud ComputingragunathNo ratings yet
- Reliability of Cloud Computing Services: Anju Mishra & Dr. Viresh Sharma & Dr. Ashish PandeyDocument10 pagesReliability of Cloud Computing Services: Anju Mishra & Dr. Viresh Sharma & Dr. Ashish PandeyIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Cloud ComputingManisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Cloud Computingliuliming100% (3)
- Unit 1Document37 pagesUnit 1yashika sarodeNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument42 pagesCloud ComputingAkansha TyagiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Seminar ReportDocument19 pagesCloud Computing Seminar ReportDank BoiiNo ratings yet
- assg 7Document8 pagesassg 7bhalaninaman7No ratings yet
- Cloud computing overviewDocument27 pagesCloud computing overviewαηαητ αφπαωαΙNo ratings yet
- SBS1207 Cloud Computing Unit IDocument14 pagesSBS1207 Cloud Computing Unit Isaravana AriyalurianNo ratings yet
- CBSE Computer Science Class XI Unit 1 Cloud ComputingDocument82 pagesCBSE Computer Science Class XI Unit 1 Cloud ComputingDark DevilNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument82 pagesCloud ComputingKartheeswari SaravananNo ratings yet
- Transformation To CloudsDocument7 pagesTransformation To Cloudsarunanand4101No ratings yet
- Survey of Cloud ComputingDocument13 pagesSurvey of Cloud ComputingijwscNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Research Activities and ChallengesDocument9 pagesCloud Computing: Research Activities and ChallengesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesChapter - 1: Introduction To Cloud ComputingPreet ChahalNo ratings yet
- Compusoft, 2 (12), 404-409 PDFDocument6 pagesCompusoft, 2 (12), 404-409 PDFIjact EditorNo ratings yet
- An Assignment On Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesAn Assignment On Cloud ComputingMD Monowar Ul IslamNo ratings yet
- Cloud NotesDocument45 pagesCloud Notesmala100% (1)
- Clearing The Clouds On Cloud Computing S-51490823 PDFDocument6 pagesClearing The Clouds On Cloud Computing S-51490823 PDFFisehaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Infrastructure Clouds: International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology-volume3Issue1 - 2012Document5 pagesA Study of Infrastructure Clouds: International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology-volume3Issue1 - 2012surendiran123No ratings yet
- CEH v12 Lesson 12 - Introduction To Cloud CompDocument23 pagesCEH v12 Lesson 12 - Introduction To Cloud CompAbhay JainNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 CSE3035 ETH VL2022230103255 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 IntroductionDocument12 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 CSE3035 ETH VL2022230103255 Reference Material I 20-07-2022 IntroductionAditi SudhirNo ratings yet
- Privacy and security issues in cloud computingDocument7 pagesPrivacy and security issues in cloud computingbasualok@rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- Comparing Cloud Computing and Grid ComputingDocument15 pagesComparing Cloud Computing and Grid ComputingRajesh RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Submitted By: Divya Khandelwal B.Tech (CSE) 7 Sem 0271352707Document31 pagesCloud Computing: Submitted By: Divya Khandelwal B.Tech (CSE) 7 Sem 0271352707divya25sepNo ratings yet
- Cloud - Computing - Chapter 1Document53 pagesCloud - Computing - Chapter 1Selhadin abduNo ratings yet
- Load Balancing: Ranjan Kumar Mondal, Payel Ray, Debabrata SarddarDocument21 pagesLoad Balancing: Ranjan Kumar Mondal, Payel Ray, Debabrata Sarddarযা ইচ্ছে তাইNo ratings yet
- Information Security in Cloud Computing: August 2014Document6 pagesInformation Security in Cloud Computing: August 2014Aseer Istiaq Azad 1813654630No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - NotesDocument6 pagesCloud Computing - Notessaiduth_f163% (8)
- FOG COMPUTING: AN ABLE EXTENSION TO CLOUDDocument16 pagesFOG COMPUTING: AN ABLE EXTENSION TO CLOUDMinahil Ahmad100% (1)
- Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesCloud Computingshariful islamNo ratings yet
- Trusted Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesTrusted Cloud ComputingAli JumaaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Overview: Key Concepts and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Overview: Key Concepts and ApplicationsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Security Algorithms in Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Security Algorithms in Cloud ComputingInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- DOM205 - Individual Project - Cloud Computing ABHARIKA MOHANTYDocument18 pagesDOM205 - Individual Project - Cloud Computing ABHARIKA MOHANTYAbharika MohantyNo ratings yet
- e-PG Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Cloud Computing Module 3: Cloud Characteristics Module No: CS/CC/3 Quadrant 1 - E-TextDocument15 pagese-PG Pathshala Subject: Computer Science Paper: Cloud Computing Module 3: Cloud Characteristics Module No: CS/CC/3 Quadrant 1 - E-TextSushrut vinayakNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Cloud Computing: Key Concepts and HistoryDocument15 pagesIntroduction to Cloud Computing: Key Concepts and HistoryAakash SoniNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Cloud ComputingDocument26 pagesAssignment - Cloud ComputingBiju PoudelNo ratings yet
- Part B ETIDocument10 pagesPart B ETISoNo ratings yet
- CloudDocument11 pagesCloudcherry grootNo ratings yet
- A Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyDocument5 pagesA Study of Cloud Computing MethodologyR Dharshini SreeNo ratings yet
- Cloud by Jagadish SirDocument71 pagesCloud by Jagadish SirBishnu BashyalNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionFrom EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNo ratings yet
- Cloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDFrom EverandCloud: Get All The Support And Guidance You Need To Be A Success At Using The CLOUDNo ratings yet
- THE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSDocument7 pagesTHE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction A Pillar of Total Quality ManagementDocument9 pagesCustomer Satisfaction A Pillar of Total Quality ManagementInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Detection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesDocument6 pagesDetection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- An Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewDocument9 pagesAn Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigations On K/s Values of Remazol Reactive Dyes Used For Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Recycled WastewaterDocument7 pagesExperimental Investigations On K/s Values of Remazol Reactive Dyes Used For Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Recycled WastewaterInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Study of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiDocument12 pagesStudy of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- THE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSDocument7 pagesTHE TOPOLOGICAL INDICES AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF n-HEPTANE ISOMERSInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- An Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewDocument9 pagesAn Importance and Advancement of QSAR Parameters in Modern Drug Design: A ReviewInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigations On K/s Values of Remazol Reactive Dyes Used For Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Recycled WastewaterDocument7 pagesExperimental Investigations On K/s Values of Remazol Reactive Dyes Used For Dyeing of Cotton Fabric With Recycled WastewaterInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Detection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesDocument6 pagesDetection of Malicious Web Contents Using Machine and Deep Learning ApproachesInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- The Mexican Innovation System: A System's Dynamics PerspectiveDocument12 pagesThe Mexican Innovation System: A System's Dynamics PerspectiveInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Study of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiDocument12 pagesStudy of Customer Experience and Uses of Uber Cab Services in MumbaiInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction A Pillar of Total Quality ManagementDocument9 pagesCustomer Satisfaction A Pillar of Total Quality ManagementInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Product Reliability Using Failure Mode Effect Critical Analysis (FMECA) - Case StudyInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Staycation As A Marketing Tool For Survival Post Covid-19 in Five Star Hotels in Pune CityDocument10 pagesStaycation As A Marketing Tool For Survival Post Covid-19 in Five Star Hotels in Pune CityInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization of Road by Using Spent WashDocument7 pagesSoil Stabilization of Road by Using Spent WashInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Design and Detection of Fruits and Vegetable Spoiled Detetction SystemDocument8 pagesDesign and Detection of Fruits and Vegetable Spoiled Detetction SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Advanced Load Flow Study and Stability Analysis of A Real Time SystemDocument8 pagesAdvanced Load Flow Study and Stability Analysis of A Real Time SystemInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Digital Record For Privacy and Security in Internet of ThingsDocument10 pagesA Digital Record For Privacy and Security in Internet of ThingsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Effective Communication To Enhance Management SkillsDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Effective Communication To Enhance Management SkillsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 On Employment Opportunities For Fresh Graduates in Hospitality &tourism IndustryDocument8 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On Employment Opportunities For Fresh Graduates in Hospitality &tourism IndustryInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Deep Learning Based Assistant For The Visually ImpairedDocument11 pagesA Deep Learning Based Assistant For The Visually ImpairedInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Analysis of Two Biggest Upi Paymentapps: Bhim and Google Pay (Tez)Document10 pagesA Comparative Analysis of Two Biggest Upi Paymentapps: Bhim and Google Pay (Tez)International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Performance of Short Transmission Line Using Mathematical MethodDocument8 pagesPerformance of Short Transmission Line Using Mathematical MethodInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced by Speciality Restaurants in Pune City To Retain Employees During and Post COVID-19Document10 pagesChallenges Faced by Speciality Restaurants in Pune City To Retain Employees During and Post COVID-19International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Datasets For Myocardial Infarction Based On Actual DatasetsDocument9 pagesSynthetic Datasets For Myocardial Infarction Based On Actual DatasetsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Anchoring of Inflation Expectations and Monetary Policy Transparency in IndiaDocument9 pagesAnchoring of Inflation Expectations and Monetary Policy Transparency in IndiaInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Secured Contactless Atm Transaction During Pandemics With Feasible Time Constraint and Pattern For OtpDocument12 pagesSecured Contactless Atm Transaction During Pandemics With Feasible Time Constraint and Pattern For OtpInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Predicting The Effect of Fineparticulate Matter (PM2.5) On Anecosystemincludingclimate, Plants and Human Health Using MachinelearningmethodsDocument10 pagesPredicting The Effect of Fineparticulate Matter (PM2.5) On Anecosystemincludingclimate, Plants and Human Health Using MachinelearningmethodsInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Fondazione Prada - January 2019Document6 pagesFondazione Prada - January 2019ArtdataNo ratings yet
- Indies Top Marks For Murder Window Display T&CsDocument1 pageIndies Top Marks For Murder Window Display T&CsSonia RazviNo ratings yet
- The Project Saboteur1Document28 pagesThe Project Saboteur1pharezeNo ratings yet
- 21 CFR Part 11 Complete Guide To International Computer Validation Compliance For Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument287 pages21 CFR Part 11 Complete Guide To International Computer Validation Compliance For Pharmaceutical IndustryFabio Green100% (1)
- Day1 S2 Gravity IntroDocument21 pagesDay1 S2 Gravity IntroPedro Hortua SeguraNo ratings yet
- Advacc 2 Chapter 1 ProblemsDocument5 pagesAdvacc 2 Chapter 1 ProblemsClint-Daniel Abenoja100% (1)
- Barredo Vs Garcia and AlmarioDocument10 pagesBarredo Vs Garcia and AlmarioRson RTacastacasNo ratings yet
- Rural Houses of The North of Ireland - Alan GaileyDocument6 pagesRural Houses of The North of Ireland - Alan Gaileyaljr_2801No ratings yet
- Cooperative by LawsDocument24 pagesCooperative by LawsMambuay G. MaruhomNo ratings yet
- Cargo Record BookDocument7 pagesCargo Record BookTusharsorte100% (1)
- Classical Philosophies Guide Business Ethics DecisionsDocument48 pagesClassical Philosophies Guide Business Ethics DecisionsDanielyn GestopaNo ratings yet
- InvoiceDocument1 pageInvoiceDp PandeyNo ratings yet
- Memorandum Personnel Memo 21-11 To:: A B G D. WDocument2 pagesMemorandum Personnel Memo 21-11 To:: A B G D. WLEX18NewsNo ratings yet
- Women in Indian CinemaDocument16 pagesWomen in Indian CinemaahmerkhateebNo ratings yet
- XCVBNMK, 54134Document49 pagesXCVBNMK, 54134fakersamNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Tong Hop Ve 12 Thi Trong Tieng Anh Co Dap An Day Du 1286849230Document9 pagesBai Tap Tong Hop Ve 12 Thi Trong Tieng Anh Co Dap An Day Du 1286849230Linh Nguyễn Lê ÁiNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument30 pagesDiphtheriaBinayaNo ratings yet
- First CaseDocument2 pagesFirst Caseaby marieNo ratings yet
- 978191228177Document18 pages978191228177Juan Mario JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Basic Etiquettes Inc IntroductionsDocument8 pagesBasic Etiquettes Inc Introductionsayesha akhtarNo ratings yet
- Trial Memorandum SampleDocument9 pagesTrial Memorandum SampleLacesand solesNo ratings yet
- Astm d4921Document2 pagesAstm d4921CeciliagorraNo ratings yet
- 8 deadly sins of investing: Overlooking fundamentals, myopic vision, ignoring portfolioDocument4 pages8 deadly sins of investing: Overlooking fundamentals, myopic vision, ignoring portfolionvin4yNo ratings yet
- Common Law MarriageDocument3 pagesCommon Law MarriageTerique Alexander100% (1)
- FM AssignmentDocument10 pagesFM AssignmentPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- New Venture Creation IdeasDocument6 pagesNew Venture Creation IdeasDaoud HamadnehNo ratings yet
- Boltanski Thevenot Los Usos Sociales Del CuerpoDocument52 pagesBoltanski Thevenot Los Usos Sociales Del CuerpoAngélica VeraNo ratings yet
- List of Solar Energy Operating Applications 2020-03-31Document1 pageList of Solar Energy Operating Applications 2020-03-31Romen RealNo ratings yet
- Prossional Ethics Notes CH-1 To CH-6 by DbrathodDocument64 pagesProssional Ethics Notes CH-1 To CH-6 by Dbrathodtempuser26No ratings yet
- 19 Preposition of PersonalityDocument47 pages19 Preposition of Personalityshoaibmirza1No ratings yet