Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 2)
Uploaded by
Ranjan PrasadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 2)
Uploaded by
Ranjan PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
1
Key Answers:
1. d 2. a 3. c 4. b 5. d 6. a 7. 5 8. 4 9. 2 10. 6
11. 3 12. b 13. b 14. b 15. c 16. a 17. b 18. 19. 20. b
21. c 22. c 23. d 24. d 25. c 26. 3 27. 4 28. 7 29. 9 30. 1
31. d 32. b 33. a 34. c 35. a 36. c 37. 38. 39. b 40. a
41. a 42. a 43. d 44. c 45. 7 46. 2 47. 2 48. 4 49. 2 50. c
51. a 52. d 53. c 54. d 55. c 56. 57.
18. A r, B p, C s, D q; 19. A q, B r, C p, D s;
37. A p,q, B r, C r,s, D p,q; 38. A q, B r, C s, D-r;
56. A p,r, B p,q, C s, D p; 57. A p,q,s, B p,q,r, C p,q,s, D p,q,r;
Solutions:
Chemistry
1. No of lone pair of 0 Xe = and number of bond pair 5 =
Hybridisation of
3
Xe sp d =
Hence shape
3 2
XeO F should be trigonal bipyramidal and not octahedral
2. For the desired reaction
( )
1 ,
1
G
AgCl e Ag Cl E
F
A
+ + =
the needed , G A can be obtained by adding the values of , G A for the recton
'
1 ; Ag e Ag G nFE
+ A =
; ln ,
sp
AgCl Ag Cl G RT K
+
+ A = giving
, G A = ( )
( ) ( )
4 1 10
1 9.648 10 (298 ) ln 1.56 10 mol J mol K
77.10 55.95 21.15 kJ kJ kJ + =
The potential is
( )
( )( )
21.15
0.2192
1 96.485
E V
= = +
3.
4. Alkenes with even number of cumulative double bonds are optically active if both sides are
dissymmetric
5. None of the acids evolve
2
H gas with alkali metals
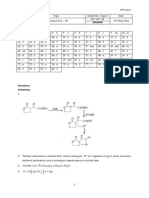
CH
3
C
2
H
5
O
OH
OH
O
CH
3
C
2
H
5
O
-H
2
O
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
2
6. Given 0.1 , 18.0
HCl HCl
M M V mL = =
3 3
0.125 , ?
NaHCO NaHCO
M M V = =
on applying ,
3 3
HCl HCl NaHCO NaHCO
M V M V =
3
0.1 18 0.125
NaHCO
V =
3
14.4
NaHCO
M mL =
Thus, 14.4mL of
3
1.25M NaHCO solution is needed to neutralise 18.0 mL of the 0.100
M HCl solution
7. The destruction reaction for
3
O is given as
3 2
2 3 O O
The net rate of production of
3
O =
15 1 1
7.2 10 rate of thisreaction mol h
= =
Now
| |
( )
2 3
2
;
d O
k a x
dt
=
but initially
0 x =
So
| |
( )
2
3 2 15 8
2 2
7.2 10 2 10
d O
k a k
dt
= =
15
1 1
2
16
7.2 10
4 10
k mol h
1 1 1 1
2
18
18
60 60
k mol h mol s
= =
3 1 1
5 10 . mol s
= So value of 5 x =
8. We know that ,
d d
p RT or M RT
M P
= =
given,
3
775
2.64 / ;
760
d g dm P atm = =
3 1 1
0.0821 , 310 273 583 R dm atmK mol T K
= = + =
2.64 0.0821 583 760
123.9 /
775
M g mol
= =
Atomic mass of 31 / P g mol =
Number of P atoms in a molecule
123.9
4
31
M = =
9. There are 2t bonds in ( ) C which is and ( ) B is
2 3
Na SO
10. Total number of unpaired electrons 6 =
11. ( ) C is an amide which on heating with
2 5
P O gives propane nitrole and so ( ) C is propanamide
2 5
3 2 2 3 2
PO
CH CH CONH CH CH CN
NaO S
S
O
ONa
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
3
( ) C is formed by the action of
3
NH on acid ( ) B , so acid ( ) B is propanoic acid
3 2 3 3 2 4 3 2 2
CH CH COOH NH CH CH COONH CH CH CONH
A A
+
( ) B ( ) C
(iii) Acid ( ) B is formed from hydrolysis of A as well as ( ) A fumes in moist air, so ( ) A is
acid halide. Thus ( ) A is
3 2 3 2
CH CH COCl HOH CH CH COOH HCl + + |
Also, (A)
3 2
(propanoyl chloride) CH CH COCl
(B)
3 2
(Propanoicacid) CH CH COOH
(C)
3 2 2
(propanamide) CH CH CONH
(i)
3 2
CH CH COCl (ii)
3 2
CH COCH Cl (iii)
2 2
ClCH CH CHO
12. Na metal is soluble in liquid ammonia. The reaction takes place in a homogeneous solution
phase
13. More highly substituted alkenes are adsorbed on metal catalyst effectively so are not readily
reduce
14. The least stable alkenes has highest heat of hydrogenation
15. Yellow curdy precipitate with Ag
+
confirms the presence of I ion
in the compound The
precipitate ( ) AgI is insoluble in
4
NH OH
16. Compound A gives brown precipitate with
4
CuSO which becomes white when
2 2 3
Na S O is
added. Thus, compound A should be KI
17.
4 2 2 4
2 CuSO KI CuI K SO + +
( ) A
2 2 2 2
2CuI Cu I I +
brown
2 2 3 2 2 4
2 2 Na S O I Na S O NaI + +
white
(sodium tetrahtionate)
18. Magnetic moment, ( ) 2 n n BM = +
(where n = number of unpaired electrons)
For ( )
2
, 0, 0 0 2 0.00 Fe n BM
+
= = + =
For ( )
3
, 1, 1 1 2 1.73 Ti n BM
+
= = + =
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
4
For ( )
2
, 2, 2 2 2 2.83 Ni n BM
+
= = + =
For ( )
3
, 5, 5 5 2 5.91 Fe n BM
+
= = + =
19. , order of reaction
n
dC
KC n
dt
= =
or, ( ) ( )
1
/ time /
n
mol lit k mol lit
=
or, ( ) ( )
1 1 1
time
n n
K mol lit
=
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
5
Mathematics
20. Favourable number of ways
12 47 4
1 1 1
1 C C C = +
Required probability
51 51
52 51 221
= =
21. For the vector a and b to be inclined at an obtuse angle, we must have
( ) . 0 0, a b for all x < e
( )
2
2 2
log 12 6 log 0 c x c x + < for all ( ) 0, xe
2
6 12 0 cy cy + < for all y R e
Where
2
log y x =
2
0 and 36 48 0 c c c < + <
(using
2
0 if 0 and 0 ax bx c x R a D + + < e < <
( )
4
0 3 4 0 , 0
3
c and c c c
| |
< + < e
|
\ .
22. We have ( ) ( )( )
2 2
0 0 a b c a b c a b c = + =
Line 0 ax by c + + = passes through either of the points ( ) 1, 1 and ( 1,1)
23. Let 2 and 3 y t z u = = then the equation becomes , where 1, 2, 3........... 2, 4, 6 x y u n x t + + = = =
and 3, 6, 9 u =
Hence, the number of solution of this equation
=
( )
2 3
coefficient of ......
n
x in x x x + + +
( )( )
2 4 6 3 6 9
..... .... x x x x x x + + + + + +
=
( )( )( )
6 2 2 4 3 6
coefficient of 1 ... 1 .... 1 .......
n
x in x x x x x x x + + + + + + + + +
( )
( ) ( )
1 1
1 6 2 3
coefficient of in 1 1 1
n
x x x x
=
24. The given quadratic equation is satisfied by , and x a x b x c = = = Hence the quadratic
equation has three roots, which is only possible if it is an identify, hence it has infinite roots
25. Let z ie =
z ie =
2
Arg Argz + =
t
e
3
arg
4
z =
t
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
6
26. ( )
3 2
. 5 7 A A A A A I = =
2
5 7 A A =
( ) 5 5 7 7 A I A =
18 35 A I
Now ( )
4 3
. 18 35 A A A A A I =
2
18 35 A A
( ) 18 5 7 35 A I A
55 126 A I
( )
5 4
. 55 126 A A A A A I = =
2
55 126 A A
( ) 55 5 7 126 A I A
149 385 a and b = =
2 3 2 149 3 385 a b =
298 1155 1453 = + =
27. The period of
| |
sin
12
x t | |
|
\ .
is
2
24
t
t
=
as
| | | | 24 24
sin sin
12 12
x x t t | | | | + +
=
| |
\ . \ .
| | | |12
sin 2 sin
12
x x t t
t
| | | |
= + =
| |
\ . \ .
similarly the period of
| |
tan
3
x t | |
|
\ .
is 3 and the period of cos
4
x t | |
|
\ .
is
2
8
4
t
t
=
Hence the period of the given function
24,8,3 24 LCM of = =
201 201 24 4824 = =
28.
( )
( )
( )
2 3 97
1
.... 1 1 1 ....1
lim
1 x
x x x x
x
+ + + + + +
1 2 3 .... 97 = + + + +
( )
97
1 97 97 49 4753
2
+ = =
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
7
29. If r be the radius and ' ' h be the height of the cylinder
Volume
2 3 3 2 3
2 2 4
3 3 3
V r h r r r h r t t t t t = + + = +
( )
( )
2 2
4
2 .3
3
V r h h r v tr r t t t A = A + A + A
2 2
2 4 r h rh r r r t t t = A + A + A
( )
2
2 4
4
3
r r h h r r r
V
V
r rh r
t
t
A + A + A
A
= =
| |
+
|
\ .
( )
2
1.5 0.05 2 4 0.01 4 1.5 0.01
4
1.5 4 1.5
3
+ +
=
+
0.215
9
=
0.215 21.5
100 100 2.389%
9 9
V
V
A
= = = =
2389 abcd =
30. Let
1 2 3 4, 5
, , , E E E E E and
6
E be the events of occurrence of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 on the dice
respectively, and let E be the even of getting a sum of numbers equal to 9
( ) ( ) ( )
1 2 3
1 1 2 1
, ; ;
6 6 6
k k k
P E P E P E
+
= = =
( ) ( ) ( )
4 5 6
1 1 2 1
; ;
6 6 6
k k k
P E P E P E
+ +
= = =
and
1 2
( )
9 9
P E < s
Then, E= ( )( )( )( ) { }
3, 6 6, 3 4, 5 5, 4
Hence, ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
3 6 6 3 4 5 5 4
( ) P E P E E P E E P E E P E E = + + +
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
6 6 3 4 5 5 4
3 P E P E P E P E P E P E P E P E = + + +
= ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
6
2 3 2 4 5 P E P E P E P E +
{ }
1, 2 3 4
Since , , are independent E E E E
1 1 1 1 2
2 2
6 6 66
k k k k + + | || | | || |
= +
| | | |
\ .\ . \ .\ .
2
1
2 2
18
k k
(
=
since,
( )
1 2
9 9
P E s s
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
8
2
1 1 2
2 2 ...............(1)
9 18 9
k k
(
s s
2
2 2 2 4 k k s s
2
2 2 2 k k s
2
2 2 2 k k + + s
2
2 0 k k + s
( ) 2 1 0 k k + s
1
0
2
K s s
Hence, integral value of k is zero and for 0 k = from equation (1)
Set of integral value of { } 0 k =
Number of integral solutions of k is 1
31. Here 1 0 a = > therefore we make the substitution
2
2 2 x x t x + + = Squaring both sides of this
equality and reducing the similar terms, we get
( )
( )
2 2
2
2
2 2 2
2 2 2 ;
2 1
2 1
t t t
x tx t x dx dt
t
t
+ +
+ = = =
+
+
( ) ( )
2 2
2
2 4 4
1 2 2 1
2 1 2 1
t t t
x x t
t t
+ +
+ + + = + =
+ +
substituting into the integral, we get
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )( )
2
2 2
2 2
2 1 2 2 2 2
4 4 2 1 1 2
t t t t t dt
I dt
t t t t t
+ + + + +
= =
+ + + + +
} }
Now let us expand the obtained proper rational fraction into per tail fractions
( )( ) ( )
2
3 2
2 2
1 2
1 2 2
t t A B D
t t
t t t
+ +
= + +
+ +
+ + +
32.
2
1
dx
I
x x x
=
+ +
}
Since here 1 0, c = > we can apply the second Euler substitution
2
1 1 x x tx + = ( )
( )
2 2
2
2 1
2 1 1 ;
1
t
t x t x x
t
= =
substituting into I, we can get an integral of a rational fraction
( )( )
2
2
2
2 2 2
,
1 1
1
dx t t
dt
t t t
x x x
+
=
+
+ +
} }
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
9
Now,
( )
( )
2
2
2 2 2
1 9 1 1 1
1
t t A B D E
t t t t t t
t
+
= + + +
+ +
+
33. In this case 0 0 a and c < < therefore, nether the first, nor the second Euler substitution is
applicable, But the quadratic
2
7 10 x x has the real roots 2, 5 = = o | . Therefore we
use the third Euler substitution
( )( ) ( )
2
7 10 2 5 2 x x x x x t = =
( )
2
5 2 ; x x t =
2
2
5 2
1
t
x
t
+
=
+
34. Ans (c)
35. Ans (a)
36. Let the equation of the circle be
2 2
2 2 0 x y gx fy c + + + + = ..(1)
The line 1 lx my + + = will touch the circle (1) if the length of perpendicular from the centre
( ) , g f of the circle on the line is equal to its radius,
i.e.,
( )
( )
2 2
2 2
1 gl mf
g f c
l m
+
= +
+
( )
( )( )
2 2 2 2
1 gl mf l m g f c + = + +
( ) ( )
2 2 2 2
2 2 2 1 0 ( ) c f l c g m gl fm gflm ii + + + =
But the given condition of tangency is
2 2
4 5 6 1 0 l m l + + = .(iii)
Comparing equations (ii) and (iii), we get
2 2
4 5, 2 6, 2 , 2 0 c f mc g g f c gf = = = = = =
solving we get 0, 3, 4 f g c = = =
substituting these values in equation (i), the equation of the circle is
2 2
6 4 0 x y x + + = .
any point on the line 1 0 x y + = is ( ) ,1 , t t t R e
Chord of the contact generated by this point for the circle is ( ) ( ) 1 3 4 0 tx y t t x + + + = or
( ) ( ) 3 3 4 0 t x y x y + + + = which are concurrent at point of intersection of the 3 0 x y = and
3 4 0 x y + + = for all values of t. Hence, lines are concurrent at
1 5
,
2 2
| |
|
\ .
Also point ( ) 2, 3 lies outside the circle from which two tangents can be drawn
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
10
37. (A) 2 7 z i z i k + = is ellipse if 7 2 5 k i i or k > >
(B) We have, for z eC
( ) 2 2 2 i z i z z i z = + s +
2 2 z z i s +
Thus, minimum value of 2 z z i + is 2 and it is attained for any z lying on the segment joining
2 . z i =
(C) 3 4 z z i k = is hyperbola, if 3 4 0 5 k i k < < <
(D)
( ) 3 4
50
k
z i az az b + = + +
( ) 3 4
5 2 3 4
az az b
k
z i
i
+ +
+ =
+
This is hyperbola if 1 5
5
k
k > >
38. ( ) ( ) ( )
1
.
12
P A B P A P B = =
( )
1 1 1 4 3 1 6 1
3 4 12 12 12 12
P A B
+
= + = = =
( ) ( ) ( )
1
2
3
/ /
1
3
2
P A A B P A P A B = = =
( )
( )
( )
/ ' ' 0
' '
P
P B A B
P A B
|
= =
( )
( )
( )
( ) ( )
( )
'
'/
P A s P B P A B
P A B
P B P B
= =
1
1 2
12
1 1
1
3 3
4
= = =
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
11
Physics
39. The centre of mass will follow the same path.
2
R
mx m mR = +
or
3 3 100
150
2 2
R
x
= = = m
40.
4 4 4
1 2 3
1 2 3
Pr Pr Pr
, ,
8 8 8
V V V
l l l
t t t
q q q
= = = and
4
Pr
8
V
l
t
q
=
Now
1 2 3
V V V V = + +
Substituting the values, we get
1 2 3
1 2 1 2 2 3
l l l
l
l l l l l l
=
+ +
1 2 3 6
1 2 1 3 2 3 11
= =
+ +
m
41.
1 2
( )
1
nR T T
e
2/3 2/3
1 2
(5.6) (0.7) T T =
2 1
4 T T =
1
1
3 9
2
2
3
nR T
nRT e = =
But
1
4
n =
1
9
8
RT e =
42.
2
2 2
1
1 1
13.6(1)
2 3
hC
| |
=
|
\ .
2
2 2
2
1 1
13.6(2)
2 4
hC
| |
=
|
\ .
Dividing
( )
( )
2
1
1 5 / 36
4 3/ 16
2 1
5
1215
27
o
A = =
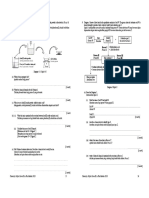
x
R/2
R
m
m m
COM
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
12
43.
2
1
2
2
i
u v =
2 2
(2 )
2 10 5
t
V V
u
= =
Loss of energy
2 2
2
4
5 5
V V
V = =
% loss
2
2
4 / 5
100
V
V
= = 80%
44. Ratio of magnetic moment and angular momentum is given by
2
M q
L m
=
Which is a function of q and m only. This can be derived as follows :
2
( )( ) M iA qf r t = =
2
2
( ) ( )
2 2
q r
q r
e e
t
t
| |
= =
|
\ .
and
2
( ) L I mr e e = =
2
2
2
2
r
q
M q
L m
mr
e
e
= =
45. Distance between two cars leaving from station X is,
1
60 10
6
d
| |
= =
|
\ .
km
Man meets the first car after time,
1
60 1
60 60 2
t h = =
+
He will meet the next car after time,
2
10 1
60 60 12
t h = =
+
In the remaining half an hour, number of cars he will meet again is,
1/ 2
6
1/ 12
n = =
Total number of cars would be meet on route will be 7.
46. From work energy theorem
net
KE W A =
or
f i
K K pdt =
}
or
2
2 2
0
1 3
2 2
mv t dt
| |
=
|
\ .
}
( 2 m = kg)
or
2
3
2
0
2
t
v
(
= (
(
or 2 v = m/s
2
s
1
2 F
8 F
V
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
13
47.
2
4 cos
2
o
I I
| | |
=
|
\ .
2
4 cos
2
o o
I I
| | |
=
|
\ .
1
cos
2 2
| | |
=
|
\ .
or
2 3
| t
=
or
2 2
3
x
t t
|
| |
= = A
|
\ .
or
1 1
.
3
d
D
| |
=
|
\ .
yd
x
D
| |
A =
|
\ .
7
4
6 10
3 10
3
y
d
D
= =
3
2 10
= m = 2 mm
48. / ,
E
v m s t s
m v
= = = =
7 9
2
2 10 2 10
For 200 neutrons generation: T t = 200
s
=
7
4 10
49.
d
dq idt
R
|
= = = Area under i - t graph
d| = (Area under i - t graph) ( R )
1
(4)(0.1)(10) 2
2
Wb = =
50. For rod
2
( 3 )
1:
(2 )(16 ) / 3
N l
m l
o =
or
32
3 3
ml
N
o
=
N
A
3l
-
N
mg
30
o
B
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
14
51. (2 ) (2 )(2 ) 4
c
N F m a m l ml o o = = =
32 12 3
4
3 3
F N ml ml o o
| |
= =
|
|
\ .
52.
2
2
2
2
( cos30 ) (2 sin30 )
( )(2 ) / 3
m gl N l
m l
o
=
2
2
32
( 3 / 2)
3 3 8
3 3
8 3 (4 / 3)
ml
mgl
g
l
ml
o
o
| |
= = |
|
\ .
53. (4)(2)(1) 8 V Bvl V = = =
, R C and L all are in parallel. Therefore, ,
R C
V V and
L
V all are 8V .
L
di
V L
dt
=
or 8 (4)
di
dt
= 2
di
dt
= A/s
i.e.., rate of exchange of current through L is constant. After 2s current will be 4A.
54. ( ) ( )
applied m
F rightwards F leftwards =
IlB =
1 2 3
( ) I I I lB = + +
3
I we have already calculated at 2 which is 4 A.
( )
2
(8) 0
C
dq d d
I CV
dt dt dt
= = = =
and
1
8
4
2
R
V
I A
R
= = =
(4 4)(1)(4) 32
applied
F N = + =
55. . (32)(2) 64 / P F v J s = = =
2
1
1
( )
2
d di
p Li Li
dt dt
| | | |
= =
| |
\ . \ .
3
(4)(4)(2) 32 / ( ) J s i I = =
2 2
2 1
(4) (2) 32 / ( ) P i R J s i I = = =
N
a
2l
2
c
a lo =
C
F
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
15
56. (A) Since 0 E = and 0, B = so path will be straight line if velocity is parallel to B . Or path will be
circular if V B . Or path will be helical (with uniform pitch) if V is at some other angle to B .
Hence. (A) p, r
(B) Since 0 E = and 0, B = so path will be straight line if V B or parabola otherwise.
Hence (B) p, q
(C) 0 E = , 0, B = E B
Helical path with non-uniform pitch Hence, (C) s
(D) Straight line path if V B E =
Hence. (D) (p)
57.
F f ma + =
,
a
Fx fR Ia a
R
= =
Solve to get
2
( ) F MxR I
f
I MR
=
+
B
E
90
o
v
B
E
V
F
a
x
a
R
k
f
, M l
IIT Section
Subject Topic Grand Test Paper II Date
C + M + P Grand Test 07
IIT GT 07
10
th
May 2014
I20140510
16
0, f = if
1
x
MR
=
0, f > if
1
x
MR
>
So friction will act in forward direction.
0 F < if / x I MR < , so friction will act in backward direction.
Also solved to get
2
( ) FR x R
a
I MR
+
=
+
A is positive for all cases, hence body will accelerate in forward direction in all cases.
It means o will be in clockwise direction. Hence bodies will rotate in clockwise direction.
You might also like
- Automatic ControlDocument255 pagesAutomatic ControlAlfa BetaNo ratings yet
- EE3CL4: Introduction To Linear Control Systems: Section 6: Design of Lead and Lag Controllers Using Root LocusDocument57 pagesEE3CL4: Introduction To Linear Control Systems: Section 6: Design of Lead and Lag Controllers Using Root LocusRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- EE3CL4: Introduction To Linear Control Systems: Section 6: Design of Lead and Lag Controllers Using Root LocusDocument57 pagesEE3CL4: Introduction To Linear Control Systems: Section 6: Design of Lead and Lag Controllers Using Root LocusRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- 11-JEE-Adv Grand Test 11 Question Paper (P 1) - 18-05-2014Document18 pages11-JEE-Adv Grand Test 11 Question Paper (P 1) - 18-05-2014Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 1)Document18 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 1)Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- BSC Maths SubjectsDocument21 pagesBSC Maths Subjectssathya_k_83100% (1)
- Questions On Semiconductor CircuitsDocument10 pagesQuestions On Semiconductor CircuitsRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- P 2013Document16 pagesP 2013Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Questions On Semiconductor CircuitsDocument10 pagesQuestions On Semiconductor CircuitsRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chem Model PapersDocument41 pagesChem Model PapersRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 2) - 10-05-2014Document18 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 2) - 10-05-2014Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 1) - 10-05-2014Document23 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 1) - 10-05-2014Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- IIT Grand Test Paper 1 Key Answers and SolutionsDocument22 pagesIIT Grand Test Paper 1 Key Answers and SolutionsRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 1)Document17 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 1)Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 1) - 12-05-2014Document24 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 1) - 12-05-2014Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- CMI Ugmath2013 SolutionsDocument9 pagesCMI Ugmath2013 SolutionsHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 2) - 12-05-2014Document19 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 2) - 12-05-2014Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- 08-JEE-Adv Grand Test 08 Solutions (P 2)Document13 pages08-JEE-Adv Grand Test 08 Solutions (P 2)Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- Figuring Made EasyDocument98 pagesFiguring Made EasyBosco GodfreyNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 2) - 14-05-2014Document20 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 2) - 14-05-2014Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- IIT GT PAPER KEYDocument13 pagesIIT GT PAPER KEYRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 1) - 14-05-2014Document24 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 1) - 14-05-2014Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- The Book of NumbersDocument146 pagesThe Book of NumbersAnu Rajendran100% (6)
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 1)Document22 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Solutions (P 1)Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- CMI Ugmath2013 SolutionsDocument9 pagesCMI Ugmath2013 SolutionsHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- JEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 2) - 08-05-2014Document19 pagesJEE-Adv Grand Test Question Paper (P 2) - 08-05-2014Ranjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- IIpuc PRCTCLQP ChemDocument3 pagesIIpuc PRCTCLQP ChemRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- IIpuc Modelqp PhyDocument10 pagesIIpuc Modelqp PhyRanjan PrasadNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Petrochemical Processes: Segment 3Document9 pagesPetrochemical Processes: Segment 3Thab's VilakaziNo ratings yet
- Problems in BiochemDocument3 pagesProblems in BiochemIrish Marie Da-antonNo ratings yet
- Thermal Optimization of Ammonia Production ProcessDocument17 pagesThermal Optimization of Ammonia Production ProcessGarvit Chopra100% (4)
- Unit 2 RacDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Racozair arshadNo ratings yet
- NJEETS FULL TEST-9 - Paper - SolutionDocument24 pagesNJEETS FULL TEST-9 - Paper - SolutionAvinash100% (2)
- Mock #12 - Full ExamDocument45 pagesMock #12 - Full ExamtonetoNo ratings yet
- 1936-Gilbert Chemistry Outfit Manual M1706 PDFDocument66 pages1936-Gilbert Chemistry Outfit Manual M1706 PDFПабло Авалос100% (1)
- 40103e PDFDocument6 pages40103e PDFGuadalupeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Ammonia ReportDocument75 pagesChemical Ammonia Reportibiceng100% (1)
- Longhorn Secondary Chemistry FORM 4Document345 pagesLonghorn Secondary Chemistry FORM 4anabelle.pangatungan1998No ratings yet
- Compost Maturity Index: California Compost Quality CouncilDocument26 pagesCompost Maturity Index: California Compost Quality CouncilLalith VaradhanNo ratings yet
- Equilibria in The Ammonium Carbamate Urea-Water System: K. G. Clark, L. C. DDocument5 pagesEquilibria in The Ammonium Carbamate Urea-Water System: K. G. Clark, L. C. DjcortezcNo ratings yet
- Development of Combination of Environmentally Friendly Biofloc and Aquaponic Systems in The Maintenance of Oreochromis NiloticusDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Combination of Environmentally Friendly Biofloc and Aquaponic Systems in The Maintenance of Oreochromis NiloticusInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Brochure RMIT UniversityDocument119 pagesBrochure RMIT UniversityLuis EspinosaNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document36 pagesCH 7Tr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- The Axolotl Is Unusual in Nature Because It Retains Its Larval Form Into Adulthood PDFDocument30 pagesThe Axolotl Is Unusual in Nature Because It Retains Its Larval Form Into Adulthood PDFCarla FirstyNo ratings yet
- Silver Diagnosis in Neuropathology - Principles, Practice and Revised InterpretationDocument17 pagesSilver Diagnosis in Neuropathology - Principles, Practice and Revised InterpretationMartin SNo ratings yet
- Analysis System: Foodlab FoodlabDocument2 pagesAnalysis System: Foodlab FoodlabMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument26 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentLimbaji shindeNo ratings yet
- Electrode Position of PT PMR v32 I4 188 197Document10 pagesElectrode Position of PT PMR v32 I4 188 197bissonaNo ratings yet
- Chloramine (Mono) and Nitrogen, Free AmmoniaDocument8 pagesChloramine (Mono) and Nitrogen, Free AmmoniaDody PurmadaniNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration & Air Conditioning GuideDocument24 pagesRefrigeration & Air Conditioning GuideUtsav ParsanaNo ratings yet
- Topik 7 Kertas 1Document39 pagesTopik 7 Kertas 1faggotisyourmomNo ratings yet
- Salt Solution Larutan Garam Lead (II) Oxide Powder Serbuk Plumbum (II) Oksida 50 CM of 1.0 Moldm Nitric Acid 50 CM Asid Nitrik 1.0 MoldmDocument4 pagesSalt Solution Larutan Garam Lead (II) Oxide Powder Serbuk Plumbum (II) Oksida 50 CM of 1.0 Moldm Nitric Acid 50 CM Asid Nitrik 1.0 MoldmTENGKU AHMAD NAQIUDDIN BIN TENGKU NADZUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ElectrodesDocument7 pagesEnzyme Electrodesahmadalijee70No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument22 pagesChemistry超开心No ratings yet
- Phase 3Document13 pagesPhase 3Vansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nickel-Ammonia Complex Wastewater.Document5 pagesNickel-Ammonia Complex Wastewater.Richard.nlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionDocument107 pagesChapter 19 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionHani ShamsedeenNo ratings yet
- Classic Traveller.-.1983.-.SS2 - Exotic AtmospheresDocument13 pagesClassic Traveller.-.1983.-.SS2 - Exotic Atmospherestsothggua100% (2)