Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Itpro 2013 DB Poster
Uploaded by
davidlam0109Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Itpro 2013 DB Poster
Uploaded by
davidlam0109Copyright:
Available Formats
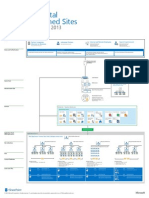
DATABASES THAT SUPPORT SHAREPOINT 2013
2012 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. To send feedback about this documentation, please write to us at ITSPDocs@microsoft.com.
Microsoft SQL Server databases are integral to SharePoint 2013. The databases used in a specific environment are determined by the product,
version, edition, and features that are running. Database size, and the edition of SQL Server that you run are determined by the capacity and
feature requirements of your environment.
SHAREPOINT SERVICE APPLICATIONS SQL SERVER
Co-location guidance: Whether a database must or must not be
located on the same server instance with another database.
I/O patterns: Whether the database is mostly used for reading or
writing data.
Scaling guidance:
Scale up: to increase the size available to the database, move to a
larger server.
Scale out: to increase the size available to the database, add
another database. Multiple database icons indicate scale out.
Recommended SQL Server edition: A specific edition of SQL Server
that is recommended, and why. In general, in this poster,
recommendations are made based on the assumption that you are
running an enterprise environment.
Definitions
SHAREPOINT
Legend
SQL Server 2008 R2
SQL Server 2012
SQL Server 2008 R2 Reporting
Services
SQL Server 2012 Reporting
Services
SharePoint 2013
common databases
(Foundation, Server)
SharePoint Server 2013
(Standard, Enterprise)
User Profile service
application
Search service application SharePoint 2013
systemdatabases
(Foundation, Server)
Large:
Up to 1 terabyte
Extra-large:
1 terabyte or more
Very Small:
100 MB or less
Small:
Up to 1 GB
Medium:
Up to 100 GB
Support multiple
databases
(scales out)
Database types
Database size ranges
(Database icons shown are not to
scale)
Other notations
SharePoint Server 2013
service application databases
Project Server 2013
(Project Server service application , ProjectWebApp)
The database stores all the data for a single Project Web App (PWA) enabled
site, along with the following:
All Project and Portfolio Management (PPM) data
Time tracking and Timesheet data
Aggregated SharePoint project site data
Significant database growth is unlikely.
Scaling guidance: Scale up the SQL Server that hosts the Project Server
service application databases.
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Small - medium
SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application
(PowerPivot Service service application,
DefaultPowerPivotServiceApplicationDB_<GUID>)
Stores data refresh schedules, and PowerPivot usage data that is copied
from the central usage data collection database. Significant growth is
unlikely.
When in use, PowerPivot stores additional data in content databases and in
the Central Administration content database.
Requirements: SQL Server 2012 Analysis Services, Business Intelligence or
Enterprise Edition.
Scaling guidance: Scale up.
SQL Server 2008 R2 (SP1) & SQL Server 2012
system databases
master
Records all system level information for a SQL Server instance,
including logins, configurations, and other databases.
Scaling guidance: Scale up. (Significant growth is unlikely).
model
Used as the template for all databases created in an instance.
Scaling guidance: Scale up. (Significant growth is unlikely).
msdb
Records operators, and used by SQL Server Agent to schedule alerts
and jobs.
Scaling guidance: Scale up. (Significant growth is unlikely).
tempdb
Holds all temporary tables and temporary stored procedures and
fills any other temporary storage needs. The tempdb database is re-
created every time the SQL Server instance is started.
Co-location guidance: Locate on a separate spindle from all other
databases
Scaling guidance: Scale up
App Management
(App Management service application,
App_Management_<GUID>)
Stores the App licenses and permissions that are downloaded from the
Global Marketplace.
Scaling guidance: Scale-out only on SharePoint Online
I/O patterns: Write-heavy during Apps installation and license renewal.
SharePoint 2013 (Foundation and Server)
service application databases
SharePoint User Profile service databases (Server)
Profile
(User Profile service application,
User Profile Service Application_ProfileDB_<GUID>)
Stores and manages users and their social information.
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database that supports the service
application instance.
Scale-out by creating additional instances of the service application,
however, the decision to create a separate service application is likely to be
based on business, rather than scale, requirements.
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Synchronization
(User Profile service application,
User Profile Service Application_SyncDB_<GUID>)
Stores configuration and staging data for use when profile data is being
synchronized with directory services such as Active Directory. Size is
determined by number of users, groups, and the ratio of users to groups.
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database that supports the service
application instance.
Scale-out by creating additional instances of the service application,
however, the decision to create a separate service application is likely to be
based on business, rather than scale, requirements.
I/O patterns: Even
Social Tagging
(User Profile service application and the Metadata Management service
application, if tags are used for metadata,
User Profile Service Application_SocialDB_<GUID>)
Stores social tags and notes created by users along with their respective
URLs. Size is determined by the number of tags and ratings created and
used.
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database that supports the service
application instance. Scale-out by creating additional instances of the service
application, however, the decision to create a separate service application is
likely to be based on business, rather than scale, requirements.
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Medium - large
Small extra-large
Search Administration
(Search service application,
Search_Service_Application_DB_<GUID>)
Hosts the Search application configuration and access control list (ACL) for
the crawl component.
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database that supports the service
application instance.
Scale-out by creating additional instances of the service application,
however, the decision to create a separate service application is likely to be
based on business, rather than scale, requirements.
Analytics Reporting
(Search service application,
Search_Service_Application_AnalyticsReportingStoreDB_<GUID>)
Stores the results for usage analysis reports and extracts information from
the Link database when needed.
Scaling guidance: Scale-out add additional Analytics Reporting database
using a split operation when the main database size becomes >200GB.
I/O patterns: Write-heavy during nightly analytics update.
Crawl
(Search service application,
Search_Service_Application_CrawlStoreDB_<GUID>)
Stores the state of the crawled data and the crawl history.
Co-location guidance: In large-scale environments.
Scaling guidance: Scale-out add additional Crawl database per every 20
million items crawled.
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Recommended SQL Server edition:
SQL Server 2008 R2 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) or SQL Server 2012, Enterprise
edition, so that the Search service application can take advantage of data
compression.
Link
(Search service application,
Search_Service_Application_LinkStoreDB_<GUID>)
Stores the information that is extracted by the content processing
component and the click through information.
Co-location guidance: On sites with heavy traffic we recommend the Links
database to utilize separate spindles from other databases.
Scaling guidance: Scale-out add additional Link database per 60 million
documents crawled. Also add additional Link database per 100 million
expected queries per year. The Link database grows on disk by 1 GB per 1
million documents fed. The click data grows linearly with query traffic, 1 GB
per million queries.
I/O patterns: Write-heavy during content processing
SharePoint Search Service Application databases
(Foundation and Server)
Medium
Medium - large
Medium
Medium - large
Small - large
Content
(WSS_Content)
Stores all site content, including site documents or files in document
libraries, list data, Web part properties, audit logs, apps for
SharePoint, and user names and rights. All of the data for a specific
site resides in one content database. Content databases can contain
more than one site collection. Also stores data for Office Web
Applications, if in use. The database size varies based on usage
pattern, for example the number and size of documents and the
number of users.
Important guidance: We strongly recommend limiting the size of
content databases to 200 GB to help ensure system performance.
Content database sizes up to 1 terabyte are supported only for large,
single-site repositories and archives with non-collaborative I/O and
usage patterns, such as Records Centers.
Scaling guidance:
Scale up a database that supports a site collection.
Scale-out at the Web application level: add more content
databases as needed to support additional site collections.
Small
Central Administration Content
(SharePoint_AdminContent_<GUID>)
Content database for the Central Administration site.
Requirements:
Must be co-located with Configuration database
Only one Central Administration Content database is supported per
farm.
Scaling guidance: Scale up only, significant growth is unlikely.
SharePoint system databases
Configuration
(SharePoint_Config)
Contains data about all SharePoint databases, all Internet Information
Services (IIS) Web sites or Web applications, trusted solutions, Web
Part Packages, site templates, and Web application and farm settings
specific to SharePoint 2013, such as default quota and blocked file
types.
Requirements:
Must be co-located with Central Administration Content database
Only one Configuration database is supported per farm.
Scaling guidance: Scale up only, significant growth is unlikely.
Small
SQL Server Reporting Services is installed on a SQL Server report server. It stores items
such as reports, report-related items and resources, schedules, and subscriptions. It can
be configured as a stand-alone server (native mode), multiple servers in a farm, or it can
be integrated with SharePoint Server (SharePoint mode).
SQL Server Reporting Services can be used with SharePoint Server 2013 Excel Services,
PerformancePoint Services, Access Services, Project Server, and Visio Services. If you are
running Access Services, then SQL Server 2012 is required.
Report Server Catalog
(ReportingService_<GUID>)
Stores all report metadata including report definitions, report
history and snapshots, and scheduling information. When
ReportServer is in use, report documents are stored in
SharePoint content databases.
Requirements: Must be located on the same database server
as the ReportServerTempDb database.
Supports service applications: Often used with Access
Services, Excel Services, PerformancePoint Services, and Visio
Services, but not required.
Scaling guidance: Scale up
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
ReportServerTempDB
(ReportingService_<GUID>_TempDB)
Stores all of the temporary snapshots while reports are
running. The size varies frequently, depending on use of
cached report snapshots.
Report Server Alerting
(ReportingService_<GUID>_Alerting)
This database is found in SQL Server 2012 only. Stores all Data
Alerts metadata and runtime information required to
produce Data Alerts for Reporting Services operational
reports. Data from reports is processed within the database
to match rules defined in Alert Definitions. The size varies
frequently, depending on use of Data Alerts
Scaling guidance: Scale up; optimize file I/O; optimize
memory usage
I/O patterns: Read-heavy, Write-heavy
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 (SP1) Reporting Services
&
Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Reporting Services
Small
Small
Medium - large
Business Data Connectivity
(Business Data Connectivity service application,
Bdc_Service_DB_<GUID>)
Stores external content types and related objects.
Relative size: Small
Scaling guidance: Scale up, (significant growth is unlikely).
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Small
Medium
Small
Small
Small
Extra - large
Small extra-large
Small
PerformancePoint Services
(PerformancePoint Services service application,
PerformancePoint Service _<GUID>)
Stores temporary objects and persisted user comments and settings.
Scaling guidance:
Scale up the database that supports the service application instance.
Scale out by creating additional instances of the service application,
however, the decision to create a separate service application is likely to
be based on business, rather than scale, requirements.
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Small
Medium - large
State Service
(State service application, InfoPath Forms Services, Visio Services,
SessionStateService_<GUID>)
Stores temporary state information for InfoPath Forms Services, Exchange,
the chart Web Part, and Visio Services. Database size depends on the usage
of features that store data in it.
Scaling guidance: Scale-out by adding another State database using
Windows PowerShell cmdlets.
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Word Automation Services
(Word Automation Services service application,
WordAutomationServices_<GUID>)
Stores information about pending and completed document conversions
and updates.
Relative size: Small
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database that supports the service
application instance. (Significant growth is unlikely).
I/O patterns: Read and write-heavy once per conversion item.
Small
Medium
Managed Metadata Service
(Managed Metadata Service service application,
Managed Metadata Service Application_Metadata_<GUID>)
Stores managed metadata and syndicated content types.
Also stores the Taxonomy service metadata in a hierarchical structure for
items that are used for tagging content and building site collections.
Relative size: Medium
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database that supports the service
application instance.
Scale-out by creating additional instances of the service application.
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Subscription Settings Service
(Microsoft SharePoint Foundation Subscription Settings service application,
SettingsServiceDB)
Stores features and settings information for hosted customers. This
database is not created by default but must be created by using Windows
PowerShell or SQL Server.
Scaling guidance:
Scale up the database that supports the service application instance.
Scale-out by creating additional instances of the service application,
however, the decision to create a separate service application is likely to
be based on business, rather than scale requirements.
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Small
Apps for SharePoint
(Apps_<GUID>)
Stores information about apps for SharePoint and Access Apps.
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database that supports the apps instance.
(Significant growth is unlikely).
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
Very small
Usage
(Usage and Health Data Collection service application,
SharePoint_Logging)
Installed on SharePoint Online or SQL Azure and also on-premise but not
provisioned by default.
Stores health monitoring and usage data temporarily, and also used for
reporting and diagnostics. The Usage database is the only SharePoint
database that can be queried directly and have schema modified by either
Microsoft or third-party applications.
The database size varies based on retention policy and actual traffic load.
Co-location guidance: Place on separate spindle
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database.
Requirements: Only one Usage and Health Data Collection service
application instance is supported per farm.
I/O patterns: Write-heavy
Extra - large
Secure Store Service
(Secure Store service application,
Secure_Store_Service_DB_<GUID>)
Stores and maps credentials such as account names and passwords.
Co-location guidance: For secure credential storage, it is recommended that
the secure store database be hosted on a separate database instance with
limited access to one administrator.
Scaling guidance:
Scale up the database that supports the service application instance.
Scale out by creating additional instances of the service application,
however, the decision to create a separate service application is likely to
be based on business, rather than scale, requirements.
Small
Small
Machine Translation Services
(SharePoint Translation Services service application,
SharePoint Translation Services_<GUID>)
Stores information about pending and completed batch document
translations with file extensions that are enabled.
Relative size: Small
Scaling guidance: Scale up the database that supports the service
application instance. (Significant growth is unlikely).
I/O patterns: Read-heavy
You might also like
- Mobile Device Management Guide v9 - 1Document217 pagesMobile Device Management Guide v9 - 1davidlam0109No ratings yet
- APC Symmetra RMDocument64 pagesAPC Symmetra RMdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sps 2013 Design Sample Corporate Portal Path Based Sites PDFDocument1 pageSps 2013 Design Sample Corporate Portal Path Based Sites PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- TestLabGuide IntranetAndTeamSites EbookDocument41 pagesTestLabGuide IntranetAndTeamSites EbookShashank VeerkarNo ratings yet
- Server ChecklistsDocument2 pagesServer Checklistsdavidlam0109100% (1)
- Neutral Density Calculation TableDocument1 pageNeutral Density Calculation Tabledavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sps 2013 Design Sample Corporate Portal Host Named Sites PDFDocument1 pageSps 2013 Design Sample Corporate Portal Host Named Sites PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Brocade - Trouble Shooting and Diagnostic GuideDocument146 pagesBrocade - Trouble Shooting and Diagnostic GuideuthramNo ratings yet
- Configure and Environment For Apps SharePoint 2013Document20 pagesConfigure and Environment For Apps SharePoint 2013davidlam0109No ratings yet
- SPC 2013 Bcs Hybrid Model PDFDocument1 pageSPC 2013 Bcs Hybrid Model PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sps 2013 Design Sample Extranet PDFDocument1 pageSps 2013 Design Sample Extranet PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- SP2013 AuthenticationDocument1 pageSP2013 Authenticationdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sps 2013 Streamlined Topology Model PDFDocument1 pageSps 2013 Streamlined Topology Model PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sps-2013-Enterprise Farm-Model PDFDocument1 pageSps-2013-Enterprise Farm-Model PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sharepoint 2013Document674 pagesSharepoint 2013Euclides Pereira da Silva100% (2)
- Sps 2013 Architecture Overview PDFDocument1 pageSps 2013 Architecture Overview PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sps 2013 Traditional Topology Model PDFDocument1 pageSps 2013 Traditional Topology Model PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- SP 2013 Enterprise Search ModelDocument1 pageSP 2013 Enterprise Search Modeldavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sp2013 Upgrade ProcessDocument1 pageSp2013 Upgrade Processdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Share Point 2013 On Premises SocialDocument1 pageShare Point 2013 On Premises Socialdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Svs Single Farm Sharepoint Services 2013 PDFDocument1 pageSvs Single Farm Sharepoint Services 2013 PDFdavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Plan and Use The Distributed Cache ServiceDocument1 pagePlan and Use The Distributed Cache Servicedavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Sp2013 Upgrade Testing XDocument1 pageSp2013 Upgrade Testing XplanetsridharNo ratings yet
- SP 2013 Internet Sites Search ModelDocument1 pageSP 2013 Internet Sites Search Modeldavidlam0109No ratings yet
- Oit2013 Model Sharepoint Search ArchitectureDocument1 pageOit2013 Model Sharepoint Search Architecturemully31No ratings yet
- SharePoint 2013 End UserDocument90 pagesSharePoint 2013 End Userdavidlam0109100% (1)
- Global Solutions SharePoint 2013Document1 pageGlobal Solutions SharePoint 2013davidlam0109No ratings yet
- Multi Farm Sharepoint 2013Document1 pageMulti Farm Sharepoint 2013davidlam0109100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Database Final AssignmentDocument8 pagesDatabase Final AssignmentCaijunn TanNo ratings yet
- RajarajanSadhasivam (9 0)Document7 pagesRajarajanSadhasivam (9 0)AbhinavNo ratings yet
- About Containers and Codecs: DataDocument3 pagesAbout Containers and Codecs: DataLuca CastelloNo ratings yet
- Debian HandbookDocument513 pagesDebian HandbookHarey Kosong TojoehNo ratings yet
- DCS 5010L A1 QIG v1 00 EU PDFDocument80 pagesDCS 5010L A1 QIG v1 00 EU PDFFederico ViciosoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Formal Languages and Automata 5th Edition Solution ManualDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To Formal Languages and Automata 5th Edition Solution ManualEvelyn RM25% (4)
- Exastack Ready Sol Brief Guide 454530Document4 pagesExastack Ready Sol Brief Guide 454530jomer17No ratings yet
- Documentation PDFDocument42 pagesDocumentation PDFBoyko LazarovNo ratings yet
- Improved Cloud Computing Security Through Dynamic Key GenerationDocument6 pagesImproved Cloud Computing Security Through Dynamic Key Generationsabah21No ratings yet
- Dolby Atmos Master Adm Profile v1.0Document25 pagesDolby Atmos Master Adm Profile v1.0Giles HulleyNo ratings yet
- MySQL Constraints GuideDocument23 pagesMySQL Constraints Guideaabid ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Upload Data From Excel File in ABAP Using TEXT - CONVERT - XLS - TO - SAPDocument8 pagesUpload Data From Excel File in ABAP Using TEXT - CONVERT - XLS - TO - SAPKabil RockyNo ratings yet
- Rtos PDFDocument12 pagesRtos PDFAqib AsadNo ratings yet
- Automated Mobile Testing with AppiumDocument68 pagesAutomated Mobile Testing with Appiumvaditya2005No ratings yet
- Open Development Tool Installation Oracle FLEXCUBE Universal Banking Release 12.1.0.0.0Document32 pagesOpen Development Tool Installation Oracle FLEXCUBE Universal Banking Release 12.1.0.0.0swift adminNo ratings yet
- Migrating Magento Ecommerce Platform To Aws: April 2020Document32 pagesMigrating Magento Ecommerce Platform To Aws: April 2020dileep.sNo ratings yet
- Dial Communication Framework Setup LogDocument2 pagesDial Communication Framework Setup LogJUAL AEROPUERTONo ratings yet
- AppLocker Design GuideDocument82 pagesAppLocker Design GuideMSFTSIR100% (1)
- 数据库原理与实践 Database Systems-Principle and PracticeDocument182 pages数据库原理与实践 Database Systems-Principle and Practicerajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting DNS IssuesDocument3 pagesTroubleshooting DNS IssuesMir Farhan Ali AbediNo ratings yet
- SAPFTPDocument25 pagesSAPFTPvnod613100% (1)
- Yogek Garg ResumeDocument1 pageYogek Garg ResumeYogek GargNo ratings yet
- Nessus 8 11 PDFDocument475 pagesNessus 8 11 PDFStéphane ATIDIGANo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument33 pagesExercisesJeype Malbas VillarubiaNo ratings yet
- SSC Service Utility 4.30Document23 pagesSSC Service Utility 4.30Nico DolzaniNo ratings yet
- Adobe Acrobat 8 Professional V810 Keygen ZWT 5 PDFDocument4 pagesAdobe Acrobat 8 Professional V810 Keygen ZWT 5 PDFDougNo ratings yet
- Order Total Discounts For R11: An Oracle White Paper January 2018Document20 pagesOrder Total Discounts For R11: An Oracle White Paper January 2018Siva KumaranNo ratings yet
- Photoshop For Beginners Tastytuts PDFDocument44 pagesPhotoshop For Beginners Tastytuts PDFHenizion100% (3)
- Cs101-Latest - Solved-Midterm Paper 6Document7 pagesCs101-Latest - Solved-Midterm Paper 6Hani KhanNo ratings yet
- AWS CP QuestionDocument5 pagesAWS CP QuestionitsmathanjoeNo ratings yet