Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemmatrix
Uploaded by
api-2454420730 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views14 pagesOriginal Title
chemmatrix
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views14 pagesChemmatrix
Uploaded by
api-245442073Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
CHEMISTRY CAPACITY MATRIX / QUALITY LEARNING TRANSCRIPT
Learner's Name: Dayton Clark
LEARNING PROCESS
Purpose &
Vision:
UNDERSTAND AND APPLY CHEMISTRY
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
SCIENTIFIC METRIC SYSTEM Definitions of mass, length, volume and temp. X
MEASUREMENT Prefixes. X
Metric Conversions. X
Conversions between metric and English. X
(Chapter 3) SIGNIFICANT FIGURES Know the five rules for significant figures. X
Identify the number of Sig. Figs. in a number. X
Be able to add or subtract, multiply and divide S.F. X
Know the amount of certain and uncertain digits. X
SCIENTIFIC NOTATION What is it? Why do we use it? X
Convert a number to scientific notation. X
Convert scientific notation to a number. X
Be able to add or subtract. X
Be able to multiply or divide. X
DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS Indentify the unknown. X
Indentify what is known or given. X
Plan a solution. X
Do the calculation (using ratios equal to one) X
Make sure answer has correct units. X
DENSITY Definition of density X
Formula D=M/V X
Calculate D, given M and V. X
Calculate M, given D and V. X
Calculate V, given M and D. X
Compare densities of different substances. X X Atom Project
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 1
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
MATTER SUBSTANCES Explain what a substance is X
AND CHANGE Elements X X Atom Project
(Chapter 2) Compounds X
Chemical Symbols X
(Elements, MIXTURES Explain/define a mixture X
Compounds, and Homogeneous mixtures X
Mixtures Heterogeneous mixtures X
P4.p2 CHEMICAL REACTIONS What is a chemical reaction? X
P4.p2A,B,C,D) Equations: products, reactants X X Applications
Endothermic reactions X
Exothermic reactions X
Conservation of mass X
ATOMIC 3 BASIC SUBATOMIC PARTICLES ELECTRONS: charge, location, mass X X Atom Project
STRUCTURE PROTONS: charge, location, mass X X Atom Project
(Chapter 4) NEUTRONS: charge, location, mass X X Atom Project
C4.8A,B,C,D ATOMIC NUMBER Explain what it is X
C1.1 C1.2 How is the periodic table arranged X X Trends
(C4.10A,B MASS NUMBER Define mass number X
Netrual Atoms, How do you use it to find # of neutrons? X
Ions, Isotopes) Average atomic mass X X Trends
(C4.10x Define Isotopes X
C4.10c,d,e IONS Define an ion (cation and anion) X
Average Atomic Calculate # of p+, e-, and n for ions of elements X
Mass) DIAGRAMS Be able to draw a Bohr model of an atom X X Atom Project
Be able to draw a Bohr model of an ion X
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 2
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
STATES OF KINETIC THEORY (K.T.) AND Explain Kinetic Energy and the Kinetic Theory X
MATTER KELVIN TEMPERATURE Compare Kelvin Temperature to Celsius Scale X
(Chapter 13) Explain the significance of Absolute Zero X
Explain the relationship btwn absolute temperature X
of a substance and the kinetic energy of its particles
(Kinetic Molecular THE NATURE OF GASES Describe a gas according to the kinetic theory X
Theory Interpret gas pressure in terms of kinetic energy X
C4; P4.p1A,B,C) Convert Units of pressure: atm, kPa, mm Hg X
THE NATURE OF LIQUIDS Describe liquids according to the kinetic theory X
(C1.2) Explain the vaporization of liquids accd. to K.T. X
Explain dynamic equilibrium X
Boiling Point of a Liquid X
Normal Boiling Point of a Liquid X
THE NATURE OF SOLIDS Describe a solid according to the K.T. X
Explain the melting point/freezing point X
Describe crystalline solids X X Alloy Project
Describe amorphous solids X
Explain allotropes X
SUBLIMATION AND Explain sublimation X
PHASE DIAGRAMS Describe a phase diagram and triple point X
Be able to make predictions using a phase diagram X
PLASMA Describe the formation of plasma X
Describe the properties of plasma X
Explain the use of plasma in a plasma arc welder X
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 3
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
ELECTRONS THE DEVELOPMENT OF ATOMIC MODELS Summarize the development of the atomic theory X
IN ATOMS Explain the significance of quantized energies X
(Chapter 5) and the quantum mechanical model of the atom
ATOMIC ORBITALS Distinguish among principal energy level, X X Atom Project
(C1.1 C1.2) energy sublevel, and atomic orbital
(Electron ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS Apply the Aufbau principle, the Pauli exclusion
Movement principle, and Hund's rule to write the electron X X Atom Project
C2.4x configurations of the elements
C2.4a,b,c,d) Explain why the electron configurations of
(Electron some elements like chromium and copper don't X
Configuration follow the Aufbau diagram
C4.8x LIGHT AND ATOMIC SPECTRA Describe relationship btwn wavelength and X
C4.8e,f,g,h,i) frequency of light (c=v)
Calculate the frequency of light X
Calculate the wavelength of light X
Identify the source of atomic emission spectra X
Perform flame test to see pattern within groups X
THE QUANTUM CONCEPT Calculate the energy of a photon associated with
a given wavelength or frequency of light (E=hv) X
using Planck's constant
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 4
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
THE PERIODIC DEVELOPMENT OF THE PERIODIC TABLE Describe the origin of the periodic table. X
TABLE Distinguish between a group and a period. X X Atom Project
(Chapter 6) Distinguish between metals, nonmetals, metalloids.
ELECTRON CONFIGURATIONS & PERIODICITY Categorize elements as representative elements, X
(Electron Energy noble gases, transitional metals or inner transitional
Levels C4.9x Notice the pattern in e- config for each category X X Atom Project
C4.9b,c) PERIODIC TRENDS IN ATOMIC SIZE How is atomic radius calculated? X
Interpret the group trends. X X Trends
Interpret the periodic trends. X X Trends
PERIODIC TRENDS IN IONIZATION ENERGY Define iionization energy. X X Trends
Interpret the group trends X
Interpret the periodic trends. X
Explain the variation in ionization energies. X X Trends
PERIODIC TRENDS IN IONIC SIZE Explain ionic size of cation compared to atom X
Explain ionic size of anion compared to atom X
Interpret the group trends X
Interpret the periodic trends. X
PERIODIC TRENDS IN ELECTRONEGATIVITY Define elecronegativity. X
Interpret the group trends X
Interpret the periodic trends. X
COMPARISONS OF TRENDS Graph the specific trends to show patterns. X X Trends
Compare/contrast the trends and note relations X X Trends
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 5
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
IONIC AND IONS Determine the # of valence e- in an atom X
METALLIC Explain octet rule for metallic and nonmetallic X
BONDING Describe how cations form X
Explain how anions form X
(Chapter 7) IONIC BONDS AND IONIC COMPOUNDS Explain electrical charge of an ionic compound X
Describe 3 properties of ionic compounds X
(Chemical Bonds Define formula unit X
C5.5x C5.5d,e) BONDING IN METALS Model the valence e- of metal atoms X
(Solids C4.3x, Describe the arrangement of atoms in a metal X
C4.3c,e,h,i) Recognize body-centered cubic, face-centered X X Alloy Project
cubic, and hexagonal close-packed arrangements
Explain the importance of alloys X X Alloy Project
Differentiate betweeen interstitial & substitutional alloys X X Alloy Project
COVALENT MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Define a molecular compound X
BONDING Distinguish btwn melting points and boiling points X
(Chapter 8) of molecular and ionic compounds
Describe the information a molecular compound provides X
(Chemical Bonds Define and identify diatomic molecules X
C5.5x C5.5d,e) NATURE OF COVALENT BONDING Describe how e- are shared to from covalent bonds X
(Molecular Polarity Describe how atoms from double or triple covalent bonds X
C4.4x) Describe how the strength of a covalent bond is related to its X
(Chemical Bonds/ bond dissociation energy
Trends C5.5A) POLAR BONDS AND MOLECULES Use electronegativity values to determine the type of bond X
Evaluate the strength of intermolecular attractions compared X
to the strength of ionic and covalent bonds
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 6
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
CHEMICAL UNDERSTAND THE ORGANIZATION Groups and Periods X
NAMES AND OF THE PERIODIC TABLE Representative elements X
FORMULAS Metals X
Metalloids X
(Chapter 9) Nonmetals X
NAMING IONS Identify charges of monatomic ions using the periodic table X
(C5.5B) Name ions: cations and anions X
(Periodic Table Define polyatomic ion X
C4.9 C4.9A) Write names & formulas of the most common polyatomic ions X
(Nomenclature NAMING & WRITING FORMULAS FOR Apply rules for naming binary ionic compounds X
C4.2A,B IONIC COMPOUNDS Apply rules for writing formulas for binary ionic compounds X
C4.2x,c,d) Apply rules for naming compounds with polyatomic ions X
(Acids & Bases Write formulas for compounds with polyatomic ions X
C5.7, C5.7A) NAMING & WRITING FORMULAS FOR Interpret prefixes in the names of molecular compounds X
MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Apply the rules for naming binary molecular compounds X
Write formulas for binary molecular compounds X
NAMING & WRITING FORMULAS FOR Apply 3 rules for naming acids X
ACIDS AND BASES Apply rules in reverse to write formulas of acids X
Apply the rules for naming bases X
LAWS GOVERNING FORMULAS AND NAMES Define the Law of Definite Proportions X
Define the Law of Multiple Porportions X
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 7
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
CHEMICAL THE MOLE Define Avogadro's Number X
QUANTITIES Identify the type of Representative Particles of a substance X
Convert atoms to moles/moles to atoms X
(Chapter 10) Convert moles to molecules/molecules to moles X
MOLAR MASS Distinguish between atomic mass and molar mass X
(Moles C4.6x, Calculate the mass of a mole of a compound X
C4.6a,b) MOLE-MASS RELATIONSHIPS Convert moles to grams X
(Molecular and Convert grams to moles X
Empirical MOLE-VOLUME RELATIONSHIPS understand Molar Volume X
Formulae C4.1x, Recognize STP conditions X
C4.1a,b,c) Calculate the Volume of a Gas at STP X
(C5.2g) Convert Volume of a Gas to Moles X
PERCENT COMPOSITION Define Percent Composition X X Alloy Project
Calculate Percent Composition from a formula X
Calculate Percent Composition from experimantal data X
EMPIRICAL AND MOLECULAR FORMULAS Interpret and empirical formula X
Distinguish between Empirical & Molecular Formulas X
Determine the Empirical Formula of a Cmpound X
Find the Molecular Formula of a Compound X
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 8
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
CHEMICAL DESCRIBING CHEMICAL REACTIONS Identify basic parts of a chemical equation X X Applications
REACTIONS Write a word equation X X Applications
Write a skeleton equation X X Applications
(Chapter 11) BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS Understand the Rules for balancing equations X X Applications
Balance a skeleton equation X
(chemical Write word equations as balanced chemical equations X X Applications
changes C5.2, TYPES OF REACTIONS Identify a Combination/synthesis reaction X X Applications
C5.2A,B,C) Identify a Decomposition reaction X X Applications
(Balancing Identify a Single-Replacement reaction X X Applications
Equations C5.2x) Identify a Double-Replacement reaction X X Applications
Identify a Combustion reaction X X Applications
(Reduction/ Predict the products of the 5 general types of reactions X X Applications
Oxidation REACTIONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS Use solibility rules to predict formation of precipitate X
Reactions C5.6x Write a Complete ionic equation X
C5.6b) Define and identify Spectator ions X
Write a balanced Net ionic equation X
REACTIONS IN EVERY-DAY LIFE Research and learn about chemical reactions X X Applications
used in catalytic converters, airbags, and X X Applications
oxyacetlyene torches. X X Applications
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 9
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
STOICHIOMETRY INTERPRETING EQUATIONS Explain how balanced equations apply to both chemistry X
and everday life
(Chapter 12) Interpret a balanced chemical equation in terms of moles, X
representative particles, mass, and gas volume at STP
(Balancing Use a balanced equation to model nonchemical quantities X
Equations C5.2x, Identify quantities always conserved in chemical reactions X
C5.2d,e,f,g) CHEMICAL CALCULATIONS Define a mole ratio X
Construct mole ratios from balanced chemical reactions X
Apply mole ratios in stoichiometric calculations X
Calculate stoichiometric quantities from balanced chemical X
equations using units of moles, mass, representative X
particles, and volumes of gases at STP X
LIMITING REAGENT Define limiting reagent and excess reagent X
Determine the limiting reagent in a reaction X
Use limiting reagent to find the quantity of product X
Determine the amount of excess reagent left over X
PERCENT YIELD Define actual yield, theoretical yield, & percent yield X
Calculate the theoretical yield, actual yield, or percent X
yield given appropriate information X
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 10
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
ALLOYS and an MATERIAL SCIENCE CONCEPTS Define metals and list 5 properties X
INTRODUCTION Define alloys and explain their importance X
to METALLURGY Describe properties of common alloys and X
give applications of each
(also see IDENTIFICATION SYSTEMS Understand the Steel alloys: AISI-SAE system X
concepts from Understand the Aluminum alloys: AA system X
Chapter 7 Understand the Copper Alloys: CDA system X
Bonding in Understand the Unified Numbering System X
Metals) PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS Define metallurgy X
OF METALLURGY Explain what a metallurgist does X
(Chemical Bonds Describe how metallurgy knowledge can be X
C5.5x C5.5d,e) used to solve industrial problems
METALLURGICAL AND CHEMICAL Understand how chemistry is related to metallurgy X
(Solutions C4.7x) TERMINOLOGY Define chemical terms such as element, atom, X
compound, molecule, & solutions
(Solids C4.3x MATERIAL PROPERTIES Explain the relationship between strength, X
C4.3e,h) hardness, and ductility (mechanical properties)
Compare various types of stresses X
(Nomenclature Describe stress-strain diagrams X
C4.2) Explain modulus of elasticity X
Explain physical properties of alloys X
(Scientifc HEAT TREATING Define "heat treating" and explain its importance X X Alloy Project
Reflection and Annealing: describe and give application X X Alloy Project
Social Implications Normalizing: describe and give application X X Alloy Project
C1.2 Quenching: describe and give application X X Alloy Project
C1.2C,D,E,f,g,j) Tempering: describe and give application X X Alloy Project
Understand how heat treating changes the X X Alloy Project
mechanical properties of alloys
LEARNING PROCESS
Page 11
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
THE BEHAVIOR PROPERTIES OF GASES Explain why gases are easier to compress than solids or liquids X
OF GASES Describe 3 factors that affect gas pressure X
(Chapter 14) Describe the relationship among T, P, and V X
BOYLE'S LAW Calculate Pressure from the P-V relationship X
Calculate Volume from the P-V relationship X
(C5.2f) CHARLES'S LAW Calculate the T from the T-V relationship X
(Ideal Gas Law Calculate the V from the T-V relationship X
C4.5x GAY - LUSSAC'S LAW Calculate the T from the T- P relationship X
C4.5a,b,c) Calculate the P from the T-P relationship X
THE COMBINED GAS LAW Calculate the P, V, or T from the P-V-T relationship X
Be able to algebraically rearrange the equation X
THE IDEAL GAS LAW Calculate amount of gas at any conditions of P, V, T X
Know the ideal gas constant & its correct units X
Compare and contrast real and ideal gases X
Explain van der Waals equation of state X
DALTON'S LAW OF PARTIAL PRESSURE Calculate the total P of a mixture of gases X
Calculate the partial P of a gas in a mixture of gases X
ACIDS AND GENERAL INFORMATION List properties of acids and bases X
BASES Describe how [H+] and [OH-] are related in aq solution X
(Chapter 19) THE pH CONCEPT Classify a solution as neutral, acidic, or basic, given X
the hydrogen-ion or hydroxide-ion concentration
(Acids and Calculate the pH of a solution given the hydrogen-ion X
Bases C5.7 concentration or the hydroxide-ion concentration
C5.7A, B, C, D) Calculate the hydrogen-ion or hydroxide-ion X
concentration given the pH of a solution
(Bronsted-Lowry Describe at least 2 methods used to measure pH X
C5.7x COMPARE AND CONTRAST THE Define and give examples of Arrhenius acids & bases X
C5.7 f,g,i) ACIDS AND BASE THEORIES Distinguish between monoprotic, diprotic, triprotic acids X
Classify substances as acids or bases, and identify conjugate X
acid-base pairs in reactions using the Bronsted-Lowry theory
Define amphoteric X
Classify substances as either Lewis acids or bases X
LEARNING PROCESS
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
Page 12
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
SOLUTIONS HOMOGENEOUS SYSTEMS Distinguish between a solvent and a solute X
(Chapter 16 and Describe what happens in the solution process X
Chapter 15.2) Explain why all ionic compounds are electrolytes X
SOLUTION FORMATION
List 3 factors that determine how fast a soluble substance
dissolves
X
SOLUBILITY Define solubility X
(Solutions C4.7x
Explain the difference among saturated, unsaturated,and
supersaturated solutions
X
C4.7a,b) Distinguish between miscible and immiscible liquids X
FACTORS AFFECTING SOLUBILITY Apply Henry's law to solve gas solubility problems X
Explain how changing temperature may affect the solubility of a
substnace
X
Explain how thermal pollution is related to solubility X
Understand solubilty trend of gases in water at different
temperatures X
MOLARITY
Be able to define concentration and use the terms dilute solution
and concentrated solution when comparing solutions
X
Define and work problems involving the molarity of a solution X
COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES OF SOLUTIONS Define & identify colligative properties of solutions X
Define vapor pressure & explain on why a solution has a lower
vapor pressure than the pure solvent of that solution
X
Define boiling point elevation & explain why a solution has a
higher boiling point than the pure solvent of that solution
X
Define freezing point depression & explain why a solution has a
lower freezing point than the pure solvent of that solution
X
MOLALITY Define molality and calculate the molality of a solution X
CALCULATING BOILING POINT AND Calculate the boiling point elevation of an aqueous solution X
FREEZING POINT CHANGES
Calculate the freezing point depression of an
aqueous solution
X
LEARNING PROCESS
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
Page 13
I
N
F
O
R
M
A
T
I
O
N
K
N
O
W
L
E
D
G
E
K
N
O
W
-
H
O
W
W
I
S
D
O
M
CAPACITY CAPACITY BREAKDOWN SKILLS BREAKDOWN PORTFOLIO
HYDRO- ALIPHATIC HYDROCARBONS Construct the electron dot structure of alkanes X
CARBON Write condensed molecular structures of alkanes X
COMPOUNDS Write structural formula of alkane given IUPAC X
(Chapter 22) name and vice versa
Write structural formula of an alkane given IUPAC X
(carbon name , and vice versa
chemistry C5.8x Be able to name and identify simple alkenes and alkynes X
C5.8A,B,C) Compare and contrast alkanes, alkenes, alkynes X
HYDROCARBONS IN PLASTICS Distinguish between a monomer and a polymer X
(scientific Explain polymerization X
reflection and Give examples of polymers used in plastics X
social List additives to plastics and their purpose X
implications C1.2 Compare and contrast thermosets and thermoplastics X
C1.2B,E,g,I,j,k) Recognize that there are natural polymers such as proteins, X
starches, and latex
(scientific PLASTIC PROCESSING METHODS Explain the basics of injection molding X
inquiry C1.1 Explain the basics of blow molding X
C1.1f,I) Explain the basics of thermoforming X
Explain the basics of extrusion X
COAL, NATURAL GAS & PETROLEUM Describe origins of coal & products it yields X
Describe the formation of petroleum deposits X
Describe the formation of natural gas deposits X
Define petroleum refining & cracking X
Page 14
You might also like
- EEE - 201 Course PalnDocument7 pagesEEE - 201 Course PalnkannanchammyNo ratings yet
- XI Chemistry Important Questions on Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding and EquilibriumDocument37 pagesXI Chemistry Important Questions on Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonding and EquilibriumAliLakhoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge iGCSE Chemistry Revision GuideDocument3 pagesCambridge iGCSE Chemistry Revision GuideHồ Liên KhảiNo ratings yet
- PDF DocumentDocument4 pagesPDF DocumentCHENFEI LIUNo ratings yet
- UHS MCAT Entry Test Syllabus 2015Document36 pagesUHS MCAT Entry Test Syllabus 2015Shawn Parker89% (9)
- IGCSE Combined Science (0654) - Chemistry ChecklistDocument4 pagesIGCSE Combined Science (0654) - Chemistry ChecklistHồ Liên KhảiNo ratings yet
- UHS Lahore Entrance Test Syllabus 2011Document37 pagesUHS Lahore Entrance Test Syllabus 2011Junaid AlamNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - Part 1Document4 pagesTopic 1: Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - Part 1MohamudNo ratings yet
- Syllabus & Model Paper: Entrance TestDocument60 pagesSyllabus & Model Paper: Entrance TestTanzil RahmanNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument78 pagesChemistryShabnam Fatima SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Physics Question Bank 2023 - KVKDocument3 pagesPhysics Question Bank 2023 - KVKkartik.doye2005No ratings yet
- Madras Christian College, UG Chemistry Question PapersDocument44 pagesMadras Christian College, UG Chemistry Question PapersShekhar NarwalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry G-12Document42 pagesChemistry G-12Bereket AsefaNo ratings yet
- M Topics: Chapters 5-9 ReviewDocument10 pagesM Topics: Chapters 5-9 Reviewbluemoon4777No ratings yet
- 2022-23 Class - 11TH Assignment of Chemistry Chapters - 1 To 4Document8 pages2022-23 Class - 11TH Assignment of Chemistry Chapters - 1 To 4carsk403No ratings yet
- Essay Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesEssay Type QuestionspoorviNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Curriculum 20201598663098Document24 pagesChemistry Curriculum 20201598663098Hilal AmjadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CurriculumDocument106 pagesChemistry Curriculumas1pkNo ratings yet
- Tutorials PT 1 - Materials ScienceDocument19 pagesTutorials PT 1 - Materials ScienceVassish DassagneNo ratings yet
- You May Not Start To Read The Questions Printed On The Subsequent Pages of This Question Paper Until Instructed That You May Do So by The InvigilatorDocument5 pagesYou May Not Start To Read The Questions Printed On The Subsequent Pages of This Question Paper Until Instructed That You May Do So by The InvigilatorSpringOrchidNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Virtual Mode Test-Partb I-V 17-01-2021Document7 pagesQuestion Bank-Virtual Mode Test-Partb I-V 17-01-2021Logeshwer SPNo ratings yet
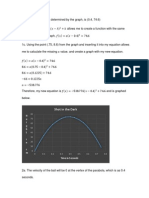
- Molecular Structure and Thermodynamic Properties of HCN and DCNDocument5 pagesMolecular Structure and Thermodynamic Properties of HCN and DCNBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- REVISION SEE Chemistry 2023Document10 pagesREVISION SEE Chemistry 2023Sahitya SumanNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives As91390Document2 pagesLearning Objectives As91390api-252561013No ratings yet
- Chem 150 PS1 2014Document5 pagesChem 150 PS1 2014Jay CaoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Important QuestionsDocument11 pagesChemistry Important QuestionsRahul Nagesh 9BNo ratings yet
- S.K.N.R. Degree College.: Dept. of ChemistryDocument2 pagesS.K.N.R. Degree College.: Dept. of ChemistryRajani KumbalaNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument19 pagesQuestion BankKUNALNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unified PYQDocument29 pagesChemistry Unified PYQoyes2minNo ratings yet
- Win Ref Q Phy 4113 July 2017.iutDocument2 pagesWin Ref Q Phy 4113 July 2017.iutirqoviNo ratings yet
- (London MathematicG. J. O. Jameson - The Prime Number Theorem (2003, Cambridge University Press)Document264 pages(London MathematicG. J. O. Jameson - The Prime Number Theorem (2003, Cambridge University Press)emilio0% (1)
- Austrian Chem Olympiad 2019Document38 pagesAustrian Chem Olympiad 2019Matei PascariuNo ratings yet
- PhysRev TheoryofBondingDocument8 pagesPhysRev TheoryofBondinguzairiqbal800_696794No ratings yet
- 962 Chemistry (PPU) Semester 1 TopicsDocument9 pages962 Chemistry (PPU) Semester 1 TopicsJosh, LRTNo ratings yet
- Physics Theory-FinalDocument26 pagesPhysics Theory-Finaladibsadman10No ratings yet
- Madras Christian College, UG Physics Question PapersDocument35 pagesMadras Christian College, UG Physics Question PapersShekhar Narwal100% (1)
- MIT Problem Set #2 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMIT Problem Set #2 SolutionsĐạt LêNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: One Mark QuestionsDocument9 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry: One Mark QuestionsTanvi KishoreNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Problems 5th EditionDocument3 pagesCH 11 Problems 5th Editionnisannn0% (1)
- Ho-6 (2011)Document2 pagesHo-6 (2011)Jashanjib MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics I Course OutcomesDocument2 pagesEngineering Mathematics I Course OutcomesGUNDAM VENU GOPAL REDDY, CSE2020 Vel Tech, ChennaiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 - Computational ChemistryDocument11 pagesExperiment 4 - Computational ChemistryOsama AnatyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For Short AnswerDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank For Short AnswerUmesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Questions For Cbse 2011Document65 pagesQuestions For Cbse 2011NAVEEN KUMAR GARGNo ratings yet
- SR Physics - Chapter Wise Important QuestionsDocument11 pagesSR Physics - Chapter Wise Important Questionsgitha71% (248)
- 2112 Exam 08Document5 pages2112 Exam 08Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- CAPE Chemistry U1 - Breakdown of SyllabusDocument24 pagesCAPE Chemistry U1 - Breakdown of SyllabusJevon SiddonNo ratings yet
- 654 Guess Paper Physics 10th ClassDocument9 pages654 Guess Paper Physics 10th ClassMuhammad MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document9 pagesWa0000.Ramya. RNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics I Question BankDocument14 pagesEngineering Physics I Question BankBALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- 2 MarksDocument1 page2 MarkshelloNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER+6+Drills Tro F14Document5 pagesCHAPTER+6+Drills Tro F14PAUL ALEGRENo ratings yet
- Checklist - Unit 1 AQA Chemistry A-LevelDocument5 pagesChecklist - Unit 1 AQA Chemistry A-LevelChalfin Aitashe MutambwaNo ratings yet
- Physics IADocument2 pagesPhysics IAPriyam SarkarNo ratings yet
- Atomic Energy Levels and Grotrian Diagrams: Hydrogen I - Phosphorus XVFrom EverandAtomic Energy Levels and Grotrian Diagrams: Hydrogen I - Phosphorus XVNo ratings yet
- Group Theory in Quantum Mechanics: An Introduction to Its Present UsageFrom EverandGroup Theory in Quantum Mechanics: An Introduction to Its Present UsageNo ratings yet
- Mess PaperDocument53 pagesMess Paperapi-245442073No ratings yet
- RexairinternshipDocument11 pagesRexairinternshipapi-245442073No ratings yet
- Seminars s2 13 14Document2 pagesSeminars s2 13 14api-245442073No ratings yet
- Employability Skills Matrix 09 10Document1 pageEmployability Skills Matrix 09 10api-245442073No ratings yet
- HydrocarbonreviewDocument3 pagesHydrocarbonreviewapi-245442073No ratings yet
- Time-Cost Sheet For Pot ProtectorsDocument1 pageTime-Cost Sheet For Pot Protectorsapi-245442073No ratings yet
- PpcoverDocument1 pagePpcoverapi-245442073No ratings yet
- ShotinthedarkDocument2 pagesShotinthedarkapi-245442073No ratings yet
- AlgiimatrixDocument7 pagesAlgiimatrixapi-245442073No ratings yet
- MatrixelaDocument18 pagesMatrixelaapi-245442073No ratings yet
- Mla Work CitedDocument2 pagesMla Work Citedapi-245442073No ratings yet
- PresentationoutlineDocument3 pagesPresentationoutlineapi-245442073No ratings yet
- BMC LabelDocument1 pageBMC Labelapi-245442073No ratings yet
- AirbagsDocument2 pagesAirbagsapi-245442073No ratings yet
- CatconvertersDocument2 pagesCatconvertersapi-245442073No ratings yet
- ProjectsDocument1 pageProjectsapi-245442073No ratings yet
- MentormatrixDocument2 pagesMentormatrixapi-245442073No ratings yet
- Cartridge Brassc26000Document15 pagesCartridge Brassc26000api-245442073No ratings yet
- ToursDocument2 pagesToursapi-245442073No ratings yet
- TrendsingraphsDocument2 pagesTrendsingraphsapi-245442073No ratings yet
- Coverd 6Document4 pagesCoverd 6api-245442073No ratings yet
- Bodyd 6Document19 pagesBodyd 6api-244584762No ratings yet
- Thermal Dynamic Principals StandardsDocument1 pageThermal Dynamic Principals Standardsapi-244954731No ratings yet
- KissesevidenceDocument1 pageKissesevidenceapi-245442073No ratings yet
- Logistical Engineering StandardsDocument1 pageLogistical Engineering Standardsapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Materials and Engineering StandardsDocument1 pageMaterials and Engineering Standardsapi-244958549No ratings yet
- Project Planning StandardsDocument19 pagesProject Planning Standardsapi-245213984No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering StandardsDocument1 pageMechanical Engineering Standardsapi-245297609No ratings yet
- Engineering Graphical Communications StandardsDocument5 pagesEngineering Graphical Communications Standardsapi-243909487No ratings yet
- Organic 4Document3 pagesOrganic 4Racheal KirbyNo ratings yet
- 11th Grade ChemistryDocument98 pages11th Grade ChemistryRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Tritylamine (Triphenylmethylamine) in Organic Synthesis Baze SchiffDocument10 pagesTritylamine (Triphenylmethylamine) in Organic Synthesis Baze SchiffNickly NickNo ratings yet
- Mezzanine Finance 12Document8 pagesMezzanine Finance 12bryant_bedwellNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Infra Merah-LengkapDocument63 pagesKuliah Infra Merah-LengkapM Nur M. MahmudNo ratings yet
- CMO and Stripped MBS Structures ExplainedDocument18 pagesCMO and Stripped MBS Structures ExplainedViplove SinghNo ratings yet
- Electron pushing reviews and tips for organic reactionsDocument5 pagesElectron pushing reviews and tips for organic reactionsJesús PortilloNo ratings yet
- Risk Return Analysis-IIFLDocument131 pagesRisk Return Analysis-IIFLPrathapReddy100% (1)
- MDOT - 2012 Standard Specifications For ConstructionDocument930 pagesMDOT - 2012 Standard Specifications For ConstructionKhaled Hesham HyariNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 - Molecular Orbital RepresentationDocument7 pagesExercise 5 - Molecular Orbital Representationapi-235187189No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Intermolecular Interactions 2013 Essentials in Modern HPLC SeparationsDocument29 pagesChapter 4 Intermolecular Interactions 2013 Essentials in Modern HPLC SeparationsCrystyRojasNo ratings yet
- EXP2Document9 pagesEXP2Kavisha Asha100% (1)
- Bond Price Volatility: Dr. Himanshu Joshi FORE School of Management New DelhiDocument51 pagesBond Price Volatility: Dr. Himanshu Joshi FORE School of Management New Delhiashishbansal85No ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 - Key Carbon Compounds ConceptsDocument9 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 - Key Carbon Compounds ConceptsSofiyyahOpieNo ratings yet
- Cyanuric Acid and CyanuratesDocument24 pagesCyanuric Acid and CyanurateskrommhgNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Course OutlineDocument7 pagesChemistry Course OutlinePhillip CookNo ratings yet
- RMN ProblemsDocument7 pagesRMN ProblemsAnonymous llSDP0tNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Inter 2 UTS - Wo AnsDocument3 pagesQuiz - Inter 2 UTS - Wo AnsNike HannaNo ratings yet
- AKTU Financial Market and Commercial Banking Unit IV NotesDocument50 pagesAKTU Financial Market and Commercial Banking Unit IV NotesGaurav SonkarNo ratings yet
- Final Exam ACS 360 PreviewDocument10 pagesFinal Exam ACS 360 PreviewStarrx714No ratings yet
- Country Default Spreads and Risk PremiumsDocument3 pagesCountry Default Spreads and Risk PremiumsFAISAL CHNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate Theories and CatalysisDocument7 pagesReaction Rate Theories and CatalysisJosephine ChenNo ratings yet
- SBUX Project Manual SpecsDocument202 pagesSBUX Project Manual Specsryan rivalesNo ratings yet
- Therm DynDocument13 pagesTherm DynSumathi SrinivasNo ratings yet
- 2 - Magdalena Estates Inc Vs RodriguezDocument3 pages2 - Magdalena Estates Inc Vs RodriguezLariza Aidie100% (1)
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument22 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundsapi-24735088294% (17)
- Stereochemistry Impacts Drug ActivityDocument36 pagesStereochemistry Impacts Drug Activityfajra dinda crendhutyNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesVictor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- Mortgage Markets Chapter 11 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMortgage Markets Chapter 11 Multiple Choice QuestionsSoraLeeNo ratings yet
- 1, Naperville, Illinois 60566: AmocoDocument8 pages1, Naperville, Illinois 60566: AmocoGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet