Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PSP Unit I Notes
Uploaded by
TPVANITHA0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
161 views73 pagesLECTURE NOTES
Original Title
Psp Unit I Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLECTURE NOTES
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
161 views73 pagesPSP Unit I Notes
Uploaded by
TPVANITHALECTURE NOTES
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 73
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NANDHA ENGINEERING COLLEGE
(Autonomous Institution)
Erode-638 052
LECTURE NOTES
13 CS101- PROBLEM SOLVING AND C PROGRAMMING
I Semester
B.E /B.TECH (COMMON TO ALL BRANCHES)
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
NANDHA ENGINEERING COLLEGE, ERODE-52
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
UNIT 1
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
Computer Basics - Applications of Computer - Computer organization -
Number systems - Computer Software- Types of software - Software
Development steps - Basic Internet terminologies- Introduction to Office
packages
INTRODUCTION:
The term Computer is derived from the Latin word computare which means to
compute or to calculate. So it is considered to be a calculating device.
Computer is the most powerful tool created by the man and it influences day to day
jobs in our life.
Today, computer technology has spread toe very sphere of existence of modern man
from Railway reservation to medical diagnosis, from TV programmes to satellite launching
everywhere we witness the elegance, sophistication and efficiency possible only with the help
of computers.
DEFINITIONS:
Computer is a fast operating electronic device which automatically accepts and stores
input data, processes them and produces results under the direction of a detailed step
by step program
A computer is an electronic device machine devised for performing calculations and
controlling operations that can be expressed either in logical or numerical terms.
A computer is an electronic device that performs diverse operations with the help of
instructions to process the information in order to achieve desire results.
A computer is an electronic device, operation under the control of instructions stored
in its own memory unit, that can accepts data(input), process data arithmetically and
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
logically, produce information(output) from the processing and store the results for
future use.
DATA:
It is the facts about anything whatever we call them or it is the raw materials of
information.
Data refer to any form of raw facts on paper or in electronic form. In electronic form,
data refers to data fields, records, files and databases, word processing documents,
images, etc.
INFORMATION:
The processed data is called the information and the data or information comes in
various shapes or sizes depending upon the application.
Computer can store process and retrieve such data or information as and when
required.
BASIC OPERATIONS OF A COMPUTER:
The computer has the following five basic operations to carry out any task.
1. Input:It is the process of capturing or acquiring the information, or it is the raw data
or information. By using this we can do any process.
2. Process: It is the transformation process to convert the input into output.
3. Output:It is result, which comes from the transformation process or it is the outcome
of the process.
4. Storing:It is the process of saving the data or information or instructions, so that they
can be retained and retrieved whenever required.
5. Controlling:It is process of directing the manner and sequence in which all the
operations are to be performed.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
COMPARISON OF COMPUTER WITH HUMAN BEING AND
CALCULATOR
Computer is an electronic device where we can store large amount of
information.
The information can be retrieved in any manner or in any form.
It can be processed in any form to produce the result.
COMPUTER Vs HUMAN BEING
The computer can perform any arithmetic task with high speed which a man
cannot perform.
The advantage of using computer is that it can execute tasks with more
accuracy and speed than human being.
Human being is not restricted by any limits, but computer is restricted by
limited step by step instructions called program.
COMPUTER Vs CALCULATOR:
S. No Characteristics Calculator Computer
1. Speed Fast Much Faster
2. Performance
Simple Calculations
and numeric
processing
Complex problem
and non numeric
processing
3. Memory
Less internal memory
and no permanent
storage, temporary
storage only
Large internal
memory and large
permanent storage
available.
4. Machine Electronic device Electronic device
5. Operation Arithmetic
Arithmetic and
Logical
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
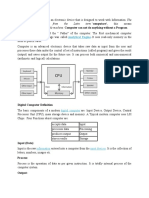
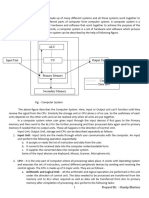
BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION:
A computer is an information processing machine. It can be viewed as a system,
which consists of number of interrelated components that work together with the
aim of converting data into information.
To attain information, data is entered through input devices.
This data is processed using the central processing unit and then the processed
data is displayed to the users using various output devices.
All these parts (input devices, central processing unit and output devices) are
referred to as hardware of the computer.
The block diagram of the computer system have the following three units, each
functional unit corresponds to their basic operations performed as described in
detail
1. Input Unit
2. Central Processing Unit
3. Output Unit
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
INPUT DEVICES:
Input devices are electromechanical devices that allow the user to feed
information into the computer for analysis, storage and to give commands to the
Central Processing Unit.
Data and instructions are entered into the memory of a computer through input
devices.
It captures information and translates it into a form that can be processed by the
central processing unit.
Computer accepts input in two ways, either manually or directly.
In case of manual data entry, the user enters the data into the computer by hand.
For example, by using keyboard and mouse.
In case of direct entry, information is fed into the computer automatically from a
source document (like barcode).
Some of the important input devices are: Keyboard, Mouse, Lightpen, Trackball,
Joystick, etc.
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT:
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) referred to as the brain of a computer
system. It converts data (input) into meaningful information (output).
A CPU controls all internal and external devices, performs arithmetic and logic
operations and also it controls the usage of main memory to store data and
instructions and controls the sequence of operations.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
The CPU is sub-divided into the following four sub system
1. Control Unit
2. Arithmetic and Logic Unit
3. Memory Unit
4. Secondary Storage
CONTROL UNIT:
This unit checks the correctness of sequence of operations.
It fetches program instruction from the primary storage unit, interprets them and
ensures correct execution of the program.
It also controls the input / output devices and directs the overall functioning of the
other units of the computer.
ARITHMETIC / LOGIC UNIT (ALU):
The arithmetic / logic unit (ALU) contains the electronic circuitry that executes all
arithmetic and logical operations on the data made available to it.
Arithmetic Unit:
This unit is responsible for performing the actual computing and carrying out the
arithmetic calculations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
It can perform these operations at a very high speed.
Logic Unit:
The logic unit enables the CPU to perform logical operations based on the
instructions provided to it.
The unit can compare numbers, letters or special characters and can then take
action based on the result of the comparison.
Logical operations of logic unit can test for three conditions : (1) equal to
condition, (2) less than condition, (3) greater than condition.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
MEMORY UNIT:
Computers require memory to process data and store output. Memory refers to the
electronic holding place for instructions and data.
We can classify memory into two broad categories:
i) Primary memory (to handle the data)
ii) Secondary memory (to store)
Primary Memory: (Volatile Memory)
Primary memory, also known as main memory stores data and instructions for
processing.
This is generally used to hold the program being currently executed in the
computer, the data being received from the input unit and the intermediate and
final results of the program.
The primary memory generally loses its contents when you switch off the
computer.
Secondary Memory: (Non Volatile Memory)
It may store several programs, documents, databases, etc
Secondary memory, also known as auxiliary memory or external memory is used
for storing instructions and data.
It is the permanent storage. The data or information stored in this storage will not
be erased when the power is lost. It is a non volatile memory.
OUTPUT DEVICES:
Devices used to get the response or result of a process from the computer is called
output devices.
Output devices take the machine coded output results from the CPU and convert
them into a form that is easily readable(such as characters, graphical, or audio
visual) by human beings.
The outputs which can be easily understood and used by human beings are in the
form of hard copy and soft copy.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
The physical form of output is known as hard copy.
The electronic version of an output, which usually resides in computer memory
and disk, is known as soft copy.
Commonly used output devices are: Visual Display Unit (VDU) or Monitor,
Printers, Plotters, etc.
NUMBER SYSTEMS:
INTRODUCTION:
A number is required for counting or to express the amount of some quantity. It
consists of a group of symbols called digits, which are arranged in a definite manner.
The most widely adopted system is the decimal number system which has ten digits
(0, 1, 2 9), the octal system has eight digits (0, 1, 2, ..7), the hexadecimal system has
sixteen digits (0, 1 9, A, B, C, D, E, F) and the binary system has only two (0 & 1).
The number systems are basically of two types:
i) Non positional number system
ii) Positional number system
Non positional number system:
The non positional number system with which all of us are familiar is the Roman
number system.
This number system is difficult to use as it has no symbol for zero.
Positional number system:
The most widely used number system is the positional number system.
In this system the position of a digit indicates the significance to be attached to that
digit.
For e.g.: 3977
7 * 10
0
-> Unit Position
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
7 * 10
1
-> Tenth Position
9 * 10
2
-> 100
th
Position
3 * 10
3
-> 1000
th
Position
DECIMAL NUMBER SYSTEM:
The number system that is most commonly used is the decimal number system.
In this number system the base or radix is 10 and there are altogether ten number i.e.
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9.
In the decimal number system, the successive position to the left of the decimal point
represents units, tens, hundreds, thousands, etc.
Example:
In decimal number system 258.34
10
or 258.34 consists the digits
4 in the position (4 * 10
-2
)
3 in the position (3 * 10
-1
)
8 in the unit position (8 * 10
0
)
5 in the tenth position (5 * 10
1
)
2 in the hundred position (2 * 10
2
)
and its values can be written as
2 * 10
2
+ 5 * 10
1
+ 8 * 10
0
. 3 * 10
-1
+ 4 * 10
-2
2 * 100 + 5 * 10 + 8 * 1 . 3 * 1 / 10 + 4 * 1 / 100
200 + 50 + 8 . 0.3 + 0.04
(258.34)
10
= 258.34
BINARY NUMBER SYSTEM:
Almost all digital computers are based on binary number system
Binary means two, the binary system uses only two digits i.e. 0s and 1s.
The base or radix of binary number system is (2) because it contains only two
numbers.
The weight assigned to bits in this system is power of 2.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
2
4
2
3
2
2
2
1
2
0
. 2
-1
2
-2
2
-3
2
-4
OCTAL NUMBER SYSTEM:
The number system with base or radix (8) is known as octal number system. There are
only eight digits i.e. 0, 1,2,3,4,5,6,7.
8
4
8
3
8
2
8
1
8
0
. 8
-1
8
-2
8
-3
8
-4
HEXADECIMAL NUMBER SYSTEM:
It has a base of 16 and this requires 16 distinct symbols to represent the number.
The base 16 suggests choices of 16 single character digits or symbols.
The first 10 digits are digits of decimal system (0 to 9) and the remaining 6 digits are
denoted by (A to F) where A = 10, B = 11, C = 12, D = 13, E = 14 and F = 15.
Since numbers (0 to 9) and alphabets (A to F) are used to represent the digits in
hexadecimal number system, it is also called the Alphanumeric Number System
The weight assigned to bits in this system is power of 16.
16
4
16
3
16
2
16
1
16
0
. 16
-1
16
-2
16
-3
16
-4
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
COMPUTER SOFTWARE
INTRODUCTION:
A set of instructions that cause a computer to perform one or more tasks. The set of
instructions is often called a program or, if the set is particularly large and complex, a system.
Computers cannot do any useful work without instructions from software; thus a combination
of software and hardware (the computer) is necessary to do any computerized work.
COMPUTER SOFTWARE DEFINITION
Computer software is a general term used to describe a collection of computer programs,
procedures and documentation that perform some task on a computer system. The term
includes application software such as word processors which perform productive tasks for
users, system software such as operating systems, which interface with hardware to provide
the necessary services for application software, and middleware which controls and co-
ordinates distributed systems.
Software is created with programming languages and related utilities, which may come in
several of the above forms: single programs like script interpreters, packages containing a
compiler, linker, and other tools; and large suites (often called Integrated Development
Environments) that include editors, debuggers, and other tools for multiple languages.
COMPUTER HARDWARE DEFINITION
Hardware is a comprehensive term for all of the physical parts of a computer, as
distinguished from the data it contains or operates on, and the software that provides
instructions for the hardware to accomplish tasks.
A typical computer (Personal Computer, PC) contains in a desktop or tower case the
following parts:
Motherboard which holds the CPU, main memory and other parts, and has slots for
expansion cards
power supply - a case that holds a transformer, voltage control and fan
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
storage controllers, of IDE, SCSI or other type, that control hard disk , floppy disk,
CD-ROM and other drives; the controllers sit directly on the motherboard (on-board)
or on expansion cards
graphics controller that produces the output for the monitor
the hard disk, floppy disk and other drives for mass storage
interface controllers (parallel, serial, USB, Firewire) to connect the computer to
external peripheral devices such as printers or scanners
TYPES OF SOFTWARE
SYSTEM SOFTWARE
System software is responsible for controlling, integrating, and managing the individual
hardware components of a computer system. Generally, system software consists of an
operating system and some fundamental utilities such as disk formatters, file managers,
display managers, text editors, user authentication (login) and management tools, and
networking and device control software.
OPERATING SYSTEM SOFTWARE
The operating system software makes the computer perform its basic operational functions.
Disk operating system (DOS) is one of the earlier types of operating system software used to
power IBM-compatible computers. Commands are typed at a prompt to direct the computer
to carry out its functions.
Windows is the most common operating system today. It permits several programs to be
opened simultaneously and provides ease of movement between the open programs.Windows
NT is used for business networks. Once this operating system is downloaded and running,
other kinds of software are opened to perform the desired functions.The Macintosh Operating
System (Mac OS) is designed for use with Apple, Mac, and Power Mac computers
APPLICATION SOFTWARE
Application software allows performance of specific tasks, such as writing letters, computing
formulas, playing games, or carrying out desktop publishing tasks
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Word-processing software: Writing tasks previously done on typewriters with
considerable effort can now be easily completed with word-processing software.
Writing tasks such as keying in reports, letters, and tables, as well as merging
documents, can be performed easily. Documents can be easily edited and formatted.
Revisions can be made by deleting (cutting), inserting, moving (cutting and pasting),
and copying data. Documents can be stored (saved) and opened again for revisions
and/or printing. Many styles and sizes of fonts are available to make the document
attractive.
Spreadsheet software: Spreadsheet software permits performance of an almost
endless variety of quantitative tasks such as budgeting, keeping track of inventory,
preparing financial reports, or manipulating numbers in any fashion, such as
averaging each of ten departmental monthly sales over a six-month period. A
spreadsheet contains cells, the intersection of rows and columns. Each cell contains a
value keyed in by the user. Cells also contain formulas with many capabilities, such as
adding, multiplying, dividing, subtracting, averaging, or even counting. An
outstanding feature is a spreadsheet's ability to recalculate automatically. If one were
preparing a budget, for example, and wanted to change a variable such as an increase
in salary or a change in amount of car payments, the formulas would automatically
recalculate the affected items and the totals.
Database software: A database contains a list of information items that are similar in
format and/or nature. An example is a phone book that lists a name, address, and
phone number for each entry. Once stored in a database, information can be retrieved
in several ways, using reports and queries. For example, all the names listed for a
given area code could be printed out and used for a commercial mailing to that area.
Desktop publishing software: This software permits the user to prepare documents
by using both word-processing devices and graphics. Desktop publishing software
uses word-processing software, with all its ease of entering and revising data, and
supplements it with sophisticated visual features that stem from graphics software.
For example, one can enhance a printed message with virtually any kind of
illustration, such as drawings, paintings, and photographs.
Presentation software: A speaker may use presentation software to organize a slide
show for an audience. Text, graphics, sound, and movies can easily be included in the
presentation. An added feature is that the slide show may be enhanced by inclusion of
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
handouts with two to six slides printed on a page. The page may be organized to
provide space for notes to be written in by the audience as the presentation ensues. An
example of this is Power Point. Preparation of the software is simplified by the use of
'wizards' that walk the user through the creation of the presentation.
COMMUNICATION SOFTWARE
Using telephone lines and working through the computer's modem, communications software
makes it possible to communicate to any location in the world using either fax or electronic
mail. A fax transmits whatever copy is on an original sheet of paper (text, graphics, or
handwriting) to another computer or fax machine. Electronic mail (e-mail) is a text message.
It remains in the receiver's computer until retrieved. The message can be stored in either the
sender's or the receiver's computer for later processing. Attachments or files can also be sent
via e-mail.
UTILITY SOFTWARE
Utility software is used to diagnose computer problems and repair them. A major type is a
virus (or "illness") checker. It checks for viruses the computer may have received from
downloading information received from the Internet, e-mail, or another disk. Although some
viruses may do little damage, others can cause serious damage to files and/or the computer
operating system. It is important for a computer owner to find a virus-check program, install
it, use it, and keep it continually updated. New viruses are found continually, and the only
way to be safe is to update. Some antivirus software allows easy updating by downloading
new files from the Internet.
SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT STEPS:
Software development life cycle model is also called as waterfall model which is followed by
majority of systems. This software development life cycle process has the following seven
stages in it namely
1. System Requirements Analysis
2. Feasibility study
3. Systems Analysis and Design
4. Code Generation
5. Testing
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
6. Maintenance
7. Implementation
Let us discuss each of these to have an overview about teach of the following steps in
software development life cycle.
1. System Requirements Analysis:
The first essential or vital thing required for any software development is system. Also the
system requirement may vary based on the software product that is going to get developed.
So a careful analysis has to be made about the system requirement needed for the
development of the product. After the analysis and design of the system requirement phase
the system required for the development would be complete and the concentration can be on
the software development process.
2. Feasibility study:
In this phase development team has to make communication with customers and make
analysis of their requirement and analyze the system. By making analysis this way it would
be possible to make a report of identified area of problem. By making a detailed analysis on
this area a detailed document or report is prepared in this phase which has details like project
plan or schedule of the project, the cost estimated for developing and executing the system,
target dates for each phase of delivery of system developed and so on.
3. Systems Analysis and Design:
This is an important phase in system development .Here analysis is made on the design of the
system that is going to be developed. In other words database design, the design of the
architecture chosen, functional specification design, low level design documents, high level
design documents and so on takes place. Care must be taken to prepare these design
documents because the next phases namely the development phase is based on these design
documents. If a well structured and analyzed design document is prepared it would reduce the
time taken in the coming steps namely development and testing phases of the software
development life cycle.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
4. Code Generation:
This is the phase where actual development of the system takes place. That is based on the
design documents prepared in the earlier phase code is written in the programming
technology chosen. After the code is developed generation of code also takes place in this
phase. In other words the code is converted into executables in this phase after code
generation.
5. Testing:
A software or system which is not tested would be of poor quality. This is because this is the
phase where system developed would be tested and reports are prepared about bugs or errors
in system. To do this testing phase there are different levels and methods of testing like unit
testing, system test and so on. Based on the need the testing methods are chosen and reports
are prepared about bugs. After this process the system again goes to development phase for
correction of errors and again tested. This process continues until the system is found to be
error free. To ease the testing process debuggers or testing tools are also available.
6. Mainanence:
After the testing phase is completely through and the system is found to be error free it is
delivered to the customer. But no real system would be error free even then. This is because
when the system gets executed in real user system scenarios there would be possibilities of
lot of bugs and errors. This phase is called the maintenance phase and the errors in this are
recorded and changes has to be made in the system accordingly and again testing phase
comes into picture.
7. Implementation:
This is the final stage when the system gets into live.
The above software development process are all vital for a system to get developed with
quality and thus to achieve customer satisfaction which is the main objective of any software
development process.
BASIC INTERNET TERMINOLOGY:
Domain abbreviations (last three characters in URL or address)
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
edu - Educational institutions
com - Commercial businesses
gov - U.S. government
mil - The U.S. military
org - Other organizations
net - Network/Internet Service Providers
Favorites - A menu option at the top of the screen that shows any websites that have been
previously saved for you to return to on a different day, much like a traditional bookmark is
used for books.
Go - A command in Explorer that sits on the top of the screen with other commands. In Go,
Explorer keeps track of most sites that a user has visited during a session of using Explorer.
This is not saved once you quit Explorer.
Home page - Default setting, or the page that opens up when you start your Browser. A
homepage can also be the entry point for people viewing information that is provided.
Internet - Network of millions of computers used to send information back and forth to one
another. There is no authority agency or company that decides what can and cannot be
published on the internet. This means that virtually anyone can publish, and means that there
are large numbers of sites that contain false and misleading information. It is important to
check who takes credit for the site you are viewing.
Links - Hypertext which, when clicked, connects you to another site or another page within
the same site. In most cases, these links are usually highlighted in blue and are always
underlined.
Page - What is on your screen at any given time. The page includes all the information
available to you by scrolling up or down; however, when you click on hypertext your
computer will 'jump' to a new page.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Search Engines - Software that allows you to search the Web by typing in a topic of interest.
Examples of search engines we use are Google, HotBot, and Northern Light. These search
engines find exact matches from what has been typed in the search screen to either
documents (files) or subjects of files on the WWW.
URL or Uniform Resource Locator - The address for a specific file on the web, as well as a
method for directing users to a specific file, at a specific site. To type in a different URL,
press command and L at the same time on a Macintosh computer, control and L on a PC, or
locate the address bar at the top of the screen, type in the URL, and then press return. The
URL for the Blaine School District Home page is: http://www.blaine.k12.wa.us.
Web Browser - To access the WWW, you need a Browser. A Web Browser is client
software that gets information from a server. It interprets the information, formats it, and
displays it on your computer screen. The most popular browser, and the one we use most
often in Blaine, is Internet Explorer.
WWW, World Wide Web or Web - Interactive collection of hypertext pages linked to one
another. They may include text, graphics and/or links to other spots in the Web. The Web is
interactive because a user can click on text or graphics to navigate (move) to more
information or other graphics, sounds and video that is of interest to them.
Components of the Internet
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (abbreviated as the Web or WWW) is a system of Internet servers that
supports hypertext to access several Internet protocols on a single interface.The World Wide
Web consists of files, called pages or home pages, containing links to documents and
resources throughout the Internet.
Electronic mail, or e-mail, allows computer users locally and worldwide to exchange
messages.
FTP
FTP stands for File Transfer Protocol. This is both a program and the method used to transfer
files between computers.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Chat & Instant Messaging
Chat programs allow users on the Internet to communicate with each other by typing in real
time.
OFFICE PACKAGES:
MS-WORD
INTRODUCTION
MS-WORD is a part of the bigger package called MS OFFICE, which can do
much more than word processing. In fact when we open up MS OFFICE we
will find four main components in it. They are MS-WORD (for word
processing), MS EXCEL (for spreadsheet), MS ACCESS (for database
management) and MS POWERPOINT (for presentation purposes).
Word Processor is a Software package that enables we to create, edit, print and
save documents for future retrieval and reference. Creating a document involves
typing by using a keyboard and saving it. Editing a document involves
correcting the spelling mistakes, if any, deleting or moving words sentences or
paragraphs.
IMPORTANT FEATURES OF MS-WORD
Ms-Word not only supports word processing features but also DTP features.
Some of the important features of Ms-Word are listed below:
i. Using word we can create the document and edit them later, as and when
required, by adding more text, modifying the existing text,
deleting/moving some part of it.
ii. Changing the size of the margins can reformat complete document or part
of text.
iii. Font size and type of fonts can also be changed. Page numbers and
Header and Footer can be included.
iv. Spelling can be checked and correction can be made automatically in the
entire document. Word count and other statistics can be generated.
v. Text can be formatted in columnar style as we see in the newspaper. Text boxes can
be made.
vi. Tables can be made and included in the text.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
vii. Word also allows the user to mix the graphical pictures with the text. Graphical
pictures can either be created in word itself or can be imported from outside like from
Clip Art Gallery.
viii. Word also provides the mail-merge facility.
ix. Word also has the facility of macros. Macros can be either attached to some
function/special keys or to a tool bar or to a menu.
x. It also provides online help of any option.
GETTING STARTED WITH MS-WORD
While working in MS-WORD we have to work with a mouse. Also one can
work, to some extent, through the keyboard. The use of mouse is simpler as it is
fully menu driven. In MS-WORD every command is available in the form of
icons.
We can go inside MS-WORD by the following way
1. Take the mouse pointer to START button on the task bar. Click the left
mouse button. The monitor will show like as follows:
2. Move the pointer to programs. We will notice another menu coming up
to the right.
3. In that menu identify where Microsoft word is placed. Move the cursor
horizontally to come out of programs.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
4. Move into the rectangular area meant for Microsoft word. Click the left
mouse button there. The computer will start MS-WORD. We will find the
screen as follows.
Let us discuss the important components of the screen.
a. Title Bar
The title bar displays the name of the currently active word document. Like
other WINDOWS applications, it can be used to alter the size and location of
the word window.
b. Tool Bars
Word has a number of tool bars that help we perform task faster and with great
ease. Two of the most commonly tool bars are the formatting tool bar and the
standard tool bar. These two toolbars are displayed just below the title bar. At
any point of time any tool bar can be made ON or OFF through the tool bar
option of View Menu.
(d) Status Bar
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
The Status Bar displays information about the currently active document. This
includes the page number that we are working, the column and line number of
the cursor position and so on.
(e) Scroll Bar
The Scroll Bar helps we scroll the content or body of document. We can do so
by moving the elevator button along the scroll bar, or by click in on the buttons
with the arrow marked on them to move up and down and left and right of a
page.
(f) Workspace
The Workspace is the area in the document window where we enter/type the
text of document.
(g) Main Menu
The Word main menu is displayed at the top of the screen as shown in the Fig.
9.1. The main menu further displays a sub menu. Some of the options are
highlighted options and some of them appear as faded options. At any time,
only highlighted options can be executed, faded options are not applicable.
Infect if the option is faded we will not be able to choose it. We may not that
any option faded under present situation may become highlighted under
different situations.
Menus
When we begin to explore Word 2000, we will notice a significant change in the
menu structure if we are familiar with previous versions of Word. The menus in
Word 2000 display only the commands we have recently used. To view all
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
options in each menu, we must click the double arrows at the bottom of the
menu. The images below show the Format menu collapsed (left) and expanded
(right) after the double arrows at the bottom of the menu were clicked:
Follow the steps below to display menus similar to previous versions of Word
with all the choices listed initially:
Select View|Toolbars|Customize from the menu bar.
Click on the Options tab.
Uncheck the Menus show recently used commands first check box.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Shortcut Menus
These features allow we to access various Word commands faster than using the
options on the menu bar. View shortcut menus by right-clicking with the mouse.
The options on this menu will vary depending on the element that was right-
clicked. For example, the shortcut menu below is produced by right-clicking on
a bulleted list.
Actions such as "Decrease Indent" and "Increase Indent" are only applicable to
lists and therefore only appear on the list shortcut menu. The shortcut menus are
helpful because they only display the options that can be applied to the item that
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
was right-clicked and, therefore, prevent searching through the many menu
options.
Toolbars
Many toolbars displaying shortcut buttons are also available to make editing and
formatting quicker and easier. Select View|Toolbars from the menu bar to
select the toolbars. The toolbars that are already displayed on the screen are
checked. Add a toolbar simply by clicking on the name.
Customizing Toolbars
There may be certain actions on a toolbar that we do not use and there may also
be commands that we execute often but that are not located on any toolbar.
Word toolbars can be customized so these commands can be added and deleted
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Select View|Toolbars|Customize and click the Commands tab.
By highlighting the command categories in the Categories box, the
choices will change in the Commands box to the right.
Select the command we would like to add to the toolbar by selecting it in
the Commands box.
Drag the command with the mouse to the desired location on the toolbar
and release the mouse button.
Remove a button from the toolbar by clicking and dragging the button off
the toolbar.
MS-EXCEL
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet application used to create and manage business
transactions that deal with accounting. To make this possible, it can assist we
with creating lists of transactions, then using those list to create charts and other
analysis tools..
To use Microsoft Excel, there are various ways we can start it:
As a regular Microsoft Windows application, to use Microsoft Excel, we
can click Start -> (All) Programs -> Microsoft Office -> Microsoft Office
Excel 2007
We can also create a shortcut on the desktop, in Windows Explorer, or in
My Computer. To create a shortcut, we can click Start -> (All) Programs
-> Microsoft Office, right-click and hold right mouse on Microsoft Office
Excel and drag (with the right mouse button) to the desktop. On the menu
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
that appears, click Create Shortcut Here. Another technique we can use
consists of opening My Computer, expanding the drive, the Program Files
folder, the Microsoft Office folder, the Office12 folder, right-clicking
Excel, clicking Create Shortcut, right-clicking the new shortcut and
clicking Cut, right-click wer desktop and click Paste.
If we are using My Computer or Windows Explorer, we can open the
Program Files folder, then Microsoft Office, then Office, and double-
click Excel
We can create an empty document on wer desktop and use it to launch
Microsoft Excel. To do that, we would right-click an empty area on the
desktop, position the mouse on New -> Microsoft Office Excel
Worksheet, type a name for the document, such as Time Sheet, and press
Enter twice
If we see a file in My Computer, Windows Explorer, My Network Places,
Microsoft Outlook, or we receive a document by e-mail, we can launch
Microsoft Excel by double-clicking the file or the attachment.
Excel allows we to create spreadsheets much like paper ledgers that can perform
automatic calculations. Each Excel file is a workbook that can hold many
worksheets. The worksheet is a grid of columns (designated by letters) and
rows (designated by numbers). The letters and numbers of the columns and
rows (called labels) are displayed in gray buttons across the top and left side of
the worksheet. The intersection of a column and a row is called a cell. Each cell
on the spreadsheet has a cell address that is the column letter and the row
number. Cells can contain text, numbers, or mathematical formulas.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Microsoft Excel 2000 Screen
Elements
Adding and Renaming Worksheets
The worksheets in a workbook are accessible by clicking the worksheet tabs just
above the status bar. By default, three worksheets are included in each
workbook. To add a sheet, select Insert|Worksheet from the menu bar. To
rename the worksheet tab, right-click on the tab with the mouse and select
Rename from the shortcut menu. Type the new name and press the ENTER
key.
The Standard Toolbar
This toolbar is located just below the menu bar at the top of the screen and
allows we to quickly access basic Excel commands.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
New - Select File|New from the menu bar, press CTRL+N, or click the New
button to create a new workbook.
Open - Click File|Open from the menu bar, press CTRL+O, or click the Open
folder button to open an existing workbook.
Save - The first time we save a workbook, select File|Save As and name the
file. After the file is named click File|Save, CTRL+S, or the Save button on the
standard toolbar.
Print - Click the Print button to print the worksheet.
Print Preview - This feature will allow we to preview the worksheet before it
prints.
Spell Check - Use the spell checker to correct spelling errors on the worksheet.
Undo and Redo - Click the backward Undo arrow to cancel the last action we
performed, whether it be entering data into a cell, formatting a cell, entering a
function, etc. Click the forward Redo arrow to cancel the undo action.
MS-POWER POINT:
Open Power Point and we will be prompted by a dialog box with four choices.
Each of these options are explained on this page. If Power Point is already open
or this box does not appear, select File|New from the menu bar.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
AutoContent Wizard
The AutoContent Wizard provides templates and ideas for a variety of
presentation types. Page through the wizard by clicking the Next button on the
bottom of each page after making necessary choices.
Design Template
Power Point provides many templates with different backgrounds and text
formatting to begin power point presentation. Preview each design by
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
highlighting the template name on the list. Press OK.
v
Blank Presentation
Select Blank Presentation to build the presentation from scratch with no preset
graphics or formatting.
Open an Existing Presentation
Select this option to open a Power Point presentation that already exists. Select
the folder the file is located in from the Look in: drop-down menu and highlight
the file on the list. Click Open to open the presentation.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
AutoLayout
After selecting the presentation type, we will be prompted to choose the layout
of the new slide. These layouts include bulleted lists, graphs, and/or images.
Click on each thumbnail image and a description will be printed in the message
box. Highlight the layout we want and click OK.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
INTRODUCTION TO OFFICE AUTOMATION
In MS OFFICE we will find four main component
They are
MS-WORD (for word processing)
MS EXCEL (for spreadsheet)
MS ACCESS (for database management)
MS POWERPOINT (for presentation purposes).
MS-WORD
Using word we can create the document and edit them later, as and when
required, by adding more text, modifying the existing text,
deleting/moving some part of it.
Changing the size of the margins can reformat complete document or part
of text.
Font size and type of fonts can also be changed. Page numbers and
Header and Footer can be included.
Spelling can be checked and correction can be made automatically in the
entire document.
Tables can be made and included in the text.
Word also allows the user to mix the graphical pictures with the text.
Word also provides the mail-merge facility.
Screen Layout
Menus
The menus in MS-WORD display only the commands you have recently
used. To view all options in each menu, you must click the double arrows
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
at the bottom of the menu. The images below show the Format menu
collapsed (left) and expanded (right) after the double arrows at the bottom
of the menu were clicked:
Toolbars
Many toolbars displaying shortcut buttons are also available to make
editing and formatting quicker and easier. Select View | Toolbars from
the menu bar to select the toolbars. The toolbars that are already
displayed on the screen are checked. Add a toolbar simply by clicking on
the name
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Creating and Opening Documents
Creating and Opening Documents
There are several ways to create new documents, open existing
documents, and save documents in Word:
Create a New Document
Click the New Document button on the menu bar.
Choose File | New from the menu bar.
Open an Existing Document
Click the Open File button on the menu bar.
Choose File | Open from the menu bar.
Save a Document
Click the Save button on the menu bar.
Select File|Save from the menu bar.
Renaming Documents
To rename a Word document while using the program, select
File|Open and find the file you want to rename.
Right-click on the document name with the mouse and select
Rename from the shortcut menu.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Type the new name for the file and press the ENTER key.
Close a Document
Close the current document by selecting File|Close or click the
Close icon if it's visible on the Standard Toolbar.
Formatting Text
The formatting toolbar is the easiest way to change many attributes of text. If
the toolbar as shown below isn't displayed on the screen, select View|Toolbars
and choose Formatting.
FONTS
The Font dialog box allows you to choose from a larger selection of formatting
options. Select Format | Font from the menu bar to access the box
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Formatting Paragraphs
Format a paragraph by placing the cursor within the paragraph and
selecting Format | Paragraph from the menu bar.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Lists
Bulleted and Numbered Lists
Highlight the entire list to change all the bullets or numbers, or Place the
cursor on one line within the list to change a single bullet.
Access the dialog box by selecting Format|Bullets and Numbering
from the menu bar or by right-clicking within the list and selecting Bullets and
Numbering from the shortcut menu.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Select the list style from one of the seven choices given
Click OK when finished
Tables
Tables are used to display data and there are several ways to build them
in Word.
select Table | Insert Table from the menu bar. Select the number of rows
and columns for the table and click OK.
Inserting Rows and Columns
Once the table is drawn, insert additional rows by placing the cursor in
the row you want to be adjacent to. Select Table|Insert|Rows Above or Rows
Below. Or, select an entire row and right-click with the mouse. Choose Insert
Rows from the shortcut menu.
Much like inserting a row, add a new column by placing the cursor in a cell
adjacent to where the new column will be added. Select Table|Insert|Columns
to the Left or Columns to the Right. Or, select the column, right-click with the
mouse, and select Insert Columns.
Moving and Resizing a Table
A four-sided moving arrow and open box resizing handle will appear on
the corners of the table if the mouse is placed over the table. Click and drag the
four-ended arrow to move the table and release the mouse button when the table
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
is positioned where you want it. Click and drag the open box handle to resize
the table. Change the column widths and row heights by clicking the cell
dividers and dragging them with the mouse.
Graphics
To add a clip art image from the Microsoft library to a document, follow
these steps:
Select Insert|Picture|Clip Art from the menu bar.
Follow these steps to add a photo or graphic from an existing file:
Select Insert|Picture|From File on the menu bar.
Click the down arrow button on the right of the Look in: window to find
the image on your computer.
Highlight the file name from the list and click the Insert button.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Editing A Graphic
More picture effects can be changed using the Picture toolbar. The
Picture toolbar should appear when you click on the image. Otherwise, select
View|Toolbars|Picture from the menu bar to activate it.
Insert Picture will display the image selection window and allows you to
change the image.
Image Control allows to to make the image grayscale, black and white, or a
watermark.
More/Less Contrast modifies the contrast between the colors of the image.
More/Less Brightness will darken or brighten the image.
Click Crop and drag the handles on the activated image to delete outer portions
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
of the image.
Line Style will add a variety of borders to the graphic.
Text Wrapping will modify the way the document text wraps around the
graphic.
Format Picture displays all the image properties in a separate window.
Reset Picture will delete all the modifications made to the image.
Auto Shapes
The AutoShapes toolbar will allow you to draw many different geometrical
shapes, arrows, flow chart symbols, stars, and banners on the document.
Activate the AutoShapes toolbar by selecting Insert|Picture|AutoShapes or
View|Toolbars|AutoShapes from the menu bar
Spelling and Grammar Check
To use the spelling and grammar checker, follow these steps:
Select Tools|Spelling and Grammar from the menu bar.
The Spelling and Grammar dialog box will notify you of the first
mistake in the document and misspelled words will be highlighted
in red.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
As long as the Check Grammar box is checked in the Spelling and
Grammar dialog box, Word will check the grammar of the document in
addition to the spelling
If Word finds a grammar mistake, it will be shown in the box as the
spelling errors. The mistake is highlighted in green text.
Synonyms
Word 2000 has a new feature for finding synonyms. Simply right-click on
the word and select Synonyms from the shortcut menu. From the list of
suggested words, highlight the word you would like to use or click Thesaurus...
for more options.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Page Formatting
The margins can also be changed using the Page Setup dialog box
Select File|Page Setup and choose the Margins tab in the dialog box.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Page Size and Orientation
Change the orientation page within the Page Setup dialog box.
Select File|Page Setup and choose the Paper Size tab.
Headers and Footers
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
A header is text that is added to the top margin of every page such as a
document title or page number and a footer is text added to the bottom margin.
Follow these steps to add or edit headers and footers in the document:
Select View | Header and Footer from the menu bar. The Header and
Footer toolbar will appear and the top of the page will be highlighted as shown
below.
Page Numbers
Follow these instructions for another way to add page numbers to a
document.
Select Insert|Page Numbers from the menu bar and the following
dialog box will appear
MS-EXCE
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet application used to create and manage
business transactions that deal with accounting.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Each Excel file is a workbook that can hold many worksheets.
The worksheet is a grid of columns (designated by letters) and rows
(designated by numbers).
The letters and numbers of the columns and rows (called labels) are
displayed in gray buttons across the top and left side of the worksheet.
The intersection of a column and a row is called a cell.
Each cell on the spreadsheet has a cell address that is the column letter
and the row number.
Cells can contain text, numbers, or mathematical formulas.
Microsoft Excel Screen Elements
Modifying A Worksheet
Moving Through Cells
Use the mouse to select a cell you want to begin adding data to and
use the keyboard strokes listed in the table below to move through the cells of a
worksheet.
Adding Worksheets, Rows, and Columns
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Worksheets - Add a worksheet to a workbook by selecting
Insert|Worksheet from the menu bar.
Row - To add a row to a worksheet, select Insert|Rows from the
menu bar, or highlight the row by clicking on the row label, right-click with the
mouse, and choose Insert.
Column - Add a column by selecting Insert|Columns from the
menu bar, or highlight the column by click on the column label, right-click with
the mouse, and choose Insert.
Formatting Cells
For a complete list of formatting options, right-click on the highlighted
cells and choose Format Cells from the shortcut menu or select
Format|Cells from the menu bar.
Formulas and Functions
Formulas are entered in the worksheet cell and must begin with an equal
sign "=". The formula then includes the addresses of the cells whose
values will be manipulated with appropriate operands placed in between.
After the formula is typed into the cell, the calculation executes
immediately and the formula itself is visible in the formula bar
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Basic Functions
Functions can be a more efficient way of performing mathematical
operations than formulas.
For example, if you wanted to add the values of cells D1 through
D10, you would type the formula
"=D1+D2+D3+D4+D5+D6+D7+D8+D9+D10".
A shorter way would be to use the SUM function and simply
type
"=SUM(D1:D10)".
FunctionExampleDescription
SUM = SUM(A1:100) finds the sum of cells A1 through A100
AVERAGE = AVERAGE(B1:B10) finds the average of cells B1
through B10
MAX = MAX(C1:C100) returns the highest number from cells
C1 through C100
MIN = MIN(D1:D100) returns the lowest number from cells D1
through D100
SQRT = SQRT(D10) finds the square root of the value in cell D10
TODAY = TODAY() returns the current date (leave the
parentheses empty)
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Sorting
To execute a basic descending or ascending sort based on one column,
highlight the cells that will be sorted and click the Sort Ascending (A-Z)
button or Sort Descending (Z-A) button on the standard toolbar.
Complex Sorts
To sort by multiple columns, follow these steps:
Highlight the cells, rows, or columns that will be sorted.
Select Data|Sort from the menu bar.
From the Sort dialog box, select the first column for sorting from
the Sort By drop-down menu and choose either ascending or descending.
Select the second column and, if necessary, the third sort column
from the Then By drop-down menus.
CHARTS
Charts allow you to present data entered into the worksheet in a visual
format using a variety of graph types
Chart Wizard
The Chart Wizard brings you through the process of creating a chart by
displaying a series of dialog boxes.
Enter the data into the worksheet and highlight all the cells that will be
included in the chart including headers.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Click the Chart Wizard button on the standard toolbar to view the first
Chart Wizard dialog box.
Chart Type - Choose the Chart type and the Chart subtype if
necessary. Click Next.
Chart Source Data - Select the data range and click Next.
Chart Options - Enter the name of the chart and titles for the X- and Y-
axes. Other options for the axes, grid lines, legend, data labels, and data table
can be changed by clicking on the tabs. Press Next to move to the next set of
options.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Chart Location - Click As new sheet if the chart should be placed on a new,
blank worksheet or select As object in if the chart should be embedded in an
existing sheet and select the worksheet from the drop-down menu.
Click Finish to create the chart.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
MS-POWER POINT
A user may use presentation software to organize a slide show for an
audience.
Text, graphics, sound, and movies can easily be included in the
presentation.
An added feature is that the slide show may be enhanced by inclusion of
handouts with two to six slides printed on a page.
An example of this is Power Point.
Getting Started
Open Power Point and you will be prompted by a dialog box with four
choices. Each of these options are explained on this page. If Power Point
is already open or this box does not appear, select File|New from the
menu bar
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Design Template
Power Point provides many templates with different backgrounds and text
formatting to begin your presentation. Preview each design by highlighting the
template name on the list. Press OK after you have chosen the design
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Blank Presentation
Select Blank Presentation to build the presentation from scratch with no
preset graphics or formatting.
Open an Existing Presentation
Select this option to open a Power Point presentation that already exists.
Select the folder the file is located in from the Look in: drop-down menu
and highlight the file on the list. Click Open to open the presentation
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
AutoLayout
After selecting the presentation type, you will be prompted to choose the
layout of the new slide. These layouts include bulleted lists, graphs,
and/or images. Click on each thumbnail image and a description will be
printed in the message box. Highlight the layout you want and click OK.
Screen Layout
The Power Point screen layout in Normal View
Adding Content
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Bulleted lists allow you to clearly display the main points of your presentation on
slides. The text boxes on design templates already include bulleted lists. Click the
place holder on the slide to begin adding text and press the ENTER key to return to
the next line and add a new bulleted item
Select a text box by clicking on it with the mouse. A border with nine handles will appear
around the text box. The four handles on the corners will resize the length and the width of
the box at once while the handles on the sides will resize only in one direction. Click one of
the handles and drag it with the mouse. Release the mouse button when it is the size you want
it to be
Working with Text
If the slide layout includes text boxes, simply click on the text box to add
text. To add a text box to the slide, select Insert|Text Box from the menu
bar and draw the text box with the mouse. Set text editing options by
selecting Tools|Options from the menu bar and clicking the Edit tab.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
Color Schemes
Select Format|Slide Color Scheme from the menu bar.
Click one of the preset color scheme thumbnail images in the Color
schemes box.
To make changes to the color scheme, click the Custom tab on the dialog
box.
Slide Effects
Slide Animation
Select Slide Show|Custom Animation from the menu bar.
Select the object on the slide that will be animated from the Check to
animate slide objects list.
Under the Effects tab, select the animation type and direction from the
drop-down menus and select a sound if you wish.
NEC- 13CS101-Problem Solving and C Programming
section. The drop-down menu provides options for displaying the characters for
each bulleted item.
Slide Transitions
Select Slide Show|Slide Transition from the menu bar.
From the Effect section, choose a transition from the drop-down menu and
notice the preview after the transition is selected. Select a speed for the
transition as well.
Under Advance, check "On mouse click" for the slide transition to occur by
clicking the mouse or using keystrokes or check "Automatically after" and a
number of seconds if the transition should occur automatically.
Select a Sound if necessary and check the Loop until next sound if it should
keep repeating until the next sound is played.
Click Apply to All if the transition effects should be added to every slide or
Apply if the effects should be added only to the current slide.
You might also like
- Introduction to Computers: Definition, Characteristics & ComponentsDocument143 pagesIntroduction to Computers: Definition, Characteristics & ComponentsAdnan HamadNo ratings yet
- CT-Chapter 1Document15 pagesCT-Chapter 1Om MistryNo ratings yet
- Computer Fundamentals ModuleDocument4 pagesComputer Fundamentals ModuleManniel E ErfeNo ratings yet
- Funda OCRDocument49 pagesFunda OCRHemaaHemaaNo ratings yet
- FOAC Unit-1Document16 pagesFOAC Unit-1krishnapandey77733No ratings yet
- Fcpit: Familiarisation of ComputerDocument38 pagesFcpit: Familiarisation of ComputerVipin SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer?: Techno Computers, Mysore Basic NotesDocument43 pagesWhat Is Computer?: Techno Computers, Mysore Basic NotesKarthik MNo ratings yet
- Bcastudyguide Com Computer Fundamental Office Automation CfoaDocument10 pagesBcastudyguide Com Computer Fundamental Office Automation Cfoadharmista p DumasiyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer PDFDocument121 pagesIntroduction To Computer PDFAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer FundamentalDocument63 pagesComputer Fundamentalpriyanka groverNo ratings yet
- Unit 1&2 - DCFDocument38 pagesUnit 1&2 - DCF22itu218No ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic Lab Manual Covers Computer BasicsDocument5 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Lab Manual Covers Computer BasicsAnonymous naEAR9adNo ratings yet
- Computer: A Versatile Electronic Device That Performs Calculations at High SpeedDocument34 pagesComputer: A Versatile Electronic Device That Performs Calculations at High SpeedVijay Kumar BNo ratings yet
- Notes On Computer PDFDocument19 pagesNotes On Computer PDFGolam Rasul KibriaNo ratings yet
- 1.fundamentals of Computer & Programming PDFDocument67 pages1.fundamentals of Computer & Programming PDFBhumi VavadiyaNo ratings yet
- Beato Bscpe3b Cedd Act1 EditedDocument3 pagesBeato Bscpe3b Cedd Act1 EditedBeato MichaelNo ratings yet
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDocument3 pagesCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Components of A Computer SystemDocument26 pagesComponents of A Computer SystemheheheheNo ratings yet
- Lower Secondary Answers Log On To ITDocument118 pagesLower Secondary Answers Log On To ITRene Essel100% (1)
- Cite1004 Activity 1 MidtermDocument3 pagesCite1004 Activity 1 MidtermJoshua LimbagaNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of A ComputerDocument4 pagesBlock Diagram of A Computerwoyaf61625No ratings yet
- Comp. Hardware 1stDocument7 pagesComp. Hardware 1stpriyanka groverNo ratings yet
- Computer: Without A Program. Charles Babbage Is Called The " Father" of The Computer. The First Mechanical - It UsesDocument34 pagesComputer: Without A Program. Charles Babbage Is Called The " Father" of The Computer. The First Mechanical - It UsesMEDEPALLI SANDHYANo ratings yet
- BSC Ist Year Programming in CDocument219 pagesBSC Ist Year Programming in CSAIPRASAD VEMULANo ratings yet
- An Electronic Device Which Is Capable of Receiving InformationDocument2 pagesAn Electronic Device Which Is Capable of Receiving InformationDaljit SinghNo ratings yet
- Compskill1 7Document7 pagesCompskill1 7Nikhil YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes AutonomousDocument108 pagesUnit 1 Notes AutonomoussirishaNo ratings yet
- What is a computer? Characteristics, components and basic operationsDocument2 pagesWhat is a computer? Characteristics, components and basic operationsHimanshuRanaNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Introduction To Computer System and ProgrammingDocument21 pagesCH-1 Introduction To Computer System and ProgrammingpriyeshNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to Computer Hardware and SoftwareDocument6 pagesThe Essential Guide to Computer Hardware and SoftwareAjit JainNo ratings yet
- 175 16cacca1b 2020052204230029Document119 pages175 16cacca1b 2020052204230029shrivastavabhoomi46No ratings yet
- Practical 1Document13 pagesPractical 1swan htetpyNo ratings yet
- Computer System Computer ArchitectureDocument7 pagesComputer System Computer ArchitectureSuman Samal MagarNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Computer SystemDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Computer SystemKarl Steven Adalem MaddelaNo ratings yet
- Computer Application-Sbe NotesDocument16 pagesComputer Application-Sbe NotesjenniferpeterNo ratings yet
- Unit of Computer SystemDocument3 pagesUnit of Computer SystemvishalaroraccnaNo ratings yet
- Computer Script1Document29 pagesComputer Script1AbhinawNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware and SoftwareDocument11 pagesComputer Hardware and SoftwareMartin DavidNo ratings yet
- CSC 102 Tutorial Guide on General Computing and ProgrammingDocument74 pagesCSC 102 Tutorial Guide on General Computing and ProgrammingUsman Samuel BabalolaNo ratings yet
- Final Co Notes 1 38Document38 pagesFinal Co Notes 1 38kaveri.h.hulimani1993No ratings yet
- Radian Ias Academy (Feb.2013) Computer AwarenessDocument20 pagesRadian Ias Academy (Feb.2013) Computer AwarenessjosekinNo ratings yet
- Concept of ComputerDocument47 pagesConcept of ComputerAbdullah ShoaibNo ratings yet
- ITC Week 1Document27 pagesITC Week 1Fareeha MunawarNo ratings yet
- Practical-Assignment Final OkDocument69 pagesPractical-Assignment Final Okparwinder100% (1)
- Lecture 1 Block Diagram of ComputerDocument9 pagesLecture 1 Block Diagram of ComputerGaurav BishtNo ratings yet
- ICT LESSON NOTES, Introduction To ComputersDocument34 pagesICT LESSON NOTES, Introduction To ComputersJohn muasaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systemmemoryio DevicesDocument14 pagesComputer Systemmemoryio DevicesMilan GuragainNo ratings yet
- Input Process Output: The "Unsung Hero" Behind The InternetDocument57 pagesInput Process Output: The "Unsung Hero" Behind The Internetwise4nice9opNo ratings yet
- Mba (1 Semester) Computer Fundamental Mba Unit - I: Secondary StorageDocument12 pagesMba (1 Semester) Computer Fundamental Mba Unit - I: Secondary Storageshashi shekhar dixitNo ratings yet
- Computer System ExplainedDocument49 pagesComputer System ExplainedJessalyn PaclebNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Computer SystemDocument8 pagesUnit 1 - Computer SystemAkashNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer HardwareDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Computer HardwareKadima ChitechiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers: Dr. N.Rakesh Asst. Professor (SG) Dept. Computer Science & Engineering ASE, BangaloreDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Computers: Dr. N.Rakesh Asst. Professor (SG) Dept. Computer Science & Engineering ASE, BangaloreRohith KvgNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 - Von Neumann CADocument4 pagesChapter1 - Von Neumann CAsehgalharry284No ratings yet
- Comfuter Fundamentals Networking IdT1xQZfsDocument199 pagesComfuter Fundamentals Networking IdT1xQZfsRhdheh BdhehenNo ratings yet
- Computer Functions ExplainedDocument6 pagesComputer Functions ExplainedMEGHA SASINo ratings yet
- KMB 108 Unit I: Computer Application & Management Information and SystemDocument15 pagesKMB 108 Unit I: Computer Application & Management Information and SystemDeepankar singhNo ratings yet
- Mukund Sir's CompleteDocument147 pagesMukund Sir's CompleteanuNo ratings yet
- CS4448 01 Project StarvationDocument5 pagesCS4448 01 Project StarvationMinh Tran CongNo ratings yet
- C++ Exception Handling: AdvantageDocument7 pagesC++ Exception Handling: AdvantageRohan SakiNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of AlgorithmsDocument38 pagesAnalysis and Design of AlgorithmsShivani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- FACH Bandwidth Expansion to Reduce CongestionDocument6 pagesFACH Bandwidth Expansion to Reduce CongestionWaqas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Programming Language: By: Garima MaharjanDocument10 pagesProgramming Language: By: Garima MaharjanGarima MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Deadlock Prevention and Detection in Operating SystemsDocument11 pagesDeadlock Prevention and Detection in Operating SystemsSayeed KhanNo ratings yet
- Automated FSM Error Correction For Single Event UpsetsDocument5 pagesAutomated FSM Error Correction For Single Event Upsetsكورسات هندسيةNo ratings yet
- Lab7 6437074763336854Document2 pagesLab7 6437074763336854King EverestNo ratings yet
- Arrays and Pointers - DPP 01 - Parakram GATE 2024 Computer Science Weekday (Hinglish)Document3 pagesArrays and Pointers - DPP 01 - Parakram GATE 2024 Computer Science Weekday (Hinglish)Talha AmaanNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument3 pagesOperating Systempsaravanan1985No ratings yet
- B4xidev1 6Document133 pagesB4xidev1 6Henry MagdayNo ratings yet
- DSE-1 C Short Questions.: (I) Void (Ii) Long (Iii) Char (Iv) IntDocument4 pagesDSE-1 C Short Questions.: (I) Void (Ii) Long (Iii) Char (Iv) IntSaroj KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For VHDL For Engineers Kenneth L ShortDocument24 pagesSolution Manual For VHDL For Engineers Kenneth L ShortDanaPalmerygfb100% (42)
- BS, BBA, Aut-2018Document32 pagesBS, BBA, Aut-2018Kashif RazaNo ratings yet
- Consultas Recursivas Polimórficas en JPADocument4 pagesConsultas Recursivas Polimórficas en JPAJaime SotoNo ratings yet
- PHP Form Handling - Collect and Validate User Data with $_GET, $_POST and PHPDocument15 pagesPHP Form Handling - Collect and Validate User Data with $_GET, $_POST and PHPDeekshithaNo ratings yet
- Python MCQ: M 28 N 5 Print (M // N)Document32 pagesPython MCQ: M 28 N 5 Print (M // N)VooovoNo ratings yet
- TinyTerm Reference GuideDocument102 pagesTinyTerm Reference GuidesaranveluNo ratings yet
- 1640004236SAP ABAP Training - Brochure (2) - CompressedDocument15 pages1640004236SAP ABAP Training - Brochure (2) - CompressedishanNo ratings yet
- Bootstrap DatepickerDocument37 pagesBootstrap Datepickerunme4everNo ratings yet
- SQL StatementsDocument9 pagesSQL StatementsANILNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural NetworksDocument5 pagesConvolutional Neural NetworksYazan HassanNo ratings yet
- DATA CENTER COLLEGE of The Philippines: Course SyllabusDocument10 pagesDATA CENTER COLLEGE of The Philippines: Course SyllabusAbel IngawNo ratings yet
- Job Log Before Code ChangeDocument61 pagesJob Log Before Code ChangetalupurumNo ratings yet
- Jake S Resume AnonymousDocument2 pagesJake S Resume AnonymousSrinivas KonduriNo ratings yet
- Lesson 03 Python Programming FundamentalsDocument69 pagesLesson 03 Python Programming FundamentalsSumanta SinhatalNo ratings yet
- Classes and Objects in R ProgrammingDocument25 pagesClasses and Objects in R ProgrammingDisha KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Classes ParallelismDocument4 pagesClasses ParallelismMuthukumar ManickamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 Part A - Uninformed or Blind SearchDocument92 pagesLecture 02 Part A - Uninformed or Blind SearchAsnad AhmedNo ratings yet