Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-Maximum Shear Stress Theory-Derivation
Uploaded by
Murugan ShanmugamOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1-Maximum Shear Stress Theory-Derivation
Uploaded by
Murugan ShanmugamCopyright:
Available Formats
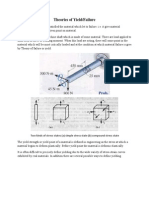
MAXIMUM SHEAR STRESS THEORY OF FAILURE
A THEORY OF FAILURE APPLICABLE TO DUCTILE MATERIALS
Statement of the theory
When Yielin! occurs in any material, the ma"im#m $hear $tre$$ at the point of failure
equals or exceeds the ma"im#m $hear $tre$$ when yielin! occurs in the ten$ion te$t
$%e&imen.
The theory applies to ductile materials only, because it is based on yielin!.
The three'imen$ional (tria"ial) $tre$$ $it#ation*
In the three-dimensional stress situation, the state of stress at a particular location is fully
defined by three principal stresses
1
,
2
, 3
.
Ma"im#m $hear $tre$$ at a lo&ation of the element
The extreme alues of shear stresses
23 13 12
, ,
, in each of the three principal planes are
then !ien by the expressions"
2
2 1
12
= ,
2
3 1
13
= ,
2
3 2
23
=
#xpressin! the principal stresses in the order of ma!nitude and si!n
3 2 1
Then the maximum shear stress is !ien by
2
3 1
13
=
THE CASE OF SIMPLE TE+SIO+ TEST ,HE+ YIELDI+- OCCURS
$or the simple tension test specimen, the three principal stresses when yieldin! occurs are"
1
% y
S
,
2
%&,
3
%&
The maximum shear stress then becomes
2 2
&
2
3 1
max 13
y y
S S
=
= =
THE CASE OF THREE DIME+SIO+AL STRESS ,HE+ YIELDI+- OCCURS
The maximum shear stress theory of failure states"
When Yielin! occurs in any material, the ma"im#m $hear $tre$$ at the point of failure
equals or exceeds the ma"im#m $hear $tre$$ when yielin! occurs in the ten$ion te$t
$%e&imen.
2 2
3 1
max
y
S
=
University of Nairobi Engineering Design II
The aboe equation implies that the shear yield stren!th of the material
2
y
sy
S
S =
'ut from analysis of plane stress situation, the maximum shear stress in plane stress is also
!ien in terms of plane stress elements
2
2
max
2
xy
y x
=
DESI-+ E.UATIO+ BASED O+ THE MAXIMUM SHEAR STRESS THEORY
This is deried by ad(ustin! the shear yield stren!th of the material with an appropriate factor
of safety
. .s f
. The desi!n equation then becomes"
. . ) 2 . . 2
3 1
max
s f
S
s f
S
y sy
= =
=
OR
. . ) 2 . . 2
2
2
max
s f
S
s f
S
y sy
xy
y x
= = +
=
for plane stress situation
APPLICATIO+ OF THE DESI-+ E.UATIO+
The principal stresses
1
/
2
/ 3
are first determined by stress analysis. *uch analysis
describes the principal stresses as a function of the loa carried, and the !eometry and
imen$ion$ of the machine or structural element.
The maximum shear stress in the desi!n equation is then expressed in terms of the
imen$ion$ of the machine or structural element, while the ri!ht hand side is a function of
the ten$ile yiel $tren!th of the material. The tensile yield stren!th of the material becomes
useful because it more easily determined from laboratory experiments.
The fa&tor of $afety is simply a number chosen by the desi!ner. The factor of safety to!ether
with the stren!th of the material, !ies the wor+in!
1
,desi!n, allowable- stress expected in the
machine part. The solution to the desi!n equation then !ies the minim#m imen$ion$
required to aoid fail#re of the element by yielin!.
1
Wor+in! *tress, pa!e .2/,0andboo+, 1etals #n!ineerin! 23esi!n, 4merican *ociety of 1echanical
#n!ineers ,4*1#-
Nyangasi 5a!e 2 of 2 01 2an#ary 3114
You might also like
- Chapter - 08 Switchboard and VSDDocument44 pagesChapter - 08 Switchboard and VSDdewidar1234100% (2)
- Bending ExperimentDocument17 pagesBending ExperimentaminNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Load and Stress AnalysisDocument96 pagesChapter-3 Load and Stress AnalysisDhinesh3693100% (1)
- Transformers and Tapchangers Version EDocument81 pagesTransformers and Tapchangers Version Emartinez_josel100% (1)
- Aakash Study PlannerDocument26 pagesAakash Study PlannerAaditya RavalNo ratings yet
- Project Report Group 4Document28 pagesProject Report Group 4Akame TakashitaNo ratings yet
- Testing of Adhesive Joints in The Wind Industry: AbstractDocument10 pagesTesting of Adhesive Joints in The Wind Industry: AbstractL.a. MayorNo ratings yet
- Theories of Yielding PDFDocument13 pagesTheories of Yielding PDFJowesh Avisheik GoundarNo ratings yet
- Tubos de CalorDocument7 pagesTubos de CalorChristo AcostaNo ratings yet
- Static Project Bridge FINALDocument34 pagesStatic Project Bridge FINALAhmad Faidhi100% (2)
- Theories of Failure 2Document23 pagesTheories of Failure 2Nagendra Manral100% (1)
- JJ310 STRENGTH OF MATERIAL Chapter 4 (B) Bending StressDocument14 pagesJJ310 STRENGTH OF MATERIAL Chapter 4 (B) Bending StressAh TiangNo ratings yet
- Lab 2-Force in A Statically Determined Cantilever TrussDocument14 pagesLab 2-Force in A Statically Determined Cantilever TrussAlif Bukhari Imran NaimNo ratings yet
- Full Report Solid MechDocument19 pagesFull Report Solid MechMUHAMMAD ARIFF DYAMIMNo ratings yet
- MOM Lab 8 NEWDocument7 pagesMOM Lab 8 NEWSaragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- Analisis Struktur C6Document47 pagesAnalisis Struktur C6Hazyema HarunNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument16 pagesLab Reportabe97No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Beam Deflection CalculationDocument21 pagesCivil Engineering Beam Deflection CalculationNajmi AimanNo ratings yet
- Assignment:2 - AML 169 - Engineering Mechanics (B Arch) : Submit in A4 SheetsDocument3 pagesAssignment:2 - AML 169 - Engineering Mechanics (B Arch) : Submit in A4 SheetsKartik MauryaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BFC34303 (Lyy)Document104 pagesChapter 1 BFC34303 (Lyy)shahrull1996No ratings yet
- Fila Table MathsDocument3 pagesFila Table MathsAsdia Aseffah FathiyaNo ratings yet
- ECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Buoyancy Sept19Document5 pagesECW 231 Tutorial and Answers Buoyancy Sept19hairinnisaNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 FMDocument17 pagesExp 4 FMKhadijah Ulol AzmiNo ratings yet
- A192 2. Syllabus SQQS1013 Student VersionDocument4 pagesA192 2. Syllabus SQQS1013 Student VersionJasmine TehNo ratings yet
- The Deflection of A Uniform Beam Subject To A Linearly Increasing Distributed Load Can Be Computed AsDocument15 pagesThe Deflection of A Uniform Beam Subject To A Linearly Increasing Distributed Load Can Be Computed AsAlodia Lulu SmileNo ratings yet
- Combined Stress (Bending + Torsion) Lab Report (ME321)Document15 pagesCombined Stress (Bending + Torsion) Lab Report (ME321)rahul kumarrNo ratings yet
- Assignment Retaining Wall - QuestionDocument6 pagesAssignment Retaining Wall - QuestionbadrulNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Assignment Flow ProfilesDocument7 pagesHydraulics Assignment Flow Profilessheikh hafiziNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test AnalysisDocument8 pagesTensile Test AnalysisNazmul HasanNo ratings yet
- Zub Indeterminate Truss DegDocument13 pagesZub Indeterminate Truss DegAnonymous jmo0bcjAsNo ratings yet
- Ces511 - Structural Engineering Laboratory Lab Experiment: Indeterminate Beam (Co2:Po5)Document4 pagesCes511 - Structural Engineering Laboratory Lab Experiment: Indeterminate Beam (Co2:Po5)Muhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Density and Porosity Lab ExperimentDocument11 pagesDensity and Porosity Lab ExperimentAriff ShasteraNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Diversity Factor of Ceiling Fans in My HouseDocument1 pageCalculation of Diversity Factor of Ceiling Fans in My HouseNaim HafizNo ratings yet
- Critical Load On StrutDocument5 pagesCritical Load On StrutelhammeNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Hydraulic Jan2012Document9 pagesFinal Exam Hydraulic Jan2012Anni SuhanaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Simple Structures in Engineering Mechanics (CENG1041Document9 pagesAnalyzing Simple Structures in Engineering Mechanics (CENG1041nvnrevNo ratings yet
- Group Asgmt No 2 EEDocument7 pagesGroup Asgmt No 2 EEHafiz Bin HarunNo ratings yet
- JJ310 STRENGTH OF MATERIAL Chapter 1 (A) Forces On MaterialDocument18 pagesJJ310 STRENGTH OF MATERIAL Chapter 1 (A) Forces On MaterialAh Tiang100% (1)
- Lab Report Inde BeamDocument10 pagesLab Report Inde Beamfauzan1698No ratings yet
- Eng MathDocument13 pagesEng MathZaKy ZubaidiNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document6 pagesLab 5AimiWaniNo ratings yet
- Example Chapter 2 - Air PollutionDocument24 pagesExample Chapter 2 - Air PollutionBright KnightNo ratings yet
- Lab Report-Strength of MaterialsDocument23 pagesLab Report-Strength of MaterialsArvin ArviniNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Eng - MechanicsDocument6 pagesLab 1 Eng - MechanicsChinna RutiranNo ratings yet
- Deflection LabDocument9 pagesDeflection LabFarid NajandNo ratings yet
- Full ReportDocument25 pagesFull ReportMuhammad Asyraf Bin RusliNo ratings yet
- Maximum Volume of a Cardboard BoxDocument2 pagesMaximum Volume of a Cardboard BoxSyafiq AimanNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bottle Filling System Circuit Diagram and ComponentsDocument15 pagesAutomatic Bottle Filling System Circuit Diagram and ComponentsNurulSyafiqahNo ratings yet
- Full As Contoh Member AkashahDocument29 pagesFull As Contoh Member AkashahWayen Bulat100% (1)
- Chapter2 PlasticityDocument34 pagesChapter2 PlasticityGowtham GanesanNo ratings yet
- Road Distress StudyDocument12 pagesRoad Distress Studyfuad haziqNo ratings yet
- Measuring Bending Moments in Beams Using Laboratory ExperimentsDocument7 pagesMeasuring Bending Moments in Beams Using Laboratory ExperimentsHawaiiChongNo ratings yet
- Test 1 BFC 32002 Hydrology - 1314 PDFDocument9 pagesTest 1 BFC 32002 Hydrology - 1314 PDFAzfarNo ratings yet
- Suspension Bridge - TARUMT Lab ReportDocument42 pagesSuspension Bridge - TARUMT Lab ReportKit YiNo ratings yet
- Assingment 1 MEC610Document14 pagesAssingment 1 MEC610MUHAMMAD NURUDIN IMAN GHANINo ratings yet
- Basic of Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument6 pagesBasic of Shear Force and Bending MomentRathin RakshitNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Lab ReportDocument20 pagesDynamic Lab ReportJohnsheng LeeNo ratings yet
- Bending Lab Report FinalDocument21 pagesBending Lab Report FinalNasri JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Student Code of Ethics Report TemplateDocument13 pagesStudent Code of Ethics Report TemplateKerol Kerol Kerol0% (1)
- Chapter+1+-+main+hydrological+concepts+ EditedDocument11 pagesChapter+1+-+main+hydrological+concepts+ EditedMARVINNo ratings yet
- Failure Theories Made Easy: Maximum Principal Stress (Rankine's)Document2 pagesFailure Theories Made Easy: Maximum Principal Stress (Rankine's)Nang TruongNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 2Document7 pagesTutorial 1 2nasserNo ratings yet
- Theories of FailuresDocument18 pagesTheories of FailuresZain ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Theories of Failure: Introduction: Due To Large Numbers of Examples of Compound Stresses MetDocument23 pagesUnit IV Theories of Failure: Introduction: Due To Large Numbers of Examples of Compound Stresses MetMohtasham NaeemNo ratings yet
- Odd Sem Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesOdd Sem Lesson PlanMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Notification SAIL Management Trainee PostsDocument9 pagesNotification SAIL Management Trainee PostsAnusha PalakurthyNo ratings yet
- Journey Planner From Cbe To SaDocument1 pageJourney Planner From Cbe To SaMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Part ProgrammingDocument5 pagesPart ProgrammingMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Me53 Design of Machine Elements L T P CDocument2 pagesMe53 Design of Machine Elements L T P CajithjkingsNo ratings yet
- Mark AllotmentDocument1 pageMark AllotmentMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Design of Fluid Power Systems for Industrial ApplicationsDocument2 pagesDesign of Fluid Power Systems for Industrial ApplicationsMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Design of Fluid Power Systems for Industrial ApplicationsDocument2 pagesDesign of Fluid Power Systems for Industrial ApplicationsMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Part-A (9X2 18 Marks) Answer ALL Questions Part-A (9X2 18 Marks) Answer ALL QuestionsDocument1 pagePart-A (9X2 18 Marks) Answer ALL Questions Part-A (9X2 18 Marks) Answer ALL QuestionsMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- DME Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDME Lesson PlanMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Caad LabDocument2 pagesCaad LabMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- MT 1Document1 pageMT 1Murugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Sri ShakthiDocument2 pagesSri ShakthiMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- How To Use AutoCADDocument20 pagesHow To Use AutoCADMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- 2013 Regulation Syllabus ITDocument108 pages2013 Regulation Syllabus ITNagendra KumarNo ratings yet
- 60 AutoCAD Tips in 60 Minutes FinalDocument21 pages60 AutoCAD Tips in 60 Minutes FinalMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- LIST OF EXPERIMENTS and Viva Voice QuestionDocument3 pagesLIST OF EXPERIMENTS and Viva Voice QuestionMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- 2013 Regulation Syllabus ITDocument108 pages2013 Regulation Syllabus ITNagendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Visitors To ICCCI 2014 ExhibitionDocument3 pagesIndustrial Visitors To ICCCI 2014 ExhibitionMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- FORMAT For Utilization CertificateDocument1 pageFORMAT For Utilization CertificateMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- FORMAT For Utilization CertificateDocument1 pageFORMAT For Utilization CertificateMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- PF (EPS) Withdrawal - Form 10CDocument6 pagesPF (EPS) Withdrawal - Form 10Cd0101No ratings yet
- BoundaryConditions CAEA PDFDocument28 pagesBoundaryConditions CAEA PDFMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Notification SAIL Management Trainee PostsDocument9 pagesNotification SAIL Management Trainee PostsAnusha PalakurthyNo ratings yet
- SPMCIL EPF Form 19 - Withdrawal and SuperannuationDocument2 pagesSPMCIL EPF Form 19 - Withdrawal and SuperannuationMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- SPMCIL EPF Form 19 - Withdrawal and SuperannuationDocument2 pagesSPMCIL EPF Form 19 - Withdrawal and SuperannuationMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- SPMCIL EPF Form 19 - Withdrawal and SuperannuationDocument2 pagesSPMCIL EPF Form 19 - Withdrawal and SuperannuationMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Kirchoff LawsDocument36 pagesKirchoff LawsMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- FEM INTRODocument21 pagesFEM INTROMurugan ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Power System Transmission and Security: DR Nuraddeen MagajiDocument68 pagesPower System Transmission and Security: DR Nuraddeen MagajiNuraddeen MagajiNo ratings yet
- Module6 - Ideal Gas ProcessesApplicationDocument20 pagesModule6 - Ideal Gas ProcessesApplicationJohn Dalton ValenciaNo ratings yet
- 9702p2vectorsallcompleted 150816104932 Lva1 App6891Document17 pages9702p2vectorsallcompleted 150816104932 Lva1 App6891Suman Pant0% (1)
- Earth Spin Sun OrbitDocument4 pagesEarth Spin Sun Orbitmrshong5bNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design CHE 311 Final Project MSUDocument15 pagesHeat Exchanger Design CHE 311 Final Project MSUnefoussiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Magnetism Questions With Full SolutionsDocument5 pagesAssignment Magnetism Questions With Full SolutionsSholihah AmirullahNo ratings yet
- The Seepage Control of The Tunnel Excavated in High-Pressure Water Condition Using Multiple Times Grouting Method PDFDocument17 pagesThe Seepage Control of The Tunnel Excavated in High-Pressure Water Condition Using Multiple Times Grouting Method PDFMarsheal FisongaNo ratings yet
- U-Tube ManometerDocument5 pagesU-Tube ManometerHarold Lee BolingetNo ratings yet
- Problem Term oDocument1 pageProblem Term oAnggiariniMutmainahNo ratings yet
- Introduction 2Document30 pagesIntroduction 2niteshNo ratings yet
- Physics 10 Reviewer Question SheetDocument5 pagesPhysics 10 Reviewer Question SheetAntonette TabilNo ratings yet
- Fom Lec Week 6Document35 pagesFom Lec Week 6nishan_ravin0% (1)
- MTL Grounding Tp1121-1Document16 pagesMTL Grounding Tp1121-1mongo55No ratings yet
- Mechanical 2nd Semester Notes PDFDocument6 pagesMechanical 2nd Semester Notes PDFchannu rolliNo ratings yet
- Material Engineering in CompositesDocument31 pagesMaterial Engineering in CompositesCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- 4PH0 1P Rms 20120823 PDFDocument24 pages4PH0 1P Rms 20120823 PDFwalyatNo ratings yet
- ME 218 - Spring 2018 - Week05 HandoutDocument7 pagesME 218 - Spring 2018 - Week05 HandoutNitin BhatiNo ratings yet
- Crystal GrowthDocument6 pagesCrystal GrowthArunmaalaNo ratings yet
- SEMIKRON DataSheet SKKE 15 07170871 PDFDocument4 pagesSEMIKRON DataSheet SKKE 15 07170871 PDFVinicius Veiverberg DillNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Volume & Bulk Density of BricksDocument25 pagesCalculation of Volume & Bulk Density of BricksKuntal PaulNo ratings yet
- Determine Amount of Oxygen in Tank from Pressure and TemperatureDocument3 pagesDetermine Amount of Oxygen in Tank from Pressure and Temperatureyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Chem Mid-Ch QsDocument61 pagesChem Mid-Ch QsSTUDIESEXAMS ONLYYYNo ratings yet
- Motion in PlaneDocument1 pageMotion in Planerina85293No ratings yet
- Thermal Transmission (Winter)Document20 pagesThermal Transmission (Winter)Robin Charles SamuelNo ratings yet