Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3BHS230517 E01 - Main Circuit Breaker Design For VSD
Uploaded by
srmohapatra50860 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
623 views2 pagescb design for VVVF drives
Original Title
3BHS230517 E01 - Main Circuit Breaker Design for VSD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentcb design for VVVF drives
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
623 views2 pages3BHS230517 E01 - Main Circuit Breaker Design For VSD
Uploaded by
srmohapatra5086cb design for VVVF drives
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
ABB MV Drives
3BHS230517 ZAB E01 Rev. F Page 1 of 2
Important note on main circuit breaker design for frequency converters
Function of the MCB
The main circuit breaker (MCB) is a major protection device of the frequency converter. If a serious
fault occurs in the frequency converter, the MCB must disconnect the main power supply to the
frequency converter immediately, on an open or trip command, to prevent hazard to the personnel
and further damage to the equipment. Depending on the main power supply configuration of the drive
system, the MCB is either located on the primary side of the converter transformer or on the primary
side of the frequency converter if the frequency converter is connected directly to the line (DTL); see
figure 1 for illustration.
Figure 1 shows a conceptual single-line diagram
of a typical drive system, including main power
supply, MCB, converter transformer, frequency
converter and electrical motor.
The MCB is defined as a switching device to
disconnect the power supply whenever required
by the process or when a fault occurs. Typical
devices used as MCBs are:
Vacuum circuit breakers
SF6 circuit breakers
Fused contactors or motor control
centers
A dedicated protection relay is used for:
Transformer or converter primary cable
protection (DTL)
Transformer protection (if applicable)
Transformer secondary cable protection
(if applicable)
Backing up the frequency converter
protection
M
MCB
Converter
transformer
Frequency
converter
Motor
MCB control
interface
Higher-level
control system
Local MCB control
CT Protection
relay
Figure 1: Drive system overview
In general, these protective measures are not included in the frequency converter as provided by
ABB.
Safety and protection requirements
For safety and protection reasons, the MCB must meet the stipulated minimum requirements of the
specifications of ABB MV Drives. It is the system integrators responsibility to ensure that the
minimum requirements are met and therefore ABB assumes no liability whatsoever for any damages
or losses arising from non-compliance with such minimum standards by the system integrator or any
other third party not under the responsibility of ABB. The minimum requirements for the MCB are
stated in this note and in the respective MCB specifications, which are available for each medium
voltage drive from ABB.
The safety requirements for the frequency converter are based on the following standards:
ISO 13849-1: Safety of machinery Safety-related parts of control systems - Part 1: General
principles for design, section 6.2.6 Category 3
ABB MV Drives
3BHS230517 ZAB E01 Rev. F Page 2 of 2
IEC 60204-1: Safety of machinery Electrical equipment of machines - Part 1: General
requirements
Minimum requirements for MCB and MCB control
The MCB open and / or trip command has to be wired directly from the frequency converter to the
MCB. It is not permitted to wire the trip command through any PLC or DCS system if it is not
certified to meet SIL 3 level requirements and to fulfill the timing requirements outlined below. The
opening of the MCB by the frequency converter shall be possible at any time. It is not permitted to
interrupt the open and / or trip command wiring (for example by a local / remote switch in the
MCB).
Whenever the MCB is in service position the frequency converter must have exclusive control of
closing the MCB, local closing of the MCB is not permitted.
The maximum opening time of the MCB shall never exceed the product or project-specific
maximum time defined in the MCB specifications. Typical maximum values are defined in the
table below:
ACS 1000 ACS 2000 ACS 5000 ACS 6000 MEGADRIVE-LCI
Max. protection trip time
1
120 ms 75 ms 75 ms 75 ms Not applicable
Max. safety trip time
2
250 ms 250 ms 500 ms 500 ms 500 ms
1
Maximum allowed breaking time (open and arcing) of the breaking device after the open command has been initiated
to prevent further damage to the frequency converter, e.g. diode failures.
2
Maximum allowed time to ensure safe disconnection of the main power supply to prevent any hazard to personnel.
Max. protection trip time
No further damage of frequency converter
Max. safety trip time
No hazard to personnel
Short circuit occurs
Open and / or trip command is set at the
frequency converter control output
Figure 2: MCB opening timing diagram
In order to meet the stipulated safety requirements, it is recommended that:
the MCB is equipped with two independent opening coils, or
the MCB is equipped with one opening coil and an undervoltage coil for monitoring of the
control voltage, or
an upstream protection coordination scheme is provided which uses the breaker failure
(ANSI 50BF) signal to automatically trip the upstream breaker, in case the MCB does not
open. The upstream breaker must open within the maximum safety trip time after a failure has
occurred.
Maintenance recommendation
The MCB trip circuits should be checked once yearly.
You might also like
- 3BHS125149 E50 RevB ACS 5000 MCB Specification PDFDocument8 pages3BHS125149 E50 RevB ACS 5000 MCB Specification PDFserkalemtNo ratings yet
- Practical Power System and Protective Relays CommissioningFrom EverandPractical Power System and Protective Relays CommissioningRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- 7TKK000116 Joslyn Hi-Voltage - Catalogue - US - Lo PDFDocument44 pages7TKK000116 Joslyn Hi-Voltage - Catalogue - US - Lo PDFJorge Esteban Castro GualdronNo ratings yet
- TRAX Manual enDocument58 pagesTRAX Manual enJack Duff100% (3)
- 2UEB000095 ACS 2000 4 KV MV Switchgear Specification Rev ADocument5 pages2UEB000095 ACS 2000 4 KV MV Switchgear Specification Rev ABrankko Jhonathan Torres SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Atprulebooktr PDFDocument1,170 pagesAtprulebooktr PDFing.jmsolis0% (1)
- SATURACIÓN IEC 61869-100. Ejemplo 5.2.1: M VA VADocument18 pagesSATURACIÓN IEC 61869-100. Ejemplo 5.2.1: M VA VAJIMENEZPS100% (1)
- FRAanalyzer Article FRA Condition Assessment Power Transformers OMICRON Magazine 2009 ENUDocument5 pagesFRAanalyzer Article FRA Condition Assessment Power Transformers OMICRON Magazine 2009 ENUGianc87No ratings yet
- ABB High Voltage Capacitor Fuses ABB CIL HV FusesDocument19 pagesABB High Voltage Capacitor Fuses ABB CIL HV FusesrocketvtNo ratings yet
- GCB Application GuideDocument61 pagesGCB Application GuideAnonymous fbeCwgBFYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document13 pagesChapter 4Kishore SarkarNo ratings yet
- Nader NDW3 Series Products SpecificationDocument117 pagesNader NDW3 Series Products SpecificationaktrctqNo ratings yet
- IEEE Standard Requirements For Instrument Transformers: SASO IEEE C 57:2018 IEEE C 57:2013Document81 pagesIEEE Standard Requirements For Instrument Transformers: SASO IEEE C 57:2018 IEEE C 57:2013ivaneg825No ratings yet
- Sweep Frequency Response AnalysisDocument69 pagesSweep Frequency Response AnalysisBash MatNo ratings yet
- 03 CB - Routine Tests-NewDocument15 pages03 CB - Routine Tests-NewaaaygugNo ratings yet
- Completely Self Protected Distribution (CSP) TransformersDocument11 pagesCompletely Self Protected Distribution (CSP) Transformersjobpei2No ratings yet
- RUS USDA C84 Voltage TolerancesDocument47 pagesRUS USDA C84 Voltage Toleranceskcirrenwod100% (1)
- Iec62271-203 (Ed1.0) en DDocument8 pagesIec62271-203 (Ed1.0) en Demy118850% (2)
- máy cắt sf6 abbDocument7 pagesmáy cắt sf6 abbQuảng Thành NamNo ratings yet
- Transformer Bushings: IEEE/ANSI Standard, COTA 150 - COTA 2050Document12 pagesTransformer Bushings: IEEE/ANSI Standard, COTA 150 - COTA 2050Sajjad PirzadaNo ratings yet
- Manual Controlador C90Document442 pagesManual Controlador C90Fabián MejíaNo ratings yet
- 1 3BHS260164 - ACS 2000 Power Cable Specification - Rev.DDocument8 pages1 3BHS260164 - ACS 2000 Power Cable Specification - Rev.DNguyen HungNo ratings yet
- Instrument Transformer GuideDocument124 pagesInstrument Transformer GuidejoshNo ratings yet
- SEPAM S80 - Transformer Differential ANSI 87T PDFDocument38 pagesSEPAM S80 - Transformer Differential ANSI 87T PDFMartin KakartinNo ratings yet
- 09 Cycloconverter - Protection Functions PDFDocument14 pages09 Cycloconverter - Protection Functions PDFIrving Dirzo CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Microgrid ThesisDocument163 pagesMicrogrid ThesisAshik AhmedNo ratings yet
- 7.21 Outdoor Bus StructuresDocument191 pages7.21 Outdoor Bus StructuresEdyta MarzecNo ratings yet
- Motortronics Training - 2012Document95 pagesMotortronics Training - 2012daly2daly100% (1)
- IEEE Guide For Static Var Compensator Field Tests IEEE1303-2011Document49 pagesIEEE Guide For Static Var Compensator Field Tests IEEE1303-2011Taher El NoamanNo ratings yet
- Seminario de TransformadoresDocument42 pagesSeminario de TransformadoresMiguelNo ratings yet
- Beckwith M 3425A PDFDocument482 pagesBeckwith M 3425A PDFDavid Enrique Alanis RojasNo ratings yet
- ANSI C84.1 Table 1 - System Voltage RangesDocument2 pagesANSI C84.1 Table 1 - System Voltage Rangesangel vivasNo ratings yet
- Trip Circuit Supervision Relay Spec 0604Document5 pagesTrip Circuit Supervision Relay Spec 0604Sameera ChamingaNo ratings yet
- Iom Ing Unigear (CCM) Zs1 AbbDocument106 pagesIom Ing Unigear (CCM) Zs1 AbbHernan Olave OlguinNo ratings yet
- 1HSB439954-2en 20171101Document192 pages1HSB439954-2en 20171101Muhammad Ubair RiazNo ratings yet
- 020-Überblick 8DN9 II - ENGLDocument24 pages020-Überblick 8DN9 II - ENGLMuruganantham ChandrappanNo ratings yet
- Circuit breaker operating sequence and pre-insertion resistor (PIRDocument2 pagesCircuit breaker operating sequence and pre-insertion resistor (PIRabhi_akNo ratings yet
- P64x EN AP A11Document92 pagesP64x EN AP A11Sakthi Krishnan0% (1)
- IST-072-1 509-100 Operations Manual (English)Document34 pagesIST-072-1 509-100 Operations Manual (English)Guilherme Lopes SoledadeNo ratings yet
- Spec 112 PDFDocument36 pagesSpec 112 PDFMayank JoshiNo ratings yet
- SIAC Protection Relay ManualDocument135 pagesSIAC Protection Relay ManualarolnNo ratings yet
- Abb Ref 615 Powerfactory Relay Model Description: Digsilent Technical DocumentationDocument6 pagesAbb Ref 615 Powerfactory Relay Model Description: Digsilent Technical DocumentationYasna SuárezNo ratings yet
- IEC 60354-Ed 2.0-1991-09-Loading Guide For Oil Immersed Power Transformers PDFDocument90 pagesIEC 60354-Ed 2.0-1991-09-Loading Guide For Oil Immersed Power Transformers PDFGirish Oniyil100% (1)
- Manual For FrejaWin 6-2Document158 pagesManual For FrejaWin 6-2Corey PorterNo ratings yet
- Part 4 RTCC ReviseDocument9 pagesPart 4 RTCC ReviseqianghoNo ratings yet
- Impedance Correction FactorDocument7 pagesImpedance Correction FactorEngr Fahimuddin QureshiNo ratings yet
- Ieeeiec Measuring Relays and Protection Equipment Part 24 Common 2013Document73 pagesIeeeiec Measuring Relays and Protection Equipment Part 24 Common 2013Andrés Felipe Cárdenas CárdenasNo ratings yet
- 7SA513 ManualDocument396 pages7SA513 Manualionecir100% (1)
- ABB High Voltage Unigear GuideDocument163 pagesABB High Voltage Unigear GuideMohammad Saidul Islam ShantoNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric P3U30 LED labels printoutDocument2 pagesSchneider Electric P3U30 LED labels printoutPeter Paul Condinato100% (1)
- Reconectador GVRDocument16 pagesReconectador GVRjuanete29100% (1)
- 1250A Circuit Breaker and Disconnector Spec SheetDocument12 pages1250A Circuit Breaker and Disconnector Spec SheetPhước Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Switch Analyzer SA10Document34 pagesSwitch Analyzer SA10Edwin QuispeNo ratings yet
- DigSilent TechRef - LogdipDocument17 pagesDigSilent TechRef - LogdipАлишер ГалиевNo ratings yet
- OLTC Dynamic Testing P10Document16 pagesOLTC Dynamic Testing P10Marcio RangelNo ratings yet
- RE 615 Tech 756887 ENeDocument748 pagesRE 615 Tech 756887 ENeSekhar KarumuriNo ratings yet
- The Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsFrom EverandThe Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsNo ratings yet
- Altivar 1200 - ATV1200A50006666Document7 pagesAltivar 1200 - ATV1200A50006666srmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- ABBCheiron CatalogueDocument6 pagesABBCheiron Cataloguesrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Powerflex 4 User Manual - ANTECHDocument108 pagesPowerflex 4 User Manual - ANTECHOG100% (1)
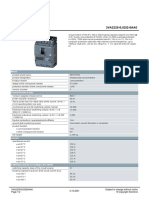
- Data Sheet 3VA2225-5JQ32-0AA0: ModelDocument5 pagesData Sheet 3VA2225-5JQ32-0AA0: Modelsrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
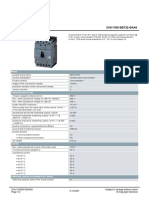
- Data Sheet 3VA1150-5EF32-0AA0: ModelDocument5 pagesData Sheet 3VA1150-5EF32-0AA0: Modelsrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- MNS-R System GuideDocument17 pagesMNS-R System Guidesrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Contact ABB India for all your electrical needsDocument2 pagesContact ABB India for all your electrical needssrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Grid Standards RegDocument19 pagesGrid Standards RegEzhil Vendhan PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Regulation PDFDocument18 pagesRegulation PDFdeepusvvpNo ratings yet
- Power Distributor Box - JSPL - Sunil - Pattnaik PDFDocument17 pagesPower Distributor Box - JSPL - Sunil - Pattnaik PDFsrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Installation of Current Limiting Reactors in Esp: - Monday, June 07, 2021Document15 pagesInstallation of Current Limiting Reactors in Esp: - Monday, June 07, 2021srmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- ABB Medium Voltage DrivesDocument4 pagesABB Medium Voltage Drivesabdur rafayNo ratings yet
- Power Distributor Box - JSPL - Sunil - Pattnaik PDFDocument17 pagesPower Distributor Box - JSPL - Sunil - Pattnaik PDFsrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- ABB - Leaflet - Smart Sensor Installation - 5.2017Document4 pagesABB - Leaflet - Smart Sensor Installation - 5.2017srmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- IE2 IndustrialDocument16 pagesIE2 Industrialsrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Product Catalog - YEWS Screw Chiller - EN - PUBL7578 (0315)Document7 pagesProduct Catalog - YEWS Screw Chiller - EN - PUBL7578 (0315)srmohapatra5086100% (1)
- RRB Je & Se PDFDocument19 pagesRRB Je & Se PDFVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- CEA Metering RegulationsDocument20 pagesCEA Metering RegulationsRavi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Equipment Initial Production Control SystemDocument1 pageEquipment Initial Production Control Systemsrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Ie Rules-1956Document191 pagesIe Rules-1956Murali MohanNo ratings yet
- Apex Series Ie2 Efficiency Ac MotorsDocument4 pagesApex Series Ie2 Efficiency Ac Motorssrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- G740 - Control Unit & Terminal Unit - RevB1 PDFDocument53 pagesG740 - Control Unit & Terminal Unit - RevB1 PDFsrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Sinamics Perfect Harmony Gh180Document338 pagesSinamics Perfect Harmony Gh180srmohapatra5086100% (2)
- DATA SHEET FOR SINAMICS S120Document1 pageDATA SHEET FOR SINAMICS S120srmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- 1756-Um521c-En-P - ControlLogix SynchLink Module User Manual PDFDocument146 pages1756-Um521c-En-P - ControlLogix SynchLink Module User Manual PDFCesar ChaconNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog - YEWS Screw Chiller - EN - PUBL7578 (0315)Document7 pagesProduct Catalog - YEWS Screw Chiller - EN - PUBL7578 (0315)srmohapatra5086100% (1)
- BJFL 30W Led I-Amaze-113009Document1 pageBJFL 30W Led I-Amaze-113009srmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Innovations in Coach DesignDocument83 pagesInnovations in Coach Designsrmohapatra5086No ratings yet
- Acs5000 O&mDocument15 pagesAcs5000 O&msrmohapatra5086100% (1)
- 10 K ThermistorDocument61 pages10 K ThermistorWuland WaisnawaNo ratings yet
- B2-Embedded System DesignDocument20 pagesB2-Embedded System DesignSailesh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument2 pagesAnnotated BibliographyWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- SNMP Tutorial PDFDocument24 pagesSNMP Tutorial PDFSrivignessh PssNo ratings yet
- Korea Battery Product Catalogue 2023Document8 pagesKorea Battery Product Catalogue 2023Cesar GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - LCD and KeyboardDocument27 pagesChapter 12 - LCD and KeyboardAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Vet. Medicine Companies in PakistanDocument6 pagesVet. Medicine Companies in PakistanRAO NABEEL AKRAM100% (1)
- Contoh Spoof TextDocument7 pagesContoh Spoof TextIndrayaniNo ratings yet
- Singtel Satellite Coverage Maps1Document12 pagesSingtel Satellite Coverage Maps1Anh TúNo ratings yet
- RapidAnalytics ManualDocument23 pagesRapidAnalytics ManualansanaNo ratings yet
- Maryland Metrics - Thread Data ChartsDocument2 pagesMaryland Metrics - Thread Data ChartsNicusor BuleteanuNo ratings yet
- 001 GetStarted EditorManual PDFDocument618 pages001 GetStarted EditorManual PDFLuka SNo ratings yet
- Air Intake AccessoriesDocument42 pagesAir Intake AccessoriesMark CarterNo ratings yet
- Oracle Fixed AssetsDocument39 pagesOracle Fixed AssetspallavipulluriNo ratings yet
- Application of PWM Speed ControlDocument7 pagesApplication of PWM Speed ControlJMCproductsNo ratings yet
- Electric Double Layer Capacitors GuideDocument20 pagesElectric Double Layer Capacitors GuideMusa Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Five Nights at Freddy's The Ultimate Guide Five Nights at Freddy's Wiki FandomDocument1 pageFive Nights at Freddy's The Ultimate Guide Five Nights at Freddy's Wiki FandomAmto Hosima0% (1)
- Proposed Changes to IRS-T-29-2000 CMS Crossing Manufacturing StandardsDocument11 pagesProposed Changes to IRS-T-29-2000 CMS Crossing Manufacturing StandardsShipra MishraNo ratings yet
- Binary WorksheetDocument4 pagesBinary WorksheetMariell EllanoNo ratings yet
- Export Ssrs Report To PDF LandscapeDocument2 pagesExport Ssrs Report To PDF LandscapeVictoriaNo ratings yet
- PP43C10-10.25-VS 43c10varDocument2 pagesPP43C10-10.25-VS 43c10varJonas RachidNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instalacion - Contador Barton-Floco-F500 PDFDocument32 pagesManual de Instalacion - Contador Barton-Floco-F500 PDFElkin TorresNo ratings yet
- MCQs DOMDocument5 pagesMCQs DOMyuvraj PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- TLE 9 1st Quarter Exam With Answer Key PDFDocument3 pagesTLE 9 1st Quarter Exam With Answer Key PDFJymaer GeromoNo ratings yet
- Optical Packet SwitchingDocument28 pagesOptical Packet Switchingarjun c chandrathilNo ratings yet
- Philips DoseRight 2.0 CT Dose ControlDocument4 pagesPhilips DoseRight 2.0 CT Dose Controlsombrero61No ratings yet
- 1.4404 enDocument5 pages1.4404 enyraju88No ratings yet
- State Bank of India - Recruitment of Probationary Officers PDFDocument2 pagesState Bank of India - Recruitment of Probationary Officers PDFTapas Kumar NandiNo ratings yet
- Account Statement 220422 210722Document14 pagesAccount Statement 220422 210722Meherun BibiNo ratings yet
- Growing Power of Social MediaDocument13 pagesGrowing Power of Social MediaKiran HanifNo ratings yet
- Brochure Ergometer ComparisonDocument1 pageBrochure Ergometer Comparisontkthird siaminterNo ratings yet