Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Note 2
Uploaded by
HossamJamaykaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Note 2
Uploaded by
HossamJamaykaCopyright:
Available Formats
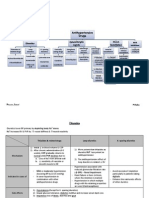
P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 1 - Treatment of Cough
|
4
It clears the excess secretions
& inhaled foreign matters.
Expectorants are used.
Productive Cough
Dry cough has no useful
function.
Anti-tussives are used.
Non-Productive
Cough
1) Acute Respiratory Infection.
Upper respiratory infection.
Pneumonia.
Bronchitis
2) Chronic Respiratory Infection.
TB.
Postnasal drip.
3) Airway Diseases.
Asthma.
COPD.
4) Irritants.
Cigarettes smoking.
Inhaled foreign bodies.
5) Drug Induced.
Inhaled drugs (aerosols).
ACE-inhibitors (anti-hypertensive).
Common causes of Cough:
Anti-tussive
They should be used for dry cough.
because it suppress cough reflex, it should not be used in
the presence of bronchial secretions.
Locally anti-
tussive
It reduces the sensitivity of periphral cough receptors to it's
activators which include irritants & autacoids (Bradykinine).
Mucoactive
Agents
They clear airway from mucus secretion by:
ability to expectorate sputum.
mucus hyper secretion.
P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 1 - Treatment of Cough
|
5
DRUDS FOR COUGH
Anti-tussives
Drugs
Centrally
Opioid
Dervatives
Codeine
Pholcodeine
Dextrome-
thorphan
Noscapine
Anti-histamins
Diphenhydram
ine
Peripherally
Above Larynx
Lozenge
Syrup
Below Larynx
steam with or without
(menthol & benzoin
tincture)
Nebulized
Lignocaine
Nebulized
Benzocaine
Centrally &
Periphrally
Benzonatate
Mucoactive
Agents
Expectorants
Hyperosmolar
saline
Na citrate
K citrate
Na
bicarbonate
Ammonium
Cloride
Na Iodide
K Iodide Guaifenesin
Creosote Guaicolate
Mucolytics
Classic
mucolytic
NAS
Peptide
mucolytic
Dornase alpha
others
Bromhexine
Ambroxol
Mucoregulatory
Anti-
cholinergic
Ipratropium
Atropine
Macrolide
Antibiotics
Azithromycin
Anti-
inflammatory
Indomethacin Corticosteroids
P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 1 - Treatment of Cough
|
6
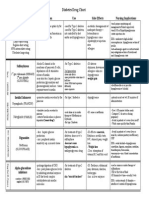
Anti-Tussives (cough suppressent)
DRUGS PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION & ITS MECHANISM USES SIDE EFFECT
A
c
t
i
n
g
C
e
n
t
a
r
l
l
y
O
p
i
o
i
d
D
e
r
v
a
t
i
v
e
Codeine They suppress cough reflex by
Derict inhibition of Cough Center in the
medulla.
Nausea.
Dizziness.
Urenary retention.
Constipation.(vi)
Pholcode
Dextromethorphan
Noscapine
A
n
t
i
-
H
i
s
t
a
m
i
n
e
Diphenhydramine
It depresses CNS including Cough Center. Sedation.
Drowsiness.
Dizziness.
A
c
t
i
n
g
P
e
r
i
p
h
r
a
l
l
y
A
b
o
v
e
L
a
r
y
n
x
Lozenges They are demulcents. They form gelatious coat that protects the
inflammed skin
Used for cough of
Sore throat.
Pharyngitis.
Syrup (honey)
B
e
l
o
w
L
a
r
y
n
x
Steam Without tooking,
it taken by
inhalation .
Taken with or
without (menthol
& benzoin
tincture)
Promote secretion of dilute mucus,
To protect inflammed mucosa
Nebulized Ligocaine 1) Local anesthesia.
2) Blooking mucosal cough receptors.
During fiber optic bronchoscopy.
intractable cough in bronchial carcinoma.
Nebulized
Benzocaine
Acting both
Centrally
&Periphrally
Benzonatate Chemichally, it is related to
tetracaine (local ansthesia).
1) In lungs, acting on
Stretch & cough receptors.
2) Act on CNS
Mucoactive Agents (Expectorants)
o They volume or hydration of airway secretion.
o They improve expectoration of respiratory mucus secretion.
DRUGS PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION & ITS MECHANISM USES SIDE EFFECT
E
x
p
e
c
t
o
r
a
n
t
s
Hyperosmolar Saline (10 ml of 6% saline).
Inhaled by ultrasonic nebulisation.
Used in fibross & bronchiectasis.
Na citrate 1) Stimulate secretion of low viscosity watery
mucus & sissolve it.
To make it thinner less sticky.
2) elasticity of bronchi.
To easily expectorate the mucus.
Used in early dry stage of acute bronchitis.
K citrate
Na bicarbonate
Ammonium Cloride Stimulate secretion of low viscosity watery mucus
By stimulation of sensory nerve ending in
the stomach.
Na Iodide 1) Stimulate secretion of low viscosity watery mucus
2) has mucolytic action.
Chronic respiratory disease.
Chronic asthma.
K Iodide
Guaifenesin 1) respiratory secretion.
2) adhesiveness & surface tension of viscid sputum
Creosote 1) sputum.
2) has mild antiseptic & deodrant action.
Lung absess.
Chronic bronchitis.
Bronchiectasis.
Guaicolate
P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 1 - Treatment of Cough
|
7
Muocoactive Agentgs (Mucolytic)
o They viscosity & of elasticity airway secretion & mucociliary & cough clearance.
DRUGS PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION & ITS MECHANISM USES SIDE EFFECT
C
l
a
s
s
i
c
M
u
c
o
l
y
t
i
c
N-acetulcysteine (NAC) Taken orally or by inhalation.
It is a precursor of intracellular
cysteine & glutathione.
1) Hydrolyse disulfid bond of mucin.
So, mucus loss its viscosity & elasticity.
2) Act as antioxidant.
So, it prevent pulmonary injury in patient
with COPD or lung cancer.
In condition associated with viscous mucus
secretion:
Chronic bronchitis, emphysema,
brochiectasis & cystic fibrosis.
(ARD): bronchitis, pneumonia & asthma.
Post-operative & post-traumatic
pulmonary complications.
Care of tracheostomy.
Act as antidote for paracetamol overdose.
Bronchospasm.
Prevent by
2-agonist.
Disagreeable odor.
Sulfur odor &
taste.
GI irritation.
Nausea.
Vomiting.
Stomatitis.
P
e
p
t
i
d
e
M
u
c
o
l
y
t
i
c
Dornase alpha
Taken by nebulisation.
For cystic fibrosis.
Allergic reaction.
Pharyngitis.
Laryngitis.
Voice alteration.
O
t
h
e
r
s
Bromhexine It is an expectorant & mucolytic
drug.
Taken orally, parentral or by
inhalation.
1) Liquefy mucus.
By viscosity of bronchial secretion.
2) Enhance expectoration.
By the rate of microciliary.
Acute bronchitis.
Chronic bronchitits.
COPD.
Rhinorrhea.
Lacrimation.
Gastric irritant.
Avoid with
antacid. Ambroxol Taken orally.
has less GI irritant.
Mucoactive Agents (Mucoregulatory Agents)
o They airway mucus hyper secretion which caused by goblet cells & submucosal gland.
DRUGS PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION & ITS MECHANISM USES SIDE EFFECT
A
n
t
i
-
i
n
f
l
a
m
m
a
t
o
r
y
Indomethacine
inflammation which leading to mucus hyper
secretion.
Panbronchiolits
Corticosteroid
A
n
t
i
c
h
o
l
i
n
e
r
g
i
c
Ipratropium
mucus volume that secreted in chronic
bronchitis.
Atropine
mucus hypersecrtion. used pre-anesthetically for endotracheal
intubation.
M
a
c
r
o
l
i
d
e
a
n
t
i
b
i
o
t
i
c
s
Azithromycin
Taken orally for long term
administion.
You might also like
- تجميعة فارماDocument1 pageتجميعة فارماAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology MedadTeam WWW EgydrDocument4 pagesClinical Pathology MedadTeam WWW EgydrOmar SiagNo ratings yet
- Doses Commonly Prescribed Antibiotics PDFDocument13 pagesDoses Commonly Prescribed Antibiotics PDFAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument7 pagesAntihypertensive Drugshamadadodo7No ratings yet
- Otc Heartburn Remedy Comparison Chart: Proton Pump Inhibitors/Ppis H2 Blockers AntacidsDocument1 pageOtc Heartburn Remedy Comparison Chart: Proton Pump Inhibitors/Ppis H2 Blockers AntacidsAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (46)
- Dna PDFDocument1 pageDna PDFAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Drug Chart: Drug Action Use Side Effects Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesDiabetes Drug Chart: Drug Action Use Side Effects Nursing ImplicationspulmonologistNo ratings yet
- Infants NutritionDocument25 pagesInfants NutritionAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Iron Metabolism LinkDocument6 pagesObesity and Iron Metabolism LinkAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Major Parasitic Infections Affecting HumansDocument2 pagesMajor Parasitic Infections Affecting HumansAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Medical: Faculty of PharmacyDocument3 pagesMedical: Faculty of PharmacyAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- 300 QuestionsDocument31 pages300 QuestionsAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Skin Aging: Skin Firmness, Elasticity, and Moisture-HoldingDocument2 pagesSkin Aging: Skin Firmness, Elasticity, and Moisture-HoldingAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Acne TreatmentDocument26 pagesAcne TreatmentAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- أسئلةDocument5 pagesأسئلةAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Note 1Document3 pagesNote 1HossamJamaykaNo ratings yet
- Ethanol: Methanol Glycerol ExperimentDocument1 pageEthanol: Methanol Glycerol ExperimentAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Medical TerminologyDocument3 pagesMedical TerminologyAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- أسئلةDocument5 pagesأسئلةAhmed SobhNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)