Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Special Torts and Legal Liability
Uploaded by
specialsection0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views1 pageThis document summarizes key concepts in special torts, including acts contra bonus mores, abuse of rights, liability without fault, general sanction for acts contrary to law, and unjust enrichment. It provides examples and definitions of each concept. Acts contra bonus mores refer to legal acts that are contrary to morals, good customs, public order or policy and done with intent to injure. Abuse of rights involves exercising a legal right or duty in bad faith to prejudice or injure another. Liability without fault covers strict liability and product liability. The general sanction under Article 20 provides for indemnification for damages caused willfully or negligently in violation of law. Unjust enrichment requires returning anything acquired at another's expense without
Original Description:
torts
Original Title
Torts Reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes key concepts in special torts, including acts contra bonus mores, abuse of rights, liability without fault, general sanction for acts contrary to law, and unjust enrichment. It provides examples and definitions of each concept. Acts contra bonus mores refer to legal acts that are contrary to morals, good customs, public order or policy and done with intent to injure. Abuse of rights involves exercising a legal right or duty in bad faith to prejudice or injure another. Liability without fault covers strict liability and product liability. The general sanction under Article 20 provides for indemnification for damages caused willfully or negligently in violation of law. Unjust enrichment requires returning anything acquired at another's expense without
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
80 views1 pageSpecial Torts and Legal Liability
Uploaded by
specialsectionThis document summarizes key concepts in special torts, including acts contra bonus mores, abuse of rights, liability without fault, general sanction for acts contrary to law, and unjust enrichment. It provides examples and definitions of each concept. Acts contra bonus mores refer to legal acts that are contrary to morals, good customs, public order or policy and done with intent to injure. Abuse of rights involves exercising a legal right or duty in bad faith to prejudice or injure another. Liability without fault covers strict liability and product liability. The general sanction under Article 20 provides for indemnification for damages caused willfully or negligently in violation of law. Unjust enrichment requires returning anything acquired at another's expense without
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as XLSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
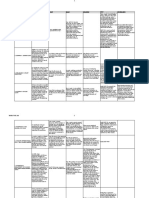
Special Torts
1. There is a legal right or duty 1. There is an act which is legal
2. The right or duty is exercised in bad faith 2. But which is contrary to morals, good custom,
3. For the sole intent of prejudicing or injuring public order or public policy
another 3. And it is done with intent to injure
Damages are recoverable even if no positive law
has been violated
Accion In Rem Verso. It is an action for
recovery of what has been paid
without just cause.
-a right that has been violated ceases to exist EXAMPLES OF ACTS CONTRA BONUS MORES:
Art. 19. Every person must, in the exercise of his rights
and in the performance of his duties, act with justice,
give everyone his due, and observe honesty and good
faith.
Art. 20. Every person who, contrary to law, willfully
or negligently causes damage to another, shall
indemnify the latter for the same.
Art. 21. Any person who willfully causes loss or injury to another
in a manner that is contrary to morals, good customs or public
policy shall compensate the latter for the damage.
-only a subisdiary action
For all other provisions of law which do not
especially provide their own sanction
a. In the exercise of his legal right or duty
b. Willfully or negligently causes damage to another
does not distinguish, the act may be
done either willfully or negligently
Common element under articles 19 and 21: the
act must be intentional
1. BREACH OF A PROMISE TO MARRY
GENERAL RULE: Breach of a promise to marry by itself is not
actionable.
EXCEPTION: In cases where there is another act independent
of the breach of a promise to marry
which gives rise to liability
a. Cases where there was financial damage
b. Social humiliation caused to one of the parties
c. Where there was moral seduction
d. If the breach was done in a manner that is clearly contrary to
good morals
Payment by mistake is an essential element
Q: In view of the general sanction provided for under
Art. 20, may a person have an absolute right to be
indemnified?
A: No. It is essential that some right of his be
impaired. Without such, he is not entitled to
indemnification. (Pineda, 2004)
ACCION IN REMVERSO SOLUTIO INDEBITI
Common element under articles 19 and 21: the
act must be intentional
Liability without Fault includes:
a. Strict Liability there is strict liability if one is made
independent of fault, negligence or intent after
establishing certain facts specified by law. It includes
liability for conversion and for injuries caused by animals,
ultrahazardous activities and nuisance.
b. Product Liability is the law which governs the liability
of manufacturers and sellers for damages resulting from
defective products.
-LWF is different from Damnum Absque Injuria
A person who only exercises his legal rights does no injury.
If damages result from such exercise of legal rights, the
consequences must be borne by the injured person alone.
The law affords no remedy for damages resulting from an
act which does not amount to a legal injury or wrong.
Article 20 speaks of the general sanction for all other
provisions of law which do not especially provide for
their own sanction.
Article 21 on the other hand, speaks of act which is legal but is
contrary to morals, good custom, public order or public policy
and is done with intent to injure.
Nemo cum alteris detrimento locupletari potest or no one shall unjustly
enrich himself at the expense of another.
Coverage: the article applies only if:
i. Someone acquires or comes into possession of something which means
delivery or acquisition of things; and
ii. Acquisition is undue and at the expense of another which means without
any just or legal ground.
NOTE: The government is not exempted from the principle of unjust
enrichment.
remedy for unjust enrichment:
It is not necessary that
payment be made by
mistake
rendition of services NOT included under Art. 22
'- If services were rendered by someone benefiting another, it does not mean
that the latter is exempted from indemnifying the former. The liability will lie
on quasicontract under Article 2146.
Art. 22. Every person who through an act of performance by another, or any
other means, acquires or comes into possession of something at the expense
of the latter without just or legal ground, shall return the same to him.
Abuse of Rights ACTS CONTRA BONUS MORES Liability Without Fault General Sanction / Acts contrary to Law Unjust Enrichment
You might also like
- Maslag vs. Monzon, 698 SCRA 584, June 17, 2013Document12 pagesMaslag vs. Monzon, 698 SCRA 584, June 17, 2013specialsection100% (1)
- Torts Position PapersDocument5 pagesTorts Position PapersspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Rescission of Aircraft Purchase Agreement Due to Rudder System MalfunctionsDocument23 pagesRescission of Aircraft Purchase Agreement Due to Rudder System MalfunctionsspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Torts I Outline: Chapter 1: An Overview of Modern Tort LiabilityDocument56 pagesTorts I Outline: Chapter 1: An Overview of Modern Tort LiabilityEric CampoloNo ratings yet
- Gasoline and Antifreeze Planning:: Dispute Resolution: Beyond The Adversarial Model Second Edition. P. 299Document8 pagesGasoline and Antifreeze Planning:: Dispute Resolution: Beyond The Adversarial Model Second Edition. P. 299Mark Michael StrageNo ratings yet
- Final Contracts OutlineDocument61 pagesFinal Contracts OutlineGrant Burchfield100% (1)
- Products Liability Issue/RuleDocument5 pagesProducts Liability Issue/RuleJane SalmaNo ratings yet
- Torts Outline-LW-CondensedDocument8 pagesTorts Outline-LW-CondensedLarry WatkinsNo ratings yet
- Bar secrets revealedDocument19 pagesBar secrets revealedsdcohen23No ratings yet
- Applicable Law? Formation: I. Agreement RequirementDocument32 pagesApplicable Law? Formation: I. Agreement RequirementeccegeorgeNo ratings yet
- Complaint Breach of Contract DRAFTDocument7 pagesComplaint Breach of Contract DRAFTspecialsection71% (14)
- Harris - Criminal Law OutlineDocument20 pagesHarris - Criminal Law OutlinePat CrawleyNo ratings yet
- C O W/C UCC & R P: Ontracts Utline Ombined Estatement RovisionsDocument24 pagesC O W/C UCC & R P: Ontracts Utline Ombined Estatement RovisionsDawson OgletreeNo ratings yet
- Torts Outline NyuDocument64 pagesTorts Outline NyuTony ChenNo ratings yet
- Tort - Case LawsDocument21 pagesTort - Case LawsRajesh GargNo ratings yet
- MPRE Unpacked: Professional Responsibility Explained & Applied for Multistate Professional Responsibility ExamFrom EverandMPRE Unpacked: Professional Responsibility Explained & Applied for Multistate Professional Responsibility ExamNo ratings yet
- Contracts Just The RulesDocument28 pagesContracts Just The RulesfgsdfNo ratings yet
- Multiple evidentiary issuesDocument15 pagesMultiple evidentiary issuesSean Austin Parker-O'Grady Pog100% (1)
- Torts Final OutlineDocument86 pagesTorts Final Outlinebstein6087100% (1)
- MB - Torts Final OutlineDocument116 pagesMB - Torts Final OutlineMichelle BerardinoNo ratings yet
- Torts Outline - Professor Wonnell - Fall 2012Document25 pagesTorts Outline - Professor Wonnell - Fall 2012Joshua SummersNo ratings yet
- Red covenants (covenants which run with the land at law) case brief summariesDocument66 pagesRed covenants (covenants which run with the land at law) case brief summariesMissy MeyerNo ratings yet
- Checklist K's FinalDocument65 pagesChecklist K's Finalbing324No ratings yet
- Contracts Outline Fall 2005: Is There An Agreement For A Promise?Document38 pagesContracts Outline Fall 2005: Is There An Agreement For A Promise?leed2727No ratings yet
- Notes in Torts (Jurado, 2009)Document5 pagesNotes in Torts (Jurado, 2009)Lemwil Aruta SaclayNo ratings yet
- Cochran Torts Fall2010Document93 pagesCochran Torts Fall2010Vanessa Rosa100% (1)
- Twerski Tort Fall 2014Document80 pagesTwerski Tort Fall 2014riku33090No ratings yet
- Voluntary Act Voluntary Act: Common Law M PC Actus R e UsDocument7 pagesVoluntary Act Voluntary Act: Common Law M PC Actus R e Uslnm10No ratings yet
- Criminal Procedure Appeals Arguments Raised for First TimeDocument11 pagesCriminal Procedure Appeals Arguments Raised for First Timespecialsection100% (3)
- TRANSPORTATION CARRIERS LIABLE FOR DRIVER'S NEGLIGENCEDocument2 pagesTRANSPORTATION CARRIERS LIABLE FOR DRIVER'S NEGLIGENCEChoco Maphison100% (1)
- Contracts OutlineDocument28 pagesContracts OutlineKatyNo ratings yet
- Torts Fall OutlineDocument14 pagesTorts Fall OutlineTyler BuckNo ratings yet
- Torts and Damages Notes Deleon 2021Document29 pagesTorts and Damages Notes Deleon 2021rianna marie VelezNo ratings yet
- Property Outline Final-3Document35 pagesProperty Outline Final-3Santosh Reddy Somi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Case Digest 22 23 24Document3 pagesCase Digest 22 23 24specialsectionNo ratings yet
- Torts DigestDocument10 pagesTorts DigestspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Torts DigestDocument10 pagesTorts DigestspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Negligence v. Strict Liability ComparedDocument78 pagesNegligence v. Strict Liability Comparedblair_bartonNo ratings yet
- Powers and Attributes of LGUs Based on Key SC RulingsDocument10 pagesPowers and Attributes of LGUs Based on Key SC RulingsspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Del Prado Vs MeralcoDocument3 pagesDel Prado Vs Meralcolordpuppa100% (1)
- Torts OutlineDocument13 pagesTorts Outlinefashionkate2007No ratings yet
- Contracts Johnson 2009 2Document28 pagesContracts Johnson 2009 2s_shreya955122No ratings yet
- Contracts - LF100A - Outline - 111011Document17 pagesContracts - LF100A - Outline - 111011Jay HomNo ratings yet
- TORTS OutlineDocument14 pagesTORTS OutlineStella RT100% (1)
- Contracts Outline - WpsDocument55 pagesContracts Outline - WpsrockisagoodNo ratings yet
- Torts ChartDocument11 pagesTorts ChartBrandon BakerNo ratings yet
- Outline Shell Midterm TortsDocument11 pagesOutline Shell Midterm Tortsexner2014No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-First Possession, Acquisition of Property by Discovery, Capture, and Cre - AtionDocument21 pagesChapter 1-First Possession, Acquisition of Property by Discovery, Capture, and Cre - Ationluckystar384No ratings yet
- Lopez Contracts OutlineDocument65 pagesLopez Contracts Outlinewil lopezNo ratings yet
- Legal Memo Structure and ComponentsDocument14 pagesLegal Memo Structure and ComponentsAlex KozinskiNo ratings yet
- ContractsDocument125 pagesContractsMorgan ColesNo ratings yet
- Bloomberg Contract OutlineDocument11 pagesBloomberg Contract OutlineEzekyle12No ratings yet
- Contracts II - Colombo - Spring 2008Document35 pagesContracts II - Colombo - Spring 2008emoran86No ratings yet
- Civ Pro Rule Statements DraftDocument3 pagesCiv Pro Rule Statements DraftkoreanmanNo ratings yet
- Contracts Outline: Sources of Contract LawDocument15 pagesContracts Outline: Sources of Contract LawAlexis R GaryNo ratings yet
- Attorneys For Plaintiff, Daniel J. Reiman: Genova Burns LLCDocument18 pagesAttorneys For Plaintiff, Daniel J. Reiman: Genova Burns LLCjmjr30No ratings yet
- Torts OutlineDocument79 pagesTorts OutlineJanay Clougherty100% (1)
- Negligence Framework: Landowner DutyDocument4 pagesNegligence Framework: Landowner DutyDenise NicoleNo ratings yet
- Much of Tort Law Is Concerned With The Following Three QuestionsDocument10 pagesMuch of Tort Law Is Concerned With The Following Three Questionsjasmine singhNo ratings yet
- Torts OutlineDocument51 pagesTorts Outlinejs804No ratings yet
- Ivil Rocedure: Ersonal Urisdiction HO CAN BE SuedDocument45 pagesIvil Rocedure: Ersonal Urisdiction HO CAN BE SuedVicki GokhmanNo ratings yet
- MBEQuestions1998 PDFDocument103 pagesMBEQuestions1998 PDFMarco FortadesNo ratings yet
- Con Law Comprehensive Notes and Case BriefsDocument42 pagesCon Law Comprehensive Notes and Case BriefssbodfordNo ratings yet
- 00-Contracts #8 NEW Practice Exam Model AnswerDocument3 pages00-Contracts #8 NEW Practice Exam Model Answerwootenr2002100% (1)
- Contracts - Spring OutlineDocument103 pagesContracts - Spring OutlineWalker MollerNo ratings yet
- Case Facts Issue Rule Holding Other InfoDocument10 pagesCase Facts Issue Rule Holding Other InfoShannon LitvinNo ratings yet
- TortsDocument80 pagesTortstconn8276No ratings yet
- MPT 1Document3 pagesMPT 1Pato AlbujaNo ratings yet
- Torts TableDocument2 pagesTorts Tablejdebski428No ratings yet
- Torts OutlineDocument16 pagesTorts OutlineHenryNo ratings yet
- International Shoe, Which States "Due Process Requires Only That in Order To SubjectDocument4 pagesInternational Shoe, Which States "Due Process Requires Only That in Order To SubjectCory BakerNo ratings yet
- CDocument11 pagesCAlexNo ratings yet
- Short Outline ContractsDocument4 pagesShort Outline ContractsslavichorseNo ratings yet
- Ark Land Co. v. Harper Partition in KindDocument3 pagesArk Land Co. v. Harper Partition in KindLena Wassilian100% (2)
- Property I CasesDocument15 pagesProperty I CasesACDCNo ratings yet
- Torts - Case ChartDocument8 pagesTorts - Case ChartMolly ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Divorce: Why Fighting in Court Will Only Make You Both PoorerFrom EverandDivorce: Why Fighting in Court Will Only Make You Both PoorerNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines, Appellee, vs. Raul Beriber y Fuentes at Jerry Fuentes y Ignacio at Gerry Beriber at Bong at Raul Fuentes, Appellant.Document10 pagesPeople of The Philippines, Appellee, vs. Raul Beriber y Fuentes at Jerry Fuentes y Ignacio at Gerry Beriber at Bong at Raul Fuentes, Appellant.specialsectionNo ratings yet
- 16.silkair (Singapore) Pte, Ltd. vs. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, 544 SCRA 100, February 06, 2008 PDFDocument17 pages16.silkair (Singapore) Pte, Ltd. vs. Commissioner of Internal Revenue, 544 SCRA 100, February 06, 2008 PDFspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Jadewell Parking System Corporation vs. Lidua, SR., 706 SCRA 724, October 07, 2013Document18 pagesJadewell Parking System Corporation vs. Lidua, SR., 706 SCRA 724, October 07, 2013specialsectionNo ratings yet
- People of The Philippines, Appellee, vs. Raul Beriber y Fuentes at Jerry Fuentes y Ignacio at Gerry Beriber at Bong at Raul Fuentes, Appellant.Document10 pagesPeople of The Philippines, Appellee, vs. Raul Beriber y Fuentes at Jerry Fuentes y Ignacio at Gerry Beriber at Bong at Raul Fuentes, Appellant.specialsectionNo ratings yet
- Missioner of Internal Revenue vs. Court of Appeals, 242 SCRA 289, March 10, 1995Document30 pagesMissioner of Internal Revenue vs. Court of Appeals, 242 SCRA 289, March 10, 1995specialsection100% (1)
- Civil Code of the Philippines Preliminary TitleDocument8 pagesCivil Code of the Philippines Preliminary TitlespecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Nagtalon vs. United Coconut Planters Bank, 702 SCRA 615, July 31, 2013Document14 pagesNagtalon vs. United Coconut Planters Bank, 702 SCRA 615, July 31, 2013specialsectionNo ratings yet
- Polyfoam-Rgc International, Corporation and Precilla A. Gramaje, Petitioners, vs. Edgardo Concepcion, Respondent.Document15 pagesPolyfoam-Rgc International, Corporation and Precilla A. Gramaje, Petitioners, vs. Edgardo Concepcion, Respondent.specialsectionNo ratings yet
- Lim vs. Court of Appeals, Mindanao Station, 689 SCRA 705, January 30, 2013Document9 pagesLim vs. Court of Appeals, Mindanao Station, 689 SCRA 705, January 30, 2013specialsectionNo ratings yet
- Sched KoDocument1 pageSched KospecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Optima Realty Corporation vs. Hertz Phil. Exclusive Cars, Inc., 688 SCRA 317, January 09, 2013Document12 pagesOptima Realty Corporation vs. Hertz Phil. Exclusive Cars, Inc., 688 SCRA 317, January 09, 2013specialsectionNo ratings yet
- 19.allied Banking Corporation vs. Quezon City Government, 472 SCRA 303, October 11, 2005Document27 pages19.allied Banking Corporation vs. Quezon City Government, 472 SCRA 303, October 11, 2005specialsectionNo ratings yet
- Macasaet vs. Co, JR., 697 SCRA 187, June 05, 2013Document17 pagesMacasaet vs. Co, JR., 697 SCRA 187, June 05, 2013specialsectionNo ratings yet
- Executive Order 227 Family Code - AmendmentsDocument1 pageExecutive Order 227 Family Code - AmendmentsspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Civil Code of the Philippines Preliminary TitleDocument8 pagesCivil Code of the Philippines Preliminary TitlespecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Spec Pro MidtermsDocument3 pagesSpec Pro MidtermsspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- EvidenceDocument96 pagesEvidencespecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Missioner of Internal Revenue vs. Kudos Metal Corporation, 620 SCRA 232, May 05, 2010Document18 pagesMissioner of Internal Revenue vs. Kudos Metal Corporation, 620 SCRA 232, May 05, 2010specialsectionNo ratings yet
- Spec ProDocument3 pagesSpec ProHonorio Bartholomew ChanNo ratings yet
- Legal Forms: University of Cordilleras College of LawDocument1 pageLegal Forms: University of Cordilleras College of LawspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Green Notes - Case Digest - Commercial LawDocument12 pagesGreen Notes - Case Digest - Commercial LawspecialsectionNo ratings yet
- Juris LiabilityDocument35 pagesJuris Liabilityhala zafarNo ratings yet
- Case Law Ruling - 2 PDFDocument1 pageCase Law Ruling - 2 PDFrengarajan nNo ratings yet
- Leading Personal Injury Lawyers in Henderson - Benson & Bingham Accident Injury Lawyers, LLCDocument8 pagesLeading Personal Injury Lawyers in Henderson - Benson & Bingham Accident Injury Lawyers, LLCBenson & Bingham Accident Injury Lawyers, LLCNo ratings yet
- Jarco MKTG vs. CADocument2 pagesJarco MKTG vs. CAErwin BernardinoNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Construction Tort CaseDocument14 pagesMalaysian Construction Tort CaseAzrin MisriNo ratings yet
- Torts B Study NotesDocument62 pagesTorts B Study NotesTalNo ratings yet
- Professional Negligence - 2019Document16 pagesProfessional Negligence - 2019P4wnedNo ratings yet
- Vosburg V PutneyDocument2 pagesVosburg V PutneyRebekahNo ratings yet
- Parker v. Highland Park, Inc., 565 S.W.2d 512 (Tex., 1978)Document10 pagesParker v. Highland Park, Inc., 565 S.W.2d 512 (Tex., 1978)BrandonNo ratings yet
- Law on Tort DefinedDocument23 pagesLaw on Tort Definedeira87No ratings yet
- Tort Law Trespass PersonDocument2 pagesTort Law Trespass PersonZafar Azeemi100% (1)
- RespondentDocument18 pagesRespondentMayankSahuNo ratings yet
- Remoteness of Damages: Meaning and ConceptDocument12 pagesRemoteness of Damages: Meaning and ConceptNamrata BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Negligence and Strict Liability. Notes PDFDocument58 pagesNegligence and Strict Liability. Notes PDFWangalya EdwinNo ratings yet
- NuisanceDocument10 pagesNuisanceAshutosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Torts and PropertyDocument6 pagesTorts and PropertyFaris YoungNo ratings yet
- The Exiled Prince: LRT vs. NavidadDocument2 pagesThe Exiled Prince: LRT vs. NavidadKaryl Eric BardelasNo ratings yet
- 321duty To Act When Prior Conduct Is Found To Be Dangerous - WestlawNextDocument2 pages321duty To Act When Prior Conduct Is Found To Be Dangerous - WestlawNextjohnsmith37788No ratings yet
- Pantaleon v. American Express Case Brief SummaryDocument7 pagesPantaleon v. American Express Case Brief SummaryG FNo ratings yet
- Medical services and consumer protection actDocument6 pagesMedical services and consumer protection actAbhinav ChandrachudNo ratings yet
- Tort Problem Questions - Occupiers LiabilityDocument2 pagesTort Problem Questions - Occupiers LiabilityAimeeNo ratings yet
- Maryland Torts Bar Exam OutlineDocument41 pagesMaryland Torts Bar Exam Outlinerosiee0916No ratings yet