Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OB Hesi
Uploaded by
Leena LapenaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OB Hesi
Uploaded by
Leena LapenaCopyright:
Available Formats
1. 1 meter 3.
3 feet
2. 1 meter in cm 100 cm
3. Administer IV
magnesium
sulfate to
decrease hyperreflexia and minimize risk
of seizure activity.
4. amniotic fluid Pale, straw-colored fluid in which the
fetus floats. It serves as a cushion against
injury from sudden blows or movements
and helps maintain a constant body
temperature for the fetus. The fetus
modifies the amniotic fluid through the
processes of swallowing, urinating, and
movement through the respiratory tract.
5. The anterior
fontanel closes at
12 to 18 months
6. APGAR 10 is perfect; 0 is worst
7. baby low temp,
shaky hands and
lower lip
hypoglycemia, do glucose stick
8. ballottement Rebounding of the fetus against the
examiner's finger on palpation. When
the examiner taps the cervix, the fetus
floats upward in the amniotic fluid. The
examiner feels a rebound when the fetus
falls back.
9. betamethasone a glucocorticoid given (after after mag
sulfate for preterm labor) to increase
surfactant producation to stimulate fetal
lung maturation. given at 28 to 32 wks if
mag is successful in inhibiting labor for
48 hrs.
10. BMI Kg / (Meters squared)
11. Butorphanol
tartrate (Stadol)
is an opioid analgesic that provides
systemic pain relief during labor. DO
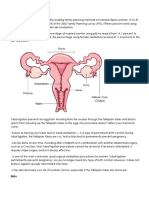
NOT use with opioid addicts bc of strong
withdrawal symptoms.
12. cephalhematoma slight abnormal deviation from delivery
trauma. it is capillary bleeding between
the periosteum and skull. often caused by
FORCEPS
13. Chadwick's sign Violet coloration of the mucous
membranes of the cervix, vagina, and
vulva that occurs at about 4 weeks of
pregnancy caused by increased
vascularity. This is considered a probable
sign of pregnancy.
14. delivery Actual event of birth; the expulsion or
extraction of the neonate.
15. dizygotic = fraternal twins
16. ductus
venosus
connect umbilical vein with inferior vena
cava, passes through/largely bypasses the
liver.
17. dystocia prolonged labor or very painful labor
18. eclampsia seizure. when preeclampsia progresses to
eclampsia, clear and maintain open airway,
give oxygen, administer mag, assess BP and
fetal HR
19. embryo Stage of fetal development that lasts from day
15 until approximately 8 weeks after
conception or until the embryo measures 3
cm from crown to rump.
20. Episodic
changes are
those that
are not associated with UCs.
21. fertilization Uniting of the sperm and ovum, which occurs
within 12 hours of ovulation and within 2 to
3 days of insemination, the average duration
of viability for the ovum and sperm.
22. Fetal heart
rate
acceleration
during
contractions
are
normal
23. food rich in
Iron:
LEGUMES, meat, liver, whole grain breads,
deep green leafy veggies, dried fruits.
24. foods that
reduce iron
absorption
milk, eggs, coffee, bran, tea
25. goal of labor
augmentation
is to achieve
three good quality contractions in ten minute
period
26. Goodell's sign Softening of the cervix that occurs at the
beginning of the second month of gestation.
This is considered a probable sign of
pregnancy.
27. gravida A pregnant woman; called gravida I
(primigravida) during the first pregnancy,
gravida II during the second pregnancy, and
so on.
28. Hegar's sign Compressibility and softening of the lower
uterine segment that occurs at about week 6
of gestation. This is considered a probable
sign of pregnancy.
29. implantation Embedding of the fertilized ovum in the
uterine mucosa 6 to 10 days after conception.
30. infant A human born alive; also, a human from 28
days of age until the first birthday.
OB Hesi
Study online at quizlet.com/_49r31
31. labor Coordinated sequence of rhythmic
involuntary uterine contractions resulting in
effacement and dilation of the cervix,
followed by expulsion of the products of
conception.
32. lecithin-to-
sphingomyelin
(L/S) ratio
Ratio of two components of amniotic fluid,
used for predicting fetal lung maturity;
normal L/S ratio in amniotic fluid is 2:1 or
greater when the fetal lungs are mature.
33. lightening In first-time pregnancies the uterus sinks
downward and forward about 2 weeks
before term, when the fetus's presenting part
(usually the fetal head) descends into the
true pelvis. also called dropping
34. lochia Discharge from the uterus that consists of
blood from the vessels of the placental site
and debris from the decidua; lasts for 2 to 6
weeks after delivery.
35. lochia alba yello or white days 10 until placenta is
healed (2 to 6 weeks after delivery)
36. lochia rubra first lochia, with debris and gunk
37. lochia serosa pink or light brown days 3 or 4 to day 10
38. Mag Sulfate It decreases neuromuscular excitability. It
produces peripheral vasodilation.
39. mag sulfate
_________
acetylcholine
decreases it; blocking neuromuscular
transmission (
40. mag
therapeutic
4-8 mg/dL
41. monozygotic = identical twins
42. Ngele's rule Determines the estimated date of birth based
on the premise that the woman has a 28-day
menstrual cycle. Add 7 days to the first day
of the last menstrual period; subtract 3
months and add 1 year. Alternatively, add 7
days to the last menstrual period and count
forward 9 months.
43. newborn A human from the time of birth to the
twenty-eighth day of life; also called
neonate.
44. parity Number of pregnancies that have reached
viability regardless of whether the fetus was
born alive or stillborn.
45. Periodic
changes are
those that
occur with UCs.
46. placenta Organ that provides for the exchange of
nutrients and waste products between the fetus
and the mother and produces hormones to
maintain pregnancy. The placenta develops by
the third month of gestation and is also called
afterbirth.
47. The
posterior
fontanel
closes by ...
by the end of the second month
48. postpartum
blues peak
around the 5th postpartum day
49. produces
flushing and
sweating
due to
decreased
peripheral
blood
pressure
mag sulfate
50. quickening Maternal perception of fetal movement for the
first time, occurring usually in the sixteenth to
twentieth week of pregnancy.
51. severe pain
after
delivery of
placenta
uterine inverstion!!!
52. surfactant Phospholipid that is necessary to keep the fetal
lung alveoli from collapsing; amount is
usually sufficient after 32 weeks' gestation.
53. third
trimester
painless
bleeding
characteristic of placenta previa and
diagnosed by transabdominal ultrasound
54. tocolytic drug used to suppress labor (toci = birth)
55. uterus Organ located behind the symphysis pubis,
between the bladder and the rectum. It has
four partsfundus (upper part), corpus (body),
isthmus (lower segment), and cervix.
56. vagina Tubular structure located behind the bladder
and in front of the rectum; it extends from the
cervix to the vaginal opening in the perineum.
It functions as the outflow tract for menstrual
fluid and for vaginal and cervical secretions,
the birth canal, and the organ for coitus.
57. viability Capability of the fetus to survive outside the
uterus; about 22 to 24 weeks of gestation or
fetal weight more than 500 g.
58. what aids in
absorption
of iron?
vitamin C!
59. when does ovulation occur? 14 days before menses
You might also like
- Maternal Hesi Q RDocument1 pageMaternal Hesi Q RSho Ngo25% (4)
- Ob HesiDocument1 pageOb HesiJoyzoey93% (27)
- MaternityDocument4 pagesMaternityErica Sanchez100% (5)
- Hesi Hints MaternityDocument4 pagesHesi Hints MaternityThomas Stewart91% (11)
- Obstetric Questions: Please State Whether The Following Statements Are TRUE or FALSEDocument8 pagesObstetric Questions: Please State Whether The Following Statements Are TRUE or FALSEjulialeo90% (10)
- DDocument56 pagesDDarren Balbas100% (1)
- Hesi Review For MaternityDocument29 pagesHesi Review For MaternitySteam Lc86% (21)
- Hesi MaternityDocument20 pagesHesi Maternityracquela_367% (3)
- Exit Hesi v3Document2 pagesExit Hesi v3Amy90% (10)
- Growth and Development Milestones HESI HintsDocument12 pagesGrowth and Development Milestones HESI HintsJen Guthrie89% (9)
- Weekly TipsDocument69 pagesWeekly TipsSharynn Kew Moore100% (1)
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text DocumentTro Wact100% (1)
- OB HESI Study GuideDocument34 pagesOB HESI Study GuideLeah Hunter97% (35)
- Pediatrics HESI Guide 2Document26 pagesPediatrics HESI Guide 2hellmanns1100% (15)
- Hesi v4 Sample 2015Document2 pagesHesi v4 Sample 2015james67% (3)
- Antenatal Glucocorticoid Therapy and Fetal Lung MaturationDocument32 pagesAntenatal Glucocorticoid Therapy and Fetal Lung Maturationcclaire197% (37)
- Medsurg and Pharm HESI ReviewDocument8 pagesMedsurg and Pharm HESI ReviewSarah Vance100% (4)
- Hesi HelpDocument5 pagesHesi HelpAna Gonzalez87% (23)
- Community Health HesiDocument5 pagesCommunity Health Hesisakurablossom0890% (31)
- Exam 1 ER Chest PainDocument10 pagesExam 1 ER Chest Paindinkinspdd50% (2)
- HESIDocument29 pagesHESIJustin Bunn100% (18)
- Ob Ati StudyDocument22 pagesOb Ati Studylpirman0580% (5)
- 2009 HESI Practice - Comprehensive ExamDocument26 pages2009 HESI Practice - Comprehensive ExamQueennitaNo ratings yet
- Peds HESI Study GuideDocument5 pagesPeds HESI Study Guidemscostello985367% (9)
- Hesi Helpful HintsDocument6 pagesHesi Helpful Hintsbirenbirenpat100% (1)
- Med-Surg HESI TOPICSDocument6 pagesMed-Surg HESI TOPICSjustjesko0l100% (3)
- HESI V2 2015 Exit ExamDocument10 pagesHESI V2 2015 Exit ExamHailey Olert100% (10)
- Nursing Skills and Concepts ReviewDocument10 pagesNursing Skills and Concepts Reviewcarol50% (2)
- Hesi RN PediatricsDocument24 pagesHesi RN Pediatricsracquela_3100% (1)
- Pediatric HESI Review 2016Document9 pagesPediatric HESI Review 2016Brittany78% (9)
- HESI Pediatric HESI ReviewDocument41 pagesHESI Pediatric HESI Reviewprogramgrabber96% (24)
- Hesi Pre TestDocument5 pagesHesi Pre Testjosie teeh100% (1)
- Med SurgDocument82 pagesMed SurgRam Nik100% (4)
- ATI Predictor 2010 Topics To ReviewDocument8 pagesATI Predictor 2010 Topics To ReviewJonathon95% (19)
- Maternity Practice TestDocument12 pagesMaternity Practice TestJoslyn Gross87% (15)
- Final Hesi ExamDocument17 pagesFinal Hesi Examapi-34152774324% (34)
- 2019 Rationales HESI TEST BANK MED SURG Version 2Document1 page2019 Rationales HESI TEST BANK MED SURG Version 2Prettygirl71650% (4)
- Med-Surg Hesi CompilationDocument71 pagesMed-Surg Hesi CompilationJbl2328100% (4)
- Test Bank For Maternity Nursing 8th Edition, LowdermilkDocument26 pagesTest Bank For Maternity Nursing 8th Edition, LowdermilkILL101100% (2)
- Psych HESI Hints: Members For The Client's Safety (E.g., Suicide Plan) and Optimal TherapyDocument7 pagesPsych HESI Hints: Members For The Client's Safety (E.g., Suicide Plan) and Optimal TherapyChristina100% (10)
- Practice Examination For HESI ExitDocument76 pagesPractice Examination For HESI ExitGod_is_Good_294486% (43)
- HESIDocument27 pagesHESIDerrick Cleveland94% (16)
- Maternity Ati RemediationDocument2 pagesMaternity Ati Remediationcse100% (1)
- Maternity Evolve ExamDocument36 pagesMaternity Evolve Examfriendofnurse100% (26)
- Comprehensive Hesi Review 1Document68 pagesComprehensive Hesi Review 1Tamara Smith-Williams100% (26)
- AtiDocument4 pagesAtirunnermn88% (8)
- Hesi GemsDocument27 pagesHesi Gemssugarplum22No ratings yet
- HESI Qbank from Quizzlet: Understanding Medication QuestionsDocument11 pagesHESI Qbank from Quizzlet: Understanding Medication Questionsnana100% (4)
- Pediatric RemediationDocument5 pagesPediatric RemediationAlvin L. Rozier67% (3)
- ATI PN Maternal Newborn NotesDocument13 pagesATI PN Maternal Newborn NotesDiamond Blackwell100% (6)
- Hesi FundamentalsDocument14 pagesHesi Fundamentalscharitoave90% (20)
- GoodDocument21 pagesGoodVanessaMUeller80% (5)
- Schaum's Outline of Maternal-Newborn Nursing: 700 Review QuestionsFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Maternal-Newborn Nursing: 700 Review QuestionsNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- NATIONAL COUNCIL LICENSURE EXAMINATION FOR REGISTERED NURSES (NCLEX-RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandNATIONAL COUNCIL LICENSURE EXAMINATION FOR REGISTERED NURSES (NCLEX-RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsFrom EverandDimensional Analysis For Nursing StudentsNo ratings yet
- 101 Ways to Score Higher on your NCLEX: What You Need to Know About the National Council Licensure Examination Explained SimplyFrom Everand101 Ways to Score Higher on your NCLEX: What You Need to Know About the National Council Licensure Examination Explained SimplyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Tuberculosis Power PointDocument20 pagesTuberculosis Power PointLeena LapenaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Made EasyDocument20 pagesStatistics Made EasyLeena LapenaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology, Heart, BP and Hematology Labs MoodleDocument70 pagesAnatomy and Physiology, Heart, BP and Hematology Labs MoodleLeena LapenaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To CHEM 1123 Unit 2 Sample ProblemsDocument3 pagesSolutions To CHEM 1123 Unit 2 Sample ProblemsLeena LapenaNo ratings yet
- Oklahoma Living WillDocument5 pagesOklahoma Living WillLeena LapenaNo ratings yet
- 236-Nanoweapons Int LawDocument34 pages236-Nanoweapons Int LawLeena LapenaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris: Dosen Pembimbing: A. M. Aziz, M. PDDocument4 pagesTugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris: Dosen Pembimbing: A. M. Aziz, M. PDMega Safira MahardiniNo ratings yet
- Abstinence and Birth Control Analysis ChartDocument3 pagesAbstinence and Birth Control Analysis ChartGabriel GalvezNo ratings yet
- Marquez - Case Study 120Document4 pagesMarquez - Case Study 120Caren Marquez100% (1)
- Alamo Heights Human Sexuality - AHJS Parent Letter and Scope & SequenceDocument2 pagesAlamo Heights Human Sexuality - AHJS Parent Letter and Scope & SequenceDebbie SimmonsNo ratings yet
- GynecologyDocument54 pagesGynecologyaimanNo ratings yet
- Health: Quarter 1-Module 2Document21 pagesHealth: Quarter 1-Module 2RisnaDPejoNo ratings yet
- Fertility Awareness Across The Life CourseDocument14 pagesFertility Awareness Across The Life CourseMaternal and Child Survival Program (MCSP)No ratings yet
- CABINUANGAN 1 Health Indicators Report Shows Success in Maternal and Child OutcomesDocument4 pagesCABINUANGAN 1 Health Indicators Report Shows Success in Maternal and Child OutcomesRonald A. SagangNo ratings yet
- Position PaperDocument2 pagesPosition Paperangelo pamatianNo ratings yet
- ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINEDDocument34 pagesASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY EXPLAINEDBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- Antenatal management and statisticsDocument64 pagesAntenatal management and statisticsHasan Dahamsheh100% (4)
- Family Planning TCLDocument2 pagesFamily Planning TCLKristine TanNo ratings yet
- SterilizationDocument6 pagesSterilizationMaria Ella Joanne DapitonNo ratings yet
- Human Sexuality and STDsDocument23 pagesHuman Sexuality and STDsGeeya Mariel AntonioNo ratings yet
- Approach To STDS2Document56 pagesApproach To STDS2Daniel ThomasNo ratings yet
- Form I MTPDocument2 pagesForm I MTPpradnyajkNo ratings yet
- Prep101 Consumer InfoDocument2 pagesPrep101 Consumer InfoCirca NewsNo ratings yet
- Sex Should Be Done Only Within MarriageDocument10 pagesSex Should Be Done Only Within MarriageriiNo ratings yet
- C11 P07 National Aids Control ProgrammeDocument32 pagesC11 P07 National Aids Control ProgrammeChandana KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument12 pagesBest Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics and GynaecologyGrit WingsNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Principles of Antenatal Care 2017Document60 pagesAntenatal Principles of Antenatal Care 2017JanielWright100% (3)
- World AIDS Day - December 1stDocument1 pageWorld AIDS Day - December 1stNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- M.Thamrin TanjungDocument17 pagesM.Thamrin TanjungJoko Pratama Atmayudha50% (2)
- List of Sex Positions - Helpful HintsDocument4 pagesList of Sex Positions - Helpful HintsRajneesh Kumar100% (2)
- La Patada QueDocument2 pagesLa Patada QueLouis Villanueva GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument10 pagesBio ProjectDipNo ratings yet
- STD BrochureDocument2 pagesSTD Brochureapi-271271455No ratings yet
- Family Planning Methods: Presented byDocument56 pagesFamily Planning Methods: Presented byNise Mon KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- How To Achieve Female Orgasm.Document11 pagesHow To Achieve Female Orgasm.Love Pandit100% (2)
- 1 - HBC207 - HIV-AIDS-Mukondombera 2013Document50 pages1 - HBC207 - HIV-AIDS-Mukondombera 2013HeruNo ratings yet