Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ece 256 Prob
Uploaded by
NarendraNariCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ece 256 Prob
Uploaded by
NarendraNariCopyright:
Available Formats
Lovely Professional University, Punjab
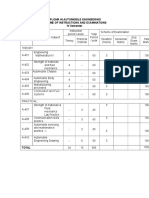
Course Code Course Title Course Planner Lectures Tutorials Practicals Credits
ECE256 PROBABILITY AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES 15921::Vineet Kumar 3.0 1.0 0.0 4.0
Course Category Courses with Numerical focus
TextBooks
Sr No Title Author Edition Year Publisher Name
T-1 Probability,Random variable and
stochastic processes
Athanasios Papoulis 4th 2002 McGraw-Hill
Reference Books
Sr No Title Author Edition Year Publisher Name
R-1 Probability & Statistics for. Engineers
& Scientists
Ronald E. Walpole
Raymond H. Myers
8th 2007 Prentice hall Delhi
R-2 Probability, Random variables and
random processes
Hwei P. Hsu 3rd 2010 Tata McGraw Hill, India
Other Reading
Sr No Journals articles as Compulsary reading (specific articles, complete reference)
OR-1 http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/courses/IIT-MADRAS/Principles_of_Communication1/ ,
Relevant Websites
Sr No (Web address) (only if relevant to the course) Salient Features
RW-1 www.math.toronto.edu/weiss/set_theory.pdf? Set theory
RW-2 www.ecs.umass.edu/~goeckel/Chapter11.pdf? Transmission of random process through LTI
Detailed Plan For Lectures
LTP week distribution: (LTP Weeks)
Weeks before MTE 7
Weeks After MTE 7
Spill Over 3
Week
Number
Lecture
Number
Broad Topic(Sub Topic) Chapters/Sections
of Text/reference
books
Other Readings,
Relevant
Websites, Audio
Visual Aids,
software and
Virtual Labs
Lecture Description Learning Outcomes Pedagogical Tool
Demonstration/ Case
Study / Images /
animation / ppt etc.
Planned
Week 1 Lecture 1 Introduction to probability
(Probability definition)
T-1:1.1
R-1:2.1
Mathematical aspect of
probability.
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of probability.
white/black board and
discussion.
Lecture 2 Introduction to probability
(Probability and induction)
T-1:1.3
R-1:2.1
Mathematical aspect of
probability
would be knowing
about its Relative
Frequency definition.
Lecture 3 Introduction to probability
(Probability and induction)
T-1:1.3
R-1:2.1
Mathematical aspect of
probability
would be knowing
about its Relative
Frequency definition.
Week 2 Lecture 4 Introduction to probability
(Causality Versus Randomness)
T-1:1.4
R-1:2.4
Mathematical aspect of
probability.
would be knowing
about the Probability
and induction.
white/black board and
discussion
Lecture 5 Axioms of probability(Set theory) T-1:2.1
R-1:2.5
RW-1 Introduction to Set
theory.
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of set theory.
white/black board and
discussion
Lecture 6 Axioms of probability(Set theory) T-1:2.1
R-1:2.5
RW-1 Introduction to Set
theory.
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of set theory.
white/black board and
discussion
Week 3 Lecture 7 Axioms of probability(Probability
space)
T-1:2.2 Introduction to
Probability space.
would be knowing
about the Probability
space and Axiom of
infinite additivity.
Lecture 8 Axioms of probability(Conditional
probability)
T-1:2.3
R-1:2.6 2.7
Introduction to
Conditional probability
and Bayes theorem
solving problems using
Conditional probability
and Bayes theorem
Lecture 9 Axioms of probability(Bayes'
theorem and
independence)
T-1:2.3
R-1:2.6 2.7
Introduction to
Conditional probability
and Bayes theorem
solving problems using
Conditional probability
and Bayes theorem
Week 4 Lecture 10 Repeated Trials(Combined
Experiments)
T-1:3.1 3.2 Introduction to
independent
Experiments.
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Bernoulli
Trials.
Lecture 11 Repeated Trials(Bernoulli Trials) T-1:3.1 3.2 Introduction to
independent
Experiments.
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Bernoulli
Trials.
Lecture 12 Test1
Week 5 Lecture 13 Concept of a random variable
(Discrete random variables)
T-1:4.1 4.2
R-1:3.1
Sinificance of
random variable
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Discrete
random variables.
Lecture 14 Concept of a random variable
(Example of random variables and
distributions function)
Concept of a random
variable.
would be knowing
about the Continuous
random variables.
Lecture 15 Concept of a random variable
(Probability density function)
T-1:4.2 Concept of a random
variable.
would be knowing
about the Probability
density function.
Week 6 Lecture 16 Concept of a random variable
(Probability density function)
T-1:4.2 Concept of a random
variable.
would be knowing
about the Probability
density function.
Lecture 17 Test2
Lecture 18 Concept of a random variable
(Probability distribution function)
T-1:4.2
R-1:3.2 3.3
Concept of a random
variable.
would be knowing
about the Probability
distribution function.
Week 7 Lecture 19 Concept of a random variable
(Probability distribution function)
T-1:4.2
R-1:3.2 3.3
Concept of a random
variable.
would be knowing
about the Probability
distribution function.
Lecture 20 Concept of a random variable
(Continuous random variables)
T-1:5.2
R-1:3.2
example of a random
variable and Lecture 21
Contingency
various Example of
distributions
Case Studies on
MATLAB
Lecture 21 Concept of a random variable
(Continuous random variables)
T-1:5.2
R-1:3.2
example of a random
variable and Lecture 21
Contingency
various Example of
distributions
Case Studies on
MATLAB
MID-TERM
Week 8 Lecture 22 Special distributions(Joint
distributions)
T-1:6.1
R-1:3.4
Introduction to Special
distributions
would be knowing
about the Joint
distributions .
Case Studies on
MATLAB
Lecture 23 Special distributions(Joint
distributions)
T-1:6.1
R-1:3.4
Introduction to Special
distributions
would be knowing
about the Joint
distributions .
Case Studies on
MATLAB
Lecture 24 Special distributions(Functions of
one and two random variables)
T-1:6.2 Introduction to Special
distributions
would be knowing
about the Functions of
one and two random
variables.
Week 9 Lecture 25 Special distributions(Moments of
random variables)
T-1:5.3 Introduction to Special
distributions.
would be knowing
about the Moments of
random variables.
Special distributions(Mean and
Variance)
T-1:5.3 Introduction to Special
distributions.
would be knowing
about the Moments of
random variables.
Week 9 Lecture 26 Special distributions(Characteristic
functions of a random variable)
T-1:5.5 Introduction to Special
distributions
would be knowing
about the Characteristic
functions of a random
variable.
Lecture 27 Special distributions(Characteristic
functions of a random variable)
T-1:5.5 Introduction to Special
distributions
would be knowing
about the Characteristic
functions of a random
variable.
Week 10 Lecture 28 Special distributions(Markov,
Chebyshev and Chernoff bounds)
T-1:7.3 Introduction to Special
distributions.
would be knowing
about the Markov,
Chebyshev and
Chernoff bounds.
Lecture 29 Random sequences and modes of
convergence(Random sequences)
T-1:10.1 OR-1 Introduction to Random
sequences
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Random
sequences.
Case Studies on
MATLAB
Lecture 30 Random sequences and modes of
convergence(Random sequences)
T-1:10.1 OR-1 Introduction to Random
sequences
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Random
sequences.
Case Studies on
MATLAB
Week 11 Lecture 31 Random sequences and modes of
convergence(Limit theorems)
T-1:8.4 Introduction to Random
sequences and modes of
convergence.
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Limit
theorems.
Lecture 32 Random sequences and modes of
convergence(Limit theorems)
T-1:8.4 Introduction to Random
sequences and modes of
convergence.
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Limit
theorems.
Lecture 33 Random sequences and modes of
convergence(Central limit
theorem)
T-1:8.4 8.5 Introduction to Random
sequences and modes of
convergence.
would be knowing
about the central limit
theorem
Random sequences and modes of
convergence(Modes of
convergence)
T-1:8.4 8.5 Introduction to Random
sequences and modes of
convergence.
would be knowing
about the central limit
theorem
Week 12 Lecture 34 Random sequences and modes of
convergence(Modes of
convergence)
T-1:8.4 8.5 Introduction to Random
sequences and modes of
convergence.
would be knowing
about the central limit
theorem
Random sequences and modes of
convergence(Central limit
theorem)
T-1:8.4 8.5 Introduction to Random
sequences and modes of
convergence.
would be knowing
about the central limit
theorem
Lecture 35 Classification of random processes
(Random process)
T-1:10.1 Types of random
processes
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Random
process
Week 12 Lecture 36 Classification of random processes
(Random process)
T-1:10.1 Types of random
processes
By the end of this
lecture students will be
able to develop the
concept of Random
process
Week 13 Lecture 37 Test3
Lecture 38 Classification of random processes
(Stationary processes)
T-1:8.3 Types of random
processes
would be knowing
about the Mean and
covariance functions
Classification of random processes
(Mean and covariance functions)
T-1:8.3 Types of random
processes
would be knowing
about the Mean and
covariance functions
Lecture 39 Classification of random processes
(Ergodicity)
T-1:12.1 Types of random
processes
would be knowing
about the Ergodicity
Week 14 Lecture 40 Classification of random processes
(Transmission of random process
through LTI)
T-1:11.4 RW-2 Types of random
processes
would be knowing
about the Transmission
of random process
through LTI
Lecture 41 Classification of random processes
(Power spectral density)
T-1:12.2 Types of random
processes and Lecture
42 Contingency
solving problems using
Power spectral density
Case Studies on
MATLAB
Lecture 42 Classification of random processes
(Power spectral density)
T-1:12.2 Types of random
processes and Lecture
42 Contingency
solving problems using
Power spectral density
Case Studies on
MATLAB
SPILL OVER
Week 15 Lecture 43 Spill Over
Lecture 44 Spill Over
Lecture 45 Spill Over
Scheme for CA:
Component Frequency Out Of Each Marks Total Marks
Test 2 3 10 20
Total :- 10 20
Details of Academic Task(s)
AT No. Objective Topic of the Academic Task Nature of Academic Task
(group/individuals/field
work
Evaluation Mode Allottment /
submission Week
Test1 The primary
objective of
assigning test to
students is to direct
them to worthwhile
revision of the
syllabus already
being taught so that
they prepare them
self MTE.
Repeated Trials, Axioms of probability, Introduction to
probability, Bayes' theorem and independence, Probability space
Individual Evaluations must be
made with
appropriate
feedback to students
by giving proper
comments on the
answer sheet.
3 / 4
Test2 The primary
objective of
assigning test to
students is to direct
them to worthwhile
revision of the
syllabus already
being taught so that
they prepare them
self ETE.
Continuous random variables, Example of random variables and
distributions function, Probability density function, Repeated
Trials
Individual Evaluations must be
made with
appropriate
feedback to students
by giving proper
comments on the
answer sheet.
5 / 6
Test3 Classification of
random processes,
Random sequences
and modes of
convergence,
Special distributions
The primary
objective of
assigning test to
students is to direct
them to worthwhile
revision of the
syllabus already
being taught so that
they prepare them
self ETE.
Individual Evaluations must be
made with
appropriate
feedback to students
by giving proper
comments on the
answer sheet.
11 / 12
Plan for Tutorial: (Please do not use these time slots for syllabus coverage)
Tutorial No. Lecture Topic Type of pedagogical tool(s) planned
(case analysis,problem solving test,role play,business game etc)
Tutorial1 Problem based on Set theory, Conditional probability,
Tutorial2 Problem based on Set theory, Conditional probability,
Tutorial3 Problem based on Concept of a random variable
Tutorial4 Problem based on Concept of a random variable
Tutorial5 Problem based on Concept of a random variable
Tutorial6 Problem based on Concept of a Special distributions
Tutorial7 function, Special distributions Special distributions
After Mid-Term
Tutorial8 Problems based on Special distributions
Tutorial9 Problems based on Special distributions
Tutorial10 Problems based on Special distributions
Tutorial11 Problems based on Special distributions
Tutorial12 Problems based on Classification of random processes
Tutorial13 Problems based on Classification of random processes
Tutorial14 Problems based on Classification of random processes
You might also like
- MTH212Document8 pagesMTH212Mandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Complex Algebra Ip mth213Document11 pagesComplex Algebra Ip mth213MohammadAneesNo ratings yet
- MTH 212Document10 pagesMTH 212CA Renu Goyal100% (1)
- Design Analysis of AlgorithmDocument8 pagesDesign Analysis of AlgorithmParinyas SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Differential Equations with Dynamical SystemsFrom EverandIntroduction to Differential Equations with Dynamical SystemsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- AutomataDocument11 pagesAutomataराहुल कुमारNo ratings yet
- Cse 408Document7 pagesCse 408Kislay SinghNo ratings yet
- Stat219 NotesDocument132 pagesStat219 Notesjmurray1022No ratings yet
- Stochastic Analysis and PDEsDocument73 pagesStochastic Analysis and PDEsa123a64No ratings yet
- SBTET AP C-14 SYLLABUS DAE IV SemesterDocument32 pagesSBTET AP C-14 SYLLABUS DAE IV SemesterthirukumarNo ratings yet
- Applied Math II ModuleDocument221 pagesApplied Math II ModuleHenok Girma100% (3)
- Stanley EcDocument100 pagesStanley EcDarius-Florentin NeatuNo ratings yet
- Wentzel, Ovcharov - Applied Problems in Probability TheoryDocument431 pagesWentzel, Ovcharov - Applied Problems in Probability TheoryLena SNo ratings yet
- Analysis I I MathsDocument150 pagesAnalysis I I MathsNasim SalimNo ratings yet
- Yuriĭ A. Rozanov - Introduction To Random ProcessesDocument126 pagesYuriĭ A. Rozanov - Introduction To Random ProcessesAlexis RosuelNo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential Equations and Stability Theory: An IntroductionFrom EverandOrdinary Differential Equations and Stability Theory: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- ODE Lectures on Existence and UniquenessDocument157 pagesODE Lectures on Existence and UniquenessmicrodotcdmNo ratings yet
- RP Tip Print NewDocument8 pagesRP Tip Print NewRakesh NainNo ratings yet
- Ece 302Document9 pagesEce 302Rohit MehtaNo ratings yet
- AdemboDocument384 pagesAdemboKelvin GuuNo ratings yet
- (Graduate Studies in Mathematics 120) Qing Han-A Basic Course in Partial Differential Equations-American Mathematical Society (2011)Document305 pages(Graduate Studies in Mathematics 120) Qing Han-A Basic Course in Partial Differential Equations-American Mathematical Society (2011)Zainab AbdNo ratings yet
- Fractional Evolution Equations and Inclusions: Analysis and ControlFrom EverandFractional Evolution Equations and Inclusions: Analysis and ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Nonlinear Optimization Lecture 1: Introduction: Professor Frank E. CurtisDocument24 pagesNonlinear Optimization Lecture 1: Introduction: Professor Frank E. CurtisbillNo ratings yet
- Advanced Econometrics - 1985 - 1era Edición - AmemiyaDocument531 pagesAdvanced Econometrics - 1985 - 1era Edición - AmemiyaAdan Graus Rios100% (1)
- C-14 Dme-Iv SemDocument39 pagesC-14 Dme-Iv SemsivaenotesNo ratings yet
- Rajendra Bhatia-Fourier Series (Mathematical Association of America Textbooks) - The Mathematical Association of America (2004)Document131 pagesRajendra Bhatia-Fourier Series (Mathematical Association of America Textbooks) - The Mathematical Association of America (2004)Claudio Ramón Rodriguez MondragónNo ratings yet
- Analytical Skills IIDocument7 pagesAnalytical Skills IIAbhishek UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Mec406 - Mechanical VibrationDocument10 pagesMec406 - Mechanical VibrationmanishtopsecretsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Modern Set TheoryDocument129 pagesIntroduction To Modern Set Theorytsilimides1No ratings yet
- HoelbookDocument214 pagesHoelbookgp3523469066100% (2)
- (Lecture Notes in Mathematics 2047) Gani T. Stamov (Auth.) - Almost Periodic Solutions of Impulsive Differential Equations - Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2012)Document235 pages(Lecture Notes in Mathematics 2047) Gani T. Stamov (Auth.) - Almost Periodic Solutions of Impulsive Differential Equations - Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg (2012)Só Cálculos MoçambiqueNo ratings yet
- EE 560-Linear Dynamical Systems-Muhammad TahirDocument3 pagesEE 560-Linear Dynamical Systems-Muhammad Tahircoolboy_usamaNo ratings yet
- UNITEXT - La Matematica Per Il 3+2: For Further VolumesDocument12 pagesUNITEXT - La Matematica Per Il 3+2: For Further Volumesnthu5566No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Mathematical Physics Edgar A KrautDocument21 pagesFundamentals of Mathematical Physics Edgar A KrautSayantanNo ratings yet
- Mecinq Cuanto Fisic NormalDocument188 pagesMecinq Cuanto Fisic NormalDiegoNo ratings yet
- RP Tip Print NewDocument8 pagesRP Tip Print NewChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Maths 101 Term PaperDocument26 pagesMaths 101 Term PaperAbhiroop SharmaNo ratings yet
- CSE420 Symbolic Logic and Logic Processing 18306::savleen Kaur 3.0 0.0 0.0 3.0 Courses With Conceptual FocusDocument9 pagesCSE420 Symbolic Logic and Logic Processing 18306::savleen Kaur 3.0 0.0 0.0 3.0 Courses With Conceptual FocusSwapnil VijayvargiyaNo ratings yet
- Mec406 - Mechanical VibrationDocument9 pagesMec406 - Mechanical VibrationmanishtopsecretsNo ratings yet
- Mec235 - Thermo FluidsDocument10 pagesMec235 - Thermo FluidsManish JainNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument242 pagesStabilityMurilo Teixeira Silva100% (1)
- Applications of Differential Equations in EngineeringDocument27 pagesApplications of Differential Equations in Engineeringishan_arora8980% (45)
- Complex Variables, Matrices, Laplace TransformsDocument3 pagesComplex Variables, Matrices, Laplace TransformsAmeya GanpatyeNo ratings yet
- Java Course MaterialDocument8 pagesJava Course MaterialParinyas SinghNo ratings yet
- Notes On (Semi-) Advanced Quantum Mechanics: The Path Integral Approach To Quantum MechanicsDocument64 pagesNotes On (Semi-) Advanced Quantum Mechanics: The Path Integral Approach To Quantum MechanicsReeshav GhoshNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration IpDocument10 pagesMechanical Vibration IpDeepak Dogra100% (1)
- Johnson's Algorithm For Optimal Scheduling Of Multi-Machine SystemsDocument8 pagesJohnson's Algorithm For Optimal Scheduling Of Multi-Machine SystemsBabyCoder HvhNo ratings yet
- DDA vs Bresenham Line Drawing AlgorithmsDocument13 pagesDDA vs Bresenham Line Drawing AlgorithmsAshagre MekuriaNo ratings yet
- Master sequence and series for JEE with free videosDocument15 pagesMaster sequence and series for JEE with free videosdevansh dewanNo ratings yet
- Multi Variate Calculus 3Document6 pagesMulti Variate Calculus 3Khushi PatelNo ratings yet
- Elementary Cam Lift Curve SynthesisDocument11 pagesElementary Cam Lift Curve Synthesisnadjib62100% (1)
- Satish Pradhan Dnyanasadhana College: Department of BMS Sample MCQ Questions Subject: Operations ResearchDocument3 pagesSatish Pradhan Dnyanasadhana College: Department of BMS Sample MCQ Questions Subject: Operations ResearchMukulNo ratings yet
- Math 301a Final Exam 2015Document3 pagesMath 301a Final Exam 2015Jonathan ShaoNo ratings yet
- EE159 Computer Aided Power System DesignDocument1 pageEE159 Computer Aided Power System DesignrameshsmeNo ratings yet
- 2the Fibonacci Sequence and The Importance of MathematicsDocument12 pages2the Fibonacci Sequence and The Importance of MathematicsBevelyn Layosa AbellonNo ratings yet
- Davis (1995) Philosophical Positivism and American Atonal Music TheoryDocument23 pagesDavis (1995) Philosophical Positivism and American Atonal Music TheoryAsher Vijay YampolskyNo ratings yet
- ICET 2014 syllabus breakdownDocument3 pagesICET 2014 syllabus breakdown9985237595No ratings yet
- Boolean Algebra1Document38 pagesBoolean Algebra1Rajdeep BorgohainNo ratings yet
- Plates Subjected to Transverse Loads EquationsDocument53 pagesPlates Subjected to Transverse Loads Equationssori1386No ratings yet
- Pound - Interest InvestigationDocument7 pagesPound - Interest InvestigationNatalia FilipowiczNo ratings yet
- Plotting and Model Building in MATLABDocument30 pagesPlotting and Model Building in MATLABMuhammad Shehzad KamalNo ratings yet
- Mock Board Examination in Mathematics D PDFDocument7 pagesMock Board Examination in Mathematics D PDFvon kervy onradeNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Matrices: Properties of Various Types of MatricesDocument7 pagesRevision Notes On Matrices: Properties of Various Types of MatricesVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- DLL Evaluating Algebraic Exp G7 q2Document6 pagesDLL Evaluating Algebraic Exp G7 q2James Russell AbellarNo ratings yet
- The TikZ-CD Package: Create Commutative DiagramsDocument11 pagesThe TikZ-CD Package: Create Commutative DiagramsjozefchristusNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document36 pagesChapter 3刘伟康No ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Energy Systems: E.G. ShehataDocument9 pagesElectrical Power and Energy Systems: E.G. Shehataanil1216kumarNo ratings yet
- Applications of Coordinate GeometryDocument28 pagesApplications of Coordinate GeometrySabyasachi DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Maths Worksheet STD 6Document116 pagesMaths Worksheet STD 6shaktiparashar2004No ratings yet
- 6 Ways to Merge Literacy With MathDocument4 pages6 Ways to Merge Literacy With Mathcariere_zzzzNo ratings yet
- Structure and Interpretation of Classical MechanicsDocument427 pagesStructure and Interpretation of Classical MechanicsGerman Toledo100% (1)
- Answers Ch2Document4 pagesAnswers Ch2kbv28420% (1)
- MPDocument2 pagesMPByun BaekHyunNo ratings yet
- Permutation and Combination, Probability: Maths Lecture # 14Document26 pagesPermutation and Combination, Probability: Maths Lecture # 14bobo boboNo ratings yet
- Absolute Value Equations: Math WorksheetsDocument2 pagesAbsolute Value Equations: Math WorksheetsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Shrinkage Parameter Selection Via Modified Cross Validation Approach For Ridge Regression ModelDocument10 pagesShrinkage Parameter Selection Via Modified Cross Validation Approach For Ridge Regression ModelGHULAM MURTAZANo ratings yet