Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Decanter Formulae
Uploaded by
Sampathkumar AttuluriOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Decanter Formulae
Uploaded by
Sampathkumar AttuluriCopyright:
Available Formats
The concept of the decanter involves the balancing of liquid heights due to differences in density of the two phases,as
well as settling velocity of the heavier phase falling through the lighter or the lighter
rising through the heavier.The phases are divided in to continuous phase and dispersed phase.To know which phase is continuous and what is dispersed the following formulae is used.
=(Flow rate of lighter phase/Flow rate of Heavy Phase)*(density of light phase*Viscosity of heavier phase/density of heavier phase*viscosity of light phase)^0.3
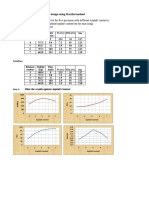
Q density
In the current example kg/sec kg/m3
MDC 0.272 1330
Water 0.005 1000
Conditions for In the current, MDC-Water system,Water is in light phase there fore it is dispersed.Continous phase is MDC.
Result
<0.3 light phase dispersed
0.3-0.5 light phase probably dispersed The next step is using the Stokes law for determining the settling velocity of the droplets to find the diameter and height of the decanter.
0.5-2.0 Phase inversion probable,design for worst case
2.0-3.3 heavy phase probably dispersed
>3.3 heavy phase always dispersed Assume the droplet size to be 150m
Terminal Settling Velocity
u
d
=d
d
2
g(
d
-c)/18
c
ud
Assume I is 80% of diameter D of the vessel and L/D=5 Where L is the length of the vessel, mts
(Q
c
/A
1
)<ud ,where A
1
=IL=(0.8D)(5D)=4D
2
(Q
c
/4D
2
)<ud
Q
c
is the volumetric flow rate of continous phase divided by the density of continous phase.
and D (0.5)*((Q
c
)/(ud))^0.5 i.e in this case
Diameter of the decanter,(D) Diameter
Length of the decanter Since;L=5*Diameter
Residence time in the decanter (Volume of tank/Total Volumetric flow rate)
0.125 hours
8 mins
The concept of the decanter involves the balancing of liquid heights due to differences in density of the two phases,as well as settling velocity of the heavier phase falling through the lighter or the lighter
rising through the heavier.The phases are divided in to continuous phase and dispersed phase.To know which phase is continuous and what is dispersed the following formulae is used.
=(Flow rate of lighter phase/Flow rate of Heavy Phase)*(density of light phase*Viscosity of heavier phase/density of heavier phase*viscosity of light phase)^0.3
Viscosity
kg/m.sec
0.000413
0.000894
0.013385
In the current, MDC-Water system,Water is in light phase there fore it is dispersed.Continous phase is MDC.
The next step is using the Stokes law for determining the settling velocity of the droplets to find the diameter and height of the decanter.
Assume the droplet size to be 150m
u
d
=d
d
2
g(
d
-c)/18
c
-0.009410756 m/sec
L is the length of the vessel, mts
Q
c
is the volumetric flow rate of continous phase divided by the density of continous phase.
0.204678363
m
3
/sec
2.331859005 mts
11.65929502 mts
(Volume of tank/Total Volumetric flow rate)
The concept of the decanter involves the balancing of liquid heights due to differences in density of the two phases,as well as settling velocity of the heavier phase falling through the lighter or the lighter
=(Flow rate of lighter phase/Flow rate of Heavy Phase)*(density of light phase*Viscosity of heavier phase/density of heavier phase*viscosity of light phase)^0.3
The next step is using the Stokes law for determining the settling velocity of the droplets to find the diameter and height of the decanter.
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Aspen Plus 12.1 TutorialDocument72 pagesAspen Plus 12.1 TutorialJoão SequeiraNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Types of Boilers PDFDocument5 pagesTypes of Boilers PDFJosé RubioNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Current Affairs Pocket PDF - May 2017 by AffairsCloudDocument37 pagesCurrent Affairs Pocket PDF - May 2017 by AffairsCloudkaran chaudhari100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Basic Principlesand Calculations in Process Technology PDFDocument81 pagesBasic Principlesand Calculations in Process Technology PDFSampathkumar Attuluri100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Pressure Relief Valve Engineering HandbookDocument93 pagesPressure Relief Valve Engineering Handbookakrouti92% (12)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Chess Book PDFDocument287 pagesChess Book PDFSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- UOP Reforming Solutions For .Improved Profits PaperDocument32 pagesUOP Reforming Solutions For .Improved Profits PaperstevemetroNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Find Function Returns Solutions to Systems of EquationsDocument11 pagesFind Function Returns Solutions to Systems of EquationsJason HernandezNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- UOP Reforming Solutions For .Improved Profits PaperDocument32 pagesUOP Reforming Solutions For .Improved Profits PaperstevemetroNo ratings yet
- CFD Modeling of Hydrodynamics of Fluidized BedDocument63 pagesCFD Modeling of Hydrodynamics of Fluidized BedSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Classification of Heat ExchangersDocument77 pagesClassification of Heat Exchangers4605566vivek100% (1)
- Packed distillation columns optimizationDocument7 pagesPacked distillation columns optimizationramsrivatsan1992No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Natural Gas Processing Principles and Technology - Part IDocument364 pagesNatural Gas Processing Principles and Technology - Part IRichard Gutierrez100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- MATLAB - Programming With MATLAB For BeginnersDocument113 pagesMATLAB - Programming With MATLAB For Beginnersc_mc2100% (3)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Coulson& Richardson - Cap.10 Liquid-Liquid SeparationDocument7 pagesCoulson& Richardson - Cap.10 Liquid-Liquid SeparationayyatullhusnaaNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- FiltrationDocument2 pagesFiltrationSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- McCabe ThieleDocument37 pagesMcCabe Thielefumanchu@fastmail.fmNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Tray Columns - DesignDocument6 pagesTray Columns - Designframon.chem35No ratings yet
- Friction FactorDocument30 pagesFriction FactorSomnath JagtapNo ratings yet
- Selecting The Proper Flare System PDFDocument6 pagesSelecting The Proper Flare System PDFjdgh1986100% (1)
- Shell& Tube HT DesignDocument8 pagesShell& Tube HT Designvsraochemical1979100% (1)
- Physical PropertiesDocument121 pagesPhysical PropertiesSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- HEN CasestudyDocument36 pagesHEN Casestudysoni_abdullahNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Panel OperationsDocument1 pagePanel OperationsSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- Panel OperationsDocument1 pagePanel OperationsSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- ETACRDDocument53 pagesETACRDSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- SteamDocument28 pagesSteamSampathkumar AttuluriNo ratings yet
- CC Batch TutorialDocument16 pagesCC Batch TutorialfernandozarateNo ratings yet
- Pump Sizing Rev1ADocument7 pagesPump Sizing Rev1ANoor Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- 50 Years of Teaching PianoDocument122 pages50 Years of Teaching PianoMyklan100% (35)
- ServiceDocument47 pagesServiceMarko KoširNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- #### # ## E232 0010 Qba - 0Document9 pages#### # ## E232 0010 Qba - 0MARCONo ratings yet
- Additional Help With OSCOLA Style GuidelinesDocument26 pagesAdditional Help With OSCOLA Style GuidelinesThabooNo ratings yet
- Marshal HMA Mixture Design ExampleDocument2 pagesMarshal HMA Mixture Design ExampleTewodros TadesseNo ratings yet
- Traffic LightDocument19 pagesTraffic LightDianne ParNo ratings yet
- Federal Complaint of Molotov Cocktail Construction at Austin ProtestDocument8 pagesFederal Complaint of Molotov Cocktail Construction at Austin ProtestAnonymous Pb39klJNo ratings yet
- QuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1Document12 pagesQuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1subhrajitm47No ratings yet
- Petty Cash Vouchers:: Accountability Accounted ForDocument3 pagesPetty Cash Vouchers:: Accountability Accounted ForCrizhae OconNo ratings yet
- Reader's Digest (November 2021)Document172 pagesReader's Digest (November 2021)Sha MohebNo ratings yet
- Inventory Control Review of LiteratureDocument8 pagesInventory Control Review of Literatureaehupavkg100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Log File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsDocument334 pagesLog File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsKossay BelkhammarNo ratings yet
- Quantification of Dell S Competitive AdvantageDocument3 pagesQuantification of Dell S Competitive AdvantageSandeep Yadav50% (2)
- Case 5Document1 pageCase 5Czan ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Approach To Estimate Feeder AccommodatiDocument16 pagesAnalytical Approach To Estimate Feeder AccommodatiCleberton ReizNo ratings yet
- Google Dorks For PentestingDocument11 pagesGoogle Dorks For PentestingClara Elizabeth Ochoa VicenteNo ratings yet
- John Hay People's Alternative Coalition Vs Lim - 119775 - October 24, 2003 - JDocument12 pagesJohn Hay People's Alternative Coalition Vs Lim - 119775 - October 24, 2003 - JFrances Ann TevesNo ratings yet
- C6 RS6 Engine Wiring DiagramsDocument30 pagesC6 RS6 Engine Wiring DiagramsArtur Arturowski100% (3)
- Nama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Document3 pagesNama: Yetri Muliza Nim: 180101152 Bahasa Inggris V Reading Comprehension A. Read The Text Carefully and Answer The Questions! (40 Points)Yetri MulizaNo ratings yet
- Liebert PSP: Quick-Start Guide - 500VA/650VA, 230VDocument2 pagesLiebert PSP: Quick-Start Guide - 500VA/650VA, 230VsinoNo ratings yet
- Take This LoveDocument2 pagesTake This LoveRicardo Saul LaRosaNo ratings yet
- Movement and Position: Question Paper 4Document14 pagesMovement and Position: Question Paper 4SlaheddineNo ratings yet
- Tension field beams: Aircraft wing spar analysisDocument19 pagesTension field beams: Aircraft wing spar analysisPrajeesh RajNo ratings yet
- Sentinel 2 Products Specification DocumentDocument510 pagesSentinel 2 Products Specification DocumentSherly BhengeNo ratings yet
- Archlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Document16 pagesArchlinux 之 之 之 之 Lmap 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 攻 略 ( 1 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 ) 、 环 境 准 备 )Goh Ka WeeNo ratings yet
- Ensayo Bim - Jaime Alejandro Martinez Uribe PDFDocument3 pagesEnsayo Bim - Jaime Alejandro Martinez Uribe PDFAlejandro MartinezNo ratings yet
- Wi FiDocument22 pagesWi FiDaljeet Singh MottonNo ratings yet
- Oracle Learning ManagementDocument168 pagesOracle Learning ManagementAbhishek Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Write UpDocument5 pagesWrite Upmourad baNo ratings yet
- Iq TestDocument9 pagesIq TestAbu-Abdullah SameerNo ratings yet