Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Business Plan
Uploaded by
kalisuryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Business Plan
Uploaded by
kalisuryCopyright:
Available Formats
Contents
Chapter 1 ....................................................................................................................................................... 2
Introduction .................................................................................................................................................. 2
Chapter 2 ....................................................................................................................................................... 3
Literature Review .......................................................................................................................................... 3
2.1 Entrepreneurial Process ...................................................................................................................... 3
2.2 Application of the Timmons Model .................................................................................................... 3
2.3 ODDS OF SUCCESS ............................................................................................................................... 4
2.4 Three Critical factors of Entrepreneurship ......................................................................................... 4
2.3.1 The Opportunity Factor ................................................................................................................ 5
2.3.2 The Team Factor .......................................................................................................................... 5
2.3.3 The Resources Factor ................................................................................................................... 6
2.4 Critical Analysis of the Timmons model .............................................................................................. 6
2.4.1. Factors for business enterprise ................................................................................................... 7
2.4.2 Analysis of Opportunity ............................................................................................................... 7
2.4.3 Marketing of the venture ............................................................................................................. 8
Chapter 3 ....................................................................................................................................................... 9
Conclusion ..................................................................................................................................................... 9
Bibliography ................................................................................................................................................ 10
List of Figures
Figure 1: Timmons Model ............................................................................................................................. 4
Figure 2: The opportunity factor ................................................................................................................... 5
Figure 3: Application of Timmons model ...................................................................................................... 7
Figure 4: VRIO Analysis ................................................................................................................................. 8
2
Chapter 1
Introduction
We are going through the age of entrepreneurship (Libial, 2003). Approximately as
many as 600 million peopleglobally are either dynamically connected in trying to begin a
novel venture or were managers of any kind of business (Timmons, Zacharakis, &
Spinelli, 2004). More than a thousand new companies are growingeach hour of
alloperational day in the world. Businesspersons are driving anuprising that is
converting and renovating economies around the globe. Entrepreneurship is the spirit of
free initiativeas the birth of new companiesprovides a market economy its strength. The
importantfeatures in the Timmons model are the founding teamand theentrepreneur, the
opportunity, and the means that are gathered to start the new business. If we analyze
carefully key element of Timmons model is the entrepreneur. If the entrepreneur has the
precisematerial, he or she will purposefullyquest for prospects, and after finding
appropriate opportunity, form it to becomea marketable element, or a high-potential
venture, according to Timmons (Timmons, Zacharakis, & Spinelli, 2004). The
entrepreneur then collects the means that are essential to begin an enterprise to benefit
fromthe opportunity. According to the Timmons model the entrepreneur and the supplier
of funds will be compensated with returns, and that together are responsible for the
risks and struggle connected with beginning, funding, and constructing the enterprise.
The entrepreneurs are typically bearer of higher return commiserating the risk of the
business.In asupremestate, all this is measured in a business plan beforehand the
business is operative (Audretsch & Acs).
3
Chapter 2
Literature Review
2.1 Entrepreneurial Process
Entrepreneurship is the method ofreasoning, thinking, and performing that is based
upon opportunities, complete in method and dealt with balanced leadership(Timmons,
Zacharakis, & Spinelli, 2004). Entrepreneurship effects in the formation, improvement,
comprehension and regeneration of value, not just from proprietors, but from all the
stakeholders. At the core of the procedure is the formation and recognition of
prospects, trailed by the motivation and creativity to grasp the opportunities. It
necessitates a disposition to take both financial and personal risk which has to be in a
calculated manner in order to continuallymove the odds of success, to mitigate the risk
with the impendingrecompense. Normally, entrepreneurs inventimaginativeplans to
organize their restricted resources(Libial, 2003).
In spite of the variation ofentrepreneurs, businesses, technologies andgeographies
Timmons recognizevital themes or driving forces that govern this vibrant entrepreneurial
procedure:
Entrepreneurship is driven by opportunity
Driven by a lead entrepreneur and his team
A creative process
It is stingy on the resources
Entrepreneurship depends upon the balance of this elements
The process is incorporated and all-inclusive
These are manageableconstituents of the entrepreneurial process that can be
measured and modified.Initiators and financiers emphasize on these forces during
vigilant analysis of the risk and define what efforts can be made to increaseendeavors
probability of success.
2.2 Application of the Timmons Model
The Timmons framework of Entrepreneurship reflects upon opportunities, teams, and
resources as the most crucial aspects which are available to any entrepreneur that
4
grasps the success of the business and also resides upon the skill of the entrepreneur
to balance these crucial aspects.
2.3 ODDS OF SUCCESS
The Timmons framework of entrepreneurshipsources itself on the entrepreneur. The
entrepreneur examines for an opportunity, and on finding it, shapes the opportunity into
a potential venture by forming up a working team and congregating the essential
resources to commence the enterprise based on the opportunity. The entrepreneur
takes several risks. Firstly he or she is sacrificing his or her career. They are taking their
personal cash towards the business which is also at the risk. Alongside the investment
of time and effort is also very much important. The Timmons model roots itself on the
principle that the entrepreneur receives rewards in accordance of the risk and effort they
make for a successful venture(Timmons, Zacharakis, & Spinelli, 2004).
And thats how the Timmons Model of Entrepreneurship works in appraisal of the
triumph of any business.
Figure 1: Timmons Model
2.4 Three Critical factors of Entrepreneurship
In the Timmons model there are three crucial factors which the model has mentioned as
the most important interrelated factors for any successful enterprise. Those are the
5
opportunity factor, the team factor and the resources factor. Brief discussion of this
factor and its application is given below
2.3.1 The Opportunity Factor
Timmons model of entrepreneurship considers that entrepreneurship is driven by
opportunity. And the opportunity is shaped by the market interaction. Any good idea
may not be a profitable business opportunity and the primary market responseregulates
the prospects of the idea. Any idea befits feasibility only when it is fastened in products
or services that generate or enhance value to customers, along with that remains
durable,attractive and timely(Timmons, Zacharakis, & Spinelli, 2004).
Figure 2: The opportunity factor
2.3.2 The Team Factor
After a successful identification of an opportunity, the entrepreneur form team to start a
business by selecting required people and gathering the necessary resources. The
scope and nature of the opportunity regulates the size and profile of the team.
Timmons model statessuperiorsignificance on the team and reflects a good team as
vital for success of any venture. A bad team can waste a profound idea. Among all
resources, only a worthy team can reveal a higher prospec with any opportunity and
achieve the relevant growth(Timmons, Zacharakis, & Spinelli, 2004).
There are two major roles of the team along with other critical factors are:
Eliminating the obscurity and insecurity of the opportunity through creative
processes
Leading to manage the existing resources in the most operationalmethod by
interrelating with exogenous forces and other uncontrollable forces
A Belief that
Achievement is
Possible
Recognizinga
desiredfuture
stateinvolving growthor
change
OPPURTUNITY
6
2.3.3 The Resources Factor
The Timmons model changes the prevalentidea of gathering extensive resources for
any startup. Rather this model decreases the risk of initiating a venture and inspires
bootstrapping or beginning with minimal resources as a way to
achieveeconomicbenefits.
The advantages of bootstrapping includes following:
Market costs are driven down
Implanting controland leanness into the venture
Boosting creative properties to attain more usingrestricted amount of capital and
other resources
Some of the applied methods of such bootstrapping include instead of buying company
might go for leasing equipment, working on free available space rather than renting.
Like the development of the team, thetype and size of opportunity regulate the amount
and extent of possessions required. While better resources are scarce, ventures with
high prospective opportunities and a good executive team will have no difficultydrawing
money and other resources.
The entrepreneurs work is not to maximize and own rather they work to minimize and
control. The character of the entrepreneur in dealing with the resources
containconstructing a good resource base to draw from when necessary and drawing
up an effective business plan using a fit and balance method that balances the
available resource with the opportunity and the prospective of the venture(Christensen
& Richardson, 2003).
2.4 Critical Analysis of the Timmons model
After analyzing the Timmons model we can have an in depth insight about the
entrepreneurial process. It is self-contained and comprehensive. The three critical
factors can be designed in sequence. So we find that any entrepreneur can go for
building a successful business following the Timmons model of entrepreneurship. Here
we can define the steps using the Timmons model. Firstly the entrepreneur is the most
important factor of any business. He or she looks for opportunity. The entrepreneur
analyzes opportunity its prospects and relevant risks. After that he or she plans for the
venture. Collects requires resources. Finds our financer and prepare the business
model. And in the last step he takes action towards the completion of the venture. The
entrepreneur is responsible for the whole process. The efficiency of the entrepreneur
can take the venture to be most successful but inefficiency can make it a loss project
too. Timmons model has also emphasized on the team of entrepreneurs as the team is
also very much important in the entrepreneurial process.
7
Figure 3: Application of Timmons model
2.4.1.Factors for business enterprise
Several factors are very much important for any business enterprise. Such are Human
resource, financial requirements, technological requirements and supply chain
management. In the Timmons model human resource is the mostly important part for
any business to form. He mentioned that the entrepreneur and his teams efficiency
determine the success of any business. For the financial purpose Timmons model
dictate that minimal required capital to manage the procedure and bootstrapping for the
processes. Technology definitely gives any process an edge. Another most important
factor which is missing in the Timmons model is the legal requirements. This comes
with the efficiency and effectiveness of the entrepreneur team. For proper maintenance
and for utilizing the resources the supply chain should be maintained effectively.
2.4.2 Analysis of Opportunity
After finding an opportunity the entrepreneur must analyze the opportunity for its
economic and business prospect. VRIO model can be very helpful for this purpose. In
the VRIO model based on the Value, Rarity, Imitating possibility and organization is
analyzed about the business and that provide some insight about the business.
Following flow chart provide a good description about VRIO analysis.
8
Figure 4: VRIO Analysis
2.4.3 Marketing of the venture
For any business marketing is very much important. For any successful marketing and
brand creation Kotler has mentioned the 3i model. In which the 3i has specific
requirement. Such are:
Brand Identity: this measures how the customer is aware of the brand and the
products or services.
Brand Integrity: This measures the wholeness and the value any brand creates in the
consumer life.
Brand Image: This measures how the customers feel about the brand.
These three factors are very much important for successful creation of any brand. So
after forming the venture the entrepreneur and his team should consider about these
Brand element.
9
Chapter 3
Conclusion
Most of the entrepreneurstry to gatherallmeansrequired to start a business before
beginninga new venture. The Timmons framework of entrepreneurship rebates this
concept and embraces three factors as vital: an opportunity driven by market,
obtainability of a qualifiedgroup and sufficientpossessions. These crucial elements of
entrepreneurship persistintertwined, with any alteration of one elementdevising an
influence on the other elements(Timmons, Zacharakis, & Spinelli, 2004).The fact is that
prospect, group, and possessionsrarely match. Timmons frameworkdeliberates that the
key responsibility of the entrepreneur to create a match of the three crucialaspects of
entrepreneurship at the correct phase. Accomplishment of the commercial venture
depends on the aptitude of the entrepreneur to confirmequilibrium by relatingleadership
and creativity, and by preservingoperational communications.Timmons frameworkroots
itself on the entrepreneur. The entrepreneur quests for prospects, and upon
finding,forms the prospect into a potential venture by forming a team and collecting the
necessary resources to commence a business that benefit fromthe opportunity. In the
procedure of beginning the business, the entrepreneur threats his or her occupation,
personal cash flow and net worth. The Timmons model bases itself on the principle that
the entrepreneur receivesrecompenses in commensuration with the risk and struggle
connected in initiating and financing the Enterprise.
10
Bibliography
Audretsch, D., & Acs, Z. (n.d.). Handbook of entrepreneurship research. In Springer Science-Business
Media. Newyork.
Christensen, P., & Richardson, T. (2003). Defining Entrepreneurship. Journal of Small Business
Management.
Libial, F. (2003). From entrepreneurship to entreprenology. Newyork.
Timmons, J. A., Zacharakis, A., & Spinelli, S. (2004). Business Plans That Work: A Guide For Small
Business. McGraw Hill.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 101 Shortcut MathsDocument188 pages101 Shortcut Mathsvhassji100% (3)
- Risk ChartDocument4 pagesRisk ChartkalisuryNo ratings yet
- Top 101 High Frequency GRE WordsDocument21 pagesTop 101 High Frequency GRE WordskalisuryNo ratings yet
- Slides 2Document18 pagesSlides 2kalisuryNo ratings yet
- GRE MathDocument11 pagesGRE MathkalisuryNo ratings yet
- PRINCE2™-: Communication Management StrategyDocument6 pagesPRINCE2™-: Communication Management StrategykalisuryNo ratings yet
- RPDocument24 pagesRPkalisuryNo ratings yet
- New Barrons 333 HF WDocument13 pagesNew Barrons 333 HF WashokatmellonNo ratings yet
- Maths ShortcutsDocument34 pagesMaths ShortcutsKalyan Nanduri91% (11)
- ZofDocument18 pagesZofkalisuryNo ratings yet
- JBsDocument43 pagesJBskalisuryNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument61 pagesReportkalisuryNo ratings yet
- Barrons HFW 333Document8 pagesBarrons HFW 333kalisuryNo ratings yet
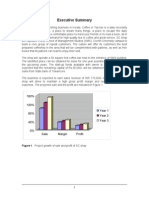
- Executive Summary: Figure 1. Project Growth of Sale and Profit of SC ShopDocument6 pagesExecutive Summary: Figure 1. Project Growth of Sale and Profit of SC ShopkalisuryNo ratings yet
- TescoDocument14 pagesTescokalisuryNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument28 pagesBusiness PlankalisuryNo ratings yet
- Business PlanDocument28 pagesBusiness PlankalisuryNo ratings yet
- TescoDocument14 pagesTescokalisuryNo ratings yet
- Assignment JCPDocument14 pagesAssignment JCPkalisuryNo ratings yet
- "Automobile Maintenance Workstation (Amw) " Business Development PlanDocument54 pages"Automobile Maintenance Workstation (Amw) " Business Development PlankalisuryNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Leaders Who Engage Cognitive Ambidexterity Must Know How To ConnectDocument6 pagesEntrepreneurial Leaders Who Engage Cognitive Ambidexterity Must Know How To ConnectkalisuryNo ratings yet
- McCain FoodDocument25 pagesMcCain FoodkalisuryNo ratings yet
- Aldi Final2Document19 pagesAldi Final2kalisury100% (1)
- RetailDocument12 pagesRetailkalisuryNo ratings yet
- Rob Stokes-eMarketing The Essential Guide To Online Marketing-Quirk Emarketing (2008)Document189 pagesRob Stokes-eMarketing The Essential Guide To Online Marketing-Quirk Emarketing (2008)iarinadem2011100% (1)
- Elementary AlgebraDocument904 pagesElementary Algebrakalisury100% (1)
- Wahhabism and Its Refutation by The Ahl As SunnatDocument29 pagesWahhabism and Its Refutation by The Ahl As SunnatkalisuryNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument60 pagesHuman Resource Managementkalisury100% (1)
- Arab Culture Awareness - 10 FactsDocument66 pagesArab Culture Awareness - 10 FactsNaboliNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Arbitration in KenyaDocument10 pagesArbitration in KenyaJames Tugee100% (2)
- Crisis ManagementDocument9 pagesCrisis ManagementOro PlaylistNo ratings yet
- The MountDocument6 pagesThe Mountcrazykate000No ratings yet
- Hart Fuller DebateDocument10 pagesHart Fuller DebatePulkit GeraNo ratings yet
- Alexis Karpouzos - The Mathematics of ImaginationDocument4 pagesAlexis Karpouzos - The Mathematics of ImaginationAlexis karpouzos100% (2)
- DECS Values FrameworkDocument14 pagesDECS Values FrameworkKevin Mirasol100% (1)
- Haves Without Have-Nots - Mortimer J. AdlerDocument377 pagesHaves Without Have-Nots - Mortimer J. AdlerA100% (1)
- Organizational Development InterventionsDocument57 pagesOrganizational Development InterventionsAmr YousefNo ratings yet
- MAE552 Introduction To Viscous FlowsDocument5 pagesMAE552 Introduction To Viscous Flowsakiscribd1No ratings yet
- The Definition of Public SpeakingDocument12 pagesThe Definition of Public SpeakingAngeline Limbaga TrayfalgarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Implications of Adolescent IntrospectionDocument8 pagesClinical Implications of Adolescent IntrospectionJoshua RyanNo ratings yet
- OPS Solutions ManualDocument85 pagesOPS Solutions ManualAndreza AlvesNo ratings yet
- If Poem Worksheet PDFDocument12 pagesIf Poem Worksheet PDFRaniaGF100% (2)
- MetaphysicsDocument148 pagesMetaphysicsMonizaBorges100% (3)
- Legacy of Ansel Adams and Minor WhiteDocument7 pagesLegacy of Ansel Adams and Minor WhiteMaria DiamantopoulouNo ratings yet
- Compensation: Third Canadian Edition Milkovich, Newman, ColeDocument28 pagesCompensation: Third Canadian Edition Milkovich, Newman, ColeNeha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- FR Seraphim Rose Pastoral Letters On Sexual SinDocument3 pagesFR Seraphim Rose Pastoral Letters On Sexual SinAndrew WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Chap8 PDFDocument16 pagesChap8 PDFscribddownload1232No ratings yet
- Org Culture by Anand Mohan & Abhishekh K.Document38 pagesOrg Culture by Anand Mohan & Abhishekh K.chintu2789No ratings yet
- The Right Way To Manage ExpatsDocument2 pagesThe Right Way To Manage ExpatsShayne RebelloNo ratings yet
- Elliot Self HandicappingDocument28 pagesElliot Self HandicappingNatalia NikolovaNo ratings yet
- SQ4R StrategyDocument2 pagesSQ4R StrategyRelu ChiruNo ratings yet
- Geography World Landmark Game Presentation-3Document12 pagesGeography World Landmark Game Presentation-34w6hsqd4fkNo ratings yet
- Boscombe Valley MisteryDocument20 pagesBoscombe Valley Misteryronie1988No ratings yet
- Electrical Theory - Learning OutcomesDocument6 pagesElectrical Theory - Learning OutcomesonaaaaangNo ratings yet
- Jalal Al-Din Rumi, Maulana, 1207-1273 - Shams-I Tabrizi, D. 1246 - Nicholson, Reynold Alleyne, 1868-1945, Ed - Divani Shamsi TabrizDocument132 pagesJalal Al-Din Rumi, Maulana, 1207-1273 - Shams-I Tabrizi, D. 1246 - Nicholson, Reynold Alleyne, 1868-1945, Ed - Divani Shamsi Tabrizalex_neumann_15No ratings yet
- Grade 1 Syllabus 2019-2020Document15 pagesGrade 1 Syllabus 2019-2020SiiJuliusKhoNo ratings yet
- My Husband Wants To Spend My Inheritance MoneyDocument2 pagesMy Husband Wants To Spend My Inheritance MoneyDANIELANo ratings yet
- Math LogicDocument44 pagesMath LogicJester Guballa de Leon100% (1)
- Waiting For GodotDocument9 pagesWaiting For GodotKNo ratings yet