Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz 1 K53
Uploaded by
HàMềm0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
292 views4 pagesManagers study the number of days per month over the last year that employees called in sick. Determining the averages they can expect next year is an example of what type of statistics.
Original Description:
Original Title
Quiz_1_K53
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentManagers study the number of days per month over the last year that employees called in sick. Determining the averages they can expect next year is an example of what type of statistics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
292 views4 pagesQuiz 1 K53
Uploaded by
HàMềmManagers study the number of days per month over the last year that employees called in sick. Determining the averages they can expect next year is an example of what type of statistics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Statistics for Business
(Time allowed: 30 minutes)
Please circle your selection for the questions below:
1. Managers study the number of days per month over the last year that employees in the payroll department
called in sick to determine the averages they can expect next year. Collecting the data and determining the
averages last year is an example of what type of statistics? Determining the averages they can expect next
year is an example of what type of statistics?
A. They are both examples of inferential statistics because averages are inferred in both instances
B. Inferential statistics; descriptive statistics.
C. They are both examples of descriptive statistics because they deal with analyzing data.
D. Descriptive statistics; inferential statistics.
2. The grades that a random sampling of students in the psychology degree program received over the last
decade of "Abnormal Psychology" classes are an example of what statistical concept?
A. The grades are an example of a parameter.
B. The grades are an example of a sample.
C. The grades are an example of a population.
D. The grades are an example of a statistic.
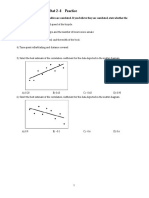
3. The first quartile of a set of data is 45; the second quartile is 65 and the third quartile is 85.Which of the
following best describes the shape of this distribution?
A. Skewed left B. Skewed right C. Symmetric D. None of the above
4. Which of the following statements is false?
A. If we find the deviation of each value from the median, the sum of these deviations is always zero.
B. The interquartile range is the difference between the first and third quartile
C. The median and the second quartile is the same.
D. The standard deviation is the positive square root of the variance
5. The average score for a class of 30 students was 70. The twenty male students in the class averaged 65.
Find the average score for the female students
A 95 B 80 C Not enough information given D 85 E 90
6. Calculate the median value of the following eight numbers: 14, 48, 34, 50, 10, 24, 11, 32, 20.
Re-arrange 10,11,14,20,24,32,34,48,50
A. 20 B. 22 C. 24. D. 24.4
7. Which of the following is an example of inferential statistics?
A. The average price of gasoline in a large, urban city was found during the week of December.
B. A circle graph depicts the type of cancer treated by a certain hospital.
C. On this graph, 2% of patients were treated for kidney cancer and 19% were treated for breast cancer.
D. A bar graph depicts the grade distribution of an undergraduate statistics class.
E. A sample of 36 oranges was selected from the population of all oranges from a certain orange grove in
Florida. The mean weight of this sample of 36 oranges was found and used to estimate the mean weight of
oranges from this particular grove.
8. Referring to Table 2-1, suppose a cumulative relative frequency distribution for the number of payoff
demand notices received by the escrow company is constructed with a first class of 10 but less than 15. The
cumulative percentage frequency of the 20, but less than 25 class would be
A 24% B. 44% C. 64% D. 84% E. 100%
9. Which statement is false? Explain.
A. If = 52 and = 15, then X = 81 would be an outlier.
B. If the data are from a normal population, about 68% of the X values will be within .
C. If = 640 and = 128 then the coefficient of variation is 20 percent.
10. So far this year, stock A has had a mean price of $6.58 per share with a standard deviation of $1.88,
while stock B has had a mean price of $10.57 per share with a standard deviation of $3.02. Which stock is
more volatile?
A. Stock A B. Stock B They are the same.
11. The sum of the relative frequencies for all classes in a histogram always equals
A. the number of classes.
B. the class width.
C. the total of all the frequencies.
D. one.
12. Which of the following statements about shapes of histograms is true?
A. A histogram is said to be symmetric if, when we draw a vertical line down the center of the histogram,
the two sides are identical in shape and size.
B. A negatively skewed histogram is one with a long tail extending to the left.
C. A positively skewed histogram is one with a long tail extending to the right.
D. All of these choices are true.
13. What values are displayed on a cumulative relative frequency distribution?
A. The number of observations that fall into each class interval.
B. The proportion of observations that fall into each class interval.
C. The number of observations that fall below each class interval.
D. The proportion of observations that fall below each class interval.
14. Which of the following describes a positive linear relationship between X and Y?
A. As the X values increase, the Y values increase in a linear manner.
B. As the X values decrease, the Y values decrease in a linear manner.
C. The X and Y values move uphill together in a linear manner.
D. All of these choices are true.
15. When extreme values are present in a set of data, which of the following descriptive summary measures
are most appropriate?
A. Coefficient of variation and range
B. Mean and standard deviation
C. Interquartile range and median
D. Variance and interquartile range
16. In a perfectly symmetric distribution, which of the following statements is false?
A. The distance from Q
1
to Q
2
equals to the distance from Q
2
to Q
3
B. The distance from the smallest observation to Q
1
is the same as the distance from Q
3
to the largest
observation
C. The distance from the smallest observation to Q
2
is the same as the distance from Q
2
to the largest
observation
D. The distance from Q
1
to Q
3
is half of the distance from the smallest to the largest observation
17. Assuming a linear relationship between X and Y, if the coefficient of correlation (r) equals 0.80, this
means that:
A. there is very weak correlation.
B. the slope b
1
is = 0.80.
C. the value of X is always greater than the value of Y.
D. None of these choices are true.
18. If two events are collectively exhaustive, what is the probability that one or the other occurs?
A. 0.00 B. 0.50 C. 1.00 D. Cannot be determined from the
information given
19. If A and B are mutually exclusive events, with P(A) = 0.20 and P(B) = 0.30, then the probability that
both events will occur simultaneously is:
A. 0.50
B. 0.06
C. 0
D. None of these choices.
20. Suppose a basketball player is an excellent free throw (shots awarded when a player is fouled) shooter
and makes 80% of his free throws (or he has an 80% chance of making a single free throw). Assume that
free throw shots are independent of one another. Suppose this player gets to shoot four free throws. Find the
probability that he makes four consecutive free throws. 0.8^4
A. 0.5904 B. 0.9984 C. 0.0016 D. 0.4096
21. If events A and B are independent and P(A) = .6 and P(B) = .4, which of the following is correct? Pa
+Pb - Pab
A. P(A and B) = 0; B. P(A or B) = .24; C. P(A or B) = .76; D. P(A and B) = 1.00
22. Independent events A and B would be consistent with which of the following statements:
A. P (A) = .5, P (B) = .4, P (A B) = .3 B. P (A) = .4, P (B) = .3, P (A B) = .5
C. P (A) = .3, P (B) = .5, P (A B) = .4 D. P (A) = .4, P (B) = .5, P (A B) = .2
23. Investing is a game of chance. Suppose there is a 40% chance that a risky stock investment will end up
in a total loss of your investment. Because the rewards are so high, you decide to invest in four independent
risky stocks. Find the probability that at least one of your investments becomes a total loss.
probability of total loss of one risky investment = 0.4, you take 4 risky investments, each with a
probability of total loss of 0.4 , since the probability of total loss of each investment is 0.4, then the
probability that the investment will not be a total loss is 1 0.4 = .6, the probability that none of the 4
investments will be a total loss is .6^4 = 0.1296., the probability that at least one of these investments
will be a total loss is 1 - .6^4. , that probability would be 0.8704
A. 0.8704 B. 0.9744 C. 0.0256 D. 0.40
24. The probability that house sales will increase in the next 6 months is estimated to be 0.25. The
probability that the interest rates on housing loans will go up is estimated to be 0.7. The probability that
house sales and interest rates will go up during the next 6 months is estimated to be 0.20.
The probability of an increase in house sales and not an increase in interest rates is
A 0.2 B. 0.05 C. 0.25 D. 0.5
25. If the events A and B are independent with P(A) = 0.30 and P(B) = 0.40, then the probability that both
events will occur simultaneously is:
A. 0 B. 0.12 C. 0.70 D. Not enough information to tell.
You might also like
- Sex and Sexuality - BookDocument981 pagesSex and Sexuality - BookJohn Chalukulu100% (1)
- TB Chapter 18 AnswersDocument44 pagesTB Chapter 18 AnswersMahmoudElbehairyNo ratings yet
- Data Types and DistributionsDocument1 pageData Types and Distributionssk112988No ratings yet
- Business Statistics Exam Prep SolutionsDocument3 pagesBusiness Statistics Exam Prep SolutionsSalamaAlAmryNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis testing two populations quiz answersDocument29 pagesHypothesis testing two populations quiz answersvuduyduc100% (1)
- Holtrop Mennen An Approximate Power Prediction Method PDFDocument6 pagesHoltrop Mennen An Approximate Power Prediction Method PDFSahil JawaNo ratings yet
- Regression Analysis ProjectDocument4 pagesRegression Analysis ProjectAsif. MahamudNo ratings yet
- Comparing Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion for Statistical DataDocument12 pagesComparing Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion for Statistical Datasinh77No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions Business StatisticsDocument60 pagesMultiple Choice Questions Business StatisticsChinmay Sirasiya (che3kuu)No ratings yet
- Chapter 7:sampling and Sampling DistributionsDocument50 pagesChapter 7:sampling and Sampling DistributionsThe Tun 91No ratings yet
- Nat-Statistics and ProbabilityDocument7 pagesNat-Statistics and ProbabilityArnel LomocsoNo ratings yet
- Midtermtest 158-1Document5 pagesMidtermtest 158-1minhchauNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam IIIDocument8 pagesPractice Exam IIIAdam Hylton100% (2)
- Sample Mid-Term Exam (The Sample Contains Only 20 Questions)Document5 pagesSample Mid-Term Exam (The Sample Contains Only 20 Questions)Phan Huỳnh Châu TrânNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and Statistics (IPS) : EndtermDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Probability and Statistics (IPS) : Endterm208vaibhav bajajNo ratings yet
- Sexual Harrasment ThesisDocument262 pagesSexual Harrasment Thesisanonymous unknow100% (1)
- III Sem. BA Economics - Core Course - Quantitative Methods For Economic Analysis - 1Document29 pagesIII Sem. BA Economics - Core Course - Quantitative Methods For Economic Analysis - 1Agam Reddy M50% (2)
- CH 17Document4 pagesCH 17HàMềm0% (1)
- Multiple Regression ExamDocument16 pagesMultiple Regression ExamKNo ratings yet
- NSE BA Sample Paper With SolutionDocument18 pagesNSE BA Sample Paper With SolutionSanjay Singh100% (1)
- MCQs Basic Statistics 1Document6 pagesMCQs Basic Statistics 1secret student100% (1)
- Statistics and Probability 4th QEDocument5 pagesStatistics and Probability 4th QEDaniel BerdidaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 - Practice PDFDocument8 pagesQuiz 4 - Practice PDFNataliAmiranashvili100% (2)
- Descriptive Statistics QuestionsDocument33 pagesDescriptive Statistics QuestionsPARUL SINGH MBA 2019-21 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questionsdrugdrug0% (1)
- MGMT E-5070 2nd Examination SolutionDocument8 pagesMGMT E-5070 2nd Examination Solution13sandip100% (1)
- NAT REVIEW in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument52 pagesNAT REVIEW in Statistics and ProbabilityMarielleNo ratings yet
- Road Safety AwarenessDocument9 pagesRoad Safety AwarenessasadNo ratings yet
- Basics of Research and Statistical ToolsDocument103 pagesBasics of Research and Statistical ToolsFilJearenNo ratings yet
- Article Review On TQMDocument21 pagesArticle Review On TQMKaemon BistaNo ratings yet
- NAT REVIEWER Statistics ProbabilityDocument8 pagesNAT REVIEWER Statistics ProbabilityMTCDP FILESNo ratings yet
- Stat&Prob Questionnaire Midterm SecondSemesterDocument9 pagesStat&Prob Questionnaire Midterm SecondSemesterElaiza Mae SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers Chapter - 7 Set 1Document6 pagesQuestions & Answers Chapter - 7 Set 1FaridOrahaNo ratings yet
- Par Inc.Document6 pagesPar Inc.HàMềm71% (7)
- Research Proposal - Problems EncounteredDocument25 pagesResearch Proposal - Problems EncounteredJohn Deyritz Balino50% (6)
- B.SC - Mathematics MathematicalstatisticsII 18UMA2A2Document27 pagesB.SC - Mathematics MathematicalstatisticsII 18UMA2A2aepatil74No ratings yet
- PPSC MCQS Statistics DataDocument9 pagesPPSC MCQS Statistics DataMaryam AliNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Probability: Chapter 4Document24 pagesConcepts of Probability: Chapter 4Zeaweed . OceanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Multiple Choice: Chapter 2 Review of ProbabilityDocument35 pages2.1 Multiple Choice: Chapter 2 Review of Probabilitydaddy's cockNo ratings yet
- Mba Statistics First Long QuizDocument7 pagesMba Statistics First Long QuizEllaine Jane FajardoNo ratings yet
- Stat Paper For 2 YearDocument3 pagesStat Paper For 2 Yearfazalulbasit9796100% (1)
- Linear RegressionDocument4 pagesLinear RegressionDaniel FongNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Testbank HandoutDocument14 pagesCh5 Testbank Handoutjoebloggs1888No ratings yet
- MCQ Week07ansDocument6 pagesMCQ Week07ansSiu SiuNo ratings yet
- English and Stastics SAT 1Document5 pagesEnglish and Stastics SAT 1Kassahun TerechaNo ratings yet
- TIME SERIES ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES FOR DETERMINING SEASONAL VARIATIONDocument1 pageTIME SERIES ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES FOR DETERMINING SEASONAL VARIATIONKumuthaa Ilangovan100% (1)
- Kode B: Final Exam Second Semester 2019/2020Document12 pagesKode B: Final Exam Second Semester 2019/2020reviandiramadhan100% (1)
- Mcqs Prob 2Document6 pagesMcqs Prob 2rashid MehrajNo ratings yet
- Regression Slope Same Intercept Zero Correlation PerpendicularDocument2 pagesRegression Slope Same Intercept Zero Correlation PerpendicularDr. Shailendra Kumar SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Index NumbersDocument50 pagesIntroduction to Index NumbersAngelica AllanicNo ratings yet
- Doane - Stats - Chap 007 - Test AnswersDocument83 pagesDoane - Stats - Chap 007 - Test AnswersBG Monty 1100% (2)
- COMPLETELY RANDOM DESIGN (CRDDocument16 pagesCOMPLETELY RANDOM DESIGN (CRDEDUARD VALDIVIA TORRESNo ratings yet
- Estimation and Confidence Intervals ExplainedDocument49 pagesEstimation and Confidence Intervals Explainedasvanth100% (1)
- CH 10Document18 pagesCH 10Erjohn PapaNo ratings yet
- Tyba Sem 5 - Paper - V - Mcqs Set 2Document14 pagesTyba Sem 5 - Paper - V - Mcqs Set 2Rohan bhatkalNo ratings yet
- DOANE - Stats Answer Key Chap 008Document73 pagesDOANE - Stats Answer Key Chap 008BG Monty 1100% (1)
- Cooperative Society ManifestoDocument2 pagesCooperative Society ManifestobeulahNo ratings yet
- CH 01 TestDocument22 pagesCH 01 TestNeeti GurunathNo ratings yet
- Statistics - DispersionDocument7 pagesStatistics - DispersionAmritha VNo ratings yet
- MB0024 Mba-I Statistics For Management Sample PaperDocument16 pagesMB0024 Mba-I Statistics For Management Sample PaperKalpesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Statistics Final ReviewDocument21 pagesStatistics Final ReviewtkdforceNo ratings yet
- Probablity and StatisticsDocument11 pagesProbablity and StatisticsJeevitha BandiNo ratings yet
- BA 578 Live Fin Set2Document17 pagesBA 578 Live Fin Set2Sumana Salauddin100% (1)
- Descriptive Statistics Multiple ChoiceDocument14 pagesDescriptive Statistics Multiple ChoicePurnima Sidhant BabbarNo ratings yet
- Exam # 1 STAT 110Document9 pagesExam # 1 STAT 110Aneera MohamdNo ratings yet
- Copy-of-StatProb Questionnaire Midterm SecondSemesterDocument8 pagesCopy-of-StatProb Questionnaire Midterm SecondSemesterPaul DgreatNo ratings yet
- R9 Common Probability DistributionsDocument33 pagesR9 Common Probability Distributionsszssg888No ratings yet
- National Achievement Test Reviewer in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument5 pagesNational Achievement Test Reviewer in Statistics and ProbabilityJacinthe Angelou D. PeñalosaNo ratings yet
- C3 Evaluating Companys External EnvironmentDocument64 pagesC3 Evaluating Companys External EnvironmentSyahid AshariNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document1 pageBook 1HàMềmNo ratings yet
- IPPTChap 002Document58 pagesIPPTChap 002HàMềmNo ratings yet
- IELTS Reading Practice Test 01Document11 pagesIELTS Reading Practice Test 01HàMềmNo ratings yet
- 19e CaseAsssignmentQuestionsTNCase 17 PDFDocument1 page19e CaseAsssignmentQuestionsTNCase 17 PDFHàMềmNo ratings yet
- 51 de Speaking Moi Va CuDocument13 pages51 de Speaking Moi Va CuHàMềmNo ratings yet
- Draft Circular Stipulating Minimum Safety Limits and RatiosDocument5 pagesDraft Circular Stipulating Minimum Safety Limits and RatiosHàMềmNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document4 pagesCH 18HàMềmNo ratings yet
- Business Strategy and PolicyDocument47 pagesBusiness Strategy and PolicyHàMềmNo ratings yet
- DeAnhD DHDocument7 pagesDeAnhD DHlyly1995No ratings yet
- Accounting standards and principles in SingaporeDocument5 pagesAccounting standards and principles in SingaporeHàMềmNo ratings yet
- Applications A+BDocument1 pageApplications A+BHàMềmNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document9 pagesCase Study 2HàMềm100% (2)
- Specialty Toys Case Study Recommends 18,784 Unit OrderDocument10 pagesSpecialty Toys Case Study Recommends 18,784 Unit OrderHàMềmNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument12 pagesExecutive SummaryHàMềmNo ratings yet
- A2.Abcd ThanhHaDocument9 pagesA2.Abcd ThanhHaHàMềmNo ratings yet
- What ZDocument5 pagesWhat ZHàMềmNo ratings yet
- 2009-07-16 030945 Ex ParDocument2 pages2009-07-16 030945 Ex ParHàMềmNo ratings yet
- Statistics Group3Document36 pagesStatistics Group3HàMềmNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Answer: DDocument41 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Answer: Dlichelles82% (11)
- ReferenceDocument5 pagesReferenceHàMềmNo ratings yet
- Perception Towards Online Advertising & Its Influences Consumer BehaviorDocument12 pagesPerception Towards Online Advertising & Its Influences Consumer BehaviorHàMềmNo ratings yet
- Tin 1Document84 pagesTin 1HàMềmNo ratings yet
- Business Plan ReportDocument19 pagesBusiness Plan ReportHàMềmNo ratings yet
- Chap 001Document52 pagesChap 001HàMềmNo ratings yet
- Perceptions and Influences of Online AdvertisingDocument41 pagesPerceptions and Influences of Online AdvertisingHàMềmNo ratings yet
- 1993Document1 page1993HàMềmNo ratings yet
- SPSSDocument30 pagesSPSShimadri.roy8469No ratings yet
- The Short-Form Version of The Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21) : Construct Validity and Normative Data in A Large Non-Clinical SampleDocument13 pagesThe Short-Form Version of The Depression Anxiety Stress Scales (DASS-21) : Construct Validity and Normative Data in A Large Non-Clinical SampleVina Louis TomlinsonNo ratings yet
- Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Volume 28 Issue 12 1936 (Doi 10.1021/ie50324a027) Sieder, E. N. Tate, G. E. - Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop of Liquids in TubesDocument7 pagesIndustrial & Engineering Chemistry Volume 28 Issue 12 1936 (Doi 10.1021/ie50324a027) Sieder, E. N. Tate, G. E. - Heat Transfer and Pressure Drop of Liquids in Tubesrahulsaini855No ratings yet
- Achievement Motivation As Related To Parental Involvement of Secondary School StudentsDocument16 pagesAchievement Motivation As Related To Parental Involvement of Secondary School StudentsAnonymous CwJeBCAXpNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Factors Influencing Consumers Online Shopping DecisionDocument12 pagesE-Commerce Factors Influencing Consumers Online Shopping DecisionCrazy MechonsNo ratings yet
- 2014 Mock Exam - AM - AnswersDocument25 pages2014 Mock Exam - AM - Answers12jdNo ratings yet
- Linearly Independent, Orthogonal, and Uncorrelated VariablesDocument2 pagesLinearly Independent, Orthogonal, and Uncorrelated VariablesBrandon McguireNo ratings yet
- Anthropometric Data of Children For Non-SpecialistDocument11 pagesAnthropometric Data of Children For Non-Specialistsiirin_No ratings yet
- No - Evaluación de La Escala de Fluctuación de Parámetros GeotécnicosDocument7 pagesNo - Evaluación de La Escala de Fluctuación de Parámetros GeotécnicosCimentaciones Geotecnia RiveraNo ratings yet
- PYP Solutions V2019Document37 pagesPYP Solutions V2019Qy LeeNo ratings yet
- An Empirical Examination of The Amortized Spread: John M.R. Chalmers !, Gregory B. Kadlec"Document30 pagesAn Empirical Examination of The Amortized Spread: John M.R. Chalmers !, Gregory B. Kadlec"tsas9508No ratings yet
- Data Mining Is Defined As The Procedure of Extracting Information From Huge Sets of DataDocument6 pagesData Mining Is Defined As The Procedure of Extracting Information From Huge Sets of DataOdem Dinesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Manual Crystal BallDocument414 pagesManual Crystal Ballcarloshilario100% (1)
- Workaholism vs. Work Engagement: The Two Different Predictors of Future Well-Being and PerformanceDocument7 pagesWorkaholism vs. Work Engagement: The Two Different Predictors of Future Well-Being and PerformanceNely Noer SofwatiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Tutorial Problems UpdatedDocument2 pagesUnit 4 Tutorial Problems UpdatedDeepak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Zhao Et Al., 2014Document13 pagesZhao Et Al., 2014Daniela OspinoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Job Stress by Shahid HafeezDocument9 pagesImpact of Job Stress by Shahid HafeezShahid HafeezNo ratings yet
- CorrelationDocument17 pagesCorrelationSara GomezNo ratings yet
- Correlation 13 WaysDocument11 pagesCorrelation 13 WaysMuhammad Ali BhattiNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Amongst Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, Demographic and Tripographic1 Attributes: A Case of Star Rated Hotel Guests in EthiopiaDocument15 pagesThe Relationship Amongst Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, Demographic and Tripographic1 Attributes: A Case of Star Rated Hotel Guests in EthiopiaMammta ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Servant Leadership in Hospitality: A Meta-Analytic Review: Journal of Hospitality Marketing & ManagementDocument22 pagesServant Leadership in Hospitality: A Meta-Analytic Review: Journal of Hospitality Marketing & ManagementPhuoc NguyenNo ratings yet
- Stephen Grattan Linghe Zeng Michael C. Shannon Stacy RobertsDocument7 pagesStephen Grattan Linghe Zeng Michael C. Shannon Stacy RobertsAthena NocetoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Report AIA-360 Samples From Dogs and CatsDocument35 pagesEvaluation Report AIA-360 Samples From Dogs and Catsالواثقة باللهNo ratings yet