Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sap MM
Uploaded by
mkumarshahi80%(5)80% found this document useful (5 votes)
1K views54 pagesSAP MM
Original Title
SAP MM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSAP MM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
80%(5)80% found this document useful (5 votes)
1K views54 pagesSap MM
Uploaded by
mkumarshahiSAP MM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 54
1 | P a g e
Tell me about SAP Material Management? and its importance in SAP
R/3?
SAP MM ( Material Management ) is one of the important modules in SAP
ERP software and MM application module supports the procurement and
inventory functions occurring in day-to-day business operations. This MM
module contains many aspects such as purchasing, goods receiving, material
storage, consumption-based planning, and inventory. SAP MM module is fully
integrated with other modules in the SAP R/3 System such as Finance
(FI),Controlling (CO), Sales and Distribution (SD), Quality Management (QM),
Plant Maintenance (PM), Production Planning (PP), and Warehouse
Management(WM).
It supports all phases of materials management materials planning and control,
purchasing, goods receiving, inventory management, and invoice verification.
How SAP MM module is integrated with other SAP modules?
For FI, you know its the core module and all the accounting entries are
generated there, so when GR and IR takes place in MM
FI module is required for accounting entries.
In SD case, when sales order is generated which needs some material which is
not available, so PR cycle is created to procure the material, or when goods
issue takes place, it picks material from MM or when returns takes place,
material is returned to MM etc.
In PP case, when production order is created, all the material is required from
MM and when extra material is required again MM is called or when material is
short, PR is raised for required material through MM.
2 | P a g e
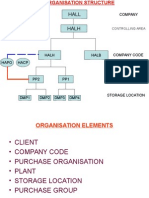
What is a Client?
The structure of an enterprise is represented in the SAP R/3 System by the
following organizational levels:
Client
A grouping or combination of legal, organizational, business and/or
administrative units with a common purpose.
Example: a corporate group.
Company code
This level represents an independent accounting unit within a client. Each
company code has its own balance sheet and its own profit and loss statement.
Example: a subsidiary company, member of a corporate group.
Plant
Operational unit within a company code.
Example: production facility, branch office.
Purchasing organization
An organizational unit responsible for procuring materials or services for one or
more plants and for negotiating general conditions of purchase with vendors.
The purchasing organization assumes legal responsibility for all external
purchase transactions.
Purchasing group
The purchasing organization is further subdivided into purchasing groups (buyer
groups), which are responsible for day-to-day buying activities.
A purchasing group can also act for several purchasing organizations.
How to create a Client in SAP Material Management module?
You can create a client in the MM module either by using the transaction code
SCC4 or by performing the following steps:
o Select SAP Menu > Tools > Administration > Administration > Client
Administration.
o Client Maintenance. The display view Clients: Overview screen appears.
o The information dialog box appears.
3 | P a g e
o The change view Clients: Overview screen appears, where you can create a
new client.
What is SAP?
What is IDES?
IDES means Internet Demonstration and Evaluation System and is used as SAP
internal system mainly for testing and training purposes. The IDES system is run
in Walldorf, the headquarter of SAP. This system has several SAP clients and
contains a sample set of master data for every SAP module of the IDES model
company. The IDES model company represents an organization with
standardized business processes and is ideal for the purposes of demonstration
and explanation of the functionality of the various SAP solutions to potential
customers, SAP students, and prospects.
Difference between SAP R/1, R/2,R/3 ?
SAP R/1
SAP R/1 was the first version and it is one tier architecture in which three layers
Presentation, Application and Database are installed in one system/server
Server one Presentation + Application + Database
SAP R/2
SAP R/2 is the mainframe version of software and it is 2 tier architecture in
which three layers Presentation, Application and Database are installed in two
separate server.
(Server one Presentation, Server two Application + Database
SAP R/3
SAP R/3 is the client/server version of the software and it is 3 tier architecture in
which three layers Presentation, Application and data base are installed in three
server/system
Server one Presentation, Server Two Application, server Three Database
4 | P a g e
What are the different modules in SAP R/3 system?
SAP Module FI (Finance Accounting) :- The following are important sub-
modules ofFinancial accounting
General Ledger(GL)
Accounts Payable(AP)
Accounts Receivable(AR)
Bank and Cash Management
Budgeting and Monitoring
Withholding Tax (TDS)
Asset Accounting(AA)
Funds Management(FM)
Treasury Management(TM)
5 | P a g e
SAP Module CO (Controlling) :- The important sub-modules of controlling are
as follows
Product Costing(CO-PC)
Periodic Allocations
Profitability Analysis(CO-PA)
Cost Center Accounting(CCA)
Profit Center Accounting(PCA)
SAP Module SD (Sales and Distribution) :-
Sales Order Processing and Monitoring
Shipping
Bill / Invoice Generation
Credit Management
Bill of Material
Pricing and Discounts
Statutory Requirements
SAP Module HR
Organizational Management
Personnel Administration
Recruitment Time Management
Management Personnel Cost
Planning Budget
Payroll Benefits Compensation
Management Personnel
Development Training & Event Management
Travel Management
SAP Module PP (Production Planning)
Production Planning
Production Order Processing
6 | P a g e
Demand Management (DM)
Materials Requirements Planning (MRP)
Shop Floor Control
Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP)
Information System
SAP Module MM (Materials Management)
Purchasing
Inventory Management
Inventory Valuation
Vendor Evaluation and Rating
Invoice Verification
Statutory Requirements
SAP Module QM (Quality Management)
Incoming Inspection
Process Inspection
Final/Delivery Inspections
Quality Reports / Certificates
Quality Notifications
SAP Module PM (Plant Maintenance)
Maintenance Planning
Breakdown Maintenance
Preventive Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance
SAP Module PS (Project Systems)
Project Planning
Project Monitoring
Project Costing
Milestone based Billing
7 | P a g e
Handling of WBS Elements
SAP Module Supply Chain Management
Technical Modules Overview
Netweaver
ABAP - Advanced Business Application Programming
IS (Information Systems) Management
XI Exchange Infrastructure
SAP Basis
BIW Business Information Warehousing+
What is mySAP ERP?
mySAP ERP is the comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution
from SAP. It has been designed to meet today`s changing demands on ERP.
What are the Important Components of SAP MM
It can be divided into five major components. They are:
- materials management,
- plant maintenance,
- quality management,
- production planning and control, and a
- project management system
8 | P a g e
module and how they are used in SAP?
Tell me about Organisational Structure of SAP
MM?
Client ->Company Code ->Plant ->Storage Location -
>Purchasing Org/ Purchasing group
Define Company and how to create company?
About Company in SAP:- Company is theorganizational unit for which
individual financial statements can be drawn according to the relevant
commercial law. A company can comprise of one or more company codes.
A Company has local currencies in which its transactions are
recorded. All company codes within a company must use the same
transaction Chart of accounts and the same Fiscal Year. Creation of company in
sap is optional.
Path to Define Company in SAP :-
SAP IMG Path: SPRO > Implementation Guide for R/3 Customizing (IMG) >
Enterprise Structure > Definition > Financial Accounting > Define
Company
Transaction code to Define Company in SAP :- OX15
Steps for creation of Company:
Step 1 :- Enter Transaction Code SPRO in the commend field and press enter on the
Keyboard
Step 2 :- Next Customizing execute project screen select SAP Reference IMG
9 | P a g e
Step 3 :- After Selecting SAP Reference IMG, a new screen IMG Path will be displayed.
SelectDefine company execute icon for creating a company
Next Screen will be displayed after selecting the define company execute icon
Step 4:- Now Select New entries icon and enter the company details
10 | P a g e
The following details are to be entered for creating a new company
1. Enter 6 character alphanumeric code key that represents the group of
company
2. Enter name of your company
3. In the Detailed information update the address Street name, PO Box#,
Postal code, City.
4. Enter Country Code of the company
5. Enter language key
6. Enter local currency for the company (also known as Company code
currency)
7. Click on Save icon or CTRL+S after updating the required information
Thus new Company ADARSH is created in SAP.
Define Company Code and how company code is created?
o About Company Code :- Company Code in SAP is the
smallest organizational unit of Financial Accounting for which you draw
individual financial statements like Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss
11 | P a g e
Account for purpose of external reporting. The Creation of company code
in sap is mandatory
o PATH :- IMG Reference > Enterprise Structure > Definition >
Financial Accounting > Edit, Copy, Delete Company Code
o Transaction code to Define company Code :- OX02
o Steps to Define Company Code: -
o Step 1 :- Enter Transaction Code SPRO in the commend field and press
enter
o
o Steps 2 :- In customizing execute project screen select SAP
Reference IMG
o Step 3 :- In next
screen select Edit, Copy, Delete check Company Code
o
o Step 4 :- The below screen displays after selecting Edit, Copy, Delete Company Code
( Define Company Code )
12 | P a g e
o
o we can create company code by selecting above two options. By selecting
first option copy, Delete, company code all the configuration and
tables get copied automatically along with assignments.
o Here we are creating company code manually configure all the
assignments by selecting second option Edit Company Code Data .
Double click on Edit Company Code Data
o
o Step 5 :- Click on New Entries and update the following details
o
1. Update new Company code key AD06
o 2. Give the company name Adarsh Technologies for identifying the
company code key
o 3. In Additional Data update the details of City, Country, local Currency of
company, Language.
o Click on Address and Update the following fields
13 | P a g e
o After updating Address
enter Click on Save icon Thus the company code AD06 is created in SAP
How do you assign company code to company?
Assign Company Code to Company
Menu Path :-
SPRO > IMG Reference > Enterprise Structure > Assignment > Financial
Accounting >Assign Company Code To Company
Transaction Code :- OX16
The following are the steps to Assign the Company Code to Company in SAP FICO
Step 1 :- Enter the T-Code SPRO in the commend field
14 | P a g e
Step 2 :- Click SAP Reference IMG
Step 3 :- Follow the Path as per below screen shot
Step 4 :- Click Position
Update company code for which you wants to assign and Enter
Step 5 :- Update Company ID in Company field and click on save icon
Thus company code AD06 was assigned to Company ADARSH
15 | P a g e
Define Plant?
What are the important Prerequisites for creating a plant in SAP?
o The plant is an operating area or branch within a company.
o Plant is an organizational logistics unit where certain important business
functions like Production, Procurement, Inventory, Inbound & Outbound
delivery processing, Plant Maintenance & Materials Planning are carried.
o
o Plant plays an important role in following areas:
o 1. Materials can be valuated at Plant Level.
o 2. A Factory Calendar is controlled at Plant Level
o 3. Certain views like MRP, Purchasingu2026 in the Material 4. Master are
maintained at Plant Level.
o 4. User level authorization can be controlled at Plant Level.
o
o Organization Unit - Plant
o
o Attributes for plant-
o 1.Name and Address
o 2.Language and Currency
o 3.Factory Calendar
o
o Application for plant -
o 1.Material Valuation
o 2.Master data maintenance
o 3.User Level Authorization
o 4.Output Type determination
How do you assign plant to company code?
Assign Plant to Company Code configuration steps :-
Transaction code Assign Plant to Company Code :- OX18
IMG Menu Path :- SPRO > SAP Customizing Implementation Guide (IMG) > Enterprise
Structure > Assignment > Logistics General >Assign Plant to Company Code
Step 1 :- Enter Transaction Code SPRO in the command field and press enter
16 | P a g e
Step 2 :- Click on SAP Reference IMG
Step 3 :- Follow the Menu Path as per below screen shot
Step 4 :- Click on New entries
17 | P a g e
Step 5 :- Update Company code in cocd field,and update plant code in plnt field and press
enter
Step 6 :- Click on save icon
o Which Organization unit is entered when creating
Purchasing view of any material
o What is Storage Location? how to maintain storage
locations?
o Transaction code :- OX09
o IMG Menu Path :- SPRO> SAP Customizing Implementation Guide >Enterprise
Structure Definition > Material Management > Maintain storage Location
o Step 1 :- Enter Transaction Code SPRO in the command field and press enter
18 | P a g e
o
o Step 2 : - Click on SAP Reference IMG
o
o Step 3 :- Follow the menu path as per below screen shot and click on maintain
storage location
o
19 | P a g e
o Step 4 :- Enter the Plant key where the storage location is to be maintained and
press enter
o
o Step 5 :- Click on new entries for creation new storage location
o
o
o Step 6 :- Enter Key in Sloc and description of storage location
20 | P a g e
o
o Step 7 :- Select storage locations and double click on address of storage locations
o
o Step 8 :- After double click on address of storage locations, click on new entries
and give 1 in NO field.
o
o Step 9 :- Update the address of the storage locations
21 | P a g e
o
How Storage Locations are created automatically?
22 | P a g e
o It will be done with Tcode OMB2, but before that please read all
prerequisites for this in SAP standard notes.
o
o Automatic creation of storage location allowed
o Indicates that automatic creation of storage location data in the material
master record at the time of the first goods receipt is allowed.
o
o Dependencies
o Storage location data is only created automatically if this is:
o
o Allowed in the relevant plant and
o Provided for in the movement type
o If these prerequisites are not satisfied, you must maintain the storage
location data of a material before you post the first goods receipt in the
relevant storage location.
o
o Note
o The storage location data is only created automatically if the quantity is
posted to the "normal" storage location stock. If you have goods
movements to special stock (for example, to sales order stock), the data
is not created.
o
o The standard system is set in such a way that the storage location data is
created automatically for all types of receipts (goods receipt with/ without
reference, stock transfers, intial entry of stock balances, reversal of goods
issues, etc.).
o
o 1. Enter for each plant whether the automatic creation of storage location
data is generally allowed.
o 2. Specify the movement types for which storage location data is created
automatically.
o
o What is Valuation Areas?
o SPRO > IMG > Financial Accounting > Financial Accounting Global Settings >
Company Code > Parallel Accounting > Integration > Parallel Accounting in
Corporate Finance Management > Parallel Valuation Areas > Organization >
Define Valuation Areas
23 | P a g e
o
o Menu Path Define Valuation Areas
What is Purchase Organisation? How it is configured?
Create Purchasing Organisation in SAP Step by Step
IMG Menu Path :- Customizing Implementation Guide > Enterprise Structure > Definition >
Material Management > Maintain > Maintain Purchasing Organisation
T Code for Maintain Purchasing Organisation :- OX08
Step 1 :- Enter T Code SPRO in the SAP Command Field
Step 2 :- Click on SAP Referrence IMG
24 | P a g e
Step 3 :- Follow the menu path as per below screen shot for creating new purchase
organisation
Step 4 :- Click on new entries
25 | P a g e
Step 5 :- Update the following data and press enter
Purch.Organisation :- Enter 4 digits Key that identifying the purchase organisation
Purch. Org. descr. :- Update the description of the purchase organisation
Step 6 :- Click on save icon
Thus Purchasing Organisation is successfully configured in SAP Material Management
What is Chart of Accounts in SAP?
Definition of Chart of Accounts :-
26 | P a g e
The chart of accounts in SAP ( COA ) is a list of GL accounts master record that are used
by the organisation. A chart of accounts must be assigned to each company code. Chart of
Accounts is defined at client level.
Types of Chart of Accounts :-
Operating chart of Accounts
Country Specific chart of Accounts
Group Chart of Accounts
Operating chart of Accounts :-
The operating chart of accounts in sap contains the G/L accounts that uses for posting in
company code for daily activities and used in both financial accounting and cost accounting.
You have to assign operating chart of accounts to a company code
Country Specific chart of Accounts
The country-specific chart of accounts in sap contains the G/L accounts needed to meet
the countrys legal requirements. country specific chart of accounts are assigned to company
codes and this is optional.
Group Chart of Accounts :-
The Group chart of accounts in sap contains the G/L accounts that are used by the entire
corporate group and this COA is used to consolidate the reports for the entire corporate
group
we can use the following methods to Create new chart of accounts in SAP
1. Transaction Code :- OB13
2. SAP Menu Path :- IMG > Financial Accounting > General Ledger Accounting > G/L
Accounts > Master Data > Preparations > Edit Chart of Accounts List
Chart of Accounts in sap Configuration Steps:-
Step 1 :- Enter the Transaction code SPRO in the SAP commend field to get the
Implementation Guide
27 | P a g e
Step 2 :- Click on SAP Reference IMG
Step 3 :- Navigate the below Path and click on Edit Chart of Accounts List to create new
Chart of Accounts
Step 4 :- The Existing Chart of Accounts which are already created are displayed below,
Click on New entries button to create new Chart of Accounts in SAP
28 | P a g e
Step 5 :- Update the required data in new entries screen
1. Chart of Accounts :- Enter the 4 digit alphanumeric code of the Chart of Accounts
2. Description :- Enter the Description of the Chart of Accounts
3. Maintain Language :- Select the language of the Chart of Accounts
4. Length of G/L Account Number :- Update the length of Gl Account Number
5. Integration :- We can have controlling Integration Manual creation of cost of elements or
Automatic creation of cost of elements. It is advisable to have Manual creation of elements in
SAP
6. Consolidation :- Enter the Group Chart of accounts for the consolidation of Reports.
7. Status :- Under status Deselect the Blocked Check box.
After updating the required data click on save icon you will get message Data was saved
Thus Chart of Accounts in SAP ADAR was created.
29 | P a g e
How many charts of accounts can be assigned to a single company
code?
First understand the basic conceptof Chart of Account
Chart Of Accounts: OB13
1. Chart of Account is the list of all G/L account used by one or several
Company Code.
2. We have to assign Chart of Account to each company code.
3. This Chart of Account is the operational Chart of account and is used for daily posting
in the Company Code.
4. We have to use the chart of accounts for all company codes, if all the company codes are in
the same country.
5. If the individual company code requires different COA, We can assign up to 2 COA, in
addition to the operational COA. : - If the company codes are in multiple countries.
Functions of COA
1. Operational COA
2. Group COA
3. Country Specific COA
OPERATIONAL CHART OF ACCOUNT:
The operational Chart of accounts contains the G/L accounts that are used for posting in the
company code during the daily activities.
Financial Accounting and Controlling use this Chart of Account.
We have to assign Operational COA to each company code.
GROUP CHART OF ACCOUNT:
Contains the G/L , that are used by the entire Corporate group.
This allows the company to provide report of the entire corporate group.
COUNTRY SPECEFIC CHART OF ACCOUNT:
It contains the G/L needed to meet the Countrys Legal requirement
30 | P a g e
What are the different types of master records data in SAP MM
module?
o please find below more master data from MM.
o Payment term
o Material group
o Material type
o unit of measurement
o currency
o Intercom
o cost center
o purchase organization
o vendor account group
o purchasing group
o External Categories,
o plants
o Company codes
What is a Material Master?
The material master database (often referred to simply as the "material master",
comprising all the individual material master records stored in the system)
contains descriptions of all materials that an enterprise procures, produces, and
31 | P a g e
keeps in stock. It is the central repository of information on materials (such as
inventory levels) for the enterprise.
The integration of all material data in a single materials database eliminates the
problem of data redundancy and permits the data to be used not only by
Purchasing, but by other applications (such as Inventory Management, Materials
Planning and Control, Invoice Verification, and so on).
Descriptions of the individual materials used in an enterprise are stored
in material master records.
The following list shows some types of information a material master record
contains and provides examples of each:
Accounting
Valuation and costing/price calculation information. Examples: Standard
price, past and future price, and current valuation.
Materials planning and control
Information for material requirements planning (MRP) and consumption-
based planning/inventory control. Examples: Safety stock level, planned
delivery time, and reorder level for a material.
Purchasing
Data provided by Purchasing for a material. Examples: Purchasing group
(group of buyers) responsible for a material, over- and underdelivery
tolerances, and the order unit.
Engineering
Engineering and design data on a material. Examples: CAD drawings,
basic dimensions, and design specifications.
Storage
Information relating to the storage/warehousing of a material. Examples:
unit of issue, storage conditions, and packaging dimensions.
Forecasting
Information for predicting material requirements. Examples: How the
material is procured, forecasting period, and past consumption/usage.
Sales and distribution
Information for sales orders and pricing. Examples: Sales price, minimum
order quantity, and the name of the sales department responsible for a
certain material.
What are the Data is maintained in Material master at client level and
company code level?
o Material Master is maintained at client level, Plant level, Storage location
level and sales org level.
32 | P a g e
o
o Venodr Master is maintained at Client level, Comapny code level, Purchase
organisation and some times with plant level.
How to delete materials permanently from material master?
o Use transaction MM70 - Material Master->Other->Reorganization-
>Material->Choose.
o Build variant with selection range of material master records to be
selected for deletion and maintain run parameters. Execute.
o Use transaction MM71 - Material Master-> other-> Reorganization-
>Material->Reorganization
o Build a second variant
o Maintain run parameters and execute.
o It is also important to remove the records manually from info record, POs,
PRs, reservation etc for successful deletion of the material.
o With regards,
How to extend materials to a new plant ?
o case one
o mm01: put the same material no. industry, mat type and take ref
material as the same..
o now u will hav one addition window that will ask origin and destination
organisational unit..
o
o case 2
o
o t.code MMAM
33 | P a g e
What is a Batch? How to create a Batch Record?
o Specify Batch Level
o Menu Path Enterprise Structure> Logistics General> Batch Management -
-> Specify batch level and activate batch status management
Transaction OMCT
o
o 2. Batch Number - Activate Internal Number Assignment
o Menu Path Enterprise Structure> Logistics General> Batch Management -
-> Batch Number Assignment --> Activate internal batch number
assignment Transaction OMCZ
o
o 3. Batch Creation - for Goods Movements
o Menu Path Enterprise Structure> Logistics General> Batch Management -
-> Creation of new batches --> Define batch creation for goods
movements Transaction
o
o 4. Characteristic Value Assignment -- Update Standard Characteristics
o Menu Path Enterprise Structure> Logistics General> Batch Management -
-> Characteristic Value Assignment --> Update Standard Characteristics
Transaction
o
o 5. Activate Batch Classification for Goods Movements in Inventory
Management
o Menu Path Enterprise Structure> Logistics General> Batch Management -
-> Characteristic Value Assignment --> Valuation for goods movements --
> Activate Batch Classification for goods movements in Inventory
Management Transaction OMCV
o
o 6. Batch Determination u2013 Batch Search Procedure
o Menu Path Enterprise Structure> Logistics General> Batch Management -
-> Batch Determination & Batch Check --> Define IM Search Procedure
Transaction OMCY
o
o 7. Batch Determination u2013 Batch Search Procedure Allocation
o Menu Path Enterprise Structure> Logistics General> Batch Management -
-> Batch Determination & Batch Check --> Allocate IM search
procedure/activate check Transaction OMCG
o
o 8. Batch Determination u2013 Make Settings for Batch Where-used list
o Menu Path Enterprise Structure> Logistics General> Batch Management -
-> Make Settings for Batch Where-used list Transaction OMBB
34 | P a g e
What is a class type and how to configure in SAP system?
Purpose
The class type is a central concept in the classification system. The class type
determines how classes are processed, and how objects can be classified and
retrieved in these classes. In Customizing for Classification, you define the
settings for a class type. You define class types for a specific object type, such
as materials. You can then use classes of this class type to classify objects of
this object type.
When you first create a class, you must enter a class type for the class. Each
class type is a closed system. There is no link between the different class types.
Features
The class type determines the following:
Which object types you can assign to a class
Which class maintenance functions you can process
Whether you can classify objects in more than one class
Which class statuses, organizational areas, and text types are supported in
class maintenance functions
Whether you can use engineering change management for classification
Which filter functions you can use to restrict the search result
Class types 001, 300, and 200 are defined for materials. In Customizing
for Classification, you define the settings for a class type.
All materials can be classified with class type 001. Class type 300 is for variant
configuration. Class type 200 is for classes that are used as class items in bills of
material. You can classify the same materials separately in these class types.
35 | P a g e
You can use class type 012 to classify characteristics. This class type is defined
only has theKeywords, Characteristics, and Texts screens in class maintenance
functions. You can only classify characteristics in characteristics maintenance
functions you cannot use the assignment functions in the classification menu.
In this case the indicator Classify master record only was set. No organizational
areas were maintained for the characteristics. For this reason, if you create a
class of class type 012, you cannot select any organizational areas.
How Vendor Master Records are created?
Create Vendor Master Data
Tutorial guides you how to create vendor master data in SAP. Creation of Vendor Master
data for material suppliers and services is documented in SAP MM module.
SAP R/3 path :- Accounting > Financial Accounting > Accounts Payable >Master records
> Maintain centrally > XK01 Create
Transaction Code :- XK01 Create
XK02 Change
XK03 Display
Step 1 :- Enter T Code XK01 in the SAP command field and press enter from key board
Create Vendor: Initial Screen
36 | P a g e
Step 2 :- Update the following fields and press enter
1. Company code :- Company Code identifying a separate legal entity for which a separate
set of accounts is maintained for purpose of external reporting . Update the company code
for which company you are going to create vendor code
2. Purchasing Organisation :- Organizational unit within Logistics, subdividing an
enterprise according to the requirements of Purchasing. Update the Purchasing
organisation code
37 | P a g e
3. Account group :- Code used to determine the classification of the vendor account
groups
Step 3:- Create Vendor : Address Screen
Update the Vendor Address in detail and press enter
Step 4:- Next screen update vendor control information and press enter
38 | P a g e
Step 5:- In next screen update bank details of vendor
Step 6:- Create Vendor: Accounting information Accounting
39 | P a g e
Recon. account :- Vendor Reconciliation account is the G/L account for a group of vendors
in SAP FI-AP module. Enter Sundry creditors GL account in reconciliation account filed. The
account must be defined as a reconciliation account for vendors. .
Step 7:- Click on Save icon to save configured vendor master record.
What are the Special Stocks available in SAP?
Subcontracting, consignement, pipeline, project, sales order,
RTP, stock transfer ,third party.
What is a Consignment stock?
o Ownership of consignment stock is passed only when the stock is used
(issued or sold in the case of a shop). Unused stock in a warehouse may
be returned to the supplier [disambiguation needed] when it concerns
standard manufactured products.
40 | P a g e
Explain Differences between Externally owned and company owned
special stocks?
Company-Owned Special Stocks:
1.Stocks that belong to the company but are stored with the
wholesaler or the customer are called company-owned special
stocks.
2. Company-owned special stocks are managed at the production
level
Externally-Owned Special Stocks :
1. Stocks that belong to the whole-saler or the customer but
are stored at the company are called externally-owned
special stocks
2. Externally-owned special stocks are managed at the place
where they are stored
Explain Procurement cycle in organisation?
Explain how Purchase Order (PO), Purchase Requisition (PR),
MRP are created?
MRP (material resource planning) creates procurement proposal and later gets
converted into Purchase Requisition. Next step is assigning source to Purchase
41 | P a g e
Requisition, and release of Purchase Requisition. The PR gets converted to
Purchase Order and upon goods receipt an invoice receipt can be done to
complete the purchasing process. Additionally payment is processed (in FI
module).
Procurement doesn't have to start by the MRP, it can be initiated by
consumption based planning or by direct creation of PR or PO.
MRP is a system function to determine the material requirements on both the
material and BoM level. A BoM (Bill of Materials) is a list of components and
subcomponents a single material is consisting of.
One of the mere basic documents in Purchasing in SAP is a purchase requisition.
Purchase requisition
Purchase requisitions can be created automatically by system or manually. They
can be converted in purchase orders but only upon release (approval of purchase
requisition).
We will cover several topic in this leson that can help understand and create the
purchase requisition.
Number ranges in purchase requisitions are required just as in other document,
for the purpose of assigning the document number to new created documents.
Later, these number ranges are being assigned to different document types we
can define to be used in purchase requisition processing.
We will also cover requirement tracking number which is basically a
number/letter combo which can be uniquely assigned to multiple documents in
order to track certain important requirements.
You will se how the source determination works and why it's useful, as well as
how this source can be assigned to our purchasing document.
Finally, you will find out how to process the purchase requisition, from its
creation until converting it to a purchase order.
Number ranges for Purchase Requisition
Assigning of number ranges for purchase requisition works on document type.
Several different number ranges can be created and afterwards assigned to a
specific purchase requisition type.
42 | P a g e
This is done in customizing. Requisition document types can have two number
ranges assigned. One internal and one external range are assigned to each
document type. Internal number ranges are being automatically incremented by
the system, and external are assigned manually.
Screen below represents a list of number ranges for purchase requisition.
From number is the first number in the range, To number is the last available
number adn the current number is the last assigned number to a document.
In addition, there is a check box indicating if this is an external number range.
For example, an internal number range can be defined as a range from
20000000 to 30000000, in this case documents of the document type that is
assigned this interval will be numerated starting from 20000001 and will be
incremented by 1 for each new document created. The last number available for
this interval will be 30000000, and if your documents fill up the entire number
range it has to be extended. It will rarely happen as it would mean that you
would have 10 million purchase requisition documents.
Document type definition
Document type definition is an action of defining different document types for a
purchase requisition. It is useful in grouping purchase requisitions and specifying
its use in more detail. For example, we can have standard PRs, subcontracting
and stock transfer. Every document type suits a special need and is configured
to be used in that way.
43 | P a g e
In document type definition, you can define a number of options. Number
intervals (internal and external), item interval, field selection key, control
indicator, overall release indicator (defines if all the items in PR are released
simultaneously or individually).
Standard Purchase Requisition document type in SAP is defined in all
installations as NB.
Requirement tracking number
This number is used for tracking specific requirements. It can be entered during
purchase requisition creation and is copied into purchase order document. It is
maintained on item level and items can be selected by this number in several
reports like MELB.
Execute MELB transaction.
Click the Choose button.
When you click Continue, you will be back to the initial selection screen.. You
also have a variety of select options and should choose the most suitable options
to narrow the search.
Enter requirement tracking number(s).
Execute.
44 | P a g e
You will be presented a list of documents containing the tracking number.
Source determination
Source determination assists in finding the most suitable source for a
requirement, for example, it can suggest which outline agreement, which
internal procurement source (plant) or which vendor can be used for ordering
specific materials at given time.
Source determination take various data as parameters for the actual
determination process. These include Outline agreement, Purchase info record,
Plant in our company, Quota arrangement, Source list.
All this is taken into account while determining the best possible source for a
requirement.
First check is done via Quota Arrangement where system determines if there
is a suitable source with the relevant quota arrangement for the material, and if
suitable source is found it is selected, and additional search for the source is
aborted.
If not, system takes source list into account and searched for valid sources
there. A source list consists of fixed and blocked records. Fixed records are for
fixed vendors for specific material valid for a certain period. Blocked
records cannot be used as a source while they are in this status.
45 | P a g e
Finally system looks up the outline agreement and info record for credible
sources and assigns them the requisition. You have seen in the previous lesson
what is a purchase info record, and outline agreement is a scheduling agreement
or contract which is also used in the source determination process as input
information.
To use the source determination, you need to tick the Determine Source check-box on the pruchase
requisition initial screen.
Assignment of source
System can perform background or foreground source assignment.
If the search is done in the foreground mode, and more than one valid source is
found, a selection list appears from which user should select the appropriate
source. If only one suitable source is found, it is assigned automatically.
If the search is done in the background, a single source must be determined and
to accomplish that the system will perform various functions in the lookup.
For example, outline agreements have priority over the purchase info record
source and in case of conflict an outline agreement source is selected.
If more than one valid source is found in outline agreements, unique valid
source will be the one for the regular vendor, and if neither record is for a
regular vendor, source will have to be determined manually.
You can see how two sources are offered by the system, from which we have to
choose the better manually.
46 | P a g e
Define consignment cycle?
Consignment cycle is similar to the purchase cycle, except that
when you create goods receipts of the consignment stocks, only
quantity (QTY) is updated and no accounting documents are
created. Once the goods are utilized, consignment is settled. The
value of the consumed or issued consignment stocks is taken
from the active purchase info record
What is Subcontracting? How subcontracting PO is created?
o Steps in Subcontracting With CIN Process :
o
o Create Infor Record of Subcontracting Type in ME11
o
o Create Bill of Material for Child Components in CS01
o
o Create Purchase Order Using ME21N
o
o If Applicable, Release Purchase Order in ME28 / ME29N
o
o Send Components to Subcontractor Using MB1B 541 or ME2O
o
o Create Subcontracting Challan Using J1IF01
o
o Make Goods Receipt Using MIGO 101
o
47 | P a g e
o Reconcile Subcontracting Challan using J1IFQ
o
o Subcontract Complete using J1IF13
o
o Invoice Verfication Through MIRO
o
o If Exists, Receive By Products / Scrap using MB1B 542 or MB1C 531
o
o Regarding Reversal
o
o Create a Return Purchase Order in ME21N with Return ITem Indicator
Checked
o Make a Goods Receipt against Return Purchase Order (161 Mov type will
automatically takes place)
o Create & Post Excise invoice for Other Movements using J1IS & J1IV
o Raise a Credit Memo against Venodr in MIRO.
What is Material Type? How to create Material Type?
Tutorial guides you how to configure/ create material types in SAP MM step by step with
screen shots.
SAP IMG Menu path :- SPRO > Logistics General > Material Master > Basic Settings >
Material Types > Define Attributes of material types
Transaction Code :- OMS2
Enter T Code OMS2 in the SAP command field and press enter.
List of material types are displayed in the screen, Select existing material type line item and
click on New Entries or copy as icon to define new material types in SAP.
48 | P a g e
Material Type :- Update New Material key
Description:- Give the description for the material key
Field Reference:- Field reference determines for each field section group is set to hide,
display, required entry or optional entry.
Item Category group :- Select item category group from the list
Special material types :- check the box for special material types
User Departments :- Select departments for the material types as per business
requirements.
Internal/external purchase orders :-Select the value as per business requirements,
Possible entries are
0- No external purchase orders allowed
1 External purchase orders allowed, but warning issued
2- External purchase orders allowed
Valuation
Price Control:- Set the price control as Standard price or moving average
price/periodic unit price
Acct. Cat. reference :- Select account category reference from list. The system uses to
check whether the valuation class you have entered is allowed the accounting data in a
material master record is maintained.
49 | P a g e
Click on save icon and then select created material type and double click on quantity/value
updating
If it is not stock item tick only value updating, if it is a stock item with value tick the both qty
updating and value updating columns
50 | P a g e
Click on save icon or (Ctrl+s) to save the configured material types data.
Successfully you configured the new material types in SAP.
How to Create material movement type in SAP?
o 1)To create a new movement type, copy one which already exit first.
o 2)then change the control parameter of new movement type
o 3)the key of the new movement type must be strat from 9,x,v,orz
o 4)when copying make sure that you also copy all dependent entries of
reference movement type
o 5)final check relevant data
o tcode-OMJJ
Explain Purchase Requisition (PR), Purchase Order (PO)
Define Tolerance Keys?
51 | P a g e
o As of my knowledge, you may need to go for ABAP development to
achieve this. My suggestion is:
o 1. Create a ztable with purchase organization, tolerance key and tolerance
percentages.
o 2. Use user exit in miro to pull the tolerance key from this ztable instead
of standard omr6 tolerance key. Please check the exit MM08R002 with
abaper. If the exit doesnt work, you may find similar exit with the help of
abaper.
o
o Another option would be use the exit MRM_HEADER_DEFAULT and
define blocking reason based on purchase organization
Explain Pricing Procedure?
o Pricing Procedure is indeed an heart of SD module, reason being if
everything else is working fine, but price is not being calculated correctly,
the purpose of billing fails.
o
o An Overview of Determination & Configuration of Pricing Procedure is as
follows:
o
o In SD, Pricing Procedure is determined based on Sales Area (Sales
Organization + Distribution Centre + Division) + Customer Pricing
Procedure + Document Pricing Procedure. Sales Area is determined in
Sales Order Header Level. Customer Pricing Procedure is determined from
Customer Master. Document Pricing Procedure is determined from Sales
Document Type / Billing Type (if configured). Once the pricing procedure
is determined, Condition records are fetched. If appropriate condition
records are found, the price is determined. If Mandatory pricing condition
is missing, system will through an error message.
o
o In SD, the steps to configure Pricing procedure are as under:
o Step 1:
o Condition table: If existing condition table meets the requirement, we
need not create a new condition table. Considering the requirement for
new condition table, the configuration will be done in spro as follows: IMG
-> Sales & Distribution -> Basic Function -> Pricing Control -> Condition
Table (select the required fields combination, which will store condition
record).
o Step 2:
o Access Sequence: If existing access sequence meets the requirement, we
need not create a new access sequence. Considering the requirement for
new sequence, the configuration will be done in spro as follows: IMG ->
Sales & Distribution -> Basic Function -> Pricing Control -> Access
Sequence (Access sequence is made up of Accesses (Tables) & the order
52 | P a g e
of priority in which it is to be accessed. Here we assign the condition table
to access sequence.
o Step 3:
o Condition Type: If existing condition type meets the requirement, we need
not create a new condition type. Considering the requirement for new
condition type, the configuration will be done in spro as follows: IMG ->
Sales & Distribution -> Basic Function -> Pricing Control -> Condition
Type. It is always recommended to copy an existing similar condition type
& make the neccessary changes. Here we assign Access sequence to
Condition type.
o Step 4:
o a. Pricing Procedure: It is recommended to copy a similar pricing
procedure & make the neccesary changes in new pricing procedure.
Pricing Procedure is a set of condition type & arranged in the sequence in
which it has to perform the calculation. Considering the requirement for
new Pricing Procedure, the configuration will be done in spro as follows:
IMG -> Sales & Distribution -> Basic Function -> Pricing Control ->
Pricing Procedure --> Maintain Pricing Procedure.
o b. Pricing Procedure: After maintaining the pricing procedure the next step
will be determination of pricing procedure. Configuration for determining
pricing procedure in SPRO is as follows: IMG -> Sales & Distribution ->
Basic Function -> Pricing Control -> Pricing Procedure --> Determine
Pricing Procedure.
o Step 5: Condition record: Condition record is a master data, which is
required to be maintained by Core team / person responsible from the
client. During new implementation, the condition records can be uploaded
using tools like SCAT, LSMW, etc.
Define Scheme group and Scheme determination?
determination of calculation schema is a customizing activity.
You have to assign a pricing procedure to a schema group purchasing
organization / schema group vendor combination.
Settings are located in Define schema determination option.
Step 1)
Choose Determination Calculation schema for Standard Purchase Orders.
53 | P a g e
Step 2)
Choose schema group for purchasing organization.
Choose schema group for vendor.
Choose calculation schema to be assigned to the purch.org/vendor schema
group combination.
Let's analyze two records on this screen.
1. In case 1, we have chosen default schema group for purchasing organization
(first field is empty), also, default schema group for vendor (second field is
empty), for this combination of both default schema groups, we assigned a
RM0000 (Purchasing document - Big) calculation schema.
2. In case 2, we have chosen schema group for purchasing organization as
0001, and schema group for vendor as 01, and assigned an RM1000
calculation schema to the combination.
How does it work?
Let's say that we have a purchase organization 0001 with blank (default)
schema group assigned to it, and a purchase organization 0002 with schema
group 0001 assigned to it (not default).
We also have a vendor 1 with assigned schema group as blank (default),
and vendor 2 with schema group defined as 01 (not default).
In case we are creating a purchase order through purchasing group 0001 for
vendor 1, our calculation schema is going to be determined as RM0000.
54 | P a g e
If we are creating a PO for vendor 2 through purchasing organization 0001,
calculation schema RM1000 will be determined.
If we are creating a PO for any of the two vendors in purchasing organization
0002, in both cases there will be determined calculation schema RM1000.
The below table clarifies the calculation schema determination.
VENDOR
VENDOR
SCH.GRP.
Vendor 1
Default
(blank)
RM0000 RM1000
Vendor 2 01 RM1000 RM1000
Default (blank) 0001 PURCH.ORG.SCH.GRP.
Purchasing
Organization 0001
Purchasing
Organization 0002
PURCHASING
ORGANIZATION
You are done. Your pricing procedure is now fully functional.
You can use some advanced features like condition exclusions, copy control,
define limits for condition types etc.
Compiled : papuchetry@gmail.com
You might also like
- SAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyFrom EverandSAP PR Release Strategy Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The A-Z Medical WritingDocument153 pagesThe A-Z Medical WritingNikhil Mali100% (2)
- 1 - MM Blue Print DocumentDocument112 pages1 - MM Blue Print DocumentRama Krishna Vemulapalli80% (5)
- SAP MM Organizational StructureDocument282 pagesSAP MM Organizational StructureAnil Kumar100% (1)
- SAP Variant Configuration: Your Successful Guide to ModelingFrom EverandSAP Variant Configuration: Your Successful Guide to ModelingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- MM BBP KCLDocument73 pagesMM BBP KCLADITYAFICO80% (10)
- Material MM User ManualDocument314 pagesMaterial MM User Manualapi-3718223100% (3)
- SAP MM Download NotesDocument62 pagesSAP MM Download NotesNiranjan BeheraNo ratings yet
- Pilog™ Master Data Record Manager: Product Catalogue Management (PCM)Document8 pagesPilog™ Master Data Record Manager: Product Catalogue Management (PCM)Naif Al-AlolaNo ratings yet
- SAP MM Configuration and Examples PDFDocument213 pagesSAP MM Configuration and Examples PDFReivel Hernández100% (3)
- SAP S/4 HANA Simple Logistics - MM (Materials Management)Document4 pagesSAP S/4 HANA Simple Logistics - MM (Materials Management)Kapil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Procurement Process FlowDocument2 pagesProcurement Process FlowmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Sap MM Project - Ecc 6.0Document20 pagesSap MM Project - Ecc 6.0Razi Ahmed Khan100% (2)
- Sap MM Functionality TechnicalDocument53 pagesSap MM Functionality Technicalmanohar_sh60% (10)
- SAP MM End User ManualDocument316 pagesSAP MM End User Manualmehta_avi94% (16)
- SAPCOOKBOOK Training Tutorials: SAP MM Inventory ManagementFrom EverandSAPCOOKBOOK Training Tutorials: SAP MM Inventory ManagementRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- MM ConfigurationDocument50 pagesMM Configurationgsamsr100% (3)
- SAP MM ConfigurationDocument136 pagesSAP MM ConfigurationSanjay P79% (24)
- SAP MM Tutorial DocumentDocument184 pagesSAP MM Tutorial DocumentAmit Kumar100% (2)
- Sap MMDocument202 pagesSap MMMayuri Srivastava67% (3)
- SAP IS-Retail Interview Questions, Answers, and ExplanationsFrom EverandSAP IS-Retail Interview Questions, Answers, and ExplanationsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (11)
- Questionnaire MMDocument111 pagesQuestionnaire MMapi-3781101100% (9)
- Chetna Mahajan Resume Version 3Document3 pagesChetna Mahajan Resume Version 3api-285721518No ratings yet
- SAP MM OverviewDocument224 pagesSAP MM OverviewBhaskar BiswasNo ratings yet
- Business PartnerDocument2 pagesBusiness PartnerAnand PatwariNo ratings yet
- Top 21 SAP MM Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesTop 21 SAP MM Interview QuestionsVishnu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Sap MM TrainingDocument235 pagesSap MM TrainingSAYANDEEP MITRA0% (3)
- Cracking the SAP S/4HANA Interview: Get Your Dream Job Today with Intelligent Responses to the EmployerFrom EverandCracking the SAP S/4HANA Interview: Get Your Dream Job Today with Intelligent Responses to the EmployerNo ratings yet
- SAP Enterprise Structure Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyFrom EverandSAP Enterprise Structure Concept and Configuration Guide: A Case StudyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- SAP MM Interview Q&ADocument39 pagesSAP MM Interview Q&ASupriyo Dutta100% (1)
- SAP Service Management: Advanced ConfigurationFrom EverandSAP Service Management: Advanced ConfigurationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- 1 Introduction To SAP MMDocument26 pages1 Introduction To SAP MMroyNo ratings yet
- SAP MM NotesDocument118 pagesSAP MM Notesatesh kumar panda100% (10)
- Sap MM Config TutorialDocument78 pagesSap MM Config TutorialSAYANDEEP MITRA50% (2)
- Sap MM Module Most Essential Notes at One PlaceDocument18 pagesSap MM Module Most Essential Notes at One PlaceSandeep Thakare86% (7)
- Mysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungFrom EverandMysap Fi Fieldbook: Fi Fieldbuch Auf Der Systeme Anwendungen Und Produkte in Der DatenverarbeitungRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- SAP MM ReportsDocument59 pagesSAP MM Reportssaprajpal95% (21)
- SAP Supply Chain Management A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionFrom EverandSAP Supply Chain Management A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionNo ratings yet
- MM Configuration - V.1.1 PDFDocument369 pagesMM Configuration - V.1.1 PDFkamranahmedaslamNo ratings yet
- SAP MM Interview Questions and AnswersDocument50 pagesSAP MM Interview Questions and AnswersGirishNo ratings yet
- SAP MM Interview QuestionsDocument8 pagesSAP MM Interview QuestionsTara Panda100% (2)
- Unleash citizen developers while staying in controlDocument10 pagesUnleash citizen developers while staying in controlNapoleao BorgesNo ratings yet
- MRP Procedures, Planned Orders, Organizational Levels, and Special Stocks in SAPDocument53 pagesMRP Procedures, Planned Orders, Organizational Levels, and Special Stocks in SAPDeepak Wagh0% (1)
- Sap MM GuideDocument316 pagesSap MM GuideAnupam Bali100% (8)
- SAP MM Interview QuestionsDocument15 pagesSAP MM Interview QuestionsHaja Peer Mohamed H75% (8)
- Standard Sap Reports (SD & MM)Document15 pagesStandard Sap Reports (SD & MM)Gaurav Harimitter50% (2)
- Epicor ERP 10Document14 pagesEpicor ERP 10murdiNo ratings yet
- Implementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesFrom EverandImplementing Integrated Business Planning: A Guide Exemplified With Process Context and SAP IBP Use CasesNo ratings yet
- Warehouse Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionFrom EverandWarehouse Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNo ratings yet
- Pravin Kumar: Fareportal India PVT LTDDocument4 pagesPravin Kumar: Fareportal India PVT LTDmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- SRN RaviDocument8 pagesSRN RavimkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Vendor Management Quick ReferenceDocument2 pagesVendor Management Quick ReferenceAmbrish NigamNo ratings yet
- Return Delevery. 122movDocument9 pagesReturn Delevery. 122movmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Ware ImpDocument30 pagesWare ImpmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- BAAN ERP Project Implementation Manufacturing Process BARCODocument1 pageBAAN ERP Project Implementation Manufacturing Process BARCOmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- WordsDocument4 pagesWordsmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Return Delevery. 161MOVDocument9 pagesReturn Delevery. 161MOVmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Po ReleaseDocument15 pagesPo ReleasemkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Testing 300Document11 pagesTesting 300mkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Return Delevery. 122movDocument9 pagesReturn Delevery. 122movmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Imp TablesDocument60 pagesImp TablesmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Org STR ModDocument18 pagesOrg STR ModmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- ModifiedDocument11 pagesModifiedmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- MM Questions for Master Data ConfigurationDocument8 pagesMM Questions for Master Data ConfigurationmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- ModifiedDocument11 pagesModifiedmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Manpower Procurement ProcessDocument2 pagesManpower Procurement ProcessmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Sap ProcurementDocument1 pageSap ProcurementKalyan ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- KeysDocument6 pagesKeysmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- KluDocument17 pagesKlumkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Construction Procurement ProcessDocument2 pagesConstruction Procurement ProcessmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- B. Spuida - Technical Writing Made EasierDocument17 pagesB. Spuida - Technical Writing Made EasieraeloysNo ratings yet
- Os ErrataDocument2 pagesOs ErratamkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- NachosDocument16 pagesNachosmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- MachDocument32 pagesMachmkumarshahiNo ratings yet
- Computer Operating SystemDocument8 pagesComputer Operating SystemDebabrata TrivediNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Information Systems in OrganizationsDocument44 pagesAn Introduction To Information Systems in OrganizationsMarkmel Pujante LoberitaNo ratings yet
- ERP System Enhances Production Planning and Supply Chain EfficiencyDocument49 pagesERP System Enhances Production Planning and Supply Chain EfficiencyDaniel John Cañares LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 KendallDocument9 pagesChapter 02 KendallPaolo BagsicNo ratings yet
- COM-61-SE Common Data in BAAN LNDocument375 pagesCOM-61-SE Common Data in BAAN LNarty121ruNo ratings yet
- 1z0 1033 DemoDocument5 pages1z0 1033 DemoAnoop GaurNo ratings yet
- WT01 2008 en Gesamt PDFDocument105 pagesWT01 2008 en Gesamt PDFRandy LangleyNo ratings yet
- Epicor 9 User ManualsDocument7 pagesEpicor 9 User Manualslouis radcliffeNo ratings yet
- Revenue Management SimplifiedDocument8 pagesRevenue Management SimplifiedSharwari ShahNo ratings yet
- Mis Vinsun Sectionc GroupgDocument7 pagesMis Vinsun Sectionc GroupgNimish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Olam Job DescrDocument3 pagesOlam Job DescrrpprayagaNo ratings yet
- Sales MGMT - Dabur Case StudyDocument17 pagesSales MGMT - Dabur Case StudyYogita Ghag GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Orion 10.6 - Getting StartedDocument25 pagesOrion 10.6 - Getting StartedM Jacksmerv SamuelNo ratings yet
- AAC Utility Partners Assisting Arizona Water Company With The Assessment of Enterprise Resource Planning NeedsDocument3 pagesAAC Utility Partners Assisting Arizona Water Company With The Assessment of Enterprise Resource Planning NeedsPR.comNo ratings yet
- Babar Shabir Ver 7.2Document2 pagesBabar Shabir Ver 7.2Babar ShabirNo ratings yet
- Air Asia FinalizeDocument38 pagesAir Asia FinalizeDesheng ChewNo ratings yet
- Simio Production Scheduling Wonder War Emes InterfaceDocument28 pagesSimio Production Scheduling Wonder War Emes InterfaceLuisSalvador1987No ratings yet
- ERP Security IssuesDocument3 pagesERP Security IssuesMr ProductNo ratings yet
- Perpule DocumentDocument2 pagesPerpule DocumentRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Integrating Physical and Software Sub-Systems in A Manufacturing Environment Through AgentificationDocument8 pagesIntegrating Physical and Software Sub-Systems in A Manufacturing Environment Through AgentificationKristin MackNo ratings yet
- Information System Based On Malaysia MadaniDocument35 pagesInformation System Based On Malaysia Madanirabiatul bhf100% (1)
- Bibliography Chapter ReferencesDocument31 pagesBibliography Chapter ReferencesstwilfredsNo ratings yet
- ERP Digital NotesDocument87 pagesERP Digital NotesChintu SisodiaNo ratings yet
- ERP Introduction Benefits The Evolution of ERP The Conceptual Model of ERP The Structure of ERPDocument15 pagesERP Introduction Benefits The Evolution of ERP The Conceptual Model of ERP The Structure of ERPSaurabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Assignment Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesWeek 1 Assignment Cloud ComputingperminusuhuruNo ratings yet