Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mode-based Dynamic Analysis of a Simple Machine in Abaqus
Uploaded by
matmean0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views15 pagesThe document provides instructions for performing a free vibration analysis using Abaqus CAE to obtain the first 30 natural frequencies and vibration modes of a simple machine. The machine geometry is created and meshed. Steel material properties are defined. Boundary conditions fixing the bottom surface and constraints on the top are applied. A linear perturbation frequency analysis step is created to extract the free vibration modes.
Original Description:
Dynamic analysis in abaqus
Original Title
Tutorial 5 Mode-based
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides instructions for performing a free vibration analysis using Abaqus CAE to obtain the first 30 natural frequencies and vibration modes of a simple machine. The machine geometry is created and meshed. Steel material properties are defined. Boundary conditions fixing the bottom surface and constraints on the top are applied. A linear perturbation frequency analysis step is created to extract the free vibration modes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views15 pagesMode-based Dynamic Analysis of a Simple Machine in Abaqus
Uploaded by
matmeanThe document provides instructions for performing a free vibration analysis using Abaqus CAE to obtain the first 30 natural frequencies and vibration modes of a simple machine. The machine geometry is created and meshed. Steel material properties are defined. Boundary conditions fixing the bottom surface and constraints on the top are applied. A linear perturbation frequency analysis step is created to extract the free vibration modes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis
Abaqus CAE Tutorial 4: Mode-based
Dynamic Analysis
___________________________________________________________
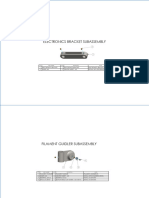
A simple machine is shown below. The machine is subject to dynamic
excitation. As a preliminary analysis perform free vibration analysis to
obtain 30 vibration modes and their natural frequencies. The machine
has a fixed bottom and a few constraints at the top. The material is steel
(Density: 7800kg/m
3
, E=210,000 MPa, =0.3).
Analysis Steps
1. In the model tree double click on the Parts node (or right click on parts and
select Create)
2. In the Create Part dialog box name the part and
a. Select 3D
b. Select Deformable
c. Select Solid
d. Set approximate size =200
e. Click Continue
3. Create the geometry shown below. (50
20)
4. Enter the base extrusion depth =25
5. Create solid: Extrude, select a plane for the extrusion.
6. a. Sketch the cylinder on the plane.: The center of the circle is (0, 5), the radius is 3.
b. Linear pattern: Use linear pattern to create two other circles.
b. Enter the extrusion depth: 6. Done.
7. Double click on the Materials node in the model tree
a. Name the new material as Steel
b. Click on the General tab, define the density of steel.
c. Click on the Mechanical tab, Elasticity, Elastic. Define Youngs Modulus and
Poissons Ratio.
8. Double click on the Sections node in the model tree
a. Name the section Machine and select Solid for the category and
Homogeneous for the type
b. Click Continue
c. Leave the section integration set to During Analysis
d. Select the material created above (Steel)
e. Click OK
9. Assign section select assign section in the red box shown below
a. Select the entire geometry in the viewport and press Enter
b. Select the section created above (Machine)
c. Click OK
10. Expand the Assembly node in the model tree and then double click
onInstances
a. Select Dependent for the instance type
b. Click OK
11. Double click on the Steps node in the model tree
a. Name the step, set the procedure to Linear Pertubation, and select Frequency
b. Click Continue
c. Eigensolver: Lanczos. Number of eigenvalue requested: 30.
d. Click OK
12. Expand the Field Output Requests node in the model tree, and then double click
on FOutput1 (FOutput1 was automatically generated when creating the step)
a. check the variables U
b. Click OK
14. Double click on the BCs node in the model tree
a. To create boundary condition on the top and bottom:
Select the top surface: U1=U2=U3=0
Select the bottom surface: U1=U2=U3=UR1=UR2=UR3=0.
b. Click Continue
15. In the model tree double click on Mesh for the part.
a. In the toolbox area click on the Global seeds, assign global seed size to 2.
b. Create partition: Select Partition cell: Extend face.
c. Create Mesh controls: Select Hex-dominated shape, Techique: Sweep,
Algorithm: Advanced.
d. Mesh the part.
16. Create and run the job.
17. View the results of first 30 modes.
You might also like
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationFrom EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3D Printer Troubleshooting Handbook: The Ultimate Guide To Fix all Common and Uncommon FDM 3D Printing Issues!From Everand3D Printer Troubleshooting Handbook: The Ultimate Guide To Fix all Common and Uncommon FDM 3D Printing Issues!No ratings yet
- Analysis of Truss Using Abaqus SoftwareDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Truss Using Abaqus SoftwareKarthick NNo ratings yet
- ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact ProblemDocument17 pagesENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 6: Contact ProblemflorinelvvNo ratings yet
- Impact With Rigid Tutorial in AnsysDocument14 pagesImpact With Rigid Tutorial in AnsysSaad Al HelyNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Tutorial 1Document4 pagesAbaqus Tutorial 1yangshaoweiNo ratings yet
- ABAQUS Tutorial - Contact AnalysisDocument17 pagesABAQUS Tutorial - Contact AnalysisSudipta BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Rigid Self Contact Tutorial Win14Document24 pagesRigid Self Contact Tutorial Win14SeyfullahYıldızNo ratings yet
- Collection Abaqus PDFDocument176 pagesCollection Abaqus PDFDeghboudj Samir100% (3)
- Abaqus CAE Self Contact Tutorial: Problem DescriptionDocument23 pagesAbaqus CAE Self Contact Tutorial: Problem DescriptionMohammed Abu SufianNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response TutorialDocument17 pagesDynamic Response TutorialsandycivilNo ratings yet
- Practical 05 - FEADocument8 pagesPractical 05 - FEAMHK ZarkNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Worksheet Jan 19 PDFDocument6 pagesAbaqus Worksheet Jan 19 PDFAMAN VERMANo ratings yet
- Getting Started with Abaqus FEADocument6 pagesGetting Started with Abaqus FEAAngel J. AliceaNo ratings yet
- 3 Axis Mill Machining Tutorial GuideDocument24 pages3 Axis Mill Machining Tutorial GuideAlexandru PrecupNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Vibrations TutorialDocument15 pagesAbaqus Vibrations Tutorialtone_n_tuneNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response TutorialDocument17 pagesDynamic Response TutorialgcanyonNo ratings yet
- UiiuDocument20 pagesUiiupravi2010No ratings yet
- I. Setup For Cadence InnovusDocument20 pagesI. Setup For Cadence Innovusijalab1No ratings yet
- Buckling TutorialDocument18 pagesBuckling Tutorialsammy_bejNo ratings yet
- I. Setup For Cadence InnovusDocument20 pagesI. Setup For Cadence InnovusMd. Ridoy Ad. SumonNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Response TutorialDocument17 pagesDynamic Response TutorialKedar A. MalusareNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 05 PDFDocument35 pagesTutorial 05 PDFJessie Radaza TutorNo ratings yet
- 1.CivilFEM - Steelbeam AnalysisDocument29 pages1.CivilFEM - Steelbeam AnalysislozadalmNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document14 pagesLab 1Flávia de Souza BastosNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Heat Transfer TutorialDocument15 pagesAbaqus Heat Transfer Tutorialhasib100% (2)
- Create STAAD model geometry and assign propertiesDocument5 pagesCreate STAAD model geometry and assign propertiesDeenNo ratings yet
- K Abdul Ajeej 17MST0002 Finite Element Laboratory: Exercise 5Document11 pagesK Abdul Ajeej 17MST0002 Finite Element Laboratory: Exercise 5abdulajeej salluNo ratings yet
- BEA/7/498 Advanced Computing and Structural Simulation: Session 2: Shell and Solid Elements in ContactDocument29 pagesBEA/7/498 Advanced Computing and Structural Simulation: Session 2: Shell and Solid Elements in ContactSovendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Tutorial: Axi-symmetric steel notched bar TensionDocument4 pagesAbaqus Tutorial: Axi-symmetric steel notched bar TensionМаксим ФедоровNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Tensile TestDocument4 pagesAbaqus Tensile TestKarim N. SalloomiNo ratings yet
- BallTank Foundation Design Guide Using AFES 21pDocument51 pagesBallTank Foundation Design Guide Using AFES 21pcgingenieros100% (1)
- Finite ElementDocument13 pagesFinite ElementChangZianLiNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of a Propped Cantilever BeamDocument15 pagesFinite Element Analysis of a Propped Cantilever BeamgiangfvuNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Interaction TutorialDocument13 pagesAbaqus Interaction TutorialhasibNo ratings yet
- CivilFEM 2016 .Beam - DesignDocument29 pagesCivilFEM 2016 .Beam - DesignSharathBanakarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 2 - Mae 456 Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 pagesTutorial - 2 - Mae 456 Finite Element AnalysisessersouNo ratings yet
- ME5554/ME5305 Part 2 - Tutorial 1 Linear Elastic and Elasto-Plastic AnalysisDocument27 pagesME5554/ME5305 Part 2 - Tutorial 1 Linear Elastic and Elasto-Plastic AnalysisRabee Shammas100% (1)
- Mae 456 Finite Element Analysis Lab Instructions Tutorial 2Document11 pagesMae 456 Finite Element Analysis Lab Instructions Tutorial 2adimaliknegoroNo ratings yet
- 2d TrussDocument19 pages2d Trussbapu28No ratings yet
- Abaqus Cae Shear WallDocument28 pagesAbaqus Cae Shear WallMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEM0% (1)
- OptiStruct - 01 - Design Concept For A Structural C-ClipDocument12 pagesOptiStruct - 01 - Design Concept For A Structural C-ClipBaljinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MSC - Patran ExercisesDocument714 pagesIntroduction To MSC - Patran ExercisesAlex da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Abaqus GuideDocument9 pagesAbaqus GuidePravin AwalkondeNo ratings yet
- NX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)From EverandNX 9 for Beginners - Part 3 (Additional Features and Multibody Parts, Modifying Parts)No ratings yet
- Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.12670) - Part 2: Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.12670)From EverandAutodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.12670) - Part 2: Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.12670)No ratings yet
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2018: Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2018: Exercise WorkbookRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Up and Running with AutoCAD 2012: 2D Drawing and ModelingFrom EverandUp and Running with AutoCAD 2012: 2D Drawing and ModelingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookFrom EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2020 Exercise WorkbookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- AutoCAD 2019: A Problem - Solving Approach, Basic and Intermediate, 25th EditionFrom EverandAutoCAD 2019: A Problem - Solving Approach, Basic and Intermediate, 25th EditionNo ratings yet
- 1 - 3 SBH Hydraulic and PneumaticDocument55 pages1 - 3 SBH Hydraulic and PneumaticmatmeanNo ratings yet
- 3D Profilometer Brochure Rtec2018Document11 pages3D Profilometer Brochure Rtec2018matmeanNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 ADocument43 pagesLec 1 AmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Adaptive MeshDocument38 pagesAdaptive Meshbooks_ukNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 CDocument12 pagesLec 1 CmatmeanNo ratings yet
- A Baq Us LinkingDocument5 pagesA Baq Us Linkingcen1510353No ratings yet
- Lec 1 CDocument12 pagesLec 1 CmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Mango Harum ManisDocument11 pagesMango Harum ManismatmeanNo ratings yet
- Mikkelsen - 2007 - Non-Linear Finite Element ModelingDocument15 pagesMikkelsen - 2007 - Non-Linear Finite Element ModelingmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 BDocument42 pagesLec 1 BmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Adaptive MeshingDocument13 pagesAbaqus Adaptive MeshingpaivensolidsnakeNo ratings yet
- AbqW1a CAEIntroDocument24 pagesAbqW1a CAEIntromatmeanNo ratings yet
- Orthotropic Modelling of The Skeletal SystemDocument258 pagesOrthotropic Modelling of The Skeletal SystemmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Compiling, linking and debugging ABAQUS user-subroutinesDocument4 pagesCompiling, linking and debugging ABAQUS user-subroutinesHanifNo ratings yet
- Module1 Beam Bending PDFDocument29 pagesModule1 Beam Bending PDFMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEM0% (1)
- Abaqus Plasticity TutorialDocument16 pagesAbaqus Plasticity TutorialSanjay Sibal100% (2)
- Simulation-6 of The Most Embarrassing Mistakes You Can Make - ENGINEERINGDocument8 pagesSimulation-6 of The Most Embarrassing Mistakes You Can Make - ENGINEERINGmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Material Modeling Virtual Biomechanical 2008 FDocument15 pagesAdvanced Material Modeling Virtual Biomechanical 2008 FmatmeanNo ratings yet
- SIMULIA Abaqus Topology Optimization ModuleDocument2 pagesSIMULIA Abaqus Topology Optimization ModulericawaltNo ratings yet
- Thesis Step by Step Abaqus optimizationFULLTEXT01 PDFDocument199 pagesThesis Step by Step Abaqus optimizationFULLTEXT01 PDFmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Aircraft ImpactDocument64 pagesAircraft ImpactmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Twu GM Final 3232012Document10 pagesTwu GM Final 3232012matmeanNo ratings yet
- 08 Havlicek Synerma Abaqus-And-AddonsDocument28 pages08 Havlicek Synerma Abaqus-And-AddonsmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Topology and Shape Optimization With AbaqusDocument41 pagesTopology and Shape Optimization With AbaqusPhuongDx100% (1)
- Abaqus Topology Optimization Sandeep Urankar ATOM SGL RUM 2011Document41 pagesAbaqus Topology Optimization Sandeep Urankar ATOM SGL RUM 2011matmeanNo ratings yet
- Module1 Beam Bending PDFDocument29 pagesModule1 Beam Bending PDFMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEM0% (1)
- Latest Enhancements in CAE and ATOMDocument37 pagesLatest Enhancements in CAE and ATOMRichard Lara RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 09 GRM TruProducts OverviewDocument26 pages09 GRM TruProducts OverviewmatmeanNo ratings yet
- Axisymm TutorialDocument15 pagesAxisymm TutorialRavi JainNo ratings yet
- Elastic Foundation AnalysisDocument6 pagesElastic Foundation AnalysismatmeanNo ratings yet
- Kairos Thermo HF Natural Circulation Solar System for Domestic Hot Water ProductionDocument4 pagesKairos Thermo HF Natural Circulation Solar System for Domestic Hot Water ProductionFILID MADNo ratings yet
- Lab 2 HardnessDocument8 pagesLab 2 HardnessMuhammad Zulhilmi0% (1)
- Response of a turbulent boundary layer to a step change in surface roughnessDocument41 pagesResponse of a turbulent boundary layer to a step change in surface roughnessFreddie RomeroNo ratings yet
- Apex Status - Issue 2 (2-01-2008)Document22 pagesApex Status - Issue 2 (2-01-2008)BorisLundbergNo ratings yet
- 2007 08 27 KermanMomtazan KHD OFF ShoreTraining Program CementGrindingProcessDocument84 pages2007 08 27 KermanMomtazan KHD OFF ShoreTraining Program CementGrindingProcessAnonymous iI88Lt100% (2)
- Sheet Metal Forming: Deep Drawing of Rectangular and Asymmetric PartsDocument17 pagesSheet Metal Forming: Deep Drawing of Rectangular and Asymmetric PartsBachLeCaoNo ratings yet
- Manual NovaturnDocument86 pagesManual NovaturnVictor SerranoNo ratings yet
- Power Screw ReportDocument15 pagesPower Screw ReportTanvesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Exercises Marine Engineer + Internal Combustion EnginesDocument3 pagesExercises Marine Engineer + Internal Combustion EnginesGeorge GaneaNo ratings yet
- KALMAR DRS 4531 - S5 Pareparts - PEÇAS Merge PDFDocument610 pagesKALMAR DRS 4531 - S5 Pareparts - PEÇAS Merge PDFBreno Cambraia Lanznaster100% (5)
- Heavy lifting skidding system specificationsDocument1 pageHeavy lifting skidding system specificationsm4l4ysiaNo ratings yet
- McCormick X60 Series (2011-2014) - RP67 - X60.50 Tractor Service Repair Manual PDFDocument25 pagesMcCormick X60 Series (2011-2014) - RP67 - X60.50 Tractor Service Repair Manual PDFfjkkekmdmNo ratings yet
- Codes and Standards: Piping EngineeringDocument23 pagesCodes and Standards: Piping EngineeringAnnieMalikNo ratings yet
- Kramer Steven PDFDocument32 pagesKramer Steven PDFFurkan YılmazNo ratings yet
- Pile CapDocument27 pagesPile CapHafeel Ahamed Ashraf AliNo ratings yet
- Andromeda V1.2 Assembly GuideDocument19 pagesAndromeda V1.2 Assembly Guidenajoko6753No ratings yet
- Characterization of Hybrid Aluminum Matrix Composites For Advanced Applications - A ReviewDocument11 pagesCharacterization of Hybrid Aluminum Matrix Composites For Advanced Applications - A ReviewMr. K.S. Raghul Asst Prof MECHNo ratings yet
- Figure R4-1: Vacuum Column FlowsheetDocument18 pagesFigure R4-1: Vacuum Column Flowsheetnico123456789No ratings yet
- Sp329a PRIMAAX EX For Mack HDT PDFDocument6 pagesSp329a PRIMAAX EX For Mack HDT PDFJonathan Smith Vargas torresNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Load Test AnalysisDocument6 pagesInduction Motor Load Test AnalysisCønstäh Van Der WüppertälärîanskíhNo ratings yet
- Dean Brochure High TempDocument10 pagesDean Brochure High TempAntonio VelardeNo ratings yet
- (Datasheet) Eriks - Ketron Peek-1000Document2 pages(Datasheet) Eriks - Ketron Peek-1000Carlos AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Nordson 2018 Replacement Parts Catalog PDFDocument318 pagesNordson 2018 Replacement Parts Catalog PDFsaadalam218_773301970% (1)
- EMTOP Tools Guide: Affordable Power Tools & Hand ToolsDocument32 pagesEMTOP Tools Guide: Affordable Power Tools & Hand ToolsDIELECTRIC INSTALACIONES S.A.SNo ratings yet
- Plugin-2004 Evinrude JohnsonDocument172 pagesPlugin-2004 Evinrude Johnsonjohnnyg02275% (4)
- 2023-05-16 Package 21 OC Rev.4Document123 pages2023-05-16 Package 21 OC Rev.4pham locNo ratings yet
- Dugoff Tire ModelDocument1 pageDugoff Tire Modelkmallon12No ratings yet
- Introduction to Ultrasonic Testing PrinciplesDocument116 pagesIntroduction to Ultrasonic Testing PrinciplesMuhamad AnwarudinNo ratings yet
- Tables of Contents: ParveenDocument7 pagesTables of Contents: ParveensambhajiNo ratings yet