Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Design Assessment Criteria
Uploaded by
hillamngOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural Design Assessment Criteria
Uploaded by
hillamngCopyright:
Available Formats
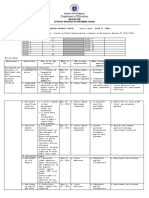
Structural systems: design and assessment 2013
Grading of projects
Methodology in conceptual design
Background information
1 General project information is given
2 The task, starting point, is well defined
3 Complete conditions are given (geo, climate, working area, urban)
4 Consequences for design are recognised (information is analysed and some conclusions are
drawn)
Design goal
1 Basic requirements are listed
2 Demands are expressed
3 Requirements and demands are analysed to developed goals (analysis)
4 A clear vision is expressed that helps to search for certain solutions
Alternative solutions
1 It is clear that more than 3 alternatives have been considered
2 Variation of building systems and materials exists
3 Variation in load distribution is also considered
4 Variation of stabilising systems is also considered
Evaluation criteria
1 Criteria are formulated and ranked
2 The criteria are specific and related to the project (not too general)
3 Developed criteria (criteria are explained: clear how to use the criteria in evaluation)
4 Reflections and development are shown (analysis)
Risk analysis
1 Critical events are identified
2 Risks are evaluated (probability and consequence are analysed)
3 The risks are considered in the evaluation
4 Solutions are developed to reduce risks
Service life design
1 Service life period is specified or assumed
2 Exposure and possible problems are identified and presented
3 Measures are taken (related to actual exposure)
4 Different components and different actions are considered and evaluated
Evaluation of alternatives
1 Evaluation matrix is given
2 Comments, motivations, pros cons for alternative solutions are given
3 Complete final alternatives are considered
4 Reflections and development are shown (analysis of evaluation results)
Proposed structural concept
Structural lay-out and configuration
1 Structural lay-out in typical plan is given
2 Structural lay-out with variations in all plans is given
3 Structural lay-out including foundation is given
4 Structural lay-out including all main structural members is given
Main structural units behaviour
1 Common structural units are denoted, but not specified concerning boundary conditions and
load direction.
2 Common structural units are explained in text or calculations, but important units are not
explained, for instance bracing units and in-plane action of floors.
3 The behaviour of all essential main units is well explained, but with minor
misunderstandings or some units are missing, for instance action of facades.
4 The behaviour of all main units is well explained.
Way to carry and distribute vertical and horizontal load
1 Typical vertical load path is presented
2 Load distribution at typical floor is presented in clear sketches
3 Relation between all vertical load paths and foundation is clear
4 Load distribution of all floors including shift of load paths is presented
Way to carry and distribute vertical and horizontal load
1 Stabilising members in two main directions are presented
2 Load path between stabilising system and foundation is clear
3 Load distribution between stabilising units is presented
4 Load paths for horizontal load are presented and explained including action of facades, floor
and roofs
Dimensions of main units
1 Dimensions of common structural units are presented but not explained
2 Dimensions of common structural units are specified based on calculations or design aids,
but important units are missing, for instance bracing units.
3 Dimensions of all essential are specified based on calculation or design aids but with minor
misunderstandings or some units are missing
4 All main units are specified on the basis of appropriate calculations or design aids.
Structural materials with specified requirements
Connections and important details
1 Selected typical connections are presented.
2 Connections are presented and explained but, important connections and details are missing,
for instance fixation of bracing units, or there are major misunderstandings.
3 All essential connections and details are presented, but with some minor mistakes in
proposed solutions.
4 All essential connections and details are presented with appropriate solutions.
Faade solutions and detailing
Production
1 Prefabricated and cast-in-place units are distinguished
2 The way of production is treated
3 Various steps in production are identified and presented
4 The production process is presented and explained
Review of other work and reflection of own work
Review of other presentation and reflection of own work
1 Questions to other group are given (repetition of opposition)
2 Advices for improvement of slide presentation are given
3 Developed advices on conceptual design procedure exist or own learning outcomes are
listed.
4 Both are presented.
You might also like
- Successful Instrumentation and Control Systems Design, Second EditionFrom EverandSuccessful Instrumentation and Control Systems Design, Second EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- IB Design Technology Grading RubricDocument4 pagesIB Design Technology Grading RubricJennifer ColemanNo ratings yet
- 3.3.2. Data Dictionary (Reference Shelly Cashman Books) 3.3.3. UML Diagrams (Any Applicable) (Use Case / Class Diagram / StateDocument2 pages3.3.2. Data Dictionary (Reference Shelly Cashman Books) 3.3.3. UML Diagrams (Any Applicable) (Use Case / Class Diagram / StateNico GallegoNo ratings yet
- Crack Guid LineDocument160 pagesCrack Guid LineSheena Peralta100% (1)
- Architecture Review - CRs-existing ProjectsDocument4 pagesArchitecture Review - CRs-existing ProjectsEdwin MbogoNo ratings yet
- Steel RCD Design Project Example FormatDocument64 pagesSteel RCD Design Project Example FormatFOEBE MARREY MANUELNo ratings yet
- Structural Modelling Manual by ARUPDocument44 pagesStructural Modelling Manual by ARUPGregor Clegane100% (2)
- Instruction Lecture 5: Evaluating and Implementing and Testing Product ModelsDocument114 pagesInstruction Lecture 5: Evaluating and Implementing and Testing Product ModelsberriebeerNo ratings yet
- Ec 4.5 PDFDocument8 pagesEc 4.5 PDFuzman1243No ratings yet
- Sample Format of Meeting Minutes ExampleDocument3 pagesSample Format of Meeting Minutes ExamplePaolo O. LozadaNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 - Object Oriented AnalysisDocument122 pagesChap 4 - Object Oriented AnalysisswathirohithNo ratings yet
- UNIT-III Chapter1,2,3 Full NotesDocument40 pagesUNIT-III Chapter1,2,3 Full NotesvijayalaxmibindlaNo ratings yet
- Solution Architecture Review Blueprint Preparation TemplateDocument15 pagesSolution Architecture Review Blueprint Preparation TemplateFoxman2kNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment Abstract (In BI) Abstrak (In BM) List of Figure List of TableDocument2 pagesAcknowledgment Abstract (In BI) Abstrak (In BM) List of Figure List of Tablex2dentNo ratings yet
- Outline of The Thesis For ComSciDocument8 pagesOutline of The Thesis For ComScijoyzkie14344No ratings yet
- Auxiliary Systems Compliance and Modification AnalysisDocument3 pagesAuxiliary Systems Compliance and Modification AnalysisFarooq Sajjad AlamNo ratings yet
- Phases and Interactions of The Design ProcessDocument3 pagesPhases and Interactions of The Design ProcessZephaniah MuneneNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis Course MaterialDocument13 pagesSystems Analysis Course MaterialHumphrey TshumaNo ratings yet
- IT Project Guidelines (Reviewed)Document3 pagesIT Project Guidelines (Reviewed)Wêēdhzæmē ApdyræhmæåñNo ratings yet
- Design Review ReportDocument3 pagesDesign Review ReportMahesh ButaniNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Structures Analysis and Design of StructuresDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Design of Structures Analysis and Design of StructuresAJNo ratings yet
- LO4 Document and Report On FindingsDocument5 pagesLO4 Document and Report On Findingsasnake bogaleNo ratings yet
- Final Project Report, How To Write ItDocument2 pagesFinal Project Report, How To Write ItDinesh_Reddy_7190No ratings yet
- UNEG Quality Checklist GuidanceDocument6 pagesUNEG Quality Checklist GuidanceAlessandra Mae SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Role of Diagramming in Systems InvestigationDocument25 pagesRole of Diagramming in Systems InvestigationAnkita Shetty100% (1)
- T P (U I) : EST LAN Nit and NtegrationDocument16 pagesT P (U I) : EST LAN Nit and NtegrationỚt NhỏNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CadDocument29 pagesUnit 1 CadMuthuvel M82% (17)
- ISYS6300 - Business Process Fundamentals Week 10 Chapter 14 Systems DevelopmentDocument32 pagesISYS6300 - Business Process Fundamentals Week 10 Chapter 14 Systems DevelopmentNajia Al UmriNo ratings yet
- Embodiment DesignDocument18 pagesEmbodiment DesignOwens Hrj100% (1)
- Guidelines For The Quality Assurance Plan ChecklistDocument8 pagesGuidelines For The Quality Assurance Plan ChecklistManish PatelNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Phases of DesignDocument9 pagesWeek-1 Phases of DesigndvarsastryNo ratings yet
- Walden University Proposal/Dissertation Rubric: Research@waldenu - EduDocument18 pagesWalden University Proposal/Dissertation Rubric: Research@waldenu - Edudominique babisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document30 pagesChapter 3AdrianNo ratings yet
- Asl Testing - Template Test PlanDocument12 pagesAsl Testing - Template Test PlanBalaji ElanchezhiyanNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Assessment Criteria For Coursework (School-Based Assessment)Document4 pages5.3 Assessment Criteria For Coursework (School-Based Assessment)Mohd Mustafa AhmadNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Master Thesis Proposal PDFDocument2 pagesStructure of The Master Thesis Proposal PDFRanein Azmy Mostafa AlkhrysatNo ratings yet
- Formal Project Reports: EN-223 Research Project & PresentationDocument64 pagesFormal Project Reports: EN-223 Research Project & PresentationFAISAL RAHIMNo ratings yet
- Template and Models in Test Management: ISYS6264 - Testing and System ImplementationDocument38 pagesTemplate and Models in Test Management: ISYS6264 - Testing and System ImplementationWeebMeDaddyNo ratings yet
- Project Study OutlineDocument14 pagesProject Study OutlineLarriza JoieNo ratings yet
- Problem AnalysisDocument6 pagesProblem AnalysisShania Sarcia0% (1)
- MED ASSY- INTRODUCTIONDocument8 pagesMED ASSY- INTRODUCTIONSimphiweNo ratings yet
- KFUPM Marketing Research Problem Definition and ProposalDocument18 pagesKFUPM Marketing Research Problem Definition and ProposalPundaleek KalloliNo ratings yet
- Review Internal I OME753Document22 pagesReview Internal I OME753priya SNo ratings yet
- Sample Outline For Comprehensive Evaluation Report PDFDocument2 pagesSample Outline For Comprehensive Evaluation Report PDFzmrmanNo ratings yet
- New Approaches in EC3 - 0Document8 pagesNew Approaches in EC3 - 0angelobacigalupo72No ratings yet
- Embodiment DesignDocument46 pagesEmbodiment Designabel shimelisNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Analyzing ArchitectureDocument46 pagesUnit 3: Analyzing ArchitectureRajavamsiNo ratings yet
- Walden University Dissertation Rubric: March 19, 2009Document15 pagesWalden University Dissertation Rubric: March 19, 2009dominique babisNo ratings yet
- Foundation Level Learning ObjectivesDocument6 pagesFoundation Level Learning ObjectivesRoshni BijuNo ratings yet
- 3.3.3 Example - Issue Management Plan, V2.2Document7 pages3.3.3 Example - Issue Management Plan, V2.2Juan VeronNo ratings yet
- Constructive Evaluation: Method HandbookDocument64 pagesConstructive Evaluation: Method HandbookhatzikideeNo ratings yet
- Rubrics For Iip Final Report 20-22Document3 pagesRubrics For Iip Final Report 20-22Rahul PatelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structural DesignDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Structural DesignSaabir Gariire100% (1)
- StructuralModellingManual Arup PDFDocument44 pagesStructuralModellingManual Arup PDFAie Bantugan100% (8)
- Doclr ArchitectureDocument18 pagesDoclr ArchitectureruwanegoNo ratings yet
- CHE513Document22 pagesCHE513toluwaniNo ratings yet
- Functional Requirements Document ChecklistDocument8 pagesFunctional Requirements Document ChecklistmcsneedyNo ratings yet
- Organizational Theory - OutlineDocument5 pagesOrganizational Theory - OutlineMichelle VikseNo ratings yet
- 06 EC2WS Frank Geotechnics PDFDocument55 pages06 EC2WS Frank Geotechnics PDFLuigiForgerone100% (1)
- Sectional AreasDocument1 pageSectional AreasOmaidTanhaNo ratings yet
- 8x8 Pergola 2d v1Document18 pages8x8 Pergola 2d v1hillamngNo ratings yet
- ETABS Building Structure Analysis and Design ReportDocument34 pagesETABS Building Structure Analysis and Design ReportBasandharaAdhikari76% (38)
- According To Leonardo: The BodyDocument8 pagesAccording To Leonardo: The BodyAquiles GuimarãesNo ratings yet
- Concrete Construction Article PDF - Evaluating Cracks in Concrete Walls PDFDocument4 pagesConcrete Construction Article PDF - Evaluating Cracks in Concrete Walls PDFhillamngNo ratings yet
- Woodspec Final - Section BDocument58 pagesWoodspec Final - Section BmcbluedNo ratings yet
- Model Earthquake Loads in Robot Structural AnalysisDocument15 pagesModel Earthquake Loads in Robot Structural Analysisliviubajenaru100% (1)
- Safety Evaluation of Concrete Structures With Nonlinear AnalysisDocument118 pagesSafety Evaluation of Concrete Structures With Nonlinear AnalysishillamngNo ratings yet
- TIMBER CONNECTION DESIGNDocument17 pagesTIMBER CONNECTION DESIGNAlexandru OlaruNo ratings yet
- DeflectionDocument16 pagesDeflection1361rahmanNo ratings yet
- Bracing Sheet Application Guide - Jan 2012 - LRDocument20 pagesBracing Sheet Application Guide - Jan 2012 - LRhillamng100% (1)
- Classification of Micropile Underpinning Methods EDocument17 pagesClassification of Micropile Underpinning Methods EhillamngNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages1 PB PDFwerdubobNo ratings yet
- Solved MDOF Example PDFDocument9 pagesSolved MDOF Example PDFhillamngNo ratings yet
- 8 Design of Walls PDFDocument48 pages8 Design of Walls PDFtutulayNo ratings yet
- Design of Mat SDDocument18 pagesDesign of Mat SDNuar FendiNo ratings yet
- Acee 2014-3 Ce A - Knoppik-WróbelDocument13 pagesAcee 2014-3 Ce A - Knoppik-WróbelhillamngNo ratings yet
- PS 33 Cracks in Structural ConcreteDocument1 pagePS 33 Cracks in Structural ConcretershyamsNo ratings yet
- Crack Control in Concrete StructuresDocument22 pagesCrack Control in Concrete StructuresErkan Şamhal100% (1)
- Flow Induced Excitation On Basic ShapesDocument26 pagesFlow Induced Excitation On Basic ShapeshillamngNo ratings yet
- Classification of Micropile Underpinning Methods EDocument17 pagesClassification of Micropile Underpinning Methods EhillamngNo ratings yet
- Sectional AreasDocument1 pageSectional AreasOmaidTanhaNo ratings yet
- Manual Roof Drainage System HRWallingford SR620Document78 pagesManual Roof Drainage System HRWallingford SR620hillamngNo ratings yet
- Pitch Roof Specs PDFDocument24 pagesPitch Roof Specs PDFyanickdouce1206No ratings yet
- Bridge Design Eurocodes Worked ExamplesDocument438 pagesBridge Design Eurocodes Worked Examplespradeepjoshi007100% (4)
- Icc - Ibc Page 231Document1 pageIcc - Ibc Page 231hillamngNo ratings yet
- Distributors Manual On Geosynthetics and GeotextilesDocument44 pagesDistributors Manual On Geosynthetics and Geotextileshillamng100% (1)
- Public Schools Band Curriculum GuideDocument53 pagesPublic Schools Band Curriculum GuideLuis BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Movers Speaking Test OverviewDocument57 pagesMovers Speaking Test OverviewThu HợpNo ratings yet
- Guidance for internal audit standards implementationDocument8 pagesGuidance for internal audit standards implementationkaranziaNo ratings yet
- 9arts GR 10 LM - Qtr4 (8 Apr 2015)Document18 pages9arts GR 10 LM - Qtr4 (8 Apr 2015)John Carlo Benitez100% (2)
- Philippine college recognizes teaching excellenceDocument13 pagesPhilippine college recognizes teaching excellenceCes ReyesNo ratings yet
- My Final NagidDocument36 pagesMy Final NagidRenalene BelardoNo ratings yet
- Notification DetailedDocument28 pagesNotification DetailedraghuNo ratings yet
- Letter To SpeakersDocument5 pagesLetter To SpeakersAnnalie Delera CeladiñaNo ratings yet
- Math7 - q1 - Mod12 - Arranging Real Numbers On A Number Line - v3Document25 pagesMath7 - q1 - Mod12 - Arranging Real Numbers On A Number Line - v3Vicente TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Plan of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSustainable Development Plan of The PhilippinesZanter GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Houran - Do Online Matchmaking Tests WorkDocument21 pagesHouran - Do Online Matchmaking Tests Workyasirzaidi1No ratings yet
- Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson PlanDocument1 pageBasic Triangle Congruence Lesson Planapi-219434647No ratings yet
- Division of Misamis Occidental Training Design Action Research Seminar Workshop Venue: TBA Date: TBA Time: 8:00 AM - 4:30 PM A. RationaleDocument6 pagesDivision of Misamis Occidental Training Design Action Research Seminar Workshop Venue: TBA Date: TBA Time: 8:00 AM - 4:30 PM A. RationaleDENMARK100% (1)
- Geometer's Sketchpad Unit for GeometryDocument3 pagesGeometer's Sketchpad Unit for Geometry'Adilin MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Technical and Business WritingDocument3 pagesTechnical and Business WritingMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- Samuel Itman: Education Awards/CertificatesDocument1 pageSamuel Itman: Education Awards/Certificatesapi-396689399No ratings yet
- General Zoology 1.28 PDFDocument1,057 pagesGeneral Zoology 1.28 PDFMelqui Magcaling100% (2)
- Learning Difficulties 1 - PrintableDocument20 pagesLearning Difficulties 1 - PrintableNona AliNo ratings yet
- Caudia Vs Superintendent of PMA-fullDocument42 pagesCaudia Vs Superintendent of PMA-fullJerome C obusanNo ratings yet
- The Hen in A Pen TBDocument5 pagesThe Hen in A Pen TBmauroNo ratings yet
- Final Professional M.B.B.S. Examination of July 2021: Select Student TypeDocument4 pagesFinal Professional M.B.B.S. Examination of July 2021: Select Student Typeasif hossainNo ratings yet
- Walled City of Lahore Authority - Wcla: S T NS T NDocument4 pagesWalled City of Lahore Authority - Wcla: S T NS T NSajidComsatsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 ArtsDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 8 ArtsArthur John BaloNo ratings yet
- 0452 s07 Ms 3 PDFDocument10 pages0452 s07 Ms 3 PDFAbirHudaNo ratings yet
- Free E Book India 2011Document414 pagesFree E Book India 2011RameshThangarajNo ratings yet
- What Great Principals Do Differently Book ReviewDocument4 pagesWhat Great Principals Do Differently Book Reviewapi-248885941100% (1)
- PR1 Sample Research MethodologyDocument25 pagesPR1 Sample Research MethodologyAliyah Wayne SunNo ratings yet
- Adult Esol Core Curriculum v1Document413 pagesAdult Esol Core Curriculum v1arnoldho_20003039100% (1)
- Enrolment Action Plan Against COVID-19Document4 pagesEnrolment Action Plan Against COVID-19DaffodilAbukeNo ratings yet
- QMS - Iso 9001-2015 Lead AuditorDocument4 pagesQMS - Iso 9001-2015 Lead AuditorSalehuddin Omar KamalNo ratings yet