Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 3 Dan Skema
Uploaded by
Cikgu FaizalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 3 Dan Skema
Uploaded by
Cikgu FaizalCopyright:
Available Formats
JABATAN PENDIDIKAN KELANTAN
SULI T Nama : .
4531/2
FIZIK Tingkatan : .
Kertas 2
2 jam
FIZIK SET 3
KERTAS 2
Masa : 2 Jam 30 minit
JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU
1. Kertas soalan ini adalah dalam dwibahasa.
2. Soalan dalam bahasa inggeris mendahului
soalan sepadan dalam bahasa Melayu
3. Calon dibenarkan menjawab keseluruhan
atau sebahagian soalan sama ada dalam bahasa
Inggeris atau bahasa Melayu.
4 Calon dikehendaki membaca maklumat
di halaman belakang kertas soalan ini
Kertas Ujian ini mengandungi 31 muka surat bercetak .../LIHAT SEBELAH
Untuk Kegunaan Pemeriksa
Bahagian
Soalan
Markah
Penuh
Markah
Diperolehi
A
1 4
2 5
3 6
4 7
5 8
6 8
7 10
8 12
B
9 20
10 20
C
11 20
12 20
Jumlah
The following information may be useful. The symbols have their usual meaning.
Maklumat berikut mungkin berfaedah. Simbol-simbol mempunyai makna yang biasa.
1. a = v u 16. Power, P = energy
t time
2. v
2
= u
2
+ 2 as 17. V = IR
3. s = ut + 1 at
2
18. Power, P = IV
2 Kuasa
4. Momentum = mv 19. N
s
= V
s
N
p
V
p
5. F = ma 20. Efficiency = I
s
V
s
x 100 %
(kecekapan) I
p
V
p
6. Kinetic energy = 1 mv
2
Tenaga kinetik 2 21. 1 = 1 + 1
f u v
7. Gravitational potential energy = mgh 22. n = sin i
Tenaga keupayaan graviti sin r
8. Elastic potential energy = 1 Fx 23. n = Real depth
Tenaga keupayaan kenyal 2 Apparent depth
9. = m 24. = ax
V D
10. Pressure, P = hg. 25. Q= It
Tekanan
11. Pressure, P = F 26. E = I (R + r)
Tekanan A
27. eV = mv
2
12. Heat, Q = mc
Haba 28. g = 10 ms
-2
13. PV = Constant (pemalar)
14. E = m c
2
15. v = f
SECTION A
BAHAGIAN A
[60 marks]
[60 markah]
Answer all questions in this section.
Jawab semua soalan dalam bahagian ini.
1. Diagram 1 shows a boy is shouting in front of a building . After 1 second, an
echo is heard.
Rajah 1 menunjukkan seorang budak berteriak di hadapan sebuah bangunan.
selepas satu saat, satu gema kedengaran.
Diagram 1
Rajah 1
(a) Complete the sentence below by ticking ( ) the correct box.
Lengkapkan pernyataan di bawah dengan () pada kotak yang betul
Sound wave is a
Gelombang bunyi adalah
transverse wave
gelombang melintang
longitudinal wave
gelombang membujur
[ 1 mark ]
[1 markah]
(b) State the wave phenomenon that occurred.
Nyatakan fenomena yang terlibat
[ 1 mark ]
[1 markah]
(c) State the change in the velocity and frequency of the sound wave after it hit the
building
Nyatakan perubahan dalam halaju dan frekuansi gelombang bunyi selepas
menghentam bangunan
(i) Velocity
Halaju
..
(ii) Frequency
frekuansi
[ 2 marks]
[2 markah]
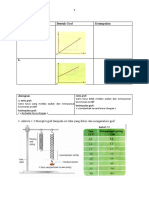
2 Diagram 2.1 shows a container filled with liquid X. Liquid X spurts through the hole
at horizontal distance, d, due to pressure.
Rajah 2.1 menunjukkan sebuah bekas berisi cecair X. Cecair X memancut keluar
melalui lubang pada jarak mengufuk , d, disebabkan tekanan.
Diagram 2.1
Rajah 2.1
(a) What is the meaning of pressure?
Apakah maksud tekanan?
..............................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) Give two factors that affect the pressure of liquid.
Beri dua faktor yang mempengaruhi tekanan cecair.
................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(c) Calculate the pressure of liquid X at the hole. The density of liquid X is
900 kgm
-3
.
Hitung tekanan cecair X pada lubang itu. Ketumpatan cecair X ialah is
900 kgm
-3
.
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(d) What happen to the horizontal distance, d, when liquid X is replaced by a higher
density of liquid.
Apakah yang berlaku kepada jarak mengufuk, d, apabila cecair X digantikan
dengan cecair yang lebih tumpat.
..............................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
3. Diagram below shows a simple electromagnet.
Rajah di bawah menunjukkan satu electromagnet ringkas.
X
(a) What is the meaning of electromagnet?
Apakah maksud elektromagnet?
..
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) When the switch is turned on:
Bila suis dihidupkan:
(i) Draw the pattern of magnetic field on Diagram above.
Lukisan corak medan magnet pada Rajah di atas.
[ 1 mark]
[ 1markah]
(ii) State the magnetic pole at X
Nyatakan kutub magnet pada X.
.
[ 1 mark]
[ 1markah]
(c) State what happens to the pin when switch is switch off
Nyatakan apa yang berlaku kepada pin itu bila suis dimatikan.
..
[ 1 mark]
[ 1markah]
(d) State on suggestion to increase the strength of electromagnet.
Nyatakan satu cara untuk meningkatkan kekuatan electromagnet.
...
[ 1 mark]
[ 1markah]
(e) State one application of electromagnet.
Nyatakan satu kegunaan electromagnet.
[ 1 mark]
[ 1markah]
4. Diagram 4.1 below shows an object, O, is placed in front of a lens. The focal point
of that lens is given as F.
Rajah 4.1 di bawah menunjukkan satu objek, O, diletakkan di hadapan sebuah
kanta. Titik fokus kanta tersebut diberikan sebagai F.
Diagram 4.1
Rajah 4.1
Based on diagram 4.1,
Berdasarkan rajah 4.1,
(a) name the type of lens.
Namakan jenis kanta tersebut.
[ 1 mark]
[ 1 markah ]
F F O
(b) (i) draw ray diagram from the object O, to show how the image of the object is
formed.
lukiskan gambarajah sinar dari objek O, untuk menunjukkan bagaimana
imej terbentuk.
[ 3 marks]
[3 markah ]
(ii) state one characteristic of the image formed.
nyatakan satu ciri imej yang terbentuk.
[ 1 mark / markah ]
(c) An object is placed 30 cm in front of that lens and the focal length 20 cm.
Calculate the image distance formed by the lens.
Satu objek diletakkan 30 cm di hadapan kanta tersebut dan panjang fokus
kanta itu adalah 20 cm. Kirakan jarak imej yang terhasil daripada kanta itu.
[ 2 marks]
[2 markah ]
5. Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2 shows an experiment to study the relationship
between the temperature and the pressure of a gas.
Diagram 5.1 shows the beaker is heated for 5 minutes while Diagram 5.2 shows
the beaker is heated for 10 minutes.
Rajah 5.1 dan Rajah 5.2 menunjukkan satu eksperimen yang dilakukan untuk
mengkaji hubungan di antara suhu dan tekanan suatu gas.
Rajah 5.1 menunjukkan bikar dipanaskan untuk 5 minit manakala Rajah 5.2
menunjukkan bikar dipanasakan selama 10 minit.
Diagram 5.1 Diagram 5.2
Rajah 5.1 Rajah 5.2
Based on diagram 5.1 and 5.2,
Berdasarkan rajah 5.1 dan 5.2,
(a) State the most suitable measuring instrument to be used at X.
Nyatakan alatan pengukuran yang paing sesuai digunakan di X.
[ 1 mark ]
[1 markah ]
(b) Compare:
Bandingkan :
(i) Temperature trapped air inside the round flask.
Suhu udara terperangkap di dalam kelalang bulat.
[ 1 mark ]
[1 markah ]
(ii) The reading of the measuring instrument X.
Bacaan alat pengukuran X.
[ 1 mark ]
[ 1 markah ]
(iii) The volume of trapped air inside round flask.
Isipadu udara terperangkap di dalam kelalang bulat.
[ 1 mark ]
[1 markah ]
(c) Using your answer in 5 (b)(i) and 5 (b)(ii), state a relationship between the
temperature of trapped air and the reading of measuring instrument X.
Menggunakan jawapan anda di 5(b)(i) dan 5(b)(ii), nyatakan hubungan di
antara suhu udara terperangkap dan alat pengukuran X.
[ 1 mark]
[1 markah ]
(d) Using the Kinetic Molecular Theory, explain your answer in 5 (c).
Menggunakan Teori Kinetik Molekul, terangkan jawapan anda di 5 (c).
[ 2 marks ]
[ 2 markah ]
(e) Name a physics law involved in the above observation.
Namakan satu hukum fizik yang terlibat dalam pemerhatian di atas.
[ 1 mark ]
[ 1markah]
6. Diagram 6.1 shows a set-up of apparatus when measuring the radioactivity of
radioactive substances using a G-M tube which is connected to a rate meter.
Rajah 6.1 menunjukkan susunan radas apabila mengukur keradioaktifan bagi
bahan radioaktif dengan menggunakan tiub G-M yang disambung kepada meter
kadar.
Diagram 6.1
Rajah 6.1
(a) What is the meaning of radioactivity?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan keradioaktifan?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) Give a reason why the reading of the rate meter does not drop to zero
when the radioactive substance is removed.
Beri satu sebab mengapa bacaan meter kadar tidak menjadi sifar
apabila bahan radioaktif dialihkan.
..
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
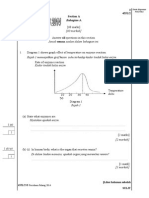
Diagram 6.2 shows an activity against time graph for radioactive substance X and Y.
Rajah 6.2 menunjukkan graf aktiviti melawan masa bagi bahan radioaktif X dan
Y.
Diagram 6.2
Rajah 6.2
Based on Diagram 6.2, compare
Berdasarkan Rajah 6.2, bandingkan
(i) The rate of decay for X and Y
Kadar pereputan bagi X dan Y
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) The half life of X and Y
Separuh hayat bagi X dan Y
.
.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) The percentage remains undecayed after 30 minutes.
Peratus yang belum mereput selepas 30 minit.
..........................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(d) Based on the answers in 6(c), state the relationship between the rate of
decay and
Berdasarkan jawapan di 6(c), nyatakan hubungan antara kadar pereputan
dan
(i) the half life of radioactive substance.
separuh hayat bagi bahan radioaktif.
..............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) the activity for the substance.
Aktiviti bagi bahan.
...........................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(e) On the Diagram 6.2, mark with T to show the half life of substance X.
Pada Rajah 6.2, tandakan T untuk menunjukkan separuh hayat bagi
bahan X.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
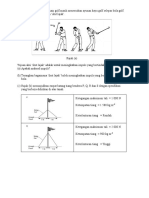
7 Diagram 7.1 shows a short- put event athlete throwing an iron ball of mass 3.0 kg.
The work done by the athlete causes the distance of projection of the iron ball is
12.0 m.
Rajah 7.1 menunjukkan seorang atlet acara lontar peluru sedang melontar sebiji
bola besi berjisim 3.0 kg.
Kerja yang dilakukan oleh atlet itu menyebabkan jarak projeksi bola besi itu sejauh
12.0 m
(a) What is the meaning of work?
Apakah maksud kerja?
...........................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(b) The iron ball is thrown by the athlete using the force of 100 N.
Bola besi itu dilontar oleh atlet menggunakan daya 100 N.
(i) Calculate the work done by the athlete to throw the iron ball
Hitung kerja yang dilakukan oleh atlet itu untuk melontar bola besi itu.
[ 2 mark ]
[ 2 markah ]
(ii) State the type of energy gained by the iron ball.
Nyatakan jenis tenaga yang diperoleh oleh bola besi itu.
...........................................................................................................................
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) Determine the horizontal velocity of the iron ball.
Tentukan halaju mengufuk bola besi itu.
[ 2 mark ]
[ 2 markah ]
(c) The modifications should be done by the athlete to increase the distance of
projection of the iron ball. State the suitable modifications and give one
reason for the modifications.
Modifikasi perlu dilakukan oleh atlet itu untuk meningkatkan jarak projeksi
bola besi itu. Nyatakan modifikasi yang sesuai dan beri satu sebab untuk
modifikasi itu.
(i) Distance of hand movement:
Jarak pergerakan tangan:
.......................................................................................................................
Reason:
Sebab:
.......................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(ii) The angle of throwing
Sudut lontaran
.......................................................................................................................
Reason:
Sebab:
.......................................................................................................................
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
8. Diagram 8 shows a toaster with specification of 240 V, 1000 W.
Rajah 8 menunjukkan sebuah pembakar roti berspesifikasi 240V, 1000W
Diagram 8
Rajah 8
(a) What is meant by the label 240V, 1000 W on the toaster?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan label 240 V, 1000W pada pembakar roti itu?
.........................................................................................................................
[ 1 mark ]
[1 markah]
(b) Based on Diagram 8, calculate
Berdasarkan Rajah 8, hitungkan
(i) current flowing through the toaster.
arus mengalir melalui pembakar roti
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(ii) resistance of the heater of the toaster?
rintangan bagi pemanas pembakar roti tersebut?
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
(c) Table 8.1 shows three different types of heater to be used in toaster in
Diagram 8 above.
Jadual 8.1 menunjukkan tiga jenis pemanas berbeza yang akan digunakan
di dalam pembakar roti pada Rajah 8 diatas.
Heater
Pemanas
Power supplied to
the toaster
Kuasa dibekalkan
kepada pembakar
roti
Power produced
(heat)
Kuasa dihasilkan
(haba)
P 450Js
-1
430Js
-1
Q 550Js
-1
525Js
-1
R 600Js
-1
575Js
-1
Table 8.1
Jadual 8.1
(i) State the effect of thickness of heater to the rate of energy loss
in the heater.
Nyatakan kesan ketebalan pemanas terhadap kadar kehilangan
tenaga pada pemanas.
...........
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) Calculate the efficiency of each heaters P,Q, and R.
Hitungkan kecekapan setiap pemanas P,Q dan R.
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
(iii) Suggest the most suitable heater to be used in the toaster.
Justify your choice.
Cadangkan pemanas yang paling sesuai digunakan di dalam
pembakar roti.
Berikan alasan bagi pilihan anda itu
...................
...................
[2 marks]
[2 markah]
SECTION B
BAHAGIAN B
[20 marks]
[20 markah]
Answer any one question from this section.
Jawab mana-mana satu soalan daripada bahagian ini.
9 Diagram 9.1 and Diagram 9.2 show two identical containers filled with same volume
of liquid X and liquid Y respectively. The density of both liquids is different. Both
liquids spurting out at different horizontal distances.
Rajah 9.1 dan Rajah 9.2 menunjukkan dua bekas yang serupa berisi cecair X dan
cecair Y dengan isipadu yang sama masing-masingnya. Ketumpatan kedua-dua
cecair itu berbeza. Kedua-dua cecair itu memancut keluar pada jarak-jarak
mengufuk yang berbeza.
Diagram 9.1 Diagram 9.2
Rajah 9.1 Rajah 9.2
(a) What is the meaning of density?
Apakah maksud ketumpatan?
[1 mark]
[ 1 markah]
(b) Based on Diagram 9.1 and Diagram 9.2,
Berdasarkan Rajah 9.1 dan Rajah 9.2,
(i) compare the depth of liquids, density of liquids and the horizontal distances
. of liquid spurting out.
bandingkan kedalaman cecair, ketumpatan cecair dan jarak pancutan
mengufuk cecair.
(ii) relate the density of liquid and the horizontal distance of liquid spurting out.
hubungkaitkan ketumpatan cecair dan jarak pancutan mengufuk cecair.
(iii) Deduce a relationship between density and the pressure of liquid.
Deduksikan hubungan antara ketumpatan dan tekanan cecair.
[5 marks]
[ 5 markah]
(c) Diagram 9.3 shows a cross section of a damn.
Rajah 9.3 menunjukkan keratan rentas sebuah empangan.
Diagram 9.3
Rajah 9.3
Compare the thickness of the wall of the damn at lower part and at upper part.
Explain your answer.
Bandingkan ketebalan dinding empangan itu pada bahagian atas dan pada
bahagian bawah. Terangkan jawapan anda.
[4 marks]
[ 4 markah]
(d) Diagram 9.4 shows a scuba diver suit
Rajah 9.4 menunjukkan pakaian seorang penyelam.
Diagram 9.4
Rajah 9.4
Using the appropriate physics concepts, explain the suggestions on the
characteristics and the design of the diver suit so that it is suitable to be worn by
a deep sea scuba diver.
Your answer should include on the following aspects:
Dengan menggunakan konsep fizik yang sesuai, terangkan cadangan bagi ciri-
ciri pakaian penyelam yang sesuai dipakai oleh seorang penyelam laut dalam.
Jawapan anda hendaklah termasuk aspek-aspek berikut:
(i) Type and characteristic of the material
Kekuatan bahan
(ii) Density of material.
Ketumpatan bahan
(iii) Thickness
Ketebalan
(iv) Size of the suit
Ukuran pakaian
[10 marks]
[ 10 markah ]
10. Diagram 10.1 and 10.2 shows an experiment to determine the wavelength of
monochromatic light waves.
Diagram 10.1 used a blue light source and Diagram 10.2 used a red light source.
Rajah 10.1 dan 10.2 menunjukkan satu eksperimen dwicelah Young untuk
menentukan panjang gelombang cahaya monokromatik.
Rajah 10.1 menggunakan sumber cahaya berwarna biru manakala Rajah 10.2
menggunakan sumber cahaya berwarna merah.
Diagram 10.1
Rajah 10.1
Diagram 10.2
Blue fringe
Pinggir biru
Red fringe
Pinggir merah
screen
skrin
Rajah 10.2
The dark and bright fringes are produced after the light passes through the slit.
Pemisahan dua celah, a, dan jarak antara dwicelah dengan skrin dalam kedua-dua
rajah, D, dalam kedua-dua rajah adalah malar. Pinggir-pinggir gelap dan cerah
dihasilkan setelah cahaya merambat melalui celah.
(a). What is meant by monochromatic light?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan cahaya monokromatik?
[1 mark / markah]
(b) Using diagram 10.1 and diagram 10.2, compare the distance between the
the dark and bright fringe separations, the wavelength and the distance
separation between two slit.
Use these observations to state the relationship between the distance
between the dark and bright fringe separations with the wavelength and
state the physics phenomenon involved.
Menggunakan rajah 10.1 dan rajah 10.2, bandingkan jarak pemisahan
antara pinggir-pinggir gelap dan cerah dihasilkan, panjang gelombang dan
jarak pemisahan antara dua celah.
Gunakan pemerhatian ini untuk menyatakan hubungan antara jarak
pemisahan pinggir-pinggir gelap dan cerah dihasilkan dengan panjang
gelombang dan nyatakan fenomena fizik yang terlibat.
[5 marks / markah]
(c) Diagram 10.3 shows ground cabin crew at airport is working. They have to
use noise-cancelling headphone to reduce the loud noise from aircraft and
also receive instruction from control tower.
Rajah 10.3 menunjukkan pekerja di landasan lapangan terbang sedang
bekerja. Mereka perlu menggunakan fon kepala batal bunyi untuk
mengurangkan bunyi bising dari pesawat dan menerima arahan dari
menara kawalan.
.
Diagram 10.3
Rajah 10.3
Diagram 10.4 shows the inside noise-canceling headphone. Explain how
the inside noise-canceling headphone can reduce the loud sound from
surrounding.
Rajah 10.4 menunjukkan bahagian dalaman fon kepala batal bunyi.
Terangkan bagaimana fon kepala batal bunyi ini dapat mengurangkan
bunyi bising daripada persekitaran.
Diagram 10.4
Rajah 10.4
[4 marks / markah]
(d) Diagram 10.5 shows the lecture room at university. Students complain
that some improvements need to be made to enhance the sound effect.
Rajah 10.5 menunjukkan keadaan bilik kuliah di sebuah universiti. Pelajar menyatakan bahawa beberapa penambahbaikkan perlu dilakukan untuk meningkatkan lagi kualiti kesan bunyi.
Using appropriate physics concepts, explain the use of the suitable equipment and furnishing to improve the sound effect during lecture.
Menggunakan konsep fizik yang sesuai, terangkan alatan dan perabot yang sesuai untuk meningkatkan lagi kesan bunyi semasa kuliah.
Diagram 10.5 / Rajah 10.5
Your answer should include the following aspects :
Jawapan anda hendaklah merangkumi aspek-aspek berikut :
(i) position of speakers and microphone
Kedudukan pembesar suara dan mikrofon
(ii) distance between two speakers
jarak antara dua pembesar suara
(iii) furniture installed in the lecture room
perabot yang dipasang di dalam bilik kuliah
(iv) other aspects that can be improve
aspek-aspek lain yang boleh ditingkatkan
[10 marks / markah]
Speaker
Pembesar
suara
Microphone
Mikrofon
SECTION C
BAHAGIAN C
[20 marks]
[20 markah]
Answer any one question from this section.
Jawab mana-mana satu soalan daripada bahagian ini.
11. Diagram 11.1 shows Mr Ali with mass 70 kg is sitting on the spring horse at a
playground. Diagram 11.2 shows Andy with mass 20 kg is sitting on the same
spring horse. The spring of the horse sat by Mr Ali is more compressed compared
to the spring of the horse sat by Andy. The mass of both spring horses, original
length of the spring and the elasticity are same.
Rajah 11.1 menunjukkan En Ali yang berjisim 70 kg sedang berada di atas spring
kuda. Rajah 11.2 menunjukkan Andy yang berjisim 20 kg sedang duduk di atas spring
kuda yang sama. Spring kuda mainan yang diduduki En Ali lebih termampat berbanding
dengan spring kuda mainan Andy. Jisim kedua kuda mainan, panjang asal spring dan
kekenyalan spring yang digunakan adalah sama.
(a) What is the meaning elasticity of a material?
Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan kekenyalan suatu bahan.
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
Diagram 11.2
Rajah 11.2
Diagram 11.1
Rajah 11.1
(b) Based on Diagram 11.1 and Diagram 11.2
Berdasarkan Rajah 11.1 dan Rajah 11.2
(i) Compare the mass of load, the extension of the springs and spring
constant.
Bandingkan jisim beban, pemanjangan spring dan pemalar
spring.
[ 3 marks]
[3 markah]
(ii) relate the forces acting on the springs and the mass.
Hubungkait daya yang digunakan ke atas spring dengan jisim
(iii) deduce a relationship between the extension of the spring and
the mass.
deduksikan hubungan antara pemanjangan spring dengan
jisim.
[ 2 marks]
[2 markah]
(c) Explain how the forces between the molecules caused the elasticity in solid
state.
Terangkan bagaimana daya-daya antara molekul - molekul
menyebabkan kekenyalan dalam keadaan pepejal.
[ 4 marks]
[4 markah]
(d) Diagram 11.3 shows a spring of suspension system of an ordinary bicycle.
Rajah 11.3 menunjukkan spring pada sistem suspensi basikal biasa.
Spring
You are required to give some suggestion to design the spring to enable it to be a
racing bicycle and effectively.
Using the knowledge and appropriate physics concept, explain your suggestions
based on the following aspects:
Anda dikehendaki memberi beberapa cadangan yang perlu dilakukan ke atas spring
untuk membolehkan ia digunakan sebagai basikal lumba dengan berkesan.
Menggunakan pengetahuan dan konsep fizik yang sesuai, terangkan cadangan anda
berdasarkan aspek aspek berikut :-
(i) Material used for the spring
Bahan yang digunakan untuk spring
(ii) The spring constant
Pemalar spring
(iii) The Length of the spring
Panjang spring
(iv) The Diameter of the spring
Diameter spring
(v ) The thicknees of spring wire
Ketebalan dawai spring
[10 marks]
[10 markah]
12 Diagram 12.1 shows a transistor circuit. The circuit is used to automatically switch
on the bulb at bright day .
Rajah 12.1 menunjukkan satu litar bertransistor. Litar ini digunakan sebagai suis
outomatik pada mentol di siang hari
Diagram 11.3
Rajah 11.3
(i) Name the type of the transistor.
Namakan jenis transistor
[ 1 mark ]
[1markah]
(ii) Explain how the bulb is lighted up at bright day
Jelaskan bagaimana mentol menyala pada siang hari
[4 marks]
[4 markah]
Diagram 12.2
Rajah 12.2
Diagram 12.2 shows a transistor circuit. Resistor M is a variable resistor and resistor N
is a fixed resistor. Bulb T will light up when the potential difference across N is at
least 1 V.
Rajah 12.2 menunjukkan satu litar transistor. Perintang M adalah perintang boleh
ubah manakala perintang N adalah perintang tetap. Mentol T akan menyala apabila
beza keupayaan merentasi N adalah sekurang-kurangnya 1 V.
(c) When the potential difference between Y and Z is 1 V,
Apabila beza keupayaan antara Y dan Z adalah 1 V,
(i) What is the potential difference across X and Z?
Berapakah beza keupayaan merentasi X dan Z?
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(ii) What is the potential difference across X and Y?
Berapakah beza keupayaan merentasi X dan Y?
Z
T
6 V
M
N
1000
X
Y
[1 mark]
[1 markah]
(iii) Calculate the maximum resistance, M that enables the bulb T is light up.
Hitungkan rintangan maksimum, M untuk membolehkan mentol T itu
menyala.
[3 marks]
[3 markah]
Diagram 12.3 shows four electronic circuits R, S, T and U with different specifications.
You are required to determine the most suitable electronic circuit to light up three
street lights 95 V, 65 W automatically with normal brightness when it is dark.
Rajah 12.3 menunjukkan empat litar elektronik R, S, T dan U dengan spesifikasi yang
berbeza. Anda dikehendaki menentukan litar elektronik yang paling sesuai untuk
menyalakan ketiga-tiga lampu jalan 95 V, 65 W secara automatik dengan kecerahan
normal apabila keadaan gelap.
Circuit Circuit diagrams
R
95 V
6 V
Relay
+
_
S
T
U
Diagram 12.3
Rajah 12.3
95 V
6 V
Relay
+
_
95 V
6 V
Relay
+
_
6 V
Study the specifications of all of the four circuits based on the following aspects:
Kaji semua spesifikasi tersebut berdasarkan aspek-aspek berikut:
The position of the light dependent resistor (LDR).
Kedudukan perintang peka cahaya (PPC).
The connection of the batteries.
Penyambungan bateri.
The arrangement of the street lights circuit.
Susunan litar lampu-lampu jalan
The use of a relay switch in the circuit.
Penggunaan suis geganti dalam litar.
Determine the most suitable circuit diagram to be chosen and give reasons for your
choice.
Tentukan gambarajah litar yang paling sesuai dipilih dan berikan sebab bagi pilihan
anda.
[10 marks]
END OF QUESTION PAPER
KERTAS SOALAN TAMAT
Question Mark Scheme
Sub
Mark
Total
Mark
1 (a)
(b)
(c) (i)
(ii)
longitudinal wave
reflection
change the direction
unchanged
1
1
1
1
4
2 (a)
Force per unit area
1
5
(b) Density
depth // gravitational acceleration
1
1
(c) P = 1.2 x 900 x 10
= 1.08 x 10
4
Pa
1
1
(d) Increase / further 1
TOTAL 5 M
3 (a)
(b) (i)
(ii)
(c)
(d)
(e)
Temporary magnet/ magnetic field produce when current
flow in the wire
Patten and direction are correct
S
Pin fall down
Increase the number of turn/electric current
Electric bell/circuit braker/relay
1
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL 6 M
4 (a)
(b) (i)
(ii)
(c)
concave lens
Kanta cekung
M1 ray from the object parallel to the principal
axis, diverge at F
sinar dari objek selari dengan paksi
utama, mencapah di F
M2 - ray from the object directly through the
centre of the lens
sinar dari objek terus ke tengah kanta
M3 - the point of intersection is the point where
image is form
titik persilangan ialah titik imej terbentuk
virtual / upright / smaller
maya / tegak / dikecilkan
M1
20
1 1
30
1
= +
v
M2 - v = -12 cm
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
7 M
5 (a)
5 (b) (i)
5 (b) (ii)
Bourdon Gauge
Tolok Bourdon
Temperaturer trapped air inside the round flask in diagram
5.2 is higher compare to diagram 5.1
Suhu udara terperangkap di dalam kelalang bulat pada rajah
5.2 lebih tinggi berbanding rajah 5.1
The reading of the measuring instrument X in diagram 5.2 is
1
1
1
F F O
I
5 (b) (iii)
5 (c)
5 (d)
5 (e)
higher compare to diagram 5.1
Bacaan alat pengukuran X pada rajah 5.2 lebih tinggi
berbanding rajah 5.1
The volume of trapped air inside round flask for diagram 5.1
and diagram 5.2 is same
Isipadu udara terperangkap pada rajah 5.1 dan rajah 5.2
adalah sama
When temperature of trapped air increase, the reading of
measuring instrument X increase.
Apabila suhu udara terperangkap meningkat, bacaan alat
pengukuran X meningkat.
M1 when the temperature of trapped air
Increas, the collision per unit area are
increase
apabila suhu udara terperangkap
meningkat, pelanggaran per unit luas
meningkat
M2 the pressure of gas will increase
Tekanan udara akan meningkat
Pressure Law
Hukum Tekanan
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL 8 M
6 (a)
(b)
(c) (i)
(ii)
(iii)
(d) (i)
(ii)
Spontaneous disintegration of unstable nucleus to become
more stable and in the process will emit radioactive rays
Gives a background reading
Rate of decay of Y is bigger than X // vice- versa
Half-life of Y is smaller than X //vice-versa
The percentage remains undecayed after 30 minutes of Y is
bigger than X // vice-versa
Half-life decreases, rate of decay increases
Activity for the substance decreases, rate of decay
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
(e)
increases.
Mark T
1
TOTAL
8 M
7 (a)
(b) (i)
(ii)
(iii)
(c) (i)
(ii)
Work = Force x displacement
Work = 100 x 12.0
= 1200 J
Kinetic energy
1200 = x 3 x V2
V = 28.28 ms-1
Further // longer
Increase the force
equal or less than 40
0
// small angle
Increase the forward velocity
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
TOTAL 10 M
8 (a)
(b)(i)
(ii)
(c)(i)
(ii)
When a potential difference of 240V is connected across
the heater, it will produce power of 1000J per second.
P = VI
1000W = 240VI
I = 1000W/240V
= 4.16A
R = V/I
= 240V/4.16A
= 57.69
The more the thickness of the wire, the lower the loss of
energy from the heater
Efficiency = Energy Output / Energy Input x 100%
E Filament P = 430 x 100 %
450
= 95.55%
E Filament Q = 525 x 100 %
550
= 95.45%
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
(iii)
E Filament R = 43 x 100 %
50
= 95.83%
Heater R has highest efficiency ie 95.83%
1
1
TOTAL 12 M
9 (a)
(b) (i)
(ii)
(iii)
(c)
(d)
Mass per unit volume
Depth of liquid in Diagram 9.1 = Diagram 9.2
Density of liquid in Diagram 9.1 > Diagram 9.2
Horizontal distance of liquid spurting out in Diagram 9.1 >
Diagram 9.2
The higher the density of liquid, the further the horizontal
distance of liquid spurting out
The higher the density, the higher the pressure
The wall at lower part is thicker than at upper part.
Water pressure is directly proportional to depth //
Water pressure increase as the depth of water increases
Higher force of water is produced at lower part.
Thicker wall is to withstand the high force
Modifications Reasons
Neoprene // elastic
synthetic
To insulate body / for thermal
protection /prevent heat loss
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
5
5
from body
Flexible Can move with the body
Low density material Lighter / small mass
Thick
Can withstand high pressure /
Protect from sharp object such
as coral
Tight fit / same size
to body
Reduce water resistance
2
2
2
2
10
TOTAL 20
10 (a)
10 (b)
10 (c)
One colour / one wavelength / one frequency of light
Satu warna / satu panjang gelombang / satu frekuensi
M1 the dark and bright fringe separation for
diagram 10.2
jarak pemisahan pinggir gelap dan cerah
bagi rajah 10.2 adalah lebih jauh
berbanding 10.1
M2 the wavelength of diagram 10.2 is longer
than diagram 10.1
panjang gelombang bagi rajah 10.2 adalah
lebih panjang berbanding rajah 10.1
M3 the distance separation between two slit
for diagram 10.1 and 10.2 is same
jarak pemisahan antara dua celah
bagi rajah 10.1 dan 10.2 adalah sama
M4 the distance between dark and bright
fringe separation increase, the wavelength
increase
jarak pemisahan pinggir gelap dan cerah
meningkat, panjang gelombang meningkat
M5 interferens
interferens
M1 microphone is used to detect noisy sound
wave from outside
mikrofon digunakan untuk mengesan
gelombang bunyi bising dari luaran
M2 sound wave is fed into noise cancelling circuit
Gelombang bunyi dihantar ke litar batal bunyi
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
5
10 (d)
M3 noise cancelling circuit will produce new
sound wave that is 180 degrees out of
phase with opposite direction from source.
Litar batal bunyi akan menghasilkan
gelombang bunyi baharu yang 180 darjah
berlainan fasa dan berlawanan arah
daripada sumber.
M4 destructive interference cancel the sound.
Gelombang memusnah membatalkan
bunyi
M1 position of speakers is in front of the microphone
Kedudukan pembesar suara adalah di hadapan
mikrofon
M2 to avoid disturbance / to prevent the sound from
speakers being amplified again by the microphones
Untuk mengelakkan gangguan / untuk mengelakkan
bunyi daripada pembesar suara dikuatkan semula oleh
mikrofon
M3 distance between two speakers is further to each
other
Jarak antara dua pembesar suara adalah berjauhan
antara satu sama lain
M4 so that constructive and destructive interference is
close together until they are hardly noticeable.
M5 covers the wall with soft board
Tutup bahagian dinding dengan lapisan lembut
M6 to reduces echoes effect
Mengurangkan kesan gema
M7 covers the floor with thick carpet
Tutup bahagian lantai dengan karpet tebal
M8 to reduces echoes effect
Mengurangkan kesan gema
M9 covers the wall with uneven/ rough surface
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
4
Tutup bahagian dinding dengan permukaan tidak rata
/ kasar
M10 to reduces echoes effect
Mengurangkan kesan gema
1
1
10
TOTAL 20 M
11 (a)
(b) (i)
(ii)
(iii)
(c)
Elasticity of a material is its property that enables it to return
to its original size and shape when the force that was acting
on it is removed.
Kekenyalan ialah sifat bahan yang boleh kembali ke saiz
dan bentuk asal apabila daya yang dikenakan ke atasnya di
alihkan.
- The mass of load in diagram 9.2 is bigger than 9.1
- Jisim beban dalam rajah 9.2 lebih besar 9.1
- The extension of the springs in diagram 9.2 is longer than
9.1
- Pemanjangan spring dalam rajah 9.2 lebih panjang 9.1
- Spring constant in diagram 9.1 is equal to 9.2
- Pemalar spring dalam rajah 9.1 sama 9.2
The increases the mass, the increases forces acting on the
springs / vice versa
Semakin bertambah jisim, semakin bertambah daya yang
bertindak terhadap spring / sebaliknya
The increases the mass, the increases the extension of the
springs / vice versa
Semakin bertambah jisim, semakin bertambah
pemanjangan spring / sebaliknya
- stretching causes molecules to be displaced away from
each other
apabila diregangkan, zarah-zarah berjauhan diantara satu
sama lain
- attractive intermolecular forces are acting to oppose the
stretching
daya tarikan antara molekul akan bertindak menentang
regangan
- when the force is removed
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
12(i) npn 1 1
12(ii) In bright day, the light-dependent resistor(LDR) has a very low
resistance.
Therefore the potential diference across LDR is low and hence
the potential difference across resistor R is high. The base
current flows
and cause a large collector current flows. The bulb lights up
1
1
1
1
Max
5
12(c)(i) V
X-Z
= 6 V 1 1
Apabila daya dialihkan
- attractive intermolecular forces greater than repulsive force
so that it can returns to its original form
daya tarikan bertambah dan melebihi daya tolakan supaya
ia kembali kepada bentuk asalnya
Modifications of the
spring
Reason
1. density is low
Ketumpatan rendah
small mass // light
jisim kecil // ringan
2. Spring constant is
high
Pemalar spring yang
tinggi
Not too stiff and can
oscillate with low frequency
Tidak terlalu keras dan
boleh bergetar dengan
frekuensi rendah
3. The length of the
Spring is short
Panjang spring ialah
pendek
- increases spring constant
- prevent mass and weight
- stiff and stronger
4. The diameter of the
spring is low
Diameter spring
ialah kecil
- increases spring constant
- prevent mass and weight
- stiff and stronger
5. The thickness of
spring wire is big
Ketebalan dawai
spring ialah besar
- increases spring constant
- prevent mass and weight
- stiff and stronger
1
2
2
2
2
2
1
TOTAL 20 M
12(c)(ii) V
X-Y
= 6 -1 = 5 V 1 1
12(c)(iii)
V
R R
R
V
N M
M
M
6
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
V
R
R
M
M
6
1000
5
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
5R
M
+ 5000 = 6R
M
R
M
= 5000
1
1
1
3
12(d) - LDR is connected at base circuit
- When intensity of light is low / dark, resistance of LDR
increases / so V
base
is large / transistor switched on
- Terminal positive of batteries is connected to collector
- So that the transistor is forward biased
- Bulbs are arranged in parallel circuit
- All bulbs are connected to voltage supply of 95V
- Relay switch is used
- So that the secondary circuit will switch on // So that the
electromagnet will switch on the secondary circuit
- Choose A
- Because LDR is connected at base circuit, terminal positive of
batteries is connected to collector; bulbs are arranged in parallel
circuit and relay switch is used.
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
10
TOTAL 20 M
You might also like
- Skema Soalan Ramalan K2 SPM Set 1 2023Document25 pagesSkema Soalan Ramalan K2 SPM Set 1 2023Gan Hock KiamNo ratings yet
- Latihan Fizik Kuantum SabahDocument13 pagesLatihan Fizik Kuantum SabahZaidah MYNo ratings yet
- SPM Trial 2017 Physics Qa KedahDocument85 pagesSPM Trial 2017 Physics Qa KedahniknadhiraNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 PPT t4 2017Document23 pagesKertas 2 PPT t4 2017Fathiyah MoradNo ratings yet
- (Spmsoalan) Soalan SPM 2014 Physics Paper 2 (Kertas 2 Fizik)Document35 pages(Spmsoalan) Soalan SPM 2014 Physics Paper 2 (Kertas 2 Fizik)SPM Soalan33% (3)
- SAINS - KOMPUTER JWPDocument15 pagesSAINS - KOMPUTER JWPsNo ratings yet
- 2022 Putrajaya Physics K2 Set - 1 JawapanDocument10 pages2022 Putrajaya Physics K2 Set - 1 Jawapanᴢᴏᴇʏ ɢᴀɴNo ratings yet
- Konsep FizikDocument16 pagesKonsep FizikMastura Hussin100% (1)
- Gelombang ElektromagnetDocument7 pagesGelombang ElektromagnetaghiillanNo ratings yet
- Pantulan DLM PenuhDocument1 pagePantulan DLM PenuhROSLINA BINTI ABDUL RASHID MoeNo ratings yet
- FIZIK2SET1Document36 pagesFIZIK2SET1Mister HafizalNo ratings yet
- Soalan Fizik Pertengahan TahunDocument28 pagesSoalan Fizik Pertengahan TahundarwishmajidNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Latihan Formatif Bab 5Document4 pagesJawapan Latihan Formatif Bab 5ROZITA BT OTHMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Bab 5b TB Fizik Tg4Document36 pagesBab 5b TB Fizik Tg4Yong Hong ThenNo ratings yet
- Fizik Kertas 2 Ting 4 Pertengahan Tahun 2012 TerengganuDocument35 pagesFizik Kertas 2 Ting 4 Pertengahan Tahun 2012 TerengganuSiew Çhung Fxyne100% (2)
- 3472-1 Add MathsDocument24 pages3472-1 Add Mathshilmi72100% (1)
- Fizik 4m Trial SPM 2021 Kertas 2Document43 pagesFizik 4m Trial SPM 2021 Kertas 2ayunie nasuhaNo ratings yet
- Fizik Tingkatan 4 Modul Bantal 2021Document114 pagesFizik Tingkatan 4 Modul Bantal 2021wan marlin100% (3)
- Johor Bahru Set 1 (MM)Document69 pagesJohor Bahru Set 1 (MM)Azrel BatistaNo ratings yet
- Tajuk Amali Fizik Ting 4 Dan 5Document8 pagesTajuk Amali Fizik Ting 4 Dan 5shuNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Buku TeksDocument58 pagesJawapan Buku TekswanyanaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Prinsip Archimedes 2021Document108 pages2.5 Prinsip Archimedes 2021taneshNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Menganalisis Graf - JawapanDocument9 pages1.2 Menganalisis Graf - JawapanZune Lee0% (1)
- FIZIKDocument20 pagesFIZIK---No ratings yet
- 5B9 (20m) Kanta Cembung SBG Pembesar, Design MikroskopDocument3 pages5B9 (20m) Kanta Cembung SBG Pembesar, Design MikroskopfazilahNo ratings yet
- Bab 12Document14 pagesBab 12Nurul HafizaNo ratings yet
- Nota Ringkas FizikDocument15 pagesNota Ringkas Fizikalyasserbinmdisa82100% (2)
- Fizik Bab 1 t4 KSSM Cikgu Sopi?Document5 pagesFizik Bab 1 t4 KSSM Cikgu Sopi?NoorhisyamIsmailNo ratings yet
- Amali 4Document8 pagesAmali 4Aslina Awang0% (1)
- Kertas 2 BHG C Esei Fizik Topik GelombangDocument2 pagesKertas 2 BHG C Esei Fizik Topik GelombangMJ Chow50% (2)
- 9.3 Transistor 9.3 Transistor: By: MR Sathya 1Document32 pages9.3 Transistor 9.3 Transistor: By: MR Sathya 1sadyehclenNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soalan Struktur (Hukum Gas)Document2 pagesLatihan Soalan Struktur (Hukum Gas)ChewLee TanNo ratings yet
- SET 1 CEMERLANG (SOALAN) BiologiDocument24 pagesSET 1 CEMERLANG (SOALAN) BiologiZorrizNo ratings yet
- SemDocument26 pagesSemshshshchinNo ratings yet
- Skema Kimia k1 k2 Ting 4Document13 pagesSkema Kimia k1 k2 Ting 4NORHIDAYAHNo ratings yet
- Jawapan ULANGKAJI BIO K2 T5 Set 1Document21 pagesJawapan ULANGKAJI BIO K2 T5 Set 1LOW HUEY-JIE Moe100% (2)
- SMK PENGKALAN AUR Fizik Tingkatan 4 Soalan KBAT Bab 1Document2 pagesSMK PENGKALAN AUR Fizik Tingkatan 4 Soalan KBAT Bab 1AlbertNo ratings yet
- Bahagian B Ikut Lajak FizikDocument3 pagesBahagian B Ikut Lajak FizikDarlene CatrinaNo ratings yet
- Diagnostik 2017 (Repaired)Document9 pagesDiagnostik 2017 (Repaired)cikgufiezaNo ratings yet
- Pascal PrincipleDocument2 pagesPascal PrincipleJeemion Jeali100% (1)
- Modul Fizik SPM Kertas 2 & 3Document291 pagesModul Fizik SPM Kertas 2 & 3Farihah Ha50% (4)
- Skema Kertas 2 Set 1Document18 pagesSkema Kertas 2 Set 1zulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Percubaan Fizik 2 Kertas 2Document29 pagesPercubaan Fizik 2 Kertas 2tini277No ratings yet
- Bab 4 Kertas 2Document16 pagesBab 4 Kertas 2Noor Hidayah IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Kimia PPT T4 2022 Kertas 2Document26 pagesKimia PPT T4 2022 Kertas 2wantanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 F4 Solution of Triangles P2Document18 pagesChapter 10 F4 Solution of Triangles P2Veloo GunasagaranNo ratings yet
- MODUL MIMS v2 2022 (SET 1) 1449/2: Matematik Kertas 2Document31 pagesMODUL MIMS v2 2022 (SET 1) 1449/2: Matematik Kertas 2Tiun Hiew VianNo ratings yet
- 2.MODUL INDUK JPN T4 EDISI GURU EditedDocument142 pages2.MODUL INDUK JPN T4 EDISI GURU Editedmohd sabila IbnuzawawiNo ratings yet
- Taklimat Menjawab Fizik SPMDocument17 pagesTaklimat Menjawab Fizik SPMaimarashidNo ratings yet
- SPM 4531 2009 Physics p2 BJWPDocument25 pagesSPM 4531 2009 Physics p2 BJWPpss smk selandar100% (1)
- JawapanBab4 PDFDocument36 pagesJawapanBab4 PDFkokseemailNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGI Jwp-1Document79 pagesBIOLOGI Jwp-1Cikgu Zurina BishanNo ratings yet
- BK 9 Kertas 2 Trial 15Document29 pagesBK 9 Kertas 2 Trial 15kinah_8250% (2)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument47 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (2)
- JUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPM K2 Set ADocument29 pagesJUJ Pahang 2014 Physics SPM K2 Set ACikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- K2 Fizik Percubaan Terengganu 2014Document27 pagesK2 Fizik Percubaan Terengganu 2014Panitia Fizik BASISNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Document25 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Cikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Trial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK K2 SET ADocument0 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2013 FIZIK K2 SET ACikgu Faizal0% (1)
- Kertas 2Document17 pagesKertas 2NOR JAMALIAH BINTI MOHAMAD TARMIZI MoeNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Document25 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2NALLATHAMBYNo ratings yet
- Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun Tahun Tingkatan 1Document14 pagesPeperiksaan Akhir Tahun Tahun Tingkatan 1Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K2Document22 pagesTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2 SkemaDocument12 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K1Document22 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K1Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Trial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K2Document23 pagesTrial Pahang Biologi SPM 2014 K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Pahang Matematik SPM 2014 K2Document31 pagesTrial Pahang Matematik SPM 2014 K2Cikgu Faizal100% (8)
- Modul Prinsip Perakaunan Penyata Pengeluaran SPM 2014Document6 pagesModul Prinsip Perakaunan Penyata Pengeluaran SPM 2014Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K1Document30 pagesTrial Terengganu Biologi SPM 2014 K1Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Menyelesaikan Maslah P & P Fizik DGN Menggunakan Reso-EqDocument6 pagesMenyelesaikan Maslah P & P Fizik DGN Menggunakan Reso-EqPhysics MGCM100% (1)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2Document19 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K2 Set 2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K2Document14 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM K2Cikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Trial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM Skema K1 K2Document14 pagesTrial Prinsip Perakaunan SPM 2014 MRSM Skema K1 K2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014 SkemaDocument83 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014 SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (4)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014Document58 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (7)
- Sejarah-Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Kertas 3 SPM 2014 (Bahagian B)Document47 pagesSejarah-Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Kertas 3 SPM 2014 (Bahagian B)Dyieba LatifNo ratings yet
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument16 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Contoh 1 - Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Open Book Test Kertas 3 Sejarah SPM 2014 PPD Kuala LangatDocument17 pagesContoh 1 - Cadangan Skrip Jawapan Open Book Test Kertas 3 Sejarah SPM 2014 PPD Kuala LangatCikgu Faizal75% (4)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaDocument18 pagesJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Perdagangan K2 Set 3 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Document25 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K2 Modul 2Cikgu Faizal100% (2)
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Kedah Trial SPM 2014 B.tamil (2BFC891C)Document13 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Kedah Trial SPM 2014 B.tamil (2BFC891C)gunaNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument47 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (2)
- Trial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K1 Modul 2Document24 pagesTrial Kedah SPM 2014 Physics K1 Modul 2Cikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 3 Dan SkemaDocument46 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 3 Dan SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument19 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument40 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K2 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal0% (1)
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Document56 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Physics SPM 2014Cikgu Faizal100% (4)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument19 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K3 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaDocument39 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 2 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (1)
- Modul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 1 Dan SkemaDocument41 pagesModul Fizik Cakna Kelantan SPM 2014 K1 Set 1 Dan SkemaCikgu Faizal100% (2)