Professional Documents
Culture Documents
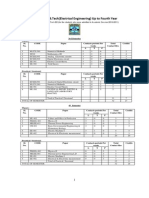
Elecrical SCHM Syllabus
Uploaded by
Ram Krishan SharmaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elecrical SCHM Syllabus
Uploaded by
Ram Krishan SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
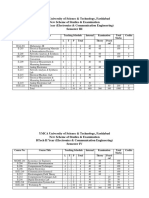
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
B.Tech. ELECTRICAL
Course of Study & Scheme of Examination
Maulana Azad National Institute of Technology, Bhopal
(Deemed University)
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
MAULANA AZAD NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, BHOPAL
(Deemed University)
COURSE OF STUDY AND SCHEME OF EXAMINATION (proposed w.e.f. July 2006)
B.Tech. (ELECTRICAL)
I-SEMESTER
Course
No.
PHY-101
CHM-101
MTH-101
C-101
HUM-101
M-101
PHY-141
CHM-141
M-141
Subject
Physics I
Engg. Chemistry I
Mathematics I
Environment Engg.
Communication Skill
Engg. Graphics
Physics Lab
Engg. Chemistry Lab
Workshop Practice
Total
Scheme of
studies periods
per week
L
T
P
3
3
3
3
3
-
1
1
1
1
1
4
-
15
No. & duration of
Theory papers
3
3
3
9
Credits
Total
Credits
No.
Hrs.
1
1
1
1
1
1
-
3
3
3
3
3
3
-
3
3
3
3
3
-
1
1
1
1
1
4
-
15
3
3
3
9
3
3
3
3
3
4
3
3
3
33
II-SEMESTER
Course
No.
Subject
PHY-151
CHM-151
MTH-151
CSE-151
C-191
M-191
Physics II
Engg. Chemistry II
Mathematics II
Computer
Programming
Basic Electrical &
Electronics Engg.
Basic Civil & Mech
Computer
Programming Lab.
Electrical & Electronics
Engg.Lab
Civil Engg. Lab.
Mechanical Engg. Lab.
E-199
General Proficiency
E-151
C-151
CS-191
E-191
Total
Scheme of
studies periods
per week
L
T
P
3
1
3
1
3
1
3
1
3
18
No. & duration
of Theory
papers
No.
Hrs.
1
3
1
3
1
3
1
3
Credits
Total
Credits
L
3
3
3
3
T
1
1
1
1
P
-
4
4
4
4
4
2
2
2
2
2
12
36
2
2
18
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
III-SEMESTER
Course No.
Subject
MTH-202
M-221
E-201
E-202
Maths III
Prime Movers
Engineering Graphics
Electrical
Measurement
Networks
Electromechanical
Energy Conversion I
Lab ( Networks &
Electrical
Measurement )
Lab(Electromechanical
Energy Conversion I)
Total
E-203
E-204
E-241
E-242
Scheme of
studies periods
per week
L
T
P
3
1
3
1
1
3
3
1
3
3
1
1
16
No. & duration
of Theory
papers
No.
Hrs.
1
3
1
3
1
3
1
3
Credits
L
3
3
1
3
T
1
1
3
1
Total
Credits
P
4
4
4
4
1
1
3
3
3
3
1
1
4
4
08
10
16
32
IV-SEMESTER
Course
No.
MTH-251
Subject
E-292
Numerical Methods &
Computer Applications
Engg. Economics and
Business Organization
Computer Arch.
Electromechanical
Energy Conversion II
Electronics I
Elect. Materials &
Electromagnetic Fields
Lab (Electromechanical
Energy Conversion II )
Lab (Electronics I )
E-299
General Proficiency
HUM-251
CSE-271
E-251
E-252
E-253
E-291
Total
Scheme of studies
periods per week
L
3
T
1
3
3
1
1
3
3
1
1
18
04
No. & duration
of Theory
papers
No.
Hrs.
1
3
Credits
Total
Credits
L
3
T
1
1
1
3
3
3
3
1
1
4
4
1
1
3
3
3
3
1
1
4
4
36
10
18
P
4
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
V-SEMESTER
Course
No.
HUM-302
E-301
E-302
E-303
E-304
E-305
E-341
E-342
Subject
Industrial Management
Generation of Electrical
Power
Elect. M/C Design
Power Electronics
Electronics II
Electromechanical
Energy Conversion III
Lab (Electronics &
Power Electronics)
Lab (Electromechanical
Energy Conversion III )
Total
Scheme of
studies
periods per
week
L
T
P
3
3
-
No. & duration
of Theory
papers
Credits
Total
Credits
No.
1
1
Hrs.
3
3
L
3
3
T
1
1
P
-
4
4
3
3
3
3
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
1
1
1
1
4
4
4
4
18
04
18
32
VI-SEMESTER
Course
No.
Subject
E-351
E-352
E-353
E-354
E-355
Instrumentation
Linear Control System
Microprocessors
Power System I
Utilization of Elect.
Energy
Lab (Instrumentation
& Microprocessors
Lab ( Control )
Minor Project &
Seminar
General Proficiency
E-391
E-392
E-398
E-399
Total
Scheme of
studies periods
per week
L
T
P
3
1
3
1
3
1
3
1
3
1
-
No. & duration
of Theory
papers
No.
Hrs.
1
3
1
3
1
3
1
3
1
3
Credits
L
3
3
3
3
3
4
4
15
04
12
T
1
1
1
1
1
15
Total
Credits
P
-
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
6
16
38
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
VII-SEMESTER
Course
No.
Subject
Scheme of
studies
periods per
week
L
T
P
3
1
3
1
-
Total
Credits
Hrs.
3
3
L
3
3
T
1
1
P
-
4
4
15
10
15
12
34
Power System II
Modern Control
System
E-403
EHV AC & DC
Transmission
E-411419
E-421429
E-441
Elective I
Elective II
Lab ( Power &
Control System )
Major Project /
Seminar
Educational Tour &
Training
Total
E-449
Credits
No.
1
1
E-401
E-402
E-448
No. & duration
of Theory
papers
Elective I : (i) Computer Applications in Power System (ii) Artificial Intelligence (iii) Communication
Engineering (iv) Software Engineering (v) Electrical Installation, Commissioning & Maintenance
Elective II : (i) Power Quality (ii) Energy Conservation & Management (iii) System Engineering (iv) Embedded
Systems (v) Project Management
VIII-SEMESTER
Course
No.
E-451
E-452
E-461469
E-471479
E-498
E-499
Subject
Scheme of
studies
periods per
week
L
T
P
3
1
No. & duration
of Theory
papers
Credits
Total
Credits
No.
1
Hrs.
3
L
3
T
1
P
-
1
1
3
3
1
1
4
4
12
12
14
12
18
12
4
16
4.0
34
Power System
Control & Stability
Electrical Drives
Elective III
3
3
Elective IV
Major Project &
Seminar
General Proficiency
Total
Elective III : (i) Power Controllers (ii) Digital Signal Processing (iii) Bio Engineering (iv) Electric Transportation & Control
Elective IV : (i) Advanced Microprocessors (ii) Intellectual Property Rights (iii) Power System Deregulation
(iv) Entrepreneurship Development (v) Non-conventional Energy Sources
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
Subject Code: E-151
UNIT I
DC Circuits - Voltage & Current sources, Loop and Nodal equations, Superposition
theorem, Thevenin's theorem, Norton's theorem, Maximum power transfer theorem, StarDelta transformations. Fundamentals of magnetic circuits.
UNIT II
Fundamentals of AC Circuits- Average value, RMS value, form factor, crest factor, AC
power and power factor, phasor representation of sinusoidal quantities.
Simple series, parallel & series-parallel circuits containing R-L, R-C, R-L-C parameters.
Active, Apparent & Reactive power, Resonance in series & parallel circuits.
UNIT III
Transformers -Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, Lenz's law, statically and
dynamically induced EMF, Working principle & Basic constructional features of
Transformer, different types, O.C. and S.C. tests of transformer, equivalent circuit and
vector diagram, losses, efficiency and regulation, autotransformer
UNIT IV
Introduction to Rotating Electrical Machines: Constructional features of rotating
electrical machines. Concepts of general terms pertaining to rotating electrical machines.
Generated E.M.F full pitched & short pitched coil. Losses & Efficiency.
UNIT V
Introduction to Electronic Components and Circuits : V-I characteristics of diodes, diode
parameters, equivalent circuits, rectifiers, derivation for rectifier efficiency, ripple factor.
Transistor Circuits-Principle of operation of transistors, Input/output & transfer
characteristics of BJT, Common Emitter, Common Base, Common Collector Transistor
configurations.
Reference Books:
1. Electrical Machines
2. Electrical Technology
3. Fundamentals of Electrical Technology
4. Electrical Circuits
5. Electrical Machinery
6. Basic Electrical Engineering.
7. Electronics Devices
8. Electronics Principles
9. Electronic Devices & Circuit Theory
10. Numerical problems on Electric Machines
- Fitzerald Kingsley
- H.Cotton
- Del Toro
- Schaum series
- Dr. P.S. Bimbhra
- V.N.Mittle & Arvind Mittal
- Millman & Halkias
- A.P.Malvino
Boylstead & Nashelsky
- Parker & Smith
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ENGINEERING GRAPHICS
Subject Code: E-201
UNIT-I
Introduction to general purpose graphics software, AutoCAD, plotting techniques,
coordinate systems, line drawings, polygon and circle generation, drawing entity
commands of computer drafting. Sectional and dimensional drawing using computer.
UNIT-II
Conventional Symbols and brief introduction to electrical equipments and electronic
devices, measuring instruments, parts of MI and MC instruments. Sketches of
transmission line structures, types of towers, insulating equipments, single line diagram
of power substation.
UNIT-III
Sectional drawing of different types of Cables, overhead conductors, wiring systems,
domestic, staircase and godown wiring, wiring installation in small residences.
UNIT-IV
Mounting and types of enclosures for electric motors , types of transformer and their
parts, core construction, sectional view of 1-phase and 3-phase transformers, H.T and L.T
windings.
DC machine and its parts, construction of pole, yoke and field coils, commutator and its
details.
UNIT-V
Estimating : Electrical schedules, Catalogues, Recording of estimates, Determination of
required quantity of material, Determination of cost of material and labour,
Contingencies, Overhead charges,
Reference Books:
1. Electrical Drawing -K.L.Narang
2. Engineering Drawing
- N.D.Bhatt
3. Engineering Drawing with AutoCAD - T.Jayapoorva
4. Electrical Engineering Drawing (Part I & II) - Surjit singh
5. Electrical Installation Estimating & Costing J.B.Gupta
6. Electrical Installation Estimating & Costing Uppal
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENT
Subject Code: E-202
UNIT I
Indicating Instruments - Basic elements of instrumentation, purpose of instrumentation,
Sources of errors, their effects and analysis. Different methods of producing deflecting,
controlling and damping torques. Torque equations, principle and operation of ammeters,
voltmeters and wattmeters, moving iron and moving coil, dynamometer. Induction &
electrostatic type of instruments. Extension of instrument range.
UNIT II
Detectors And Potentiometers -Theory and operation of ballistic , DArsonval, vibration
and spot galvanometers, flux meter, standard d.c. & a.c. potentiometers, construction and
application of polar and coordinate type potentiometers.
UNIT III
Measurement of Phase and Frequency -Power frequency meters; vibrating reed and
resonance types frequency meters. Ohm-meters, Megger and Ratio meters, CRO.
UNIT IV
Measurement of Energy- A.C. single phase and poly-phase induction type energy meters,
errors in & methods of minimization, testing of energy meters by direct and phantom
loading, maximum demand indicator, tri-vector meter, static energy meters.
UNIT V
Magnetic Measurements -B-H curve, determination of hysteresis loop by method of
reversals and point by point method, permeameters, Lloyd -Fischer square for
measurement of Iron losses.
Reference Books :
1. Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments - E.W.Golding
2. Electrical Measurement - A.K.Sawhney, Dhanpat Rai & Sons Publication
3. A Course in Electronic and Electrical Measurements & Instrumentation - J.B.Gupta
4. Electrical Measurment & Measuring Instruments Suryanarayan
5. Electrical & Electronics Measurement & Instrumentation Umesh Sinha
6. Basic Electrical Measurement M.B.Stout
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
NETWORKS
Subject Code: E-203
UNIT I
Circuit Concept RLC parameters, Independent and dependent sources, source
transformation, voltage/current relationship for individual element, mutual inductance and
coupled circuits.
Network Topology : Graph, Tree, Co-tree, incidence matrix, reduced incidence matrix, tieset, cut-set, loop impedance matrix, node admittance matrix, branch impedance/admittance
matrix, formulation of equilibrium equation based on loop/node basis, duality.
UNIT II
Steady State Analysis - Step function response to RL, RC and RLC network and concept of
time constant. Initial conditions in networks. Laplace transform method, basic theorems of
Laplace transform. Waveform synthesis . Transform of pulse and periodic functions.
UNIT III
Transient Analysis-Poles & zeros of transfer function, one and two port networks, various
two port network parameters, Interconnections of two port network, Network theorems :
Superposition, Millman, Thevenins, Nortons & Maximum power transfer theorems.
UNIT IV
Frequency Domain Analysis - Sinusoidal steady state analysis, phasors and phasor diagram,
Fourier series, expansion of Fourier series, phase and amplitude spectrum, exponential form,
Fourier integral & transforms. Relationship between Laplace & Fourier transforms.
UNIT V
Introduction to network synthesis. Driving point & transfer impedance, Positive real function
and Hurwitz polynomial. Foster form & Cauer form of RC, RL & LC networks. Conditions
for realizing an immittance function of passive elements.
Reference Books:
1. Network Analysis
- Van Valkenberg
2. Network Analysis and Synthesis
- Pankaj Swarnkar
3. Engineering Network Analysis & Filter Design Gopal G. Bhise et. al.
4. Network Synthesis
Van Valkenberg
5. Network Analysis and Synthesis
- Kuo
6. Network Theory
- Roy Choudhary
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTROMECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION-I
Subject Code: E-204
UNIT I
Introduction, Energy in electromagnetic system, Flow of energy in electromechanical
devices, Energy in magnetic field and co-energy, Dynamics of electromechanical system,
Singly excited systems, Torque and emf equations.
UNIT II
D.C. Generators-Emf equations, Armature windings, Armature reaction, Armature MMF,
Interpoles and compensating windings, commutation, characteristics of D.C. generators.
UNIT III
DC motors- Torque equation, characteristics, Starting of D.C. motors, speed control of D.C.
shunt motor, braking of D.C. motors, Losses & Efficiency of D.C. machine, Testing of D.C.
machine.
UNIT IV
Polyphase circuits : Advantages in favour of polyphase circuits, Generation of three phase
emf, phase sequence, connection of three-phase winding, line and phase quantities in starconnected circuit, line and phase quantities in delta-connected system, power in three-phase
systems with balanced load.
UNIT V
Transformer review, transformer tests : polarity test, Sumpners test, Three phase
transformers vector group, 3 to 2 and 6 phase conversion. Three phase bank of single phase
transformers, parallel operations of 1 & 3 phase transformers, load division between
transformers in parallel.
Reference Books:
1.
Electrical Machines
2.
Performance & design of A.C. Machines
3.
Electrical Machines
4.
Electrical Machines
5.
Basic Electrical Engineering
- P.S.Bhimbra
- M.G. Say
- Fitzerald Kingsley Otmans
- Nagrath & Kothari
- V.N.Mittle & A.Mittal
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTROMECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION-II
Subject Code: E-251
UNIT I
3-phase Induction Machines -Constructional features, classification, Production of
rotating magnetic field, working principle phasor diagram, equivalent circuit, slip, rotor
e.m.f., current, torque and power equations, torque-slip characteristics, No-load and
blocked rotor test, condition for maximum torque and maximum power, efficiency,
performance by circle diagram.
UNIT II
Starting & speed control of Induction Machines (with & without emf injection in the
rotor ckt.), deep bar & double cage induction motors, cogging and crawling, operation
under unbalanced supply, induction generator.
UNIT III
Synchronous Generators- Constructional features, armature windings, e.m.f. equation,
winding coefficients, distribution factor, pitch factor, harmonics in the induced e.m.f.,
armature reaction, OC & SC tests, voltage regulation : synchronous impedance method,
m.m.f. method, potiers triangle method & ASA method, parallel operation, operation on
infinite bus.
UNIT IV
Synchronous Machine II-Two reaction theory, power expressions for cylindrical and
salient pole machines, OCC & SC characteristics.
Synchronous motor : Principle of operation, starting methods, phasor diagram, torque angle
characteristics, V-curves, power factor control of synchronous motor, hunting & damping,
synchronous condenser, determination of xd and xq by slip test.
UNIT V
Single Phase Induction Motor-Double revolving field theory, equivalent circuit, no load
& block rotor tests, starting methods.
AC Commutator motors :Emf induced in commutator windings, single phase AC motors.
Reference Books :
1. Electrical Machines
2. Performance & design of A.C. Machines
3. Electrical Machines
4. Electrical Machines
- P.S.Bhimbra
- M.G. Say
- Fitzerald Kingsley
- Nagrath & Kothari
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTRONICS-I
Subject Code : E-252
UNIT I
Special Purpose Diodes- Diode Applications, Clipping, Clamping circuits, Voltage
doublers, Shunt, Series & Zener voltage regulators, photodiode, LED, tunnel diode,
Varactor diode, pin diode.
UNIT II
Transistor Biasing -Purpose of biasing, dc operating point, dc load line, different biasing
techniques Base bias, Emitter bias, Voltage divider bias, Collector feedback bias,
Thermal Runaway, Thermal stability.
UNIT III
Small Signal Amplifiers- Transistor as an amplifier, classification of amplifiers, load line,
dc equivalent circuit, operating point, RC coupled CE-amplifier, coupling and bypass
capacitors, ac equivalent circuits, ac load line, graphical analysis, current, voltage &
power gain, input and output impedance, analysis using h-parameters, frequency
response, cascading.
UNIT IV
Transistor hybrid model at low frequency, analysis of transistor amplifier and its
frequency response, emitter follower at low frequency, cascading, transistor hybrid
model at high frequency. Analysis of transistor amplifier at high frequency, miller
theorem, Gain band width product.
UNIT V
FET & MOSFET- The JFET, pinch off voltage, JFET V-I characteristics, FET small
signal model, depletion mode MOSFET, enhancement mode MOSFET, low frequency
common source and common drain amplifiers, FET biasing, FET as a voltage variable
resistor. The common source and common drain amplifier at high frequencies, MOSFET
as a switch, MOSFET driver circuits.
Reference Books:
1. Electronic Devices
Millman & Halkias
2. Electronics Principles
A.P.Malvino
3. Electronic Devices & Circuit Theory Boylstead & Nashelsky
4. Electronic Devices
David Bell
5. Electronic Devices & Circuits
Allen Mottershed
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTRICAL MATERIALS AND ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS (EM & EF)
Subject Code: E-253
UNIT I
Electrostatic Fields -Coulombs law, units, electric field intensity, electric flux density,
Gausss Law, boundary relations, physical concepts of divergence, gradient and curl. Electric
potentials. Electric field in dielectrics and conductors, capacitance, continuity equation,
Poissons and Laplaces equations. Point form of ohms law, concept of vector & scalar
fields.
UNIT II
Magnetic Fields - BoitSavart Law, Magnetic field due to steady currents, force between
current carrying elements, Stokes theorem, vector potential, Amperes circuital law. Torque
on current loops.
UNIT III
Maxwells Equations and EM Waves
Maxwells equations in various forms, Time varying field, wave equations, Propagation of
waves, skin depth, Poynting Theorem.
UNIT IV
Insulating & Dielectric Materials - Properties of insulating materials (electrical, mechanical,
thermal & chemical), classification of insulating materials, fibrous insulating materials
(wood, paper, cardboard, insulating textiles, asbestos, mica, glass, pressboard etc.),
insulating varnishes, coolanised electrical machinery, mineral oils, properties and
applications of mineral oils.
UNIT V
A) Conducting Materials :Properties of conductors (electrical and mechanical) characteristic
of good conductor materials, properties of copper, aluminium, silver and tungsten,
comparison of copper and aluminium as conductor, properties and applications of important
conductor material (tungsten, carbon, nichrome, manganin, eureka, platinum)
superconductivity.
B) Magnetic Materials: Electron spin and its influence on the properties of materials. Basic
concepts and definitions, dia, para, ferro, anti ferro, ferri magnetism, Curie Temperature,
Hysterisis and its significance, soft and hard magnetic materials, high permeability steels,
ferrites, silicon steel, their properties and uses.
Reference Books :
1.
Electromagnetic field
2.
Electromagnetics
3.
Electromagnetics
4.
Electromagnetic field
5.
Electrical Engineering Material
6.
Electrical Engineering Material
7.
Electrical Engineering Material
- William & Haytt
- J.D. Krous
Jorden
_ Joseph Edminister,Schaum's series
Decker
C.S. Indulkar
- TTTI, Madras
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
GENERATION OF ELECTRICAL POWER
Sub. Code: E-301
UNIT-I
General discussion on various types of conventional & non-conventional power
generation, power sector reforms, ecological aspects of Power Generation
Hydro-Electric Stations-Choice of site, arrangement of hydroelectric installations,
Hydrology, Mass curve, flow duration curve, water storage, classification of hydro
electric plants, pumped storage plants, operating cost of hydroelectric station, tidal
power generation, mini-micro hydro power stations.
UNIT-II
Thermal Power Stations : Choice of coal fired station site, arrangement of plant and
principal auxiliaries, coal handling plant, Ash handling plant, heat recovery
equipments, main electrical equipments, instrumentation, speed governor. Operating
cost. Diesel and Gas Power plants.
UNIT-III
Nuclear Power Stations-Nuclear Physics, Atomic energy fuels, moderator materials,
fissile and fertile materials. Fission & Fusion reactions, Choice of site, types of
reactors, principal parts of nuclear power plant, operation and control of reactors.
Comparison of various Power Plants.
UNIT-IV
Economic Aspects of Power Plant Operation-Fixed charges, interest and depreciation
charges, methods of depreciation, straight line and sinking fund methods, different
tariffs, effect of load factor, demand and diversity factors, power factor improvement
by static and synchronous capacitors, power factor improvement, Active and reactive
power control.
UNIT-V
Economic Scheduling of Power Stations-Economic operation of power systems,
criteria for loading of power plants with and without transmission loss. Iterative
methods to solve coordination equations, Load dispatching in power system
cogeneration, Base & peak load operation, Hydro thermal coordination, Methods for
computing the generation scheduling in combined hydro thermal system.
Reference Books:
1. Generation of Electrical Energy
2. Non-conventional Energy Sources
3. Elements of power station design
4. Economic Load Dispatching
B.R. Gupta
G.D. Rai
M.V.Deshpande
- L. R. Kirchmare
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTRICAL MACHINE DESIGN
Subject Code: E-302
UNIT-I
General concepts & considerations of electrical machine design: Factors affecting
design and limitations, typical problems giving insight of machine design, nameplate
specifications of electrical machines.
Heat generation in electrical machines, modes of heat dissipation, Equations for
temperature rise in electrical machines under steady state conditions. Heating and cooling
time constants, ratings of machine, significance of rating of the design aspects, types of
enclosures and their effect on design. Insulation classes & materials.
UNIT-II
D.C.Machine: Laws of magnetic circuit, magnetization curves, Calculation of magnetic
circuit for a D.C. Machine (air gap irregularities, M.M.F. of tooth section etc.), output
equation, calculation of main dimensions, design of armature winding.
UNIT-III
Transformer: Features regarding construction of transformer, choice of flux densities
for yoke and core, current density, window space factor etc., determination of the main
dimensions of the magnetic frame, design of low and high voltage windings, insulation
details, calculation of resistance and leakage reactance. Performance calculations relating
to design.
UNIT-IV
3-
Induction Motor: Main dimensions of the stator, Design of stator winding, Stator
core, length of air gap, squirrel cage rotor, wound rotor. Performance calculations relating
to design.
UNIT-V
Synchronous Machines: Main dimensions of the stator, short circuit ratio, length of air
gap, Design of stator winding, stator core, field system for salient pole alternator.
Introduction to computer aided design.
Reference Books:
1. Design of DC Machines : By Clayton
2. Performance and Design of A.C.Machines : By M.G.Say
3. Synchronous machine design : By G.C.Jain
4. Computer aided design : By Say & Sinha
5. Performance & Design of Electrical Machines:By V.N.Mittle & A.Mittal
6. Design of Electrical Machines: By A.K.Sawhney
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
POWER ELECTRONICS
Subject code: E-303
UNIT I
Basic concepts of construction, ratings of SCR, diac, triac, Static V-I characteristics, gate
characteristics, ratings, protection of SCR, turn on and turn off methods, series and
parallel operation of SCRs, switching devices like power transistors, MOSFET, GTO,
IGBT etc.
UNIT II
Converter circuits: Single phase half wave, full wave, half controlled and fully controlled
converter with resistive and inductive loads, concept of feedback diode, three phase half
wave & full wave converters, effect of source inductance.
UNIT III
Principle of operation of chopper, types of choppers (single, two and four quadrant
choppers), various commutation methods, voltage commutated chopper and current
commutated choppers, Principle of cycloconverter operation, single phase to single phase
cycloconverter circuit.
UNIT IV
Voltage & current source inverters, single phase half bridge and full bridge inverter with
resistive load and inductive load, concept of feed back diode, three phase bridge
inverters. Basics of PWM inverters.
UNIT V
Basic concepts of control circuit, synchronization circuit, isolation circuit. Basic
triggering circuits for converters, choppers, and inverters. Microprocessor/
Microcomputer based control circuit.
Reference Books:
1.
Power Electronics
2.
Power Controller
3.
Power Electronics
4.
Power Electronics
- C.Y.Lander
- G.K.Dubey, Doradla, Joshi & Sinha
- M.H. Rashid
P.S.Bhimbra
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTRONICS-II
Subject code: E-304
UNIT I
The differential amplifier, two input characteristics, AC analysis of a differential
amplifier output offset voltage, common mode gain, different characteristics, definition
of terms of operational Amplifier and its applications-opamp as zero crossing detector,
inverter, summer, integrator, differentiator, comparator, instrumentation amplifier,
current to voltage and voltage to current converter.
UNIT II
Feed back concept, general characteristics of negative feed back amplifiers, input
resistance, output resistance, Effect of feedback on amplifier bandwidth. Properties of
feed back amplifier, topologies voltage series current series, voltage shunt and current
shunt, Wien bridge oscillator RC phase shift, Hartley and Colpitt oscillator, 555 timer.
UNIT III
Large signal amplifiers class A, class B and basic idea of push pull action, distortion, the
current mirror, Power relations, darlington and complementary pairs.
UNIT IV
Boolean algebra, theorems, minterms & maxterms, truth tables, Karnaugh mappings, sum
of products & product of sums, logic gates, AND, OR, NAND, NOR & Exclusive OR.
Half Adder, Full Adder, Multiplexer, Demultiplexer.
UNIT V
Multivibrators Astable, Bistable and Mono stable multivibrator.
Flip flops, SR, JK, D Master slave, Application of flip-flop as counters, Registers,
Sequence generators.
Reference Books:
1. Electronic Devices & Circuits
- Millman & Halkies
2. Electronics Principles
- A. P. Malvino
3. Electronic Circuit Discrete and Integrated - Donald L. Schilling and Charles Belove
4. OPAMP & Linear Integrated Circuits
- Ramakant A. Gayakwad
5. Digital Electronics
- William H.Gothmann
6. Electric Devices & Circuit Theory
- Boylstad & Nashelsky
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTROMECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION-III
Subject Code : E-305
UNIT I
Basis for development of generalized approach for analysis of electrical machines,
Krons primitive machines, concepts of rotational & transformer voltages, concept of
pseudo stationary coils, voltage and flux linkages, equation of electrical machine based
on coupled circuits approach, expressions for self and mutual inductance of various
windings with respect to rotor position, Parks & inverse Parks transformations and their
physical significance, expressions for flux linkages in terms of parks variables,
transformed impedance matrix.
UNIT II
Formation and development of steady state equations based on a generalized approach for
DC machine, Steady state behavior of DC machine, interconnection of machines,
generalized model for different types of DC machines, transfer function of DC machines.
UNIT III
Basic synchronous machine parameters and generalized model of 3-phase synchronous
machine (with & without damping machine), balanced steady state analysis and power
angle characteristics, transient analysis, sudden reactive loading & unloading, sudden 3phase short circuit of synchronous machine, reactances & time constants from
Oscillogram.
UNIT IV
Development of generalized model for 3-phase induction machine, performance equation
& steady state analysis, analysis of equivalent circuit, transient analysis by using
generalized theory, effect of voltage & frequency variations on the induction motor
performance, operation of I.M. on unbalanced supply voltage.
UNIT V
Constructional features, working principle and analysis of Single Phase Series motor,
Stepper motor, Linear Induction Motor, Hysteresis motor, Universal Motor and Reluctance
motor. AC & DC servo motors, brushless DC motor, Scherage motor, repulsion motor.
Reference Books:
1. Generalised Theory of Electrical Machines -P.S.Bhimbra
2. Electrical Machines
- P.S.Bhimbra
3. Electrical Machines
- P.S.Nagrath and D.P.Kothari
4.
Electrical Machines
- Fitzerald Kingsley
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
INSTRUMENTATION
Subject Code : E-351
UNIT I
TRANSDUCERS
Classification, selection of transducers, Resistance, inductance and capacitance type of
transducers, measurement of displacement, strain, force, liquid level, pressure, velocity
and acceleration. Introduction to Biomedical Instrumentation and Sensors.
UNIT II
D.C. & A.C. BRIDGES
Measurement of low, medium, and high resistance. A.C. Bridges, Measurement of
inductance and capacitance, R.L.C. Measurement, Wagner's earthing device, De-Sauty's,
Maxwell's, Anderson's, Schering and Campbells bridges, Q & D measurements, errors in
bridge measurements.
UNIT III
INSTRUMENT TRANSFORMERS
Potential and current transformers, Phase Angle and Ratio errors, testing of instrument
transformers, Ratio meter, construction and design considerations. Application of CTs
and PTs for relays.
UNIT IV
ELECTRONIC & DIGITAL METERS
Hall effect devices, Rectifier instruments, electronic voltmeter, differential voltmeters,
multimeters, display devices, U-V and X-Y Recorders, Digital meters.
UNIT V
DATA TRANSMISSION AND TELEMETRY
Methods of Data transmission, General telemetry systems, DC and AC telemetry system.
Modulation, Pulse telemetry systems, Digital telemetry, Remote metering.
Reference Books :
1. Electrical Measurement & Measuring Instruments - E.W.Golding
2. Electrical Measurement - A.K.Sawhney
3. A Course in Electronic and Electrical Measurements & Instrumentation - J.B.Gupta
4. Biomedical Instrumentation - Khandpur
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
LINEAR CONTROL SYSTEM
Sub. Code : E-352
UNIT-I
CONTROL
SYSTEM
COMPONENTS
AND
TRANSFER
FUNCTION
System concept, open loop and closed loop systems, mathematical modeling of
mechanical and electrical systems, Transfer function of linear systems, Block diagram
representation, and reduction techniques. Signal flow graph. Masons gain formula,
system components, potentiometer, tachogenerator, a.c. and d.c. servomotors,
synchros, stepper motor.
UNIT-II TIME RESPONSE
Time response of first, second and higher order systems to impulse, step and ramp
inputs, Time response specifications, types of systems, steady state error and error
constants. Basic control action and automatic controllers, Effect of P,I, D,PI,PD and
PID controllers on system performance.
UNIT-III STABILITY ANALYSIS OF LINEAR SYSTEMS :
Concept of stability, necessary condition for stability, absolute and relative stability,
Routh Hurwitz criterion, Construction of Root loci and its application, Stability
analysis of electrical systems.
UNIT-IV FREQUENCY DOMAIN ANALYSIS :
Correlation between time and frequency response, frequency domain analysis, Bode
plot, Gain Margin, Phase Margin, Polar plot, Nyquist Criterion, effect of feed back
on frequency domain analysis, constant M circle, N circle.
UNIT-V DESIGN AND COMPENSATION
Design consideration of control system, lead, lag, lead-lag compensation, Design of
compensating network using bode plots and root locus.
Reference Books :
1. Linear control system - Prof. B.S.Manke
2. Automatic control system B.C.Kuo
3. Modern control system Nagrath Gopal
4. Automatic Control Systems - Pankaj Swarnkar
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
MICROPROCESSORS
Subject Code: E-353
UNIT I
Evolution and overview of Microprocessor, micro computer organization.
Microprocessor Architecture - introduction and pin diagram of 8085, ALU timing and
control unit, registers, data and address bus, timing and control signals, fetch and execute
operations, instruction and data flow, system timing diagram, minimum system
configuration for 8085.
UNIT II
Instruction type classification of instructions addressing modes, instruction format,
assembler directives, over view of instruction set, writing assembly language programs
with and without subroutines, concepts of stack, interrupts, interrupt service subroutine.
UNIT III
Memory types, memory organization, static RAM interfacing memory, use of RAMs and
EPROMs, RAM-6116, 6164, EPROM-2716, 2732, 2764, Programmable Peripherals
Interface (8255). Programmable Interval Timer 8253, Basic concepts in serial I/O and
data transfer schemes and their classification.
UNIT IV
Types of A/D & D/A converters, Interfacing & programming of ADC-0808/0809 and
DAC-0800. Multiplexers and demultiplexers, 8085 based data acquisition system, stepper
motor control, DC motor control, temperature control, traffic control.
UNIT V
16-bit Microprocessor 8086 and its internal architecture, instruction set. Introduction to
programming of 8086, 8086 interrupts, multi-user, multitasking, Introduction to
microcontrollers- 80286, 80386, 80486, microprocessor family, Comparison of
microprocessors.
Reference Books:
1. Fundamentals of Microprocessors and Microcomputers
2. Microprocessors and programmed logic
3. Introduction to Microcomputer
4. Microprocessors Architecture Programming and Applications
5. Assembly language programming
6. Microprocessors and Interfacing Programming and Hardware
- B.Ram
- Kenneth B.Short
-Albert Paul Malvino
- Ramesh S.Gaonkar.
-Lance P. Levanthal
- Douglas V.Hall
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
POWER SYSTEM-I
Subject Code: E-354
UNIT I
Function of electric systems, transmission of power by different systems, influence of
voltage on cost and efficiency, comparison of different systems of transmission, types of
conductors and spacing of conductors, constants of overhead transmission lines:
Main parameters of overhead transmission lines, resistance of conductor, skin and
proximity effect, calculation of inductance and capacitance of single phase and three
phase lines with equal and unequal spacings for single and bundle conductors, application
of GMD, GMR methods.
UNIT II
Representation and performance of short, medium and long lines ABCD constants, power
circle diagrams, static and synchronous phase modifiers, surge impedance loading of
transmission lines, efficiency, regulation and phasor diagrams of transmission lines,
Ferranti effect.
Phenomenon of corona, potential gradient, break down voltages, corona power loss,
effect of atmospheric conditions, Radio interference phenomenon: General effect of
positive and negative polarities as well as of a.c. and d.c. supplies on corona. Methods to
improve corona performance.
UNIT III
Mechanical Design of Transmission Lines: Main considerations in the design of
transmission lines, calculation of sag, variation of sag with load and temperature,
stringing chart, sag template, uplift in insulator string, earth wires, type of towers,
vibration dampers, line supports, spacing of conductors and guards.
Type of insulators, voltage distribution on suspension insulator string, string efficiency,
shielding and grading.
UNIT IV
Types of distribution system and their application, calculation of size and voltage drop.
Feeders-Kelvins law and modified Kelvins law for feeder conductor size, limitations of
Kelvins laws.
Comparison of cables and overhead lines, types of cables, insulation resistance, stress and
capacitance of single and multicore cables, charging current, grading of cables, sheath
effects, dielectric loss, power factor-thermal resistance.
UNIT V
Introduction, comparison of a.c. and d.c. transmission system, Advantages and limitations
of HVDC transmission, principal parts, control and applications of HVDC transmission.
Reference Books :
1. Electric Power System
2. Electric Power System
3. Elements of Power System Analysis
4. Power System Analysis & Design
5. HVDC Transmission
: By C.L.Wadhwa
: By - Asfaq Husain
: By William D.Stevenson
: By B.R.Gupta
: By - K.R. Padiyar
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
UTILIZATION OF ELECTRICAL ENERGY
Subject code: E-355
UNIT I
ILLUMINATION ENGINEERING
Nature of light, units, sensitivity of the eye, luminous efficiency, glare. Production of
Light; Incandescent lamps, arc lamps gas discharge lamps- fluorescent lamps-polar
curves, effect of voltage variation on efficiency and life of lamps, Distribution and
control of light, lighting calculations, solid angle, inverse square and cosine laws,
methods of calculations, factory lighting, flood lighting and street lighting.
UNIT II
HEATING AND WELDING
Electrical heating-advantages, methods and application, resistance over general
construction, design of heating elements, efficiency and losses control. Induction heating:
core type furnaces, core less furnaces and high frequency eddy current heating, dielectric
heating: principle and special applications, arc furnaces: direct arc furnaces, Indirect arc
furnaces, electrodes, power supply and control.
Different methods of electrical welding and electrical equipment for them.
Arc furnaces transformer and welding transformers.
UNIT III
TRACTION
Advantages and disadvantages, system of electric traction, diesel electric locomotives.
Mechanics of train movement: simplified speed time curves, average and schedule speed,
tractive effort, specific energy consumption, factors affecting specific energy
consumption.
UNIT IV
TRACTION MOTORS
DC motors, single phase and three phase motors, starting and control of traction motors,
braking of traction motors. Modern 25 KV a.c. single phase traction systems: advantages,
equipment and layout of 25 KV, single phase power frequency A.C. traction.
UNIT V
ELECTRIC DRIVES
Individual and collective drives- electrical braking, plugging, rheostatic and regenerative
braking load equalization use of fly wheel criteria for selection of motors for various
industrial drives.
Reference Books:
1. Utilization of Elect. Energy - E.O. Taylor
2. Utilization of Elect. Energy - H. Pratab
3. Utilization of Elect. Energy - J.B. Gupta
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
POWER SYSTEM II
Sub. Code: E-401
UNIT I
Faults in power systems, single line diagram, equivalent impedance diagram, per unit
reactances. Analysis (using matrices) of power systems by symmetrical components
under:
(a) Three phase short circuit (b) Line to line fault (c) Line to ground fault (d) Double line
to ground fault.
Sequence networks and their inter connections for different types of faults, effects of fault
impedance.Current Limiting Reactors: Applications, types, construction and location of
current limiting reactors, short circuit calculation using reactors.
UNIT II
Introduction, Bus Admittance Matrix, Formation of Ybus & Zbus, Load flow equation &
solution, iterative methods, Gauss-Seidel and Newton-Raphson methods, Jacobian
Matrix, Fast Decoupled load flow.
UNIT III
Philosophy of protective relaying system, construction and realization of characteristics
of different protective relays. Components of Protection System
Conventional and Static relays advantages and limitations, static amplitude and phase
comparators, level detectors, logic and training circuits, static over current, directional,
distance relays. Numerical over current and distance protection.
UNIT IV
Types & detection of faults and their effects, alternator protection scheme (stator, rotor,
reverse power protection etc.). Power transformer protection (external and internal faults
protection), bus bar protection. Transmission line protection (current/time grading,
distance, carrier aided protection).
UNIT V
Theory of current interruption- energy balance and recovery rate theory, arc quenching,
recovery and restriking voltages. Types of circuit breakers. bulk oil and minimum oil, air
break and air blast, sulphur hexa floride (SF6) and vacuum circuit breakers. Rating
selection and testing of circuit breakers/operating mechanisms. LT switchgear, HRC
fuses, types construction and applications.
Reference Books :
1. Electrical Power Systems
- C.L.Wadhwa
2. Modern Power System Analysis
- Nagrath & Kothari
3. Fundamentals of power system protection - Y.G.Paithankar & S.R.Bhinde
4. Power System Protection
- Badriram & Vishwakarma
5. Power System Protection & Switchgear - Ravindranath & Chander
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
MODERN CONTROL SYSTEM
Sub. Code : E-402
UNIT-I INTRODUCTION TO STATE SPACE
State space representation of systems, solving time invariant state equation, State
Transition Matrix, Zero input response, Zero state response, Decomposition, state
equation, Relationship between state equation and transfer function, characteristic
equation, eigen values, eigen vectors.
UNIT-II STATE SPACE ANALYSIS
Phase variable representation, canonical variable representation, diagonalisation,
canonical variable representation, controllability and observability, pole placement
design using state variable feed back.
UNIT-III NON LINEAR SYSTEMS & THEIR STABILITY
Non linear systems, common physical non linearities, phase plane method basic
concepts, construction of phase trajectories, singular points, describing function
method basic concepts, deviation of describing function, stability analysis by
describing function method.
Concepts of stability, limit cycles, Liapunov stability criterion, method of
constructing Liapunov function for non-linear systems, Popovs stability criterion.
UNIT-IV DISCRETE CONTROL SYSTEM
Introduction to discrete time system, z-transform, inverse z-transform. Pulse transfer
function, Sampling Theorem, Data re-construction, zero order hold, first order hold,
Time response of sampled data system.
UNIT-V STABILITY ANALYSIS OF DISCRETE SYSTEM
Stability criterion, methods of stability analysis, bilinear transformation, stability
analysis using Nyquist criterion and root locus, state space representation of discrete
system, state transition matrix controllability and observability of discrete time
system.
Reference Books :
1. Discrete control Engineering-Ogata
2. Automatic Control System B.C. Kuo
3. Modern Control System Nagarth Gopal
4. Linear Control System - B.S.Manke
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
EHV AC & DC TRANSMISSION
Sub. Code: E-403
UNIT I
Constitution of EHV a.c. and d.c. links, kind of d.c. links, limitation and Advantages of
a.c. and d.c. transmission, principal application of a.c. and d.c. transmission, trends in
EHV a.c. and d.c. transmission power handling capacity.
UNIT II
Extra long distance lines, voltage profile of loaded and unloaded line along the line,
compensation of lines, series and shunt compensation, shunt reactors, tuned power lines.
UNIT III
Traveling waves on transmission systems, their shape, attenuation and distortion, effect
of junction and termination on propagation of traveling waves. Over-voltages in
transmission system: lightning, switching and temporary over-voltages: control of
lighting and switching over-voltages.
UNIT IV
Converter theory and performance equations Value characteristics, converter circuits,
abnormal operation of converter circuits, harmonics and filters.
UNIT V
Control of HVDC systems Basic principles of control, control implementation,
converter firing control system, valve blocking and bypassing, starting, stopping and
power flow reversal.
Reference Books:
1. EHV AC & DC Transmission
2. EHV AC & DC Transmission
3. H.V.D.C. Transmission
- Begamudre
- S. Rao
P.Kundur, McGraw Hill Pub.
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-I (i) : COMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN POWER SYSTEM
Subject code: E-411
UNIT I
INTRODUCTION
Electric supply industry structure under Deregulation, Regulatory and policy
developments. Power system components and representation.
UNIT II
LOAD FLOW STUDIES
Analytical formulation, methods of load flow solutions, Bus mismatch and convergence
criteria, Gauss-Siedel method, Newton Rephson method, concept of decoupled methods.
Bus impedance and Bus admittance matrix formulation, bus impedance algorithm.
UNIT III
OPTIMAL LOAD FLOW STUDY OF POWER SYSTEM
Thermal system, transmission losses, optimum scheduling of thermal plants taking losses
into account, economic load scheduling of hydro-thermal plants.
UNIT IV
POWER SYSTEM RESTRUCTURING
Power System Restructuring Models, Market-power.
UNIT V
TRANSMISSION PRICING
Transmission pricing in a Restructured Electricity Market, Congestion Management in
Deregulated Market, Role of FACTS devices in competitive Power Market.
Reference Books :
1. Electrical Energy Systems Theory by O.I.Elgerd
2. Computer Methods in Power system Analysis by A.H.El.Abiad
3. Understanding FACTS concept and Technology by Hingorani N.L.
4. Power System Restructuring and Deregulation Trading Performance and IT by
L.L. Lai, John Wiley & Sons Ltd. England
5. Electricity Market Investment Performance and Analysis by B. Murrey, Mc-Hill,
1998
6. Understanding Electric Utilities and Deregulation by Lorrin Phillipson & H.Lee
Willis, Mareely Dekker Inc. New York, 1999
7. Power System Restructure Engineering & Economics by M.llic, F.Faliana and
L.Fink, Kluwer Academic Publisher, 1998
8. Restructured Electrical Power System Operation Trading and Volatility by
Mohammad Shahidhpour and Muwaffaq Almoush, Marcel Dekker, 2001
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-I (ii) : ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Subject code : E-412
UNIT I
Meaning and definition of artificial intelligence, various types of production systems,
characteristics of production systems, study and comparisons of breadth first search and
depth first search techniques, other search techniques like hill climbing, best first search,
A* algorithm AO* algorithm etc. And various types of control stragegies
UNIT II
Knowledge representation, problems in representing knowledge, knowledge
representation using proposition and predicate logic, comparisons of proposition and
predicate logic, resolution refutation, deduction, theorem proving , inferencing ,
monotonic and non-monotonic reasoning.
UNIT III
Probabilistic reasoning, Bays theorem, semantic networks, scripts schemes, frames,
conceptual dependency, fuzzy logic, forward and backward reasoning.
UNIT IV
Game playing techniques like minimax procedure, alpha-bata cut- off etc., planning study
of blocks word problem in robotics, understanding and natural language processing.
UNIT V
Introduction to learning, various techniques used I learning, neural networks, and
applications of neural networks, common sense, reasoning and expert systems.
Reference Books :
1. Artificial Intelligence by Rich & Night
2. Artificial Intelligence by Mc Dermott
3. Artificial Intelligence by Mills J Millson
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-I (iii) : COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
Subject code: E-413
UNIT I
Need for Modulation, Amplitude Modulation, AM Demodulator, SSB Modulation, Vestigial
Sideband Modulation, AM transmitter and Receiver, Noise and bandwidth in AM, Carrier
Communication, Basic Principles of Pulsed and CW Radar.
UNIT II
Frequency Modulation, FM Demodulator, Phase Modulation, FM transmitter and receiver,
Noise and bandwidth in FM, Ground wave, sky wave and space wave propagation, Basic
Principles of BW and Colour TV.
UNIT III
Sampling theorem, PAM, PWM, PPM, Pulse Code Modulation, Noise in PCM, Delta
Modulation, Adaptive Delta modulation, DPCM, Mary system, FDM and TDM.
UNIT IV
Digital Modulation, ASK, FSK, PSK, DPSK,
Communication, Satellite Comm., Mobile Comm.
Basic
Principles
of
Optical
UNIT V
Entropy, Mutual Information, Channel Capacity, Shannon Theorem, Shannon-Hartley
Theorem, Shannon-Fano code, Huffman code, Parity Check Code, Hammings Single
Error Correction Code.
Reference Books:
1. Electronics Communication System
2. Communication System-Analog & Digital
- G.Kennedy
- R.P.Singh & S.D.Sapre
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE I (iv) : SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
Subject code: E-414
UNIT I
Introduction to software engineering, software characterization and components,
software as a product, software process and process models, capability maturity model
(CMM), software metrics and measurements software project planning (Project
scheduling and tracking, cost estimation methods).
UNIT II
Requirement analysis: Analysis principles complexity, methods, structured analysis
method formal specification, data dictionary, software prototyping and specifications,
other requirement analysis methods, storage and processing time analysis, data base
requirement, SRS documentation.
UNIT III
Design principles, design concepts like abstraction, refinement, modularity, control
hierarchy, software architecture, structured partitioning, data structure, information
hiding etc., modular design, design heuristics for modularity, object oriented design, user
interface design, other design methods.
UNIT IV
Software coding and testing, influence of implementation language and coding, coding
style, coding efficiency, software quality assurance, software testing techniques, software
testing strategies, comparison of test methods, choice of test data, classification of test
data, other verification & validation methods.
UNIT V
Software maintenance process, quality management, maintenance cost and
maintainability measures, software risk analysis, configuration management and version
control system documentation, software reusability.
Reference Books:
1. An Integrated Approach to Software
published by Narosa Publishing House
2. Software Engineering by Roger S. Pressman
Engineering
by
P.
Jalote
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE I (v) :ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION, COMMISSIONING AND MAINTENANCE
Subject code: E-415
UNIT I
INSTALLATION: Study and use of theodolite. Types of heavy electrical equipment,
unloading accessories precautions for unloading, installation of small and large machines
of both static and rotating type, Installation transformer.
UNIT II
COMMISSIONING : commissioning procedure, test required before commissiong of
electrical equipment in respect of : Mechanical fixture and alignment, Electrical tests,
Initial precautions for starting. Electrical accidents, safety regulation, treatment of shock,
fire extinguishers
UNIT III
EARTHING: Reasons for earthing, earthing system earth lead and its size, permissible
earth resistance for different installation, improvement of earth resistance, double
earthing, earth resistance measurement, rules for earthing.
UNIT IV
PREVENTING MAINTENANCE AND ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION
PREVENTION: Concepts of preventive maintenance, advantages, preventive
maintenance schedule for transformer induction motor, transmission line, circuit breaker
and underground cable, preventive measures to control environmental pollution results
due to production of: smoke gases, flow of waste material and atomic reactions in
research stations, plants, elect. & electronic equipments and accessories.
UNIT V
TESTING AND MAINTENANCE OF RELAY AND CIRCUIT BREAKERS: Testing
of relays, factory test, commissioning test and preventive periodic maintenance test,
testing of circuit breakers, voltage test, type test, preventive maintenance of circuit
breaker. Insulation Testing. Electrical accidents, safety regulation, treatment of shock,
fire extinguishers
Reference Books:
1. Electrical Installation Work(Vth Metric Edition) T.G.Francist E.L.B.S
2. Electrical Installation Maintenance & Fault Location Workbook., T.T.T.I.(W.R)
Bhopal
3. Preventive Maintenance Electrical Equipment, Charles J Hurburt
4. Commission of Electrical Plant, Rch Richardson.
5. A Text Book of Electrical Installation Work Vol.2, R.A.Mee., Macdonald London.
6. Electrical Maintenance & Repairs, P.P. Gupta, Dhanpat Rai & Sons Pub.
7. Estimating Commissioning And Maintenance of Electrical Equipment, S.Rao,
Khanna Pub.
8. Fundamentals of Maintenance of Electrical Equipments, Bhatia, Khanna Pub.
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-II (i): POWER QUALITY
Subject code: E-421
UNIT-I
Understanding Power quality, types of power quality disturbances, power quality indices,
Causes and effects of power quality disturbances
UNIT II
Causes and effects of harmonics, converter configuration and their contribution to supply
harmonics, other sources of harmonics
UNIT III
Radio interference, supply standards, elimination/suppression of harmonics, classical
solutions & their drawbacks, passive input filters, high power factor pre-regulator,
switching control circuit, transformer connections.
UNIT - IV
Elimination/suppression of harmonics using active power filters topologies, and their
control methods, PWM converter as a voltage source active filter, current source active
filter.
UNIT - V
Electro-magnetic compatibility, constant frequency control, constant tolerance band
control, variable tolerance band control, discontinuous current control.
Reference Books:
1. Power Quality
- R.C. Duggan
2. Power system harmonics
A.J. Arrillga
3. Power electronic converter harmonics Derek A. Paice
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-II (ii): ENERGY CONSERVATION & MANAGEMENT
Sub. Code: E-422
UNIT I
General energy problem. Global and national energy scenario, primary energy sources,
energy use patterns, Basic Principles, laws of Thermo dynamics. Irreversibility, entropy
enthalpy, heat engine, refrigeration cycle, thermal efficiency and thermal exchange ratio.
Citical and economic thickness of insulation. Optimum use of prime movers for power
generation, techniques cogeneration technology. Energy conservation methods in power
plants, conservation of energy in energy intensive industries.
UNIT II
Maintenance engineering : friction, lubrication and tribological innovations, predictive
and preventive maintenance, Energy audit, case studies.
UNIT III
(i) Heating, lighting and Air conditioning of building and measures for conservation of
electrical energy. Energy conservation in domestic gadgets.
(ii) Industrial heating and energy conservation in electric and oil fired furnances.
(iii) Measures for Reduction of losses in Transmission and distribution systems.
UNIT IV
Energy efficient electric drives, energy efficient motors, V.S.D. power factor
improvement in power system. Energy conservation in transportation systems especially
in electric vehicle.
UNIT V
Load curve analysis and load managements, DSM, Energy storage for power systems,
(Mechanical, Thermal, electrical and Magnetic) Restructuring of electric tariff from
energy conservation considerations, pay back period.
Reference Books:
1. Electrical Energy Utilization & Conservation
2. Energy Conservation and Audit
3. Energy Audit and Conservation
- Dr. S.C.Tripathi
- Thumman
- TERI
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-II (iii): SYSTEM ENGINEERING
Subject code: E-423
UNIT-I
System philosophy, systems concepts, system modeling, system analysis, system
optimization, classification of systems, topological models of system, Anology among
different systems. Introduction to linear graph theory.
UNIT-II
Modeling of systems with two terminal component, component graph and their model,
system graph, interconnection equation and development of system model using Branch
formulation, chord formulation and state space formulation.
UNIT-III
Modeling of systems with multiterminal components, component graph, model of nterminal dissipative component, linear perfect couplers and Gyrators, model of two port
components, system models using multiterminal components using graph theoretic
approval and state space modeling.
UNIT-IV
Introduction to fuzzy logic, fuzzification, defuzzification, rule base, Design of rules &
membership functions, Applications of fuzzy logic control.
Fundamental concepts and models of Artificial Neural Network, Multilayer feedforward
networks, Applications & implementation of Neural Algorithms and systems.
UNIT-V
Stability, sensitivity, controllability, observability of the system, system optimization
using linear and dynamic programming. Technological forecasting methods.
Reference Books:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Systems Modelling and Analysis, I.J. Nagrath & M.Gopal, Tata Mc.Graw Hill
Analysis of Discrete Physical System by Koenig and Tokad, Mc. Graw Hill
Introduction to Artificial Neural Systems J.M.Zurada
Neural Networks Simon Haykin
Theory and problems of operations research Schaums Series Mc-Graw Hill Int.
Book Co.
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-II (iv): EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
Subject code: E-424
UNIT-I
Introduction embedded systems, their characteristics, modeling of systems, system
specifications, specification languages, study of specification example.
UNIT II
Specification translation, translation of various features such as state transition, message
passing communication, concurrency, exception handling etc.
UNIT III
System partitioning- Introduction, partitioning issues, partitioning algoritms, functional
portioning, hardware/software partitioning algorithms, functional partitioning for
systems.
UNIT - IV
Design quality estimation- Quality metrics, hardware estimation, software estimation.
UNIT - V
Specification refinement- Refining variable grouping, channel refinement, resolving
accesss conflict, refining incompatible interfaces, refining hardware/software interfaces.
Study of a system design methodology and study of generic synthesis system.
Reference Books :
1.
Specification and design of embedded systems, David D Gajski, Frandk vahid,
S. Narayan, J Garg
2.
Embedded system design, Heath Steve and Newns 1997
3.
Art of programming Embedded Systems, J. Gassle
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-II (v): PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Subject code: E-425
UNIT-I: Fundamentals of Management I
Management: Evolution, development, characteristics, principles, philosophy, Nature and
function, (MBO), (MBE) their importance characteristics and applications.
UNIT-II: Fundamentals of Management II
Organizational Behavior, Human behavior, group dynamics. Leadership theories, styles
and modern philosophies, motivation approaches and theories, communication, barriers
and breakdowns, management information system, use of Computer in Management.
UNIT-III: Introduction to Personnel Management
Employees, Personnel Management practices, methods, recruitment, selection,
interviews, group discussions, training, placement and employees development, wages
and incentives, labour welfare, conflict, Negotiations, best practices.
UNIT-IV: Introduction to Marketing and Sales Management
Marketing concept, principles, functions, market survey and research, concepts of
sales and distribution, channels of distribution, salesmanship, sales promotions, methods
of advertising, copy right, sales management practices.
UNIT-V: Introduction to Financial Management
Nature and scope of Financial Management, goals of financial management, Sources
of finance, Permanent long term, Short term Sources, Interest rates, annuity cost of
capital, capital structure, decisions, Break-even Analysis, Financial Planning.
Reference Books:
1.
2.
3.
4.
Management
Principle of Marketing
Industrial Management
Financial Management
- Stonner & Freeman
- Philip Kotler
- K.K. Ahuja
- S.K. Banerjee
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
POWER SYSTEM CONTROL & STABILITY
Subject Code: E-451
UNIT-I
EXCITATION SYSTEMS
Excitation system requirement, Elements of an excitation system, types of excitation
systems, comparision of the various excitation system, Development of Block diagram of
excitation system and the transfer function. Recent development and future trends.
UNIT-II
LOAD FREQUENCY CONTROL
Introduction, Nature of control problems, Basic concept of Governor Mechanism and
their performance in steady state, Turbine and Generator model. Load frequency control
of an isolated power system. Division of load between Generators, Basic concept of
control area.
UNIT-III
CONTROL OF VOLTAGE AND REACTIVE POWER
Introduction, Generation and absorption of reaction power, relation between voltage,
power and reactive power at a node, methods of voltage control. Injection of reactive
power, use of tap changing transformers, combined use of tap changing transformers and
reactive power injection.
UNIT-IV
POWER SYSTEM STABILITY
Introduction, power angle curve, transfer reactance, swing equations, steady state stability
theoretical and practical, transient stability using equal area criterion and step by step
method. Introduction to Grid Failure.
UNIT-V
METHODS OF IMPROVING STABILITY
Introduction, Methods of improving stability using traditional techniques and new
approaches eg. High speed fault clearing, reduction of transmission system reactance,
regulated shunt compensation, Dynamic braking, Independent pole operation of circuit
breaker acting automatic voltage regulation.
Reference Books:
1. Power system engineering
2. Electric Power System
3. Power System Stability & Control
4. Electrical Power System
-Nagarath & Kothari
-B.M.Weedy
-P.Kundur
-C.L. Wadhwa
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTRICAL DRIVES
Subject code: E-452
UNIT I
INTRODUCTION OF ELECTRICAL DRIVES
Introduction of Electrical Drives, Choice of Electrical Drives, Dynamics of Electrical
Drives, Fundamental torque equation, speed torque conventions and Multiquadrant
operation. Equivalent values of drives parameters, components of load torques, nature
and classification of load torques. Energy conservation in Electrical Drives.
UNIT II
DC DRIVES
Review of DC Motors, starting, braking, speed control, performance parameters, single
phase & three phase controlled rectifier fed DC drives, power factor improvement,
chopper controlled DC drives and their industrial applications.
UNIT III
INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES
Review of three phase induction motor, starting, braking, speed control, variable
frequency control. Basics of PWM Inverter fed I.M. Drive, harmonics analysis. Slip
power recovery, Rotor resistance control and their industrial applications.
UNIT IV
CONTROL OF ELECTRICAL DRIVES
Modes of operation, closed loop control of drives, current limit control, closed loop
torque control, closed loop speed control, closed loop speed control of multi-motor
drives, speed sensing, current sensing, phase locked loop (PLL) control, closed loop
position control.
UNIT V
SYNCHRONOUS & OTHER SPECIAL MOTOR DRIVES
Synchronous motor, operation from fixed frequency supply, synchronous motor variable
speed drives. Introduction of Brushless DC motor, Stepper motor and switched reluctance
motor drives and their industrial applications.
Reference Books:
1. Fundamental of Electrical Drives
2. Power Semiconductor controlled drives
3. Thyristor DC Drives
4. Power Electronics and AC Drives
G.K.Dubey
G.K.Dubey
P.C.Sen
B.K.Bose
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-III (i) : POWER CONTROLLERS
Subject code: E-461
UNIT I
POWER ELECTRONIC DEVICES
Principles, characteristics & ratings of various types of GTOs, power transistors,
MOSFETs, IGBTs, static induction transistors, comparison of controllable switches,
protection circuits for GTOs & MOSFETs.
UNIT II
AC TO DC CONVERTERS
Analysis of 1- fully controlled converter for continuous & discontinuous conduction
mode, fundamental p.f., input p.f., rms & average current & voltage, active & reactive
power, Harmonic factor. 12-pulse converter & resonant pulse converters. Problems &
solution of input current harmonics & poor p.f., Dual converters.
UNIT III
AC TO AC CONVERTERS
Single phase controllers, 3-phase half wave & full wave controllers & effect of source
and load inductance. 3-phase bidirectional delta connected controllers. 3-phase to single
phase cycloconverters. 3-phase to 3-phase cycloconverters.
UNIT IV
INVERTERS
Current source inverters single phase and three phase. Principle of operation of PWM
inverters, single pulse PWM, Multiple PWM, SPWM, Modified SPWM. Concepts of
Advance PWM techniques.
UNIT V
INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
Thyristorised ac, dc drives, UPS, Inverters, SMPS, HVDC Transmission ,SVC.
Reference Books :
1. Power Controller
2. Power Electronics
3. Power Electronics
: By Dubey, Doradla, Joshi & Sinha
: By P.S. Bhimbra
: By Rasid
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-III (ii): DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING
Sub. Code : E-462
UNIT-I
INTRODUCTION TO DSP
Classification of signals, Multichannel and multi dimensional continuous v/s discrete
time signals, continuous v/s discrete valued signals, continuous time sinusoidal signal,
discrete time sinusoidal signals, sampling of analog signal, sampling theorem,
quantification and coding of D/A conversion.
UNIT-II
DISCRETE TIME SIGNAL AND SYSTEMS
Discrete time signal, systems, Z-transform & Inverse Z-transform, analysis of discrete
time, linear time invariant systems, co-relation of discrete time systems.
UNIT-III
FREQUENCY ANALYSIS OF SIGNALS
Frequency analysis of analog signals, frequency analysis of discrete time signals.
Properties of Fourier Transform, Frequency Domain Characteristics, Time Frequency
Dualities, Sampling of signals in time and frequency domain, DFT & FFT.
UNIT-IV
DESIGN OF DIGITAL FILTERS
Design of linear phase FIR filter using window & frequency sampling method. Design of
equiripple linear phase filters. Comparison of design methods for linear phase FIR filters.
Design of IIR filters from analog filters. Direct Design Technique for digital IIR filters.
UNIT-V
DSP APPLICATIONS
Introduction to digital signal processors chips, case study of different DSP applications.
Application of filters to analog & digital signal processor, FET spectrum analyzer.
Reference Books:
1. Digital Signal Processing W.D.Stanley
2. Analog & Digital Signal Processing Ashok Ambardar
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-III (iii): BIO ENGINEERING
Sub. Code : E-463
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-III (iv): ELECTRIC TRANSPORTATION & CONTROL
Sub. Code : E-464
UNIT I
Introduction of Electric Transportation, Present Scenario in India and Abroad.
UNIT II
Overhead equipment used in Electric Transportation
UNIT III
AC & DC Traction Drives
UNIT IV
Battery operated vehicle
UNIT V
Fuel cell operated vehicle
Reference Books:
1. Electrical Traction by H.Pratap
2. Fundamental of Electric Drives by G.K.Dubey
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE IV (i): ADVANCED MICROPROCESSORS
Subject code: E-471
UNIT I
Introduction to 16-bit microprocessors, internal architecture of 8086, various types of
segments used like CS, DS, ES & SS, study of various registers used in 8086, various
types of addressing modes like immediate addressing, register addressing, direct
addressing mode & indirect addressing modes.
UNIT II
Instruction set of 8086, conversion of high level statements like assignment statement, if
statements, for loops, while loops, procedures, functions etc. to 8086 statements,
programming using 8086.
UNIT III
Interrupts in 8086, maskable & non-maskable interrupts, hardware & software interrupts,
conditional interrupts, type 0, type 1, type 2 and other such types of interrupts, timing
diagrams for interrupts, steps for interrupt handling.
UNIT IV
Introduction to microcontroller 8051, architecture, instruction set, assembly language
programming and applications.
UNIT V
Introduction to PLC, architecture, programming & applications.
Reference Books :
1. Microprocessor architecture, programming & applications with 8085 R.Gaonkar, Wiley
Eastern publication.
2. Microprocessors & interphasing by D.V.Hall, McGraw Hill
3. 8051 Microcontroller by K.J. Ayala, Penram Int. Pub.
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE IV (ii) :INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS
Subject code: E-472
UNIT I: Introduction to IPR
Introduction to IPR, Importance, need of IPR, Intellectual assets and value realization,
Forms of IPR, Patent, Copyright, Trademarks, Protection of IC layout designs,
Geographical Indicators, Protection of undisclosed information, control of anti
competitive practices and industrial design.
UNIT II: Patents
Concept of property and history of patents, Indian Patent Act and rules, Novelty,
Inventiveness and usefulness, Patent application procedure, patent able and non-patentable inventions including product vs process patents.
UNIT III: Industrial Designs
Registration, concept of novelty, originality, utility, obviousness, rights, obligations and
limitations of registration of design, offences and penalties.
UNIT IV: Trade Marks & Copy Rights
Introduction, registration, concept of deceptive similarity, rights and limitations of trade
marks, offences and penalties.
Copyright introduction, nature of copyright, subject matter of copyrights (literary works,
dramatic works, musical works, cinematography films, records, tapes etc.) rights,
obligations and limitations, registrations.
UNIT V: International Treaties:
Introduction to international treaties, conventions and organizations, TRIPS, PCT, Berne
Convention, WIPO, EPO, UPOV, Introduction to WTO, Introduction to dispute
settlement procedure (technical & legal), Indian position in global IPR structure,
Facilitating technology transfer and Capabilities building.
Reference Books:
1. Ganguly P., Intellectual Property Rights,Tata Mcgraw Hill Publication, 2004.
2. WIPO handbook/ notes Wadehra B.L, Law Relating to Patents, Trademarks,
Designs & Geographical Indications, Universal Law Pub., 2000.
3. Sullivan & Patrick H., Profiting from Intellectual Capital: extracting value from
Innovation, John Wily , 1998.
4. Correa, Carlos M., Intellectual Property Rights, the WTO and Developing Countries:
the TRIPS Agreement and Policy Options, Zed books, New York, 2000.
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE IV (iii): POWER SYSTEM DEREGULATION
Subject code: E-473
UNIT I
Need and conditions for deregulation. Introduction of Market structure, Market
Architecture, Spot market, forward markets and settlements. Review of Conceptsmarginal cost of generation, least-cost operation, incremental cost of generation.
Power System Operation: Old vs. New
UNIT II
Electricity sector structures and Ownership /management, the forms of Ownership and
management. Different structure model like Monopoly model, Purchasing agency model,
wholesale competition model, Retail competition model.
UNIT III
Framework and methods for the analysis of Bilateral and pool markets, LMP based
markets, auction models and price formation, price based unit commitment, country
practices
UNIT IV
Transmission network and market power. Power wheeling transactions and marginal
costing, transmission costing. Congestion management methods- market splitting,
counter-trading; Effect of congestion on LMPs- country practices
UNIT V
Ancillary Services and System Security in Deregulation. Classifications and definitions,
AS management in various markets- country practices. Technical, economic, &
regulatory issues involved in the deregulation of the power industry.
Reference Books:
1. Power System Economics: Designing markets for electricity - S. Stoft
2. Power generation, operation and control, -J. Wood and B. F. Wollenberg
3. Operation of restructured power systems - K. Bhattacharya, M.H.J. Bollen and
J.E. Daalder
4. Market operations in electric power systems - M. Shahidehpour, H. Yamin
and Z. Li
5. Fundamentals of power system economics - S. Kirschen and G. Strbac
6. Optimization principles: Practical Applications to the Operation and Markets
of the Electric Power Industry - N. S. Rau
7. Competition and Choice in Electricity - Sally Hunt and Graham Shuttleworth
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-IV (iv): ENTREPRENEURSHIP DEVELOPMENT
Subject code: E-474
UNIT I
The Entrepreneurship Concept, Definition, Characteristics, The Entrepreneurship
revolution, equity creation, The Timmons model, Entrepreneurial skills and
reasoning, Apprenticeship, The Opportunity- Creation, Shaping, Recognizing and
Seizing, Entrepreneurship and the INTERNET, Creation of New Business.
UNIT II
The Entrepreneurial Thinking, Leadership and human behaviour, Entrepreneurial
mind and creed, Entrepreneurial manger, Principal and theories, management
competencies, Team building, Reward, Personal ethics, Issues of Integrity,
UNIT III
The entrepreneurial approaches to resources, the human resources, the financial
resources, The business Plan, market surveys, preparation and planning, relationship
between goals and actions, segmentation and integration of information, the business
plan process and strategies. Developing a business plan, business borrowing, banking,
legal issues and taxes.
UNIT IV
Entrepreneurial finance, Venture finance, cash flow, financial strategy framework,
fund raising strategies, financial life cycle, Venture capital , Angles and informal
investors, other equity and debt sources of finance, Valuation, structure and
negotiation of venture creation skills and deals.
UNIT V
Venture growth and management, organizational paradigms, importance of Culture
and organizational climate, new developments in entrepreneurial management,
gestation period crisis, predicting trouble, threats diagnosis, intervention, the
turnaround plan, ESOP, Merger, Acquisition and Strategic Alliance.
Reference Books:
1. Timmons, Jeffry A., New Venture Creation, McGraw Hill Publication, 2001.
2. Mariotti, Steve. The Young Entrepreneurs Guide to Starting and Running a
Business., NY: Random House, Inc.2000.
3. Entrepreneurship Development and Management EDI Ahmedabad. Vasant
Desai,
4. Dynamics of Entrepreneurial Development and Management, Himalaya
Publishing House. 2000.
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTIVE-IV (v) : NON-CONVENTIONAL ENERGY SOURCES
Subject code: E-475
UNIT-I
Energy scenario in India, Renewable and Non-renewable Energy sources, Energy for
sustainable development, Direct Energy conversion systems.
UNIT-II
Renewable Hydro potential, flow, duration and storage, mini-micro hydro, small hydro
power, types of turbines, generators & controls.
UNIT-III
Wind energy potential, site selection, types of wind turbines, wind generation and
control.
UNIT-IV
Solar energy solar photovoltaics, solar thermal, applications of solar energy systems.
Renewable Energy for Rural Applications.
UNIT-V
Bio energy, wave & tidal energy, ocean thermal energy systems, MHD & fuel cells. Grid
Interactive and Off Grid / Distributed Renewable Power.
Reference Books:
1. Solar Energy
Padmashree S.P.Sukhatme
2. Solar Electricity
Tomas Markvart
3. Electrical Energy System Theory O.I.Elgerd
4. Towards Clean Energy
B.Ghosh, Saha B., S.K.Basu, Sujay
5. Power System Engineering I.J.Nagrath & D.P.Kothari
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTRICAL MACHINES AND ELECTRONICS
Subject code E-276
UNIT I
POLYPHASE SYSTEMS
Introduction to polyphase system, phase sequence, star & delta connections, phasor
diagrams, analysis of 3-phase balanced & unbalanced circuits. Measurement of 3-phase
power for balanced & unbalanced loads, measurement of reactive volt amperes.
UNIT II
TRANSFORMERS
Single phase and 3-phase transformers, Routine tests of transformer, equivalent circuit and
vector diagram, losses, efficiency and regulation, Welding transformer.
UNIT III
INDUCTION MOTORS
Production of rotating magnetic field, construction and principle of operation of a 3-phase
machines. Slip-torque characteristics, 3-phase induction motor starters, Single phases
induction motor, principle of operation and methods of starting, Testing of single phase and
three phase Induction Motors.
UNIT IV
SELECTION AND APPLICATIONS OF INDUSTRIAL MOTORS
Introduction, factors affecting selection of motors, Types of loads, steady state and Dynamic
characteristics of Electric drives, size of motor, Load equalization, application of motors for
Industrial use.
UNIT V
INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS
Thyristors and their characteristics, turn-on and turn-off methods, basics of chopper rectifiers
and inverters. Control of a.c. and d.c. motors using power electronic devices.
Reference Books:
1. Basic Electrical Engineering
V. N. Mittle & A. Mittal
2. Power Electronics
- M.D.Singh
3. Electrical Machines
- J.B.Gupta
4. Principle of Elect. Machine and Power Electronics
- P.C.Sen
5. Generation, Distribution & Utilization of Electric Energy - C.L. Wadhwa
EED BOS meeting, 24th Jan 2008
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY
Subject code E-211
UNIT I
POLYPHASE SYSTEMS
Introduction to polyphase system, phase sequence, star & delta connections, phasor
diagrams, analysis of 3-phase balanced & unbalanced circuits. Measurement of 3-phase
power for balanced & unbalanced loads, measurement of reactive volt amperes.
UNIT II
TRANSFORMERS
Single phase transformers, different types, Routine tests of transformer, equivalent circuit
and vector diagram, losses, efficiency and regulation, autotransformer, 3-phase transformers.
UNIT III
D.C. MACHINE-I
Classification of DC machines, EMF equation, Armature windings, Armature reaction
and commutation, characteristics of D.C. generators.
Torque equation, Starting of D.C. motors, speed control of D.C. shunt motor, Efficiency of
D.C. machine.
UNIT IV
INDUCTION MOTORS
Production of rotating magnetic field, construction and principle of operation of a 3-phase
machines. Slip-torque characteristics, 3-phase induction motor starters, Single phases
induction motor, principle of operation, methods of starting, speed control of single phase
and three phase Induction Motors.
UNIT V
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
Construction, emf equation, O.C. & S.C. characteristics, Synchronous Impedance, method of
calculating regulation.
Synchronous Motors : Characteristics, V Curves, salient pole machine and their performance
equations, vector diagram, power-angle characteristics.
Reference Books:
1.
Electrical Machines
- P.S. Bhimbra
2.
Electrical Machines
- Fitzrald Kingsley
3.
Measurement and Instrumentation
- A.K.Sawhney
4.
Electronics and Electrical Measurement & Instrumentation - J.B.Gupta
5.
Electrical Machines & Power Electronics
- P.C.Sen
You might also like
- Ele SyllabusDocument49 pagesEle SyllabusRitesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument68 pagesElectrical Engineering DepartmentYukti AdlakhaNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document1 pageWa0001rahulNo ratings yet
- Btech EceDocument65 pagesBtech EceSidhant MadaanNo ratings yet
- EEEDocument290 pagesEEEfaizu_ibmNo ratings yet
- VSSUT (EEE) SyllabusDocument47 pagesVSSUT (EEE) SyllabusAshutosh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument108 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFAmrit SainiNo ratings yet
- Electrical 5 and 6Document24 pagesElectrical 5 and 6vpritNo ratings yet
- NIT Warangal EEE CurriculumDocument27 pagesNIT Warangal EEE Curriculumjagadeesh_kumar_20No ratings yet
- Updated EE SyllabusDocument50 pagesUpdated EE SyllabusHimanshu JainNo ratings yet
- EE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 10.01.14Document67 pagesEE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 10.01.14smrahimNo ratings yet
- Nit Calicut Eee SyllabusDocument113 pagesNit Calicut Eee SyllabusSasi Teja KuntamukkalaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology: Instrumentation & Control Engineering)Document14 pagesBachelor of Technology: Instrumentation & Control Engineering)Mansi guptaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Drives and ControlDocument42 pagesIndustrial Drives and Controlsreeragks1989100% (1)
- Power ElectronicsDocument42 pagesPower Electronicsevonik123456No ratings yet
- UG Scheme SyllabusDocument35 pagesUG Scheme SyllabusराघवतोतलाNo ratings yet
- A Course in Electrical and Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation - A.K.sawhneyDocument14 pagesA Course in Electrical and Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation - A.K.sawhneyHarshal SonawaneNo ratings yet
- EEE 2 3 4 Year 2011-12 PDFDocument61 pagesEEE 2 3 4 Year 2011-12 PDFCharan Priya MangipudyNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies - APDocument5 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge Technologies - APNamagundla Ravines ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chhattisgarh Technical University B.E. VI Semester subjectsDocument18 pagesChhattisgarh Technical University B.E. VI Semester subjectsbitandbite20No ratings yet
- PT EeeDocument146 pagesPT Eeegovi007No ratings yet
- EEE SUST Syllabus Session 2011-12Document31 pagesEEE SUST Syllabus Session 2011-12Shahadat Hussain ParvezNo ratings yet
- BTech Ei SyllabusDocument103 pagesBTech Ei SyllabusShoaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Ganpat University Faculty of Engineering & Technology Proposed Teaching Scheme and Detailed Syllabus M.Tech Sem. III (Electrical Engineering)Document6 pagesGanpat University Faculty of Engineering & Technology Proposed Teaching Scheme and Detailed Syllabus M.Tech Sem. III (Electrical Engineering)Dhaval MerNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Power SystemsDocument49 pagesPower Electronics and Power Systemsrasim_m1146No ratings yet
- B (1) .Tech Detailed SyllabiDocument159 pagesB (1) .Tech Detailed SyllabiJynt RjNo ratings yet
- B.TECH. (Engineering Physics) 2009-2013: Delhi Technological UniversityDocument64 pagesB.TECH. (Engineering Physics) 2009-2013: Delhi Technological UniversityAkshay GuptaNo ratings yet
- CUSAT SYLLABUS EEE B.TechDocument74 pagesCUSAT SYLLABUS EEE B.TechAnupNarayananNo ratings yet
- Electrical ScienceDocument2 pagesElectrical ScienceUjjwal KumarNo ratings yet
- Calicut B.Tech Electrical and Electronics SyllabusDocument150 pagesCalicut B.Tech Electrical and Electronics SyllabusJinu Madhavan0% (1)
- Consolidated 4th Sem Scheme and Syllabus Updated0Document15 pagesConsolidated 4th Sem Scheme and Syllabus Updated0pranavrajrkmvNo ratings yet
- BTech Electrical Engineering Course CurriculumDocument4 pagesBTech Electrical Engineering Course CurriculumAnonymous 8pCXXsNo ratings yet
- EE Final Upto 3rd Year Syllabus 13.07.12Document32 pagesEE Final Upto 3rd Year Syllabus 13.07.12Ishtiaque AnwarNo ratings yet
- Punjab Technical University B.Tech Electrical Engineering Scheme and SyllabusDocument66 pagesPunjab Technical University B.Tech Electrical Engineering Scheme and SyllabuskultardeepNo ratings yet
- VSSUT Burla Electrical Engineering Syllabus 2010Document52 pagesVSSUT Burla Electrical Engineering Syllabus 2010Reeta DuttaNo ratings yet
- Ptee2204 3 1 0 4Document65 pagesPtee2204 3 1 0 4hari6krishnanNo ratings yet
- Truba College BE-104/204 Course on Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesTruba College BE-104/204 Course on Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringPavan KhetrapalNo ratings yet
- EE Curriculum & Evaluation SchemeDocument35 pagesEE Curriculum & Evaluation Schemerudraee41No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDocument48 pagesFundamentals of Electrical EngineeringGee DeeNo ratings yet
- JNTU Anantapur ECE Course StructureDocument16 pagesJNTU Anantapur ECE Course StructurecvslnNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Electrical & Electronics - BE - IV - New - Revised - 2013Document16 pagesSyllabus - Electrical & Electronics - BE - IV - New - Revised - 2013Aadil Ashraf KhanNo ratings yet
- BTech syllabus and course detailsDocument16 pagesBTech syllabus and course detailscoolunderjerkNo ratings yet
- Calicut University Ec - 2004 SyllabusDocument113 pagesCalicut University Ec - 2004 SyllabusvisitorboyNo ratings yet
- ETRXDocument57 pagesETRXasdfgbugmenotNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Instruction and Examination B.Tech (Instrumentation Engineering)Document37 pagesScheme of Instruction and Examination B.Tech (Instrumentation Engineering)Jagabandhu KarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Science 1Document41 pagesElectronic Science 1Vinit KhaiwalNo ratings yet
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai: B.E. Vii Semester Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument15 pagesChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai: B.E. Vii Semester Electrical and Electronics EngineeringrajatNo ratings yet
- Assam Science and Technology University Course Structure and Syllabus for B.Tech 5th Semester Electrical EngineeringDocument25 pagesAssam Science and Technology University Course Structure and Syllabus for B.Tech 5th Semester Electrical EngineeringRohit DuttaNo ratings yet
- DTU New Syllabus For EEEDocument84 pagesDTU New Syllabus For EEEvackyvipin100% (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 1: Synthetic Methodology to Converters and Components TechnologyFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 1: Synthetic Methodology to Converters and Components TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Converter-Based Dynamics and Control of Modern Power SystemsFrom EverandConverter-Based Dynamics and Control of Modern Power SystemsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Introduction to Bond Graphs and their ApplicationsFrom EverandIntroduction to Bond Graphs and their ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reliability Investigation of LED Devices for Public Light ApplicationsFrom EverandReliability Investigation of LED Devices for Public Light ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Protection of Substation Critical Equipment Against Intentional Electromagnetic ThreatsFrom EverandProtection of Substation Critical Equipment Against Intentional Electromagnetic ThreatsNo ratings yet
- Practical Power Electronics: Applications, Experiments and AnimationsFrom EverandPractical Power Electronics: Applications, Experiments and AnimationsNo ratings yet
- Power System Frequency Control: Modeling and AdvancesFrom EverandPower System Frequency Control: Modeling and AdvancesDillip Kumar MishraNo ratings yet