Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gce o Level 2008 Chemistry 5072 5067 Paper 1 Solutions
Uploaded by
mariamtkCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gce o Level 2008 Chemistry 5072 5067 Paper 1 Solutions
Uploaded by
mariamtkCopyright:
Available Formats
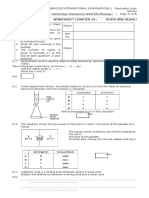
GCE O Level October/November 2008 Suggested Solutions
Chemistry (5072/5067 /01)
version 1.1
Ans
Workings/Remarks
Condenser allows unreacted M and N that have boiled off to convert back into liquid state.
The condenser is positioned vertically so that liquid M and N could flow back into the
boiling flask and continue reacting with each other.
Barium sulphate is insoluble.
Alkaline gases turn red litmus paper blue.
Ammonia reacts with water in damp litmus paper to form ammonium hydroxide, which is
alkaline.
Chlorine turns blue litmus to red then bleach.
Cation to anion ratio in ionic crystal lattice must show stoichiometry of the compound.
Giant covalent compound is insoluble in water.
Electronic configuration of O: 2.6 2.8 by providing 2 electrons to be stable
Electronic configuration of F: 2.7 2.8 by providing 1 electron to be stable
Electronic configuration of C: 2.4 2.8 by providing 4 electrons to be stable
P-Q: Change in temperature, average kinetic energy of molecules increases.
Q-R: No change in temperature, change in state occurs. Melting takes place at 0C.
R-S: Rise in temperature of water at liquid state.
T-U: Boiling, change in state, occurs at a fixed temperature 100C.
Only option A consists of one insoluble (calcium carbonate) and one soluble (sodium
chloride) salt.
Sublimation is the change from solid to gaseous state. Mercury is a liquid at room
temperature.
10
Mr of nitrogen and carbon monoxide is the same. Rate of diffusion is the same.
11
% change in vol. =
final no. of mole of gas initial no. of mol of gas
initial no. of mol of gas
A:
3/6 x 100 % = 50%
B:
5/7 x 100 % = 71.4%
C:
2/3 x 100 % = 66.7%
D:
3/3 x 100 % = 100%
100%
*note: ALL gases have same molar volume (vol. of one mole).
12
2HCl + Na2CO3 CO2 + 2NaCl + H2O
No. of mol of Na2CO3 = 25 / 1000 0.2 = 0.005
No. of mol of HCl = 0.005 x 2 = 0.01
Volume of HCl = 0.01 / 0.1 1000 = 100 cm3
13
Mass of O in X = 8 - 5.6 = 2.4g
No. of moles of O = 2.4 / 16
No. of moles of X = (2.4 / 16) (2 / 3)
For tuition, exam papers & Last-Minute Buddha Foot Hugging Syndrome treatment
+65 93805290 / missloi@exampaper.com.sg
facebook.com/JossSticksTuition
www.exampaper.com.sg
twitter.com/MissLoi
Unauthorized copying, resale or distribution prohibited.
Copyright 2008 exampaper.com.sg. All rights reserved.
1/3
GCE O Level October/November 2008 Suggested Solutions
Chemistry (5072/5067 /01)
version 1.1
14
For the same time taken, no. of electrons flowing in both the cells is the same.
15
I: melting is endothermic.
Since Q and S have different increase in mass, no. of electrons required to discharge each
cation in both cells would be different. This implies oxidation state of cation in both cells is
different and therefore different element and atomic mass.
II: boiling id endothermic
III: combustion is exothermic
IV: condensation is exothermic
16
Largest initial concentration gives fastest initial rate of reaction.
A:
40/36.5 = 1.10 mol/dm3
B:
20/36.5 = 0.548 mol/dm3
C: 10/36.5 10 = 2.74 mol/dm3
D: 4/36.5 20 = 2.19 mol/dm3
17
At time 0, pH of solution should be more than 7 due to presence of NaOH
18
Carbon dioxide is acidic.
19
Test for Al3+ ion with NaOH: Aluminium hydroxide (white ppt) is soluble in excess of
NaOH.
20
Lead (II) carbonate reacts with sulphuric acid to form lead (II) sulphate, which forms an
insoluble layer over lead(II) carbonate, preventing further reaction with acid.
21
H3PO4 + 3NaOH Na3PO4 + 3H2O
22
A: oxidation state of Mg: 0 in Mg to +2 in MgCl2 [O]
After neutralization (pH 7), pH of solution should be less than 7 due to presence of excess
HCl
Since concentration of both reactants is the same, volume of acid to volume of base ratio
should be 1:3
oxidation state of H: +1 in HCl to 0 in H2 [R]
B: no change in oxidation state
C: oxidation state of Cu: 0 in Cu to +2 in Cu(NO3)2 [O]
oxidation state of N: +5 in HNO3 to +4 in NO2 [R]
D: oxidation state of Cu: 0 in Cu to +2 in CuSO4 [O]
Oxidation state of S: +6 in H2SO4 to +4 in SO2 [R]
23
Organic acids are weak acids.
24
A: metals form basic oxides; non-metals form acidic oxides
25
One mole of sulphuric acid gives two moles of H+ ions whereas one mole of hydrochloric
acid gives one mole of H+ ion.
B: group number predicts no. of electrons involved in bonding, thus formula of compound.
CuSO4 + Na2CO3 Na2SO4 + CuCO3
No. of moles of CuSO4 = 4 / 1000 1.0 = 0.004
No. of moles of Na2CO3 = 8 / 1000 1.0 = 0.008
Compounds remained behind after reaction: colourless Na2CO3 (aq) (excess reactant),
colourless Na2SO4 (aq), green CuCO3 (s).
For tuition, exam papers & Last-Minute Buddha Foot Hugging Syndrome treatment
+65 93805290 / missloi@exampaper.com.sg
facebook.com/JossSticksTuition
www.exampaper.com.sg
twitter.com/MissLoi
Unauthorized copying, resale or distribution prohibited.
Copyright 2008 exampaper.com.sg. All rights reserved.
2/3
GCE O Level October/November 2008 Suggested Solutions
Chemistry (5072/5067 /01)
26
version 1.1
Melting point increases down the elements of Group VII.
Therefore, Y is below X in the group.
This implies Y has more protons and less reactive than X.
Group VII elements form diatomic molecules.
27
28
A: calcium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid to form salt and water only.
C: all carbonates are insoluble in water except sodium, potassium and ammonium carbonates.
D: zinc oxide reacts with sulphuric acid to form salt and water only.
29
Copper is less reactive than iron. Therefore, iron displaces copper ions from its solution,
resulting in copper deposit.
Fe (s) + Cu2+ (aq) Fe2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
30
A: Copper does not react with acid because it is less reactive than hydrogen.
B: Lead (II) sulphate is insoluble.
C: Some are colourless e.g. Pb(NO)3
31
*Note: This is different form question that is asking for % of nitrogen by mass in the
compound, in which mass of nitrogen is compared against Mr of compound.
Thus, the compound which contains the most number of nitrogen atoms in the molecular
formula should be the correct answer.
32
33
Combustion of fuels in cars and power stations produces carbon dioxide.
34
6CO2 + 12H20 C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
35
A: R, S and T contain 4 carbons.
Plants need to take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Carbon in glucose comes from
carbon in CO2.
sunlight
Syllabus states that paraffin (kerosene) is used as a fuel for heating and cooking and for
aircraft engines.
B: Alkyl group (CH3) attached to last carbon atom in linear chain is not considered as
branched chain.
C: S is but-2-ene.
36
General formula of alkane is CnH2n+2
37
Combustion hydrocarbon in excess oxygen gives carbon dioxide and water only. Therefore,
X is CO2.
Alkenes decolourise bromine spontaneously because of C=C bond. Therefore, Y is ethane.
38
Nylon is polyamide, which must contain amide linkage.
39
Esterification involves removal of one mole of H2O. (-OH from acid and H from alcohol)
40
Mg + 2CH3COOH (CH3COO)2Mg + H2
Terylene is polyester, which must contain ester linkage.
For tuition, exam papers & Last-Minute Buddha Foot Hugging Syndrome treatment
+65 93805290 / missloi@exampaper.com.sg
facebook.com/JossSticksTuition
www.exampaper.com.sg
twitter.com/MissLoi
Unauthorized copying, resale or distribution prohibited.
Copyright 2008 exampaper.com.sg. All rights reserved.
3/3
You might also like
- Group 4 elements: carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, lead and fleroviumDocument1 pageGroup 4 elements: carbon, silicon, germanium, tin, lead and fleroviummariamtkNo ratings yet
- Group 34 InfographicDocument1 pageGroup 34 InfographicmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Group 5 InfographicDocument1 pageGroup 5 InfographicmariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Lanthanides: Stable +3 IonsDocument1 pageThe Lanthanides: Stable +3 IonsmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Group 6 InfographicDocument1 pageGroup 6 InfographicmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Group 8 Noble Gases Elements Monatomic Rarely ReactDocument1 pageGroup 8 Noble Gases Elements Monatomic Rarely ReactmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Group 7 InfographicDocument1 pageGroup 7 InfographicmariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Transition MetalsDocument1 pageThe Transition MetalsJMSchultzNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Alkaline Earth Metals Properties and UsesDocument1 pageGroup 2 Alkaline Earth Metals Properties and UsesmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Synthetic radioactive transactinide elementsDocument1 pageSynthetic radioactive transactinide elementsmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Alkaline Earth Metals Properties and UsesDocument1 pageGroup 2 Alkaline Earth Metals Properties and UsesmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Book Inner 1Document1 pageBook Inner 1mariamtkNo ratings yet
- ST Love Is Brewing Test Tube LabelDocument1 pageST Love Is Brewing Test Tube LabelmariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Actinides - Radioactive Metals of the Periodic TableDocument1 pageThe Actinides - Radioactive Metals of the Periodic TablemariamtkNo ratings yet
- Scitech3Document1 pageScitech3mariamtkNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Right To KnowDocument6 pagesHazardous Substance Fact Sheet: Right To KnowmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry 13 C NMR Chemical ShiftsDocument1 pageAnalytical Chemistry 13 C NMR Chemical ShiftsmariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Maillard ReactionDocument1 pageThe Maillard ReactionmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Book CoverDocument1 pageBook CovermariamtkNo ratings yet
- Book Inner 2Document1 pageBook Inner 2mariamtkNo ratings yet
- Book Back CoverDocument1 pageBook Back CovermariamtkNo ratings yet
- CD CoverDocument1 pageCD CovermariamtkNo ratings yet
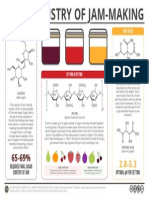
- The chemistry behind jam-makingDocument1 pageThe chemistry behind jam-makingmariamtkNo ratings yet
- CD Cover InnerDocument1 pageCD Cover InnermariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Gold Frankincense MyrrhDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Gold Frankincense MyrrhmariamtkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Warfare World War 1 Poison GasesDocument1 pageChemical Warfare World War 1 Poison GasesmariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of ChocolateDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of ChocolatemariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry Behind Champagne's BubblesDocument1 pageThe Chemistry Behind Champagne's BubblesmariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of CandyDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of CandymariamtkNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Conversion of Azobenzenes Into N, N'-Diarylhydrazines by Sodium DithioniteDocument5 pagesConversion of Azobenzenes Into N, N'-Diarylhydrazines by Sodium Dithionitehariharan rNo ratings yet
- Turning 'red wine' into 'water', 'milk', 'raspberry milkshake' and 'fizzy lemonadeDocument3 pagesTurning 'red wine' into 'water', 'milk', 'raspberry milkshake' and 'fizzy lemonadenelson_honorioNo ratings yet
- ECTFE Material Plastic Piping For H2SO4 98Document9 pagesECTFE Material Plastic Piping For H2SO4 98vinayakNo ratings yet
- 59 Comparison Study of Congo Red Dye Degradation Process Using Fenton's Reagent and Tio2Document6 pages59 Comparison Study of Congo Red Dye Degradation Process Using Fenton's Reagent and Tio2Jorellie PetalverNo ratings yet
- 10 Acids and AlkalisDocument5 pages10 Acids and Alkalisrashmi_harryNo ratings yet
- Bpharm 1 Sem Pharmaceutical Chemistry 1 Inorganic Chemistry Bop111 2020Document1 pageBpharm 1 Sem Pharmaceutical Chemistry 1 Inorganic Chemistry Bop111 2020ShvetaNo ratings yet
- Limit Test For Lead: BackgroundDocument3 pagesLimit Test For Lead: BackgroundRoshan KashyapNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 4Document35 pagesHydrocarbon 4AjayNo ratings yet
- Ekstraksi Senyawa Organik Asam, Basa, NetralDocument6 pagesEkstraksi Senyawa Organik Asam, Basa, NetralDaniel LieNo ratings yet
- Vatva Gidc CompaniesDocument2 pagesVatva Gidc CompaniesSameer Shiv Shakti100% (1)
- Chemistry FolioDocument43 pagesChemistry Folioharshini1010No ratings yet
- Biosynthesis ALKALOID 2pgDocument2 pagesBiosynthesis ALKALOID 2pgRobyn KleinNo ratings yet
- Sist Iso 6058 1996Document7 pagesSist Iso 6058 1996Cristiano PereiraNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Reactions of Cobalt Complexes PDFDocument3 pagesSynthesis and Reactions of Cobalt Complexes PDFRoberto SousaNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 20 MC PracticeDocument17 pagesTopic 10 20 MC PracticePipen 5No ratings yet
- Potassium HumateDocument7 pagesPotassium HumateAnonymous Wc69e8wpnNo ratings yet
- Aldol Condensation Mechanisms and ReactionsDocument4 pagesAldol Condensation Mechanisms and ReactionsSreeja SatheeshNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Elements: An OverviewDocument53 pagesGroup 5 Elements: An OverviewGustavo PossatoNo ratings yet
- Net Organic Chemistry For Study MaterialDocument19 pagesNet Organic Chemistry For Study MaterialRAJ VYASNo ratings yet
- Precam clXII qp4Document20 pagesPrecam clXII qp4GM Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Solvent Acid ClayDocument8 pagesSolvent Acid ClayimronmasfruriNo ratings yet
- Essential Organic Chemistry Canadian 3rd Edition by Bruice ISBN Test BankDocument13 pagesEssential Organic Chemistry Canadian 3rd Edition by Bruice ISBN Test Banknancy100% (25)
- Mind Mapping TemplateDocument15 pagesMind Mapping TemplateSuriati Bt A RashidNo ratings yet
- CC Grade 11 Chemistry Energetics CWDocument3 pagesCC Grade 11 Chemistry Energetics CWMaliq MorrisNo ratings yet
- Penta Sugars PDFDocument8 pagesPenta Sugars PDFMaryam YousifNo ratings yet
- COORDINATION CHEMISTRY TITLEDocument11 pagesCOORDINATION CHEMISTRY TITLESubhasish Sau100% (2)
- Addition Reactions I. What Is Addition?Document21 pagesAddition Reactions I. What Is Addition?Hannah LiNo ratings yet
- Sodium Cyanide Production ProcessDocument17 pagesSodium Cyanide Production ProcessAltar ParssoyNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Screening of Artabotrys Crassifolius Hook.F. & Thomson (Annonaceae Juss.)Document4 pagesPhytochemical Screening of Artabotrys Crassifolius Hook.F. & Thomson (Annonaceae Juss.)DiarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry LimestoneDocument2 pagesChemistry Limestonekhushi wNo ratings yet