Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Onion and Potato Under The Essential Commodity Act:: Act Parliament of India Hoarding or Blackmarketing
Uploaded by
Pulkit MittalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Onion and Potato Under The Essential Commodity Act:: Act Parliament of India Hoarding or Blackmarketing
Uploaded by
Pulkit MittalCopyright:
Available Formats
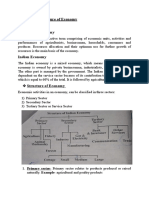
The Essential Commodities Act is an act of Parliament of India which
was established to ensure the delivery of certain commodities or products,
the supply of which if obstructed owing to hoarding or blackmarketing
would affect the normal life of the people. This includes foodstuff, drugs,
fuel (petroleum products)
onion and potato under the Essential Commodity Act:
Stepping up its battle against inflation, The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA)
on Wednesday agreed to bring onion and potato under the Essential Commodity Act in a move
to impose stock holding limits and curb hoarding of these two commodities and control
the decision will impose limits on the quantity of onions and potatoes that individuals
and wholesale traders can stockpile. The move will also empower state governments to
take measures to prevent hoarding.
This will enable state governments to continue to take effective de-hoarding operations
under the Essential Commodities Act by fixing stock limits/licensing requirements in
respect of these commodities, especially in view of rising prices, the press statement
said.
The Essential Commodities Act provides for the regulation and control of production,
distribution and pricing of commodities, which are declared as essential for maintaining
or increasing supplies or for securing their equitable distribution and availability at fair
prices
in last year,onions were in news for long period of time and it is one of the factors why congress didnt came in power
again this year.so the new govt take initiative and consider it in essential commodity act.
The Essential Commodities Act is an act of Parliament of India which was established to ensure
the delivery of certain commodities or products, the supply of which if obstructed owing to
hoarding or blackmarketing would affect the normal life of the people. This includes foodstuff,
drugs, fuel (petroleum products).
this will enable state govt to take effective
DEMAND FOR INDIAN HANDICRAFT INDUSTRY
The country of India is known for its ethnicity. Handicrafts form the gateway to this
ethnic nation. So far as art and culture is concerned, India features amongst the culturally
rich countries in the world. The country is fortunate enough to possess some highly
skilled artisans. They have increased the fame of Indian handicrafts around the globe. Till
now, many rural people earn their livelihood from their creative pieces of art.
India, a country with 26 states and 18 languages and more than 1500 dialects offers an
enormous range of handicrafts from each of the states. Major centers in Uttar Pradesh are
Moradabad also known as the "Peetalnagari" (City of Brass), Saharanpur for its wooden
articles, Ferozabad for Glass. The North Western state of Rajasthan has to offer the
famous Jaipuri quilts, Bagru and Sanganer printed textiles and wooden and wrought iron
furniture from Jodhpur. The coastal state of Gujarat comes with embroidered articles
from Kutch. Narsapur in Andhra Pradesh is famous for its Lace and Lace goods. But this
is only a small part of the total product range. India offers much more.
Though Indian Handicraft industry is considered a cottage industry, but it has evolved as
one of the major revenue generator over the years. There has been consistent growth of
15% over few years and the industry has evolved as one of the major contributor for
export and foreign revenue generation.
COUNTRY WISE EXPORT SHARE DATA
The Indian Handicraft Industry stands a unique place among all other industries. It
represents the rich culture, tradition and heritage of India. Indias rich cultural
diversity and heritage provides a unique and huge resource for developing craft
products.
The Indian Handicraft Industry is showing continuous growth rate of 20% every year
and it is one of the most important segment of decentralized sector in India. Also, it
has shown continuous growth at the rate of 15-20% over the years and contributes
major role for export and foreign earnings. The export earnings from Indian
handicrafts industry for the period 1998-99 amounted to US$ 1.2 billion
YEAR WISE EXPORT DATA OF INDIAN HANDICRAFT
FACTORS CONTRIBUTING IN INCREASING INDIAS EXPORTS
low capital investment, high ratio of value addition
highly labour intensive
decentralized i.e. spread all over the country in rural and urban areas.
Numerous artisans are engaged in crafts work on part-time basis.
The industry provides employment to over six million artisans (including those in carpet
trade), which include a large number of women and people belonging to the weaker
sections of the society.
high potential for export and foreign exchange earnings for the country.
DEMAND & SUPPLY EXPECTED IN 2015
FACTORS AFFECTING DEMAND AND SUPPLY OF INDIAN HANDICRAFT
(1) Tastes and preferences of the consumer:
Tastes include fashion, habit, customs etc. A good for which consumers tastes and
preferences are higher, claim high demand. Thus there is a shift in the demand curve.
With the change inconsumer's taste and preference in favor of handicrafts, the demand for
handicrafts increased substantially leading to a rightward shift in demand curve.
(2) Income of the people:
The demand for goods depends upon the income of the people. There is direct relation
betweenincome and demand for immodesties. A rise in income gives rise to greater
purchasing power. Thusincrease in income has a positive effect on demand for Indian
Handicrafts in foreign countries.
(3) Population:
Rise of population also gives rise to demand for necessaries of life. The composition and
size of population affect the demand. With high birth rate, the demand for handicrafts is
bound to take a rightward shift in the near future.
Note: The below diagram showcases the effects of Tastes, Income and Population on the
demand curve of Indian Handicrafts in the world.
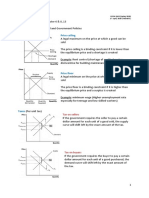
(4) Effect of Taxes:
The exporters of Indian Handicraft are facing a tough task ahead of them due to the taxes
incurred by the Government. Though, it increases revenue for the government, but at the
same time it is discouraging the suppliers to export Indian handicraft, thereby acting as a
constraint for the suppliers as they have to borne the taxes from their income. This will
lead to a leftward shift in the supply curve. The figure below showcases the effect of
taxes on the supply of Indian Handicrafts.
CROSS ELASTICITY OF HANDICRAFT WITH READYMADE (MACHINE
MADE) GOODS
In economics, the cross elasticity of demand or cross-price elasticity of demand measures
the responsiveness of the demand for a good to a change in the price of another good. It is
measured as the percentage change in demand for the first good that occurs in response to
a percentage change in price of the second good.
Ex = % change in quantity demanded of Handicraft
% change in price of readymade goods
As the cost of skilled labour is increasing, the cost of readymade goods is increasing.
This increased cost is thus decreasing the demand for ready made goods, which is
increasing the demand for Handicraft Goods.
INCOME ELASTICITY OF HANDICRAFT
In economics, income elasticity of demand measures the responsiveness of the demand
for a good to a change in the income of the people demanding the good, ceteris paribus. It
is calculated as the ratio of the percentage change in demand to the percentage change in
income.
Ey = % change in quantity demanded of Handicraft
% change in Income of People
As there is a boom in the market, people are earning more thereby the spending power of
people has increased. This has increased the demand for Indian Handicraft in the
importing countries. This has led to a rightward shift in the demand curve.
MANAGERIAL IMPLICATIONS
v Supporting the exporters to penetrate new markets.
v Upgradation of technology for production of handicrafts in large volumes as is adopted by
several countries.
v Interests of artisans should also be kept in mind in order to induce further productivity in a
relatively lesser amount of time.
v Proper training schools for improvement of skills to improve the quality and thereby
leading to increase in demand in foreign countries.
v Setting up of warehouses in major importing countries will help to boost further demand.
production Overview of Onion Industry in India
In India, onion is largely grown in the western,
northern and southern parts both in rabi and
kharif seasons. Its supply is available throughout
the year albeit with different volumes. India
produces all three varieties of onion red, yellow
and white. In the northern part of the country,
onion is usually grown in the winter (rabi) season.
While in the southern and western states of
Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat
and Maharashtra, it is grown in winter (rabi) as
well as in the rainy (kharif) seasons
a) World Scenario
India is the second largest producer of onion in
the world next to China (Table 2.1). According to
2010 FAO estimates, India contributes nearly
19.25 percent of world onion production.
Though the second largest onion producer, India
significantly lags behin Some of the reasons
behind low productivity in India include poor
irrigation facilities, use of local variety seeds, small
land holding and poor economic background of
farmers, lack of use of improved method of
cultivation, less use of chemical fertilizers and
pesticide, higher post-harvest losses and absence
of good scientific storage facilities
d in the productivity or
yield of the onion.
c) State-level Scenario
. Although onion is cultivated almost all
over the country, the major producing states are
Maharashtra, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh,
Gujarat, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Uttar
Pradesh, Orissa, and Tamil Nadu
The significant increase in the production
in the past decade was attributed to: increase in
the area under horticultural crop, improved
technology and the government efforts under
National Horticultural Mission (NHM).
You might also like
- FertilizerDocument80 pagesFertilizerJanki PatelNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Study Report of Food Processing, Krishna District, Andhra PradeshDocument33 pagesDiagnostic Study Report of Food Processing, Krishna District, Andhra PradeshSudhir ImperfectNo ratings yet
- ECO201 CheatsheetThe title "TITLE ECO201 Cheatsheet" is concise and SEO-optimized as it contains the relevant keywords "ECO201" and "CheatsheetDocument5 pagesECO201 CheatsheetThe title "TITLE ECO201 Cheatsheet" is concise and SEO-optimized as it contains the relevant keywords "ECO201" and "Cheatsheetwasif ahmedNo ratings yet
- Applied EconDocument3 pagesApplied EconGermano GambolNo ratings yet
- Handicrafts IndustryDocument24 pagesHandicrafts Industryahmadksath100% (7)
- Food Processing Sector in IndiaDocument18 pagesFood Processing Sector in IndiaSuresh Kumar VengaliNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics Douglas-All inDocument207 pagesManagerial Economics Douglas-All inMuhammad Iqbal80% (5)
- Microeconomics 8th Edition Pindyck Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesMicroeconomics 8th Edition Pindyck Solutions ManualBrettClinewdjc100% (58)
- Managerial Economics ExercisesDocument6 pagesManagerial Economics ExercisesZia NuestroNo ratings yet
- Tribal HandicraftsDocument5 pagesTribal Handicraftsnamratasachan09No ratings yet
- Project Report ON Agriculture Foreign Trade in India: Submitted By: Submitted ToDocument18 pagesProject Report ON Agriculture Foreign Trade in India: Submitted By: Submitted ToParul GirdharNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Current Scenario and Contribution of Handicrafts in Indian EconomyDocument5 pagesAn Analysis of Current Scenario and Contribution of Handicrafts in Indian EconomyMritunjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Agriculture Foreign Trade in IndiaDocument17 pagesProject Report On Agriculture Foreign Trade in IndiarriittuuNo ratings yet
- Passage To India: Country ProfileDocument14 pagesPassage To India: Country ProfileIgor DovečerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Industry ProfileDocument77 pagesChapter 1: Industry ProfileSumit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Indian HandicraftsDocument7 pagesIndian HandicraftsDr. S. P. MishraNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION Sanitaryware IndustryDocument3 pagesINTRODUCTION Sanitaryware IndustryNinandha PranavNo ratings yet
- Group- 3 - Agriculture sector in India (BEP) ReportDocument24 pagesGroup- 3 - Agriculture sector in India (BEP) ReportKeshav KumarNo ratings yet
- Rural Advertising in India: PGDMA 1403Document7 pagesRural Advertising in India: PGDMA 1403Rahul DukaleNo ratings yet
- Nature and Structure of EconomyDocument3 pagesNature and Structure of EconomyAnkita Kumari SinghNo ratings yet
- Indian EconomyDocument28 pagesIndian EconomyBHAVIK RATHODNo ratings yet
- Sector Report PDFDocument1 pageSector Report PDFJoshua AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Agribusiness PDFDocument23 pagesAgribusiness PDFNavaroon SharmaNo ratings yet
- Role of FDI in Fertilizer Industries in IndiaDocument8 pagesRole of FDI in Fertilizer Industries in IndiaInternational Journal of Current Science Research (IJCSR)No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour in The 21ST Century in The Indian BackdropDocument6 pagesConsumer Behaviour in The 21ST Century in The Indian BackdropSourajit GuptaNo ratings yet
- IPF 2016 Paper Chatterjee KapurDocument30 pagesIPF 2016 Paper Chatterjee Kapurhansdeep479No ratings yet
- Indian ConsumerDocument18 pagesIndian Consumerrumnraisin67% (3)
- Rural Marketing NotesDocument34 pagesRural Marketing NotesAnonymous d3CGBMzNo ratings yet
- 4 As in Rural MarketingDocument8 pages4 As in Rural MarketingsudhirNo ratings yet
- Agribusiness Scenario in IndiaDocument3 pagesAgribusiness Scenario in IndiaNeena BhattNo ratings yet
- Handloom VisionDocument14 pagesHandloom VisionNarasimha Reddy DonthiNo ratings yet
- Enhancing The Pungency Through "Pink Revolution" - Marketing of Onion in IndiaDocument8 pagesEnhancing The Pungency Through "Pink Revolution" - Marketing of Onion in IndiaAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Rural Market For FMCG: Around 6,00,000 Villages. Rural India Offers Tremendous GrowthDocument3 pagesRural Market For FMCG: Around 6,00,000 Villages. Rural India Offers Tremendous GrowthPrithvi BarodiaNo ratings yet
- Role of Agriculture and Importance of Rice in IndiaDocument42 pagesRole of Agriculture and Importance of Rice in IndiaYUKTA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Trends in Income in India During the Last Decade 2011-2021Document17 pagesTrends in Income in India During the Last Decade 2011-2021Suraj BoseNo ratings yet
- Impact of The NREGP On Rural Livelihoods Amir Ullah Khan and M R SalujaDocument30 pagesImpact of The NREGP On Rural Livelihoods Amir Ullah Khan and M R Salujadd_pacNo ratings yet
- FMCG Sectoral PDFDocument44 pagesFMCG Sectoral PDFSonali GharatNo ratings yet
- Fast Moving Consumer GoodsDocument44 pagesFast Moving Consumer GoodsDeenDayal50% (4)
- Central Banking ProjectDocument10 pagesCentral Banking ProjectPrashant NathaniNo ratings yet
- Indian Agriculture SectorDocument5 pagesIndian Agriculture SectorNikhil JainNo ratings yet
- India Pulses Report January 2012Document64 pagesIndia Pulses Report January 2012chandu1113No ratings yet
- General AwarenessDocument158 pagesGeneral AwarenessSri Ram SahooNo ratings yet
- AGRICULTUREDocument32 pagesAGRICULTUREbabu rsNo ratings yet
- Importance of Agriculture in Indian EconomyDocument10 pagesImportance of Agriculture in Indian EconomyAnanya sahuNo ratings yet
- Argirculture in IndiaDocument32 pagesArgirculture in Indiababu rs100% (1)
- Indian Textile & Handicrafts Industry Is The Largest Employment Generator After Agri: Ajay TamtaDocument9 pagesIndian Textile & Handicrafts Industry Is The Largest Employment Generator After Agri: Ajay TamtaAnuradha SinghNo ratings yet
- Retail Industry in Dynamic Business EnvironmentDocument19 pagesRetail Industry in Dynamic Business EnvironmentkantimbaNo ratings yet
- Rural IndiaDocument2 pagesRural IndiaAnonymous y3E7iaNo ratings yet
- The People Who Matter Most: P. SainathDocument9 pagesThe People Who Matter Most: P. SainathkannadiparambaNo ratings yet
- Rural Industry in IndiaDocument7 pagesRural Industry in IndiaShree VarshiniNo ratings yet
- India's Growing Middle Class to Transform EconomyDocument19 pagesIndia's Growing Middle Class to Transform EconomyRahman HasibNo ratings yet
- Impact of Technology On Indian EconomyDocument6 pagesImpact of Technology On Indian Economyp_saini0% (1)
- Agriculture in India: Contemporary Challenges: in the Context of Doubling Farmer’s IncomeFrom EverandAgriculture in India: Contemporary Challenges: in the Context of Doubling Farmer’s IncomeNo ratings yet
- The State of Food and Agriculture 2017. Leveraging Food Systems for Inclusive Rural TransformationFrom EverandThe State of Food and Agriculture 2017. Leveraging Food Systems for Inclusive Rural TransformationNo ratings yet
- Livestock TechnologyFrom EverandLivestock TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Summary: Planet India: Review and Analysis of Mira Kamdar's BookFrom EverandSummary: Planet India: Review and Analysis of Mira Kamdar's BookNo ratings yet
- PI PrepDocument1 pagePI PrepPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Term V Schedule From 19.10.15 To 22.11.152Document4 pagesTerm V Schedule From 19.10.15 To 22.11.152Pulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Michael DixonDocument1 pageBio Michael DixonPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Marie KlemchukDocument1 pageBio Marie KlemchukPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Scott CarterDocument1 pageBio Scott CarterPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Jake AndersonDocument1 pageBio Jake AndersonPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Michael MoritzDocument1 pageBio Michael MoritzPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Tim LeeDocument1 pageBio Tim LeePulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Jake AndersonDocument1 pageBio Jake AndersonPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Michael AbramsonDocument1 pageBio Michael AbramsonPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Doug LeoneDocument1 pageBio Doug LeonePulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Melinda DunnDocument1 pageBio Melinda DunnPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Andrew Reed, MDocument1 pageBio Andrew Reed, MPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Bio Andrew KovacsDocument1 pageBio Andrew KovacsPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- DPO Course Outline (2014-2016)Document4 pagesDPO Course Outline (2014-2016)Pulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Find fitness and diet options near youDocument15 pagesFind fitness and diet options near youPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Round 2 Shortlist PDFDocument1 pageRound 2 Shortlist PDFPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Just Dial-A Case Study in Service Marketing: Submitted To: Prof. Devang PatelDocument30 pagesJust Dial-A Case Study in Service Marketing: Submitted To: Prof. Devang PatelRahil ShahNo ratings yet
- Debreifing Questions (Kpit Cummins)Document3 pagesDebreifing Questions (Kpit Cummins)Pulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- DGB Course Outline For Sec. BCwrgwrDE 2014 24 SepDocument7 pagesDGB Course Outline For Sec. BCwrgwrDE 2014 24 SepPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Address MonaDocument1 pageAddress MonaPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- MSM Course OutlineDocument7 pagesMSM Course OutlinePulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Mumbai Angels Business Plan Pitch TemplateDocument1 pageMumbai Angels Business Plan Pitch TemplatePulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Vaseline 200 ML 120Document2 pagesVaseline 200 ML 120Pulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Lecture Intro To NetworksDocument35 pagesLecture Intro To NetworksPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Class Schederqetgule Term IDocument1 pageClass Schederqetgule Term IPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- SISS College Management (Responses)Document8 pagesSISS College Management (Responses)Pulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Production Analysis: Managerial EconomicsDocument2 pagesProduction Analysis: Managerial EconomicsPulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- Lecture DBM1Document24 pagesLecture DBM1Pulkit MittalNo ratings yet
- (R) PencilsDocument51 pages(R) PencilsMohammad Ruhul0% (2)
- CH 06 Student Handout 8eDocument11 pagesCH 06 Student Handout 8eNguyễn Vinh QuangNo ratings yet
- TBCH 12Document16 pagesTBCH 12bernandaz123No ratings yet
- BBM102 Microeconomics TMA 1Document4 pagesBBM102 Microeconomics TMA 1Jane HoNo ratings yet
- EFM College NotesDocument178 pagesEFM College Notesrahul100% (1)
- Business Economics BCADocument25 pagesBusiness Economics BCAamjoshuabNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Applications of DifferentiationDocument4 pagesAssignment: Applications of DifferentiationAbdul Hanan SheikhNo ratings yet
- MGEA02Document14 pagesMGEA02Tim SmetNo ratings yet
- ECONOMICS P2 M18 To J22 C.VDocument392 pagesECONOMICS P2 M18 To J22 C.VsukaNo ratings yet
- Q1 Performance ReviewDocument19 pagesQ1 Performance ReviewEgie Patrimonio GirayNo ratings yet
- Calculating Elasticity WorksheetDocument3 pagesCalculating Elasticity WorksheetAngelicaMaeGandolaNoolNo ratings yet
- MDS3 Ch09 Pricing Policy Nov2011Document22 pagesMDS3 Ch09 Pricing Policy Nov2011Andre SamsungNo ratings yet
- Law of SupplyDocument15 pagesLaw of SupplyZahid RaihanNo ratings yet
- ECO 561 Final Exam AnswersDocument10 pagesECO 561 Final Exam AnswersdavidslewisNo ratings yet
- Cross Elasticity of DemandDocument4 pagesCross Elasticity of DemandShaniya KoyaNo ratings yet
- B.A. Microeconomics Assignment Analyzes Cost CurvesDocument6 pagesB.A. Microeconomics Assignment Analyzes Cost CurvesVijay SarmalNo ratings yet
- BHMCT/Managerial Economics: Item Text Option Text 1 Option Text 2 Option Text 3 Option Text 4Document2 pagesBHMCT/Managerial Economics: Item Text Option Text 1 Option Text 2 Option Text 3 Option Text 4Xiaomi TvNo ratings yet
- Price Ceiling: This WeekDocument6 pagesPrice Ceiling: This WeekAdreshNo ratings yet
- A South Asian Perspective: Marketing Management, 12/eDocument23 pagesA South Asian Perspective: Marketing Management, 12/eprayank jainNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document21 pagesCH 10Shomu BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Mgea02 TT1 2011F ADocument9 pagesMgea02 TT1 2011F AexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Economics of Business EnterpriseDocument31 pagesAssignment-Economics of Business EnterpriseGivaji PradeepNo ratings yet
- Bangalore UniversityDocument64 pagesBangalore UniversityNavin TiwariNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics ModuleDocument80 pagesEngineering Economics ModuleCrisanto EncilanNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand: Types, Measurement and FactorsDocument35 pagesElasticity of Demand: Types, Measurement and FactorsShubham GuptaNo ratings yet