Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem (O) (1) Notes - Studyguidepk
Uploaded by
Smr OnlyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem (O) (1) Notes - Studyguidepk
Uploaded by
Smr OnlyCopyright:
Available Formats
www.studyguide.
pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
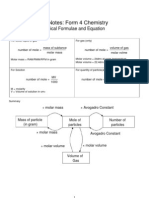
Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry
Chemical Formulae and Equation
Calculation
For Solid, liquid or gas
For gas (only)
number of mole =
mass of subtance
molar mass
number of mole =
volume of gas
molar volme
Molar mass = RAM/RMM/RFM in gram
Molar volume = 24dm3 at room temperature
Molar volume = 22.4dm3 at s.t.p.
For Solution
For quantity of particle(atom,molecule,ion)
number of mole =
MV
1000
number of mole =
quantity of particle
6.02 1023
M = molarity
V = Volume of solution in cm3
Summary
molar mass
Mass of particle
(in gram)
Avogadro Constant
Mole of
particles
molar mass
Number of
particles
Avogadro Constant
molar volume
molar volume
Volume of
Gas
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Chemical Formula
Cation (Positive Ions)
Ion
Potassium
Symbol
K+
Ion
Calcium
Symbol
Ca2+
Ion
Aluminium
Symbol
Al3+
Sodium
Na+
Magnesium
Mg2+
Iron (III)
Fe3+
Lithium
Li+
Zinc
Zn2+
Chromium(III)
Cr3+
Hydrogen
H+
Barium
Ba2+
Argentums(I)
Ag+
Iron (II)
Fe2+
Mercury(I)
Hg+
Tin (II)
Sn2+
Ammonium
NH4+
Lead(II)
Pb2+
Copper(II)
Cu2+
Manganese(II)
Mn2+
Ion
Symbol
Ion
Symbol
Anion (Negative Ions)
Ion
Symbol
Oxide
O2-
Hydroxide
OH-
Ethanoate
Fluoride
F-
Sulphate
SO42-
Manganate(VII)
MnO4-
Chloride
Cl-
Nitrate
NO3-
Dichromate(VI)
Cr2O72-
Bromide
Br-
Carbonate
CO32-
Phosphate
PO43-
Thiosulphate
S2O32-
Iodide
I-
CH3COO-
Formulae for Certain Molecule
Karbon monoxide
Carbon dioxide
Nitrogen monoxide
Nitrogen dioxide
Sulphur dioxide
Sulphur trioxide
Fluorine
Bromine
Chlorine
Iodine
CO
CO2
NO
NO2
SO2
SO3
F2
Br2
Cl2
I2
Ammonia
water
Hydrogen chloride
Tetrachloromethane
Glucose
Hydrogen bromide
Hydrogen iodide
Hydrogen sulphide
Ethanol
Ethanoic Acid
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
NH3
H2O
HCl
CCl4
C6H12O6
HBr
HI
H2S
C2H5OH
CH3COOH
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Periodic Table
Reaction of Group 1 Elements
1. Reaction with Oxygen
The entire group 1 metal can react with oxygen to form metal oxide.
4Li + O2 2Li2O
4Na + O2 2Na2O
4K + O2 2K2O
The metal oxide of group 1 elements can dissolve in water to form alkali (hydroxide) solution
Li2O + H2O 2LiOH
Na2O + H2O 2NaOH
K2O + H2O 2KOH
2. Reaction with halogen (Chlorine)
2Li + Cl2 2LiCl
2Na + Cl2 2NaCl
2K + Cl2 2KCl
3. Reaction with water
The entire group 1 metal can react with water to produce alkali (hydroxide) solution and hydrogen gas.
2Li + 2H2O 2LiOH + H2
2Na + 2H2O 2NaOH + H2
2K + 2H2O 2KOH + H2
Reaction of Group 17 Elements
1. React with water
Cl2 + H2O HCl + HOCl
Br2 + H2O HBr + HOBr
I2 + H2O HI + HOI
2. React with Sodium Hydroxide
Cl2 + 2NaOH NaCl + NaOCl + H2O
Br2 + 2NaOH NaBr + NaOBr + H2O
I2 + 2NaOH NaI + NaOI + H2O
3. React with Iron
3Cl2 + 2Fe 2FeCl3
3Br2 + 2Fe 2FeBr3
3I2 + 2Fe 2FeI3
Preparation of Chlorine Gas
2KMnO4 + 16HCl 2KCl + 2MnCl2 + 5Cl2 + 8H2O
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Electrochemistry
Electrolyte
Ionisation of Electrolyte
Ionisation of Molten Compound
PbBr2 Pb2+ + BrNaCl Na+ + ClAl2O3 2Al3+ + 3O2-
Ionisation of Aqueous Solution
NaCl Na+ + ClH2O H+ + OH-
HCl H+ + ClH2O H+ + OH-
Discharge of Positive Ion
CuSO4 Cu2+ + SO42H2O H+ + OH-
Discharge of Negative Ion
Na + e Na
2Cl- Cl2 + 2e
Observation:
Grey deposit is formed.
Observation:
Bubbles of pungent yellowish green gas are
produced. The gas turns moist litmus paper to red
and then bleaches it.
Al3+ + 3e Al
Observation:
Grey deposit is formed.
2Br- Br2 + 2e
Observation:
Molten electrolyte:
Brown colour gas is produced.
Pb + 2e Pb
2+
Observation:
Grey deposit is formed.
Aqueous solution:
Light brown solution is formed.
Cu + 2e Cu
2+
Observation:
Brown deposit is formed.
2I- I2 + 2e
Observation:
Molten electrolyte:
Brown colour gas is produced.
Ag+ + e Ag
Observation:
Silver deposit is formed.
Aqueous solution:
Light brown solution is formed. The solution turns
blue when a few drops of starch solution is added in.
2H+ + 2e H2
Observation:
Gas bubble is formed. A pop sound is produced
4OH- O2 + 2H2O + 4e
when a lighted splinter is placed near the mouth of Observation:
the test tube.
Gas bubble is formed. Gas produces light up a
wooden splinter.
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Acid and Base
Ionisation of Acid
Hydrochloric Acid
Sulphuric Acid
HCl H + Cl
HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl+
H2SO4 H+ + SO42H2SO4 + 2H2O 2H3O+ + SO42-
Nitric Acid
HNO3 H+ + NO3HNO3 + H2O H3O+ + NO3-
Ethanoic Acid
CH3COOH H+ + CH3COOCH3COOH + H2O H3O+ + CH3COO-
Chemical Properties of Acid
Acid + Reactive Metal Salt + H2
Example:
2HCl + Zn ZnCl2 + H2
6HNO3 + 2Fe 2Fe(NO3)3 + 3H2
H2SO4 + Pb PbSO4 + H2
6CH3COOH + 2Al 2Al(CH3COO)3 + 3H2
Acid + Metal Oxide Salt + H2O
Example:
2HCl + ZnO ZnCl2 + H2O
2HNO3 + MgO Mg(NO3)2 + H2O
H2SO4 + CuO CuSO4 + H2O
2CH3COOH + Na2O 2CH3COO-Na++ H2O
Acid + Metal Hydroxide Salt + H2O
Example:
2HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + 2H2O
HNO3 + NaOH NaNO3 + H2O
H2SO4 + 2NH4OH (NH4)2SO4 + 2H2O
or
- +
CH3COOH + KOH CH3COO K + H2O
H2SO4 + 2NH3 (NH4)2SO4
Acid + Metal Carbonate Salt + CO2 + H2O
Example:
2HCl + ZnCO3 ZnCl2 + CO2 + H2O
2HNO3 + CaCO3 Ca(NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O
H2SO4 + Na2CO3 Na2SO4 + CO2 + H2O
2CH3COOH + MgCO3 Mg(CH3COO)2 + CO2 + H2O
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Salt
Solubility of Salt
Salt
Salt of potassium, sodium and ammonium
Salt of nitrate
Salt of sulphate
Solubility
All are soluble in water
All are soluble in water
Mostly soluble in water except:
(Pb) Lead sulphate
(Ba) Barium sulphate
(Ca) Calcium sulphate
Mostly soluble in water except:
(Pb) Lead chloride
(Ag) silver chloride
(Hg) mercury chloride
Mostly insoluble in water except:
Potassium carbonate
Sodium carbonate
Ammonium carbonate
Solubility
Mostly insoluble in water except: K2O and Na2O.
Mostly insoluble in water except: NH4OH, KOH and NaOH
Salt of chloride
Salt of carbonate
Oxide and Hydroxide
Oxide
Hydroxide
Preparation of Salt
Preparation of Soluble Salt
Salt of Potassium, Sodium and Ammonium
Acid + Alkali Salt + Water
Example: Preparation of Sodium Chloride (NaCl)
HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O
Salt of non-Potassium, Sodium and Ammonium
Acid + Reactive metal Salt + Hydrogen Gas
Acid + Metal Oxide Salt + Water
Acid + Metal Carbonate Salt + Water + Carbon Dioxide
Example: Preparation of Zinc Sulphate (ZnSO4)
H2SO4 + Zn ZnSO4 + H2
H2SO4 + ZnO ZnSO4 + H2O
H2SO4 + ZnCO3 ZnSO4 + H2O + CO2
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Preparation of Insoluble Salt
Ionic Precipitation
Insoluble salts can be made by double decomposition. This involves mixing a solution that contains its
positive ions with another solution that contains its negative ions.
Example: Preparation of Silver Nitrate
AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq)
Ag+ (aq) + C1- (aq) AgCl (s)
(ionic equation)
Colour of Salt
Salt or metal oxide
Salt of:
Sodium, Calcium, Magnesium, Aluminium, zinc,
Lead, ammonium
Chloride, sulphate, nitrate, carbonate
Salt of Copper(II).Copper(II) Carbonate
Copper(II) sulphate, Copper(II) nitrate, Copper(II)
chloride
Copper(II) oxide
Salt of Iron (II)
Iron(II) sulphate; Iron(II) nitrate; Iron(ID chloride
Salt of Iron (III).
Iron(III) sulphate; Iron(III) nitrate; Iron(III)
chloride
Lead Iodide
Lead Chloride
Zink oxide
Lead(II) oxideMagnesium oxide, Aluminium oxide
Potassium oxide, Sodium oxide, Calcium oxide
Solid
Aqueous solution
White
Colourless
Green
Insoluble
Blue
Blue
Black
Insoluble
Green
Green
Brown
Brown
Yellow
White
Yellow when it is hot and
white when it is cold.
Brown when it is hot and
yellow when it is cold.
White
White
Insoluble
Insoluble
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
Insoluble
Insoluble
Insoluble
Colourless
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Heating effect on Salt
Heating
Effect
CO32-
NO3 -
SO42-
Cl-
Most Probably
Release CO2
Most Probably
Release NO2
Most Probably
Release SO3
Most Probably
No effect
Heating Effect on Carbonate Salt
Carbonate Salt
Equation of The Reaction
Potassium carbonate
Sodium carbonate
Calcium carbonate
Magnesium carbonate
Aluminium carbonate
Zinc carbonate
Iron (III) carbonate
Lead(II) carbonate
Copper(II) carbonate
Not decomposible
CaCO3 CaO + CO2
MgCO3 MgO + CO2
Al2(CO3)3 Al2O3 + 3CO2
ZnCO3 ZnO + CO2
Fe2(CO3)3 Fe2O3 + 3CO2
PbCO3 PbO + CO2
CuCO3 CuO + CO2
Mercury(II) carbonate
Silver(I) carbonate
2HgCO3 2Hg + 2CO2 + O2
2Ag2CO3 4Ag + 2CO2 + O2
Ammonium carbonate
(NH4)2CO3 NH3 + CO2 + H2O
Heating Effect on Nitrate Salt
Nitrate Salt
Equation of The Reaction
Potassium nitrate
2KNO3 2KNO2 + O2
Sodium nitrate
2NaNO3 2NaNO2 + O2
Calcium nitrate
Magnesium nitrate
Aluminium nitrate
Zink nitrate
Iron (III) nitrate
Lead(II) nitrate
Copper(II) nitrate
Mercury(II) nitrate
Silver(I) nitrate
Ammonium nitrate
2Ca(NO3)2 2CaO + 4NO2 + O2
Mg(NO3)2 2MgO + 4NO2 + O2
4Al(NO3)3 2Al2O3 + 12NO2 + 3O2
Zn(NO3)2 2ZnO + 4NO2 + O2
4Fe(NO3)3 2Fe2O3 + 12NO2 + 3O2
Pb(NO3)2 2PbO + 4NO2 + O2
Cu(NO3)2 2CuO + 4NO2 + O2
Hg(NO3)2 Hg + 2NO2 + O2
2AgNO3 2Ag + 2NO2 + O2
NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O
[NOTES: Nitrogen dioxide, NO2 is acidic gas and is brown in colour.]
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Heating effect on sulphate salt
Most sulphate salts do not decompose by heat. Only
certain sulphate salts are decomposed by heat when
heated strongly.
Zinc sulphate, Copper (II) sulphate, Iron (III)
sulphate
The heating effect on chloride salts
All chloride salts are not decomposable by heat
except ammonium chloride.
Example:
NH4Cl NH3 + HCl
ZnSO4 ZnO + SO3
CuSO4 CuO + SO3
2Fe2(SO4)3 Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
Ammonium sulphate
(NH4)2SO4 2NH3 + H2SO4
Identification of Gases
Gasses
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Carbon Dioxide
Chlorine
Ammonia
Characteristics
Rekindle glowing splinter.
Explode with a pop sound when brought close to a lighted splinter.
Turns lime water chalky.
Bleach moist litmus paper.
Pungent smell.
Turn moist red litmus paper to blue.
Produces white fume when reacts with concentrated hydrochloric Acid.
Pungent smell.
Bleach the purple colour of potassium manganate(VII).
Turn moist blue litmus paper to red.
Pungent smell.
Brown in colour.
Turn moist blue litmus paper to red.
Sulphur Dioxide
Nitrogen Dioxide
Qualitative analysis
Identification of Anions (Negative ions)
Diluted HCl or BaCl (aq) or Ba(NO3)2 AgNO3 follow by Brown Ring Test
( + FeSO4 (aq ) +
diluted HNO3 or (aq) follow by diluted diluted HNO3.
diluted H2SO4
concentratedH2SO4
HCl/HNO3
White precipitate is
White precipitate is
formed. It is soluble in
Carbon Dioxide is
2formed. It is soluble in
CO3
released.
diluted HCl/HNO3
diluted HNO3
2-
SO4
White precipitate is
formed. It is NOT soluble
in diluted HCl/HNO3
Formation of Brown
Ring
Cl-
White precipitate is
formed. It is NOT
soluble in diluted
HNO3
NO3-
http://one-school.net/notes.html
Downloaded From:
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Idendification of cation
NaOH(ak)
NH3(ak)
HCl or NaCl
H2SO4 or
Na2SO4
Na2CO3
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
KI
Na+
Ca2+
White
precipitate.
Mg2+
White
precipitate is
produced.
Al3+
Zn2+
Pb2+
Fe2+
Fe
3+
2+
Cu
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in
excess NaOH
solution.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in
excess NaOH
solution.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in
excess NaOH
solution.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in
excess NH3
solution.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in hot
water
White
precipitate is
produced.
White
precipitate is
produced.
Yellow
precipitate is
produced.
Dissolve in hot
water
Dirty green
precipitate is
produced.
Dirty green
precipitate is
produced.
Green
precipitate is
produced.
Red brown
precipitate is
produced.
Red brown
precipitate is
produced.
Brown
precipitate is
produced.
A red brown
solution formed.
Blue precipitate
is produced.
Blue precipitate
is produced.
Dissolve in
excess NH3
solution and
form a blue
solution.
Blue precipitate
is produced.
White
precipitate form
in brown
solution
NH4+
= No changes is observed
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
10
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Distibguish Iron(II) and Iron(III)
Reagent
Solution of potassium hecxacianoferate(II)
Solution of potassium hecxacianoferate(III)
Solution of potassium Thiocyanate(II)
Observation
Light blue precipitate
Dark Blue precipitate
Dark blue precipitate
Greenish brown solution
Pinkish solution
Blood red solution
Ion presents
Fe2+
Fe3+
Fe2+
Fe3+
Fe2+
Fe3+
Manufactured Substances in Industry
Contact Process (Making Sulphuric Acid)
Stage 1: Formation of SO2
Combustion of Sulphur
S (s) + O2 (g) SO2 (g)
or
Heating of metal sulphide such as lead(II) sulphide
2PbS(s) + 3O2(g) 2PbO(s) + 2SO2(g)
or
Combustion of hiydrogen sulphide
2H2S(g) + 3O2(g) 2SO2(g) + 2H2O(ce)
Stage 2: Formation of SO3
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2SO3 (g)
Catalyst: vanadium(V) oxide
Temperature: 450C
Pressure: 2-3 atmospheres
Stage 3 Formation of oleum H2S2O7
SO3(g) + H2SO4(aq) H2S2O7(l)
Stage 4:Formation of Sulphuric acid
H2S207 (1) + H2O (1) 2H2SO4(aq)
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
11
www.studyguide.pk
ONE-SCHOOL.NET
Haber Process (Making Ammonia)
Sources of the raw material
Hydrogen
1. Reaction between steam and heated coke
H2O + C CO + H2
2. Reaction between steam and natural gas.
2H 2 O + CH 4 CO2 + 4H2
Nitrogen
From distillation of liquid air.
The reaction
1. Ammonia is made by the Haber process from nitrogen and hydrogen:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g); H = -92 kJ mo1-1
Catalyst: Iron
Promoter: Aluminium oxide
Temperature: 450 C
Pressure: 200-1000 atm
Downloaded From:
http://one-school.net/notes.html
12
You might also like
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationJasmeet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument14 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationanisnazihahNo ratings yet
- SPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFDocument12 pagesSPM-Chemistry-Formula-List-Form4 (BM) PDFNurulNo ratings yet
- Chemistry O Level Notes 1Document12 pagesChemistry O Level Notes 1lubna naz100% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Document12 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form4api-292313678No ratings yet
- Chemistry Short Notes.Document15 pagesChemistry Short Notes.Mushaa DherreNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Document14 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form4Heng HoweNo ratings yet
- WWW - One School - Net Notes Chemistry SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Document15 pagesWWW - One School - Net Notes Chemistry SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Nur AmaleenaNo ratings yet
- Short Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationDocument12 pagesShort Notes: Form 4 Chemistry: Chemical Formulae and EquationTharmendran MaganteranNo ratings yet
- Boron Group Elements Properties and CompoundsDocument12 pagesBoron Group Elements Properties and CompoundspushpNo ratings yet
- All Chemical Reactions 2023Document29 pagesAll Chemical Reactions 2023Aryan MishraNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument18 pagesAcid BasechaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Revision notes on p-block elements group 13 to 16Document20 pagesRevision notes on p-block elements group 13 to 16Bharadwaj SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- All Chemical ReactionsDocument29 pagesAll Chemical ReactionsManeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLDocument13 pagesPreparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLDocument13 pagesPreparation of Boron:: B, Al, Ga, in & TLTushar GoelNo ratings yet
- General EquationsDocument6 pagesGeneral EquationsPyae Sone KyawNo ratings yet
- Handout For Qualitative Analysis (Group9-10)Document9 pagesHandout For Qualitative Analysis (Group9-10)twelvefeetNo ratings yet
- 9 CH 2 - Types of ReactionsDocument8 pages9 CH 2 - Types of ReactionsVenkat SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Answers For REINFORCEMENT EXERCISEDocument5 pagesAnswers For REINFORCEMENT EXERCISEAbgyyg LuRf UNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 8 SALTSDocument10 pagesCHEMISTRY SPM FORM 4 Short Notes Chapter 8 SALTSJay Bee75% (4)
- O Level Chemistry SummaryDocument22 pagesO Level Chemistry SummarySara Emad100% (1)
- The p-block elements of groups 15, 16, 17 and 18Document138 pagesThe p-block elements of groups 15, 16, 17 and 18harshadNo ratings yet
- Potassium Dichromate Properties (39Document6 pagesPotassium Dichromate Properties (39bnkjayaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 3B - by Maple Leaf International SchoolDocument36 pagesChemistry Unit 3B - by Maple Leaf International SchoolMohamed Muawwiz Kamil73% (15)
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument17 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedJoanne SiaNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument14 pagesRedoxsaraNo ratings yet
- GRP 15, 16 New P BlockDocument76 pagesGRP 15, 16 New P BlockVedantNo ratings yet
- P Block EquationsDocument10 pagesP Block EquationsDivyansh WaghmareNo ratings yet
- P Block Equations PDFDocument10 pagesP Block Equations PDFDivyansh WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Important Chemical Reactions for Class 10 ChemistryDocument9 pagesImportant Chemical Reactions for Class 10 ChemistryManish SainNo ratings yet
- Batteries & Corrosion Fall 19Document18 pagesBatteries & Corrosion Fall 19Salma SaleemNo ratings yet
- P Block EquationsDocument10 pagesP Block EquationsFarha Sh67% (9)
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument8 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsaakashb1918No ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsDocument6 pagesAP Chemistry Types of Reactions 1. Double Replacement ReactionsMr. Adham ZewainNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 Chem Summer NoteDocument22 pagesYr 10 Chem Summer NoteTokoni DanielNo ratings yet
- Viva 1Document4 pagesViva 1Nao tomoriNo ratings yet
- P-Block Board Youtube Part-2Document53 pagesP-Block Board Youtube Part-2vaibhav sainiNo ratings yet
- For JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsDocument56 pagesFor JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsLakshmi AnandNo ratings yet
- PDF SPM Chemistry Form 4 Notes DLDocument10 pagesPDF SPM Chemistry Form 4 Notes DLJames SimNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Experiment 3 CHM3011Document8 pagesLab Report Experiment 3 CHM3011Nurin Batrisyia100% (1)
- Week 3 Notes On Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDocument4 pagesWeek 3 Notes On Hydrogen and Its CompoundsDenzel MusaNo ratings yet
- Nitric AcidDocument9 pagesNitric Acidaditya varteNo ratings yet
- Stuff I Should Know For The AP Chemistry ExamDocument2 pagesStuff I Should Know For The AP Chemistry Examhunterkiller3100% (1)
- Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Student Instructions: Acids Alkalis (Bases)Document5 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations Worksheet Student Instructions: Acids Alkalis (Bases)Gopal PenjarlaNo ratings yet
- (Game Changer 1.0) - P Block, D & F Block - 6 JanDocument102 pages(Game Changer 1.0) - P Block, D & F Block - 6 JanRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Nitric AcidDocument3 pagesNitric AciduniquestarNo ratings yet
- Chlorine and Its CompoundsDocument19 pagesChlorine and Its Compoundskakembo hakimNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Revision PDFDocument2 pagesData Sheet Revision PDFShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Class XDocument5 pagesChemical Reactions Class Xaprajita royNo ratings yet
- 4-Worksheet Redox Reactions 8-9Document4 pages4-Worksheet Redox Reactions 8-9musab8450% (2)
- Stuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListDocument1 pageStuff I Should Know For The Ap Test But Do Not Know Yet: Ions ListScott AllredNo ratings yet
- Redox Titration GuideDocument47 pagesRedox Titration GuideGabby Novillo PillacaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Document15 pagesSPM Chemistry Formula List Form5Jia Hui JoanaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972From EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNo ratings yet
- Things You Should Know For: Design, Analysis and Planning: VariablesDocument7 pagesThings You Should Know For: Design, Analysis and Planning: VariablesAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Maths TipsDocument2 pagesMaths TipsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Physics TipsDocument19 pagesPhysics TipsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Reaction Reagent Condition Mechanism Example NoteDocument3 pagesSr. No. Reaction Reagent Condition Mechanism Example NoteAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- AS Level Chemistry Practical Paper 3: TitrationDocument8 pagesAS Level Chemistry Practical Paper 3: TitrationNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- Studying Tips: You Can Download My Notes HereDocument7 pagesStudying Tips: You Can Download My Notes HereCh'ng Lee KeeNo ratings yet
- 9701 Chemistry Paper 5 NotesDocument4 pages9701 Chemistry Paper 5 NotesTanvir Ahmed Mazumder75% (4)
- 23 - ElectrochemistryDocument1 page23 - ElectrochemistryAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Acyl Chlorides and PolyestersDocument1 pageCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Acyl Chlorides and PolyestersAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 30 - Organic Synthesis and AnalysisDocument1 page30 - Organic Synthesis and AnalysisAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 27 - Amines, Amides and Amino AcidsDocument2 pages27 - Amines, Amides and Amino AcidsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 25 - Arenes and PhenolsDocument2 pages25 - Arenes and PhenolsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 22 - Quantitative EquilibriaDocument1 page22 - Quantitative EquilibriaAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Addition and condensation polymers: key reactions and structuresDocument1 pageAddition and condensation polymers: key reactions and structuresAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 29 Techniques for Analyzing CompoundsDocument1 page29 Techniques for Analyzing CompoundsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 3 - KinematicsDocument1 page3 - KinematicsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 20 - Further Energy ChangesDocument1 page20 - Further Energy ChangesAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- The 3d Block Elements: Properties and Complex Ion FormationDocument1 pageThe 3d Block Elements: Properties and Complex Ion FormationAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- DDDocument21 pagesDDSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- 21 - Quantitative KineticsDocument1 page21 - Quantitative KineticsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 1 - Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument2 pages1 - Physical Quantities and UnitsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 Logic GatesDocument8 pages1.3.1 Logic GatesismaelNo ratings yet
- Physics Equations GuideDocument15 pagesPhysics Equations GuidesourceofnotesNo ratings yet
- 4 - DynamicsDocument2 pages4 - DynamicsAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- Measurement Techniques and Their AccuracyDocument1 pageMeasurement Techniques and Their AccuracyAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- h2 Physics DefinitionsDocument7 pagesh2 Physics DefinitionsSyed Osama HussainNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Tips PDFDocument4 pagesPhysics Practical Tips PDFAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 1.4.3 The Processor's Instruction SetDocument8 pages1.4.3 The Processor's Instruction SetAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- P3 Revision SummariesDocument15 pagesP3 Revision SummariesAbbas HaiderNo ratings yet
- 1.4.4 Assembly LanguageDocument6 pages1.4.4 Assembly LanguageAbbas Haider100% (1)