Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Pollution
Uploaded by
MunicipalityCarranglanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Pollution
Uploaded by
MunicipalityCarranglanCopyright:
Available Formats
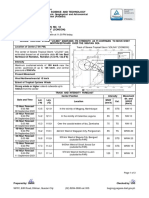
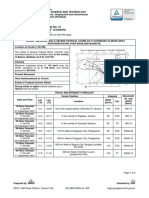
AIR POLLUTION
The condition in which air is contaminated by foreign substances, or the
substances themselves. Air pollution consists of gaseous, liquid, or solid substances
that, when present in sufficient concentration, for a sufficient time, and under
certain conditions, tend to interfere with human comfort, health or welfare, and
cause environmental damage.
CAUSES:
Combustion Engine Exhaust
Cars, trucks, jet airplanes and other combustion engine vehicles cause air
pollution. The exhaust from these contains carbon monoxide, nitrous oxide
and gaseous oxide.
Factories
Factories, office buildings, homes and power-generating stations burn fossil
fuels, which cause air pollution. The burning of oil and coal (fossil fuels) also
contributes to smog.
Pesticides/Fertilizer Dust
Pesticides used to kill indoor and outdoor pests, insecticides used to kill
insects and herbicides use to kill weeds all cause air pollution.
Dust from fertilizers used to help plants grow causes air pollution.
EFFECTS:
Acidification
Chemical reactions involving air pollutants can create acidic compounds
which can cause harm to vegetation and buildings. Sometimes, when an air
pollutant, such as sulfuric acid combines with the water droplets that make
up clouds, the water droplets become acidic, forming acid rain. When acid
rain falls over an area, it can kill trees and harm animals, fish, and other
wildlife. Acid rain destroys the leaves of plants. When acid rain infiltrates into
soils, it changes the chemistry of the soil making it unfit for many living
things that rely on soil as a habitat or for nutrition. Acid rain also changes the
chemistry of the lakes and streams that the rainwater flows into, harming fish
and other aquatic life.
Eutrophication
Rain can carry and deposit the Nitrogen in some pollutants on rivers and
soils. This will adversely affect the nutrients in the soil and water bodies. This
can result in algae growth in lakes and water bodies, and make conditions for
other living organism harmful.
Ground-level ozone
Chemical reactions involving air pollutants create a poisonous gas ozone
(O3). Gas Ozone can affect peoples health and can damage vegetation types
and some animal life too.
SOLUTION/PREVENTION:
Government (or community) level prevention
Governments throughout the world have already taken action against air
pollution by introducing green energy. Some governments are investing in
wind energy and solar energy, as well as other renewable energy, to
minimize burning of fossil fuels, which cause heavy air pollution.
Governments are also forcing companies to be more responsible with their
manufacturing activities, so that even though they still cause pollution,
they are a lot controlled.
Car manufacturing companies are also building more energy efficient cars,
which pollute less than before.
Individual Level Prevention
Encourage your family to use the bus, train or bike when commuting. If we
all do this, there will be less cars on road and less fumes.
Use energy (light, water, boiler, kettle and fire woods) wisely. This is
because lots of fossil fuels are burned to generate electricity, and so if we
can cut down the use, we will also cut down the amount of pollution we
create.
Recycle and re-use things. This will minimize the dependence of producing
new things. Remember manufacturing industries create a lot of pollution,
so if we can re-use things like shopping plastic bags, clothing, paper and
bottles, it can help.
You might also like
- Bulletin PaengDocument4 pagesBulletin PaengMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Bulletin PaengDocument3 pagesBulletin PaengMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- PAENG Accelerates West Northwestward While Maintaining StrengthDocument5 pagesPAENG Accelerates West Northwestward While Maintaining StrengthMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Ics Form 215a, Incident Action Plan Safety Analysis (v3)Document2 pagesIcs Form 215a, Incident Action Plan Safety Analysis (v3)MunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- PAGASA issues Tropical Cyclone Bulletin No. 5 on Typhoon JolinaDocument3 pagesPAGASA issues Tropical Cyclone Bulletin No. 5 on Typhoon JolinaMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- JOLINADocument3 pagesJOLINAMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- PAGASA issues Tropical Cyclone Bulletin No. 5 on Typhoon JolinaDocument3 pagesPAGASA issues Tropical Cyclone Bulletin No. 5 on Typhoon JolinaMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- DEED OF SALE OF MOTOR VEHICLE-templateDocument2 pagesDEED OF SALE OF MOTOR VEHICLE-templateIvy Mallari QuintoNo ratings yet
- Catalog 2019Document16 pagesCatalog 2019MunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- JOLINADocument3 pagesJOLINAMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- 1st Place Poster Making Contest Certificate RecognitionDocument1 page1st Place Poster Making Contest Certificate RecognitionMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Department of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Science and Technology: Republic of The PhilippinesMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Legazpi Caranglan Ate NoraDocument1 pageLegazpi Caranglan Ate NoraMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- 1st Place Poster Making Contest Certificate RecognitionDocument1 page1st Place Poster Making Contest Certificate RecognitionMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Entry FormDocument3 pagesEntry FormMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- DEED OF SALE OF MOTOR VEHICLE-templateDocument2 pagesDEED OF SALE OF MOTOR VEHICLE-templateIvy Mallari QuintoNo ratings yet
- 6th Gintong Butil Festival Talent Show Entry FormDocument4 pages6th Gintong Butil Festival Talent Show Entry FormMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- 16th CongressDocument42 pages16th CongressMunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- Tiger Grass Farming and Broom Making (Compatibility Mode) PDFDocument22 pagesTiger Grass Farming and Broom Making (Compatibility Mode) PDFMunicipalityCarranglan100% (1)
- Carranglan Town Fiesta Derby 2Document1 pageCarranglan Town Fiesta Derby 2MunicipalityCarranglanNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CAPE Biology 2006 U2 P1 PDFDocument28 pagesCAPE Biology 2006 U2 P1 PDFvedant seerattanNo ratings yet
- 700 - 900 Error Codes PDFDocument1 page700 - 900 Error Codes PDFIsai Lara OsoriaNo ratings yet
- Quickscan™ Lite Qw2100: Multi-Purpose Uses For Different ApplicationsDocument2 pagesQuickscan™ Lite Qw2100: Multi-Purpose Uses For Different ApplicationsHaythem BchirNo ratings yet
- Do We Still Need Formocresol in Pediatric DentistryDocument3 pagesDo We Still Need Formocresol in Pediatric DentistryAlexanderDetorakisNo ratings yet
- 1 QDocument45 pages1 QJared MasonNo ratings yet
- Reduced Renal Sodium Excretion: Forced Through A Narrow LumenDocument5 pagesReduced Renal Sodium Excretion: Forced Through A Narrow LumenFlowerNo ratings yet
- 02-Plant Morphology (Exercise)Document5 pages02-Plant Morphology (Exercise)varshavishuNo ratings yet
- Inu 2216 Idt - Question PaperDocument5 pagesInu 2216 Idt - Question PaperVinil JainNo ratings yet
- Marital Rape in IndiaDocument8 pagesMarital Rape in IndiaSHUBHANK SUMANNo ratings yet
- The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale PANSS ForDocument5 pagesThe Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale PANSS ForditeABCNo ratings yet
- Types of Industrial DisputesDocument12 pagesTypes of Industrial DisputesAntony MwangiNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Personality ElementsDocument1 pagePeriodic Table of Personality Elementslilian_vera_1No ratings yet
- Motor Doosan DV11Document220 pagesMotor Doosan DV11David Catari100% (4)
- Krisbow KW06-291 PDFDocument1 pageKrisbow KW06-291 PDFBoyke WinterbergNo ratings yet
- Fault Location of Overhead Transmission Line With Noncontact Magnetic Field MeasurementDocument10 pagesFault Location of Overhead Transmission Line With Noncontact Magnetic Field MeasurementJkNo ratings yet
- PP Ceylon Graphite Corp February 2023Document16 pagesPP Ceylon Graphite Corp February 2023Siddhant DhallNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Document6 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1AnatasukiNo ratings yet
- ICH Topic Q 3 B (R2) Impurities in New Drug Products: European Medicines AgencyDocument14 pagesICH Topic Q 3 B (R2) Impurities in New Drug Products: European Medicines AgencyJesus Barcenas HernandezNo ratings yet
- DC72D MK2 Genset Controller User Manual V1.5Document61 pagesDC72D MK2 Genset Controller User Manual V1.5Cristobal AvecillaNo ratings yet
- SITHCCC018 Assessment 2Document9 pagesSITHCCC018 Assessment 2Taimoor Ahmed0% (1)
- Understand TSGLI BenefitsDocument2 pagesUnderstand TSGLI BenefitsJoseph LawerenceNo ratings yet
- Tennessee Medicaid Claimed Hundreds of Millions of Federal Funds For Certified Public Expenditures That Were Not in Compliance With Federal RequirementsDocument36 pagesTennessee Medicaid Claimed Hundreds of Millions of Federal Funds For Certified Public Expenditures That Were Not in Compliance With Federal RequirementsFOX 17 NewsNo ratings yet
- Basseri TribeDocument3 pagesBasseri TribeMaddah HussainNo ratings yet
- Usos HummusDocument36 pagesUsos HummusAlisson FernandaNo ratings yet
- Fire & Gas Design BasisDocument2 pagesFire & Gas Design BasisAdil MominNo ratings yet
- Cap Dev Dimalinao 2023-2027Document4 pagesCap Dev Dimalinao 2023-2027CA T HeNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Ultra 250x Manual de Taller PDFDocument477 pagesKawasaki Ultra 250x Manual de Taller PDFAntonio Jose Planells100% (3)
- Agemp Two MarksDocument8 pagesAgemp Two MarksKishore CrazeNo ratings yet
- PPEsDocument11 pagesPPEsPrithivirajan CuddaloreNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Ship Date: Port of Discharge: Carrier: Vessel: Voyage: Quantity (MT) : Us GallonsDocument1 pageCertificate of Analysis: Ship Date: Port of Discharge: Carrier: Vessel: Voyage: Quantity (MT) : Us GallonsMercadeo BelaraviNo ratings yet