Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compare Skeletons
Uploaded by
JoshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compare Skeletons
Uploaded by
JoshCopyright:
Available Formats
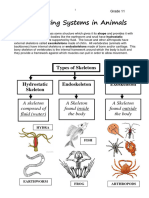
Types of Skeletons
Hydrostatic Skeleton:
A support system provided by fluid (water in body
cavities) which exerts pressure from the inside on the
body wall.
This pressure helps the organism keep its shape.
The muscles contract against this fluid.
ADVANTAGES
This skeleton does not require special support structures
or tissues.
DISADVANTAGES
1. Organisms are susceptible to drying-out.
2. Speed of movement is limited.
3. Limits the size which an animal can reach. Lightning Warrior Raidy 2
Exoskeleton: are external skeletons
that cover the bodies of arthropods,
crustaceans and insects.
ADVANTAGES
1. Reduces water loss.
2. Gives smaller animals support and
protection.
3. Muscles attach internally;
Give good, controlled movement.
4. Exoskeleton is thin & flexible at joints
presence of joints allow quick movement
DISADVANTAGES
1. Chitinous coat cant grow, therefore it has
to mould, vulnerable.
2. Incr. size of muscles, is offset by incr. in
size of exoskeleton
Endoskeleton: a support structure (of bones and
cartilage) found on the inside of the body, eg. in
humans, dogs, mice.
ADVANTAGES
1.
2.
3.
4.
Presence of joints in the skeleton allows flexibility
Does not limit the size of muscles that be attached.
More for muscle attachment improves ability to move and the power of the movement.
Overall, animals can grow too much larger sizes.
DISADVANTAGE
Organism is more vulnerable to physical injury than is the case
with an exoskeleton.
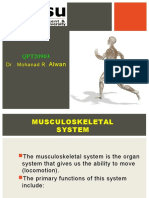
Human Skeleton
The human skeleton is made up of BONE.
The skeleton is an internal framework to which muscles are attached to allow movement.
There are 206 Bones in the human skeleton.
The smallest known bone is the ear, whilst the largest bone is the thigh bones.
Human Skeleton can be divided into two main parts
Skeleton
Axial Skeleton
Skull
Vertebral Column,
ribs and breast bone
Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral
(Shoulder) girdle
and arms
Pelvic (hip) girdle
and legs
Functions:
The skeleton forms a framework to support other parts of the body, It gives the body shape
and rigidity
Protects vital organs, for example:
The rib cage protects the heart and lungs
Muscles are attached to the skeleton, which allows movement
Bones in ear, aid/help in your hearing
The bones are a reserve store of the mineral calcium and phosphorus in the body. The
substance such as calcium phosphate give bones its hardness
Long bones manufacture red blood cells
Structure and functions of
tissues of the skeleton:
Bone:
It is made up of bone cells in a hard matrix.
The bone cells are in spaces in the matrix
Bone cells secrete minerals such as calcium phosphate in the body
In long bones, such as the femur of your thigh, only the outer part of the bone is hard tissue,
whilst inside the bone is soft and spongy tissue (also known as Marrow)
Cartilage:
Is a type of connective tissue
You might also like
- Skeletal SystemDocument19 pagesSkeletal Systemsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- PP13 Human Skeletal System Tissues 1460451284Document65 pagesPP13 Human Skeletal System Tissues 1460451284angie432meNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument5 pagesThe Skeletal SystemMika SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Module 8aDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Module 8aJayR MendonesNo ratings yet
- Biology Minor AssignmentDocument7 pagesBiology Minor AssignmentBessy MulayaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SYatemDocument188 pagesSkeletal SYatemJasmine GañganNo ratings yet
- Movement (Human Skeleton)Document65 pagesMovement (Human Skeleton)Keyondre McBeanNo ratings yet
- He2-Group 3-Skeletal System 1Document17 pagesHe2-Group 3-Skeletal System 1jeaxhedarNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesThe Skeletal SystemJoya Sugue AlforqueNo ratings yet
- Support and Movement SystemsDocument3 pagesSupport and Movement SystemsJas TingNo ratings yet
- The Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]From EverandThe Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Bio Lesson 1Document2 pagesBio Lesson 13bada.kan3anNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Skeletal SystemDocument20 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Skeletal SystemWilbert Antonino CabanbanNo ratings yet
- Module Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesModule Skeletal SystemEMEM QUENNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System E-Unit Reading - Use As Additional Resource - Same Objectives As PPT PDFDocument5 pagesSkeletal System E-Unit Reading - Use As Additional Resource - Same Objectives As PPT PDFMacks Oy IINo ratings yet
- Lect 1 Intro - MSKDocument75 pagesLect 1 Intro - MSKSivajothyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyFrom EverandAnatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Drawing Anatomy: An Artist's Guide to the Human FigureFrom EverandDrawing Anatomy: An Artist's Guide to the Human FigureRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Skeletal System Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesSkeletal System Lesson PlanNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System (2) - 2Document71 pagesSkeletal System (2) - 2alazarademe797No ratings yet
- Bone AnatomyDocument11 pagesBone AnatomyLiam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Lesson Plan 2Document12 pagesSkeletal System Lesson Plan 2Trudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- Major Functions::: Compact Bone Spongy Bone and Marrow Which Makes Red and White Blood CellsDocument9 pagesMajor Functions::: Compact Bone Spongy Bone and Marrow Which Makes Red and White Blood CellsSi Aby ReyesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Assignment (Skeletal System)Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Assignment (Skeletal System)Destined UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Bones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionFrom EverandBones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionNo ratings yet
- Bio Summary 1-10Document113 pagesBio Summary 1-10ShwwwwNo ratings yet
- Session 14 Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesSession 14 Skeletal SystemScience Of LifeNo ratings yet
- Skeleton: What Are Bones?Document6 pagesSkeleton: What Are Bones?Tik TokNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument13 pagesSkeletal Systemariolajose5No ratings yet
- ORTHO Lec PP1 AnaPhysio - DxtestsDocument102 pagesORTHO Lec PP1 AnaPhysio - DxtestsJoana Patricia Celeres SaplagioNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument8 pagesDefinitionJamesNo ratings yet
- Skeletal-System-Q2 - Earth and Life ScienceDocument41 pagesSkeletal-System-Q2 - Earth and Life ScienceArjay RamirezNo ratings yet
- Unit 3.1 - Skeltal System: Functions of The BonesDocument4 pagesUnit 3.1 - Skeltal System: Functions of The BonesEricBuguinaNo ratings yet
- MuscoskeletalDocument60 pagesMuscoskeletaltamjidbhuiyan4075No ratings yet
- Skeletal System of VerteberatesDocument2 pagesSkeletal System of VerteberatesAfaqNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية تشريح اسنان م 1Document26 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية تشريح اسنان م 1mfhrluvxxxNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Rizke, Najwa Abdelalim ADocument16 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Rizke, Najwa Abdelalim AChelo Jan GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Competency 11Document26 pagesCompetency 11Charis RebanalNo ratings yet
- 01 The Human Skeleton 2014 - WebDocument33 pages01 The Human Skeleton 2014 - Webapi-240330821No ratings yet
- Reviewer Zoo LecDocument27 pagesReviewer Zoo LecayeyedumpNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesSkeletal SystemRojan V Min KookNo ratings yet
- Types of BonesDocument2 pagesTypes of BonesbenrosemilesNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument30 pagesThe Skeletal SystemFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument59 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsilyNo ratings yet
- M2 DAN M3 ING Sistem RangkaDocument146 pagesM2 DAN M3 ING Sistem RangkaChloe LuNo ratings yet
- The Human Skeleton - 2023Document5 pagesThe Human Skeleton - 2023Milagro GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahDocument60 pagesSekolah Berasrama Penuh Integrasi Gopeng Prepared By:Muhd Fazli Bin DollahrameshkasinathanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesSkeletal SystemmikeNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lesson 1 CompletedDocument40 pagesPhysiology Lesson 1 CompletedIkenna OnyewuotuNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Bio 11 Skeletal SystemDocument46 pagesWeek 10 Bio 11 Skeletal SystemDyah AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- SKELETAL SYSTEM-WPS OfficeDocument7 pagesSKELETAL SYSTEM-WPS OfficeAlan Gandidze MotifNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesSkeletal SystemNickmor OamlinNo ratings yet
- Compact (Cortical) Bone: A Hard Outer Layer That Is Dense, Strong, and Durable. It Makes Up Around 80Document3 pagesCompact (Cortical) Bone: A Hard Outer Layer That Is Dense, Strong, and Durable. It Makes Up Around 80KiranNo ratings yet
- 11LS The Skeleton NOTESDocument28 pages11LS The Skeleton NOTESAdhi PandayNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument23 pagesUntitled PresentationSamia MustafaNo ratings yet
- Locomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesLocomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemNathanael MfumbaikaNo ratings yet
- Embriologi Tumbuhan - Materi 2Document21 pagesEmbriologi Tumbuhan - Materi 2gahanNo ratings yet
- Cavidades Corporales AnatomiaDocument4 pagesCavidades Corporales AnatomiaBOKOR5000No ratings yet
- Indirect Inguinal HerniaDocument1 pageIndirect Inguinal Herniayumi_kumiko_1No ratings yet
- Skema P2 Trial 2014 SMK SG PelekDocument11 pagesSkema P2 Trial 2014 SMK SG PelekRahoul Chicharito RooneyNo ratings yet
- EMB5, PDFDocument7 pagesEMB5, PDFSafura IjazNo ratings yet
- Maternal ExamDocument20 pagesMaternal ExamChiz EscubuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Surgical Managment of Salivary Gland DiseaseDocument35 pagesChapter 13 Surgical Managment of Salivary Gland DiseaseMohammed Qasim Al-WataryNo ratings yet
- Effects of Myofascial Release and Stretching Technique On ROM and Reaction Time PDFDocument3 pagesEffects of Myofascial Release and Stretching Technique On ROM and Reaction Time PDFfisionovaisNo ratings yet
- ArteriDocument1 pageArterifakira tanzilNo ratings yet
- Study Guide: Cytokines Associated With Innate ImmunityDocument12 pagesStudy Guide: Cytokines Associated With Innate ImmunityxxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Medico Legal CertificateDocument2 pagesMedico Legal CertificateJoanne besoyNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Hemostasis - Dr. Rahmat Dani Satria PH.D., SP - PK (K)Document27 pagesPhysiology of Hemostasis - Dr. Rahmat Dani Satria PH.D., SP - PK (K)Viand NugrohoNo ratings yet
- 2013 BAA - Glossary of Common Medical Prefixes and Suffixes For BAA and BLSDocument5 pages2013 BAA - Glossary of Common Medical Prefixes and Suffixes For BAA and BLSM GavinNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 2 PDFDocument18 pagesBIOLOGY FORM 4 Chapter 2 PDFadele30No ratings yet
- Muscular System MindmapDocument1 pageMuscular System MindmapMayeliz UrvinaNo ratings yet
- Cell StrucutreDocument40 pagesCell StrucutreJeevitha VanithaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Introduction To Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 5th Edition Leifer Test BankDocument36 pagesStudy Guide For Introduction To Maternity and Pediatric Nursing 5th Edition Leifer Test Banknephriteprimelyqihx100% (21)
- Appearances - How To Describe Someone in EnglishDocument26 pagesAppearances - How To Describe Someone in EnglishNadia Tara DilaNo ratings yet
- Cell CytoplasmDocument55 pagesCell Cytoplasmnicolaer111100% (1)
- Histologie Généralité Et Tissu Epithelume PDFDocument2 pagesHistologie Généralité Et Tissu Epithelume PDFشكوب ستانNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument38 pagesNephrotic SyndromeSwati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Normal Histology of The Lung and Pathophysiology of COPD (T Year)Document36 pagesNormal Histology of The Lung and Pathophysiology of COPD (T Year)khaledalameddineNo ratings yet
- Thyroglossal Duct Cysts: Anatomy, Embryology and TreatmentDocument7 pagesThyroglossal Duct Cysts: Anatomy, Embryology and TreatmentTasia RozakiahNo ratings yet
- Normal Delivery Checklist 2020Document4 pagesNormal Delivery Checklist 2020Ever Seneca EscaLeraNo ratings yet
- The Final Ultimate CML Case Pres Final 1 1Document113 pagesThe Final Ultimate CML Case Pres Final 1 1Levy Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Physical ExamDocument1 pagePhysical ExamJan DamesNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of TasteDocument10 pagesMaking Sense of TastetufekciosmanNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle PhasesDocument2 pagesMenstrual Cycle PhasesPatricia G ChiuNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Ncm-216)Document10 pagesMetabolism (Ncm-216)Sofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument4 pagesConnective TissuesLAKHASTH JAYASILANNo ratings yet











![The Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/238627287/149x198/b1987107b7/1617237212?v=1)