Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concepts of The BTS Multiplexing Mode
Uploaded by
RustyPrincessOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concepts of The BTS Multiplexing Mode
Uploaded by
RustyPrincessCopyright:
Available Formats
Concepts of the BTS Multiplexing Mode
This section describes BTS multiplexing, that is, the multiplexing of the LAPD signaling on the E1 timeslots of the
Abis interface. The BSC6900 provides the 64 kbit/s statistical multiplexing mode and the physical 16 kbit/s
multiplexing mode.
Timeslots and Sub-Timeslots
The bandwidth of each E1 link is 2.048 Mbit/s, which consists of 32 timeslots. The transmission rate on each
timeslot is 64 kbit/s. Each timeslot is divided into four sub-timeslots, and the transmission rate on each subtimeslot is 16 kbit/s.
Timeslot Types of the Abis Interface
The timeslots of the BTS Abis interface are classified into the following types:
Operation and maintenance link (OML)
link for operation and maintenance of a BTS. Each BTS has only one OML, and the transmission rate on the
OML is 64 kbit/s. An OML can be multiplexed with only the RSLs of the same BTS. (By default, the OML
timeslot of a BTS is timeslot 31 on port 0 of the BTS control board)
Radio signaling link (RSL)
Signaling link of a TRX. Each TRX has one RSL at a rate of 64 kbit/s. RSLs can be multiplexed with only the
OML or other RSLs of the same BTS.
Extended signaling link (ESL)
Extended signaling link. When the timeslot assignment mode on the Abis interface of the BTS is set to
FLEX_ABIS, each BTS requires one 64 kbit/s ESL for transmitting the signaling of dynamic Abis timeslot
connection. ESL can be multiplexed with only the OML of the same BTS in a 64 kbit/s timeslot of the same
E1 link.
Traffic channel (TCH)
Traffic channel of a TRX. The full transmission rate is 16 kbit/s, and the half transmission rate is 8 kbit/s.
Idle
Idle timeslot of a BTS, which has a rate of 16 kbit/s. Idle timeslots can be multiplexed with only the TCHs of
the same cabinet group.
Semi
Monitoring timeslot of a BTS, which has a rate of 8 kbit/s, 16 kbit/s, 32 kbit/s, or 64 kbit/s and cannot be
multiplexed with timeslots of other types.
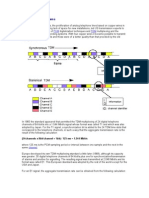
64 kbit/s Statistical Multiplexing Mode
Statistical multiplexing is a technology where n channels share one 64 kbit/s timeslot, each in a different time slice,
that is, Time Division Multiplexing (TDM). In statistical multiplexing mode, multiple channels are multiplexed onto
one 64 kbit/s bandwidth.
The 64 kbit/s statistical multiplexing mode consists of the following types:
1:1
2:1
3:1
4:1
5:1
6:1
That is, n:1 (n<=6), where n represents the number of signaling links and 1 represents one E1 timeslot (64 kbit/s)
on the Abis interface.
When the Abis interface uses a 64 kbit/s timeslot for signaling transmission, traffic channels cannot use the same
timeslot. RSLs use 64 kbit/s timeslots through multiplexing.
In all the n:1 multiplexing modes, the speech rate is 16 kbit/s or 8 kbit/s (half rate). Four full-rate traffic channels or
eight half-rate traffic channels occupy one 64 kbit/s timeslot on the Abis interface. The rate of all the signaling links
is 64 kbit/s. Based on the multiplexing mode (n:1), n signaling timeslots occupy one E1 timeslot (64 kbit/s) on the
Abis interface. All the timeslots implement 64 kbit/s switching in the Abis interface board of the BSC6900.
Physical 16 kbit/s Multiplexing Mode
In physical 16 kbit/s multiplexing mode, a 16 kbit/s sub-timeslot is permanently assigned to a channel, that is, this
channel exclusively uses this timeslot.
When the Abis interface uses a 16 kbit/s rate for signaling transmission, timeslots of the E1 link, excluding timeslot
0 (synchronization timeslot), can be configured as traffic timeslots or signaling timeslots. Therefore, the
multiplexing ratio is not involved.
You might also like
- BTS Multiplexing Mode Huawei BSC6000Document2 pagesBTS Multiplexing Mode Huawei BSC6000Ebenezer Annan100% (1)
- Bts Mux ModesDocument2 pagesBts Mux ModesjibrangillNo ratings yet
- Timeslots On The Abis InterfaceDocument18 pagesTimeslots On The Abis InterfaceHouss HoussiNo ratings yet
- Any E1 Is 2048 Mbps Divided Into 32 Timeslots Each Timeslot Is 64KbpsDocument3 pagesAny E1 Is 2048 Mbps Divided Into 32 Timeslots Each Timeslot Is 64KbpsjyotiNo ratings yet
- Fix Abis Vs Flex AbisDocument23 pagesFix Abis Vs Flex AbisJimoh Yunus100% (1)
- 15:1 Data Configuration DescriptionDocument5 pages15:1 Data Configuration DescriptionanujgujjarNo ratings yet
- T1 and E1 PCM systems explainedDocument10 pagesT1 and E1 PCM systems explainedPrafull BNo ratings yet
- 02.signalling. CAS & CCS-SSTPDocument4 pages02.signalling. CAS & CCS-SSTPAryamn ProstNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication Networks: Exercices 4Document2 pagesMobile Communication Networks: Exercices 4Shirley RodriguesNo ratings yet
- 6 OMO133040 BSC6900 GSM V9R11R12R13 Multiple Rate Algorithm and Parameters ISSUE 1.01Document80 pages6 OMO133040 BSC6900 GSM V9R11R12R13 Multiple Rate Algorithm and Parameters ISSUE 1.01KassyeNo ratings yet
- T1 Carrier SystemDocument10 pagesT1 Carrier SystemAnn MozoNo ratings yet
- BSS Interface - Presentation TranscriptDocument7 pagesBSS Interface - Presentation TranscriptFahmida AfrinNo ratings yet
- E1 Frame StructuretDocument3 pagesE1 Frame Structuretabhilash152No ratings yet
- BSS Interface (A, A-ter&A-bis) With Time Slots DetailDocument37 pagesBSS Interface (A, A-ter&A-bis) With Time Slots Detailvinaygautamgautam100% (1)
- CDMA Channels NotesDocument8 pagesCDMA Channels Notesबिभोद आले मगरNo ratings yet
- Um Layers: Physical Layer (L1)Document13 pagesUm Layers: Physical Layer (L1)naeem05No ratings yet
- The VESA Local BusDocument15 pagesThe VESA Local Busatorresh090675No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document8 pagesChapter 4Ahsen KamalNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Has 3Document11 pagesWCDMA Has 3rajneesh8545No ratings yet
- Data Communication Note 10 PDFDocument9 pagesData Communication Note 10 PDFPappu bhaiNo ratings yet
- Huawei BSC6900 Troubleshooting Guide For AccessDocument2 pagesHuawei BSC6900 Troubleshooting Guide For AccessUmar Abbas Babar100% (1)
- MIMO Capacity Under The CSIR Assumption Information (CSI) .Performance Depends On The Knowledge That TheDocument10 pagesMIMO Capacity Under The CSIR Assumption Information (CSI) .Performance Depends On The Knowledge That TheNebiye SolomonNo ratings yet
- TranscoderDocument15 pagesTranscoderanand_k_singhNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument8 pagesProblem SetADSRNo ratings yet
- Abis Interface IntroductionDocument7 pagesAbis Interface Introductionsrikanth.2335528No ratings yet
- BSC Pre TRADocument113 pagesBSC Pre TRAguili_apbNo ratings yet
- GSM AmrDocument6 pagesGSM AmrTushar ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Understanding the T1/E1 Interface: A Tutorial on TDM TechnologiesDocument16 pagesUnderstanding the T1/E1 Interface: A Tutorial on TDM Technologiesমোহাম্মাদ নাবিল নূর50% (2)
- Manchester Encoding ExplainedDocument3 pagesManchester Encoding ExplainedChinmoy GhoshNo ratings yet
- Bus and Memory TransfersDocument14 pagesBus and Memory TransfersDaniel RizviNo ratings yet
- GSMDocument38 pagesGSMapi-370641475% (8)
- Fundamentals of Microcontroller & Its Application: Unit-IvDocument17 pagesFundamentals of Microcontroller & Its Application: Unit-IvRajan PatelNo ratings yet
- Transcoder and Rate Adaptation UnitDocument1 pageTranscoder and Rate Adaptation Unitpradeepscribd123No ratings yet
- AIM: To Study GSM Channels. TheoryDocument2 pagesAIM: To Study GSM Channels. TheoryAnonymous w74p4iNo ratings yet
- Solution For Assignment 3Document3 pagesSolution For Assignment 3Faizan 'Fezar' RabbaniNo ratings yet
- 1.7. Time - Division MultiplexingDocument7 pages1.7. Time - Division Multiplexingbkm0286No ratings yet
- CH 4Document37 pagesCH 4Aravind VorugantiNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chap 2Document3 pagesExercise Chap 2chantinh_hd190No ratings yet
- Extended FHopp PDFDocument7 pagesExtended FHopp PDFvpkoffiNo ratings yet
- GSM Frame Structure-Finalwith GraphsDocument28 pagesGSM Frame Structure-Finalwith GraphsMohammed Fabin100% (1)
- Modbus Serial Transmission ModesDocument1 pageModbus Serial Transmission ModesVipper80No ratings yet
- QDocument4 pagesQSri NikethanNo ratings yet
- Oil Pipeline Communication TypesDocument14 pagesOil Pipeline Communication Typesdo AtifaNo ratings yet
- Voice Digitization and Voice/Data Integration: TCOM 370Document7 pagesVoice Digitization and Voice/Data Integration: TCOM 370saidur183No ratings yet
- Module4 Problems: 2. Five Channels, Each With A 100-Khz Bandwidth, Are To Be Multiplexed Together. WhatDocument5 pagesModule4 Problems: 2. Five Channels, Each With A 100-Khz Bandwidth, Are To Be Multiplexed Together. WhatKeerthi RajanNo ratings yet
- Trans-Coder Functionality (TRC) BasicDocument4 pagesTrans-Coder Functionality (TRC) BasicSaikat DasNo ratings yet
- Champion Compressors Modbus RTU Manual: Aircon L1 Compressor Controller Enercon Sequencer Controller & AccessoriesDocument45 pagesChampion Compressors Modbus RTU Manual: Aircon L1 Compressor Controller Enercon Sequencer Controller & Accessoriessudirmanpriyo100% (2)
- RF and BSC Training ExerciseDocument13 pagesRF and BSC Training Exercisegurit_perdanaNo ratings yet
- Technical Report On OperationsDocument16 pagesTechnical Report On OperationsSamSameleviNo ratings yet
- LGW 2 Ech 6 SolutionsDocument34 pagesLGW 2 Ech 6 SolutionsER_GIRRAJ0% (1)
- Simulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabFrom EverandSimulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Advanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondFrom EverandAdvanced Multicarrier Technologies for Future Radio Communication: 5G and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsFrom EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Festive Afternoon Tea Menu Hyde Cafe 2021 v2Document8 pagesFestive Afternoon Tea Menu Hyde Cafe 2021 v2RustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Suffering A Fake DeathDocument1 pageSuffering A Fake DeathRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Russell Hobbs Bread Maker Instructions and WarrantyDocument28 pagesRussell Hobbs Bread Maker Instructions and WarrantyRustyPrincess0% (1)
- Poem For SetveDocument1 pagePoem For SetveRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- The Sleet That Rained Like Chatting DonkeysDocument1 pageThe Sleet That Rained Like Chatting DonkeysRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Russell Hobbs Bread Maker Instructions and WarrantyDocument28 pagesRussell Hobbs Bread Maker Instructions and WarrantyRustyPrincess0% (1)
- Virginia's Tiny Torch DefenseDocument1 pageVirginia's Tiny Torch DefenseRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- The Bendy RecordDocument1 pageThe Bendy RecordRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- YoloDocument1 pageYoloswaggotNo ratings yet
- Down To Earth Annabelle SuperhalkDocument1 pageDown To Earth Annabelle SuperhalkRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- The Drizzle That Rained Like Partying HamstersDocument1 pageThe Drizzle That Rained Like Partying HamstersRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Twinkle Twinkle Little BraDocument1 pageTwinkle Twinkle Little BraRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- DIY Dog Coat PatternDocument1 pageDIY Dog Coat PatternRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Vampire in ExeterDocument1 pageVampire in ExeterRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Eggs of PlentyDocument1 pageEggs of PlentyRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- The Ribbed KettleDocument1 pageThe Ribbed KettleRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Calendar October 2014Document1 pageCalendar October 2014RustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- True Love by FateDocument5 pagesTrue Love by FateRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- MR SlimyDocument1 pageMR SlimyRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- The Wind That Blew Like Dancing MiceDocument1 pageThe Wind That Blew Like Dancing MiceRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Two Popular Uncles Jogging To The BeatDocument1 pageTwo Popular Uncles Jogging To The BeatRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Configuration of Telecommunications NetworksDocument1 pageConfiguration of Telecommunications NetworksRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Muppet - Song LyricsDocument1 pageMuppet - Song LyricsRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Two Hilarious Uncles Dancing To The BeatDocument1 pageTwo Hilarious Uncles Dancing To The BeatRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Two Selfish Uncles Rampaging To The BeatDocument1 pageTwo Selfish Uncles Rampaging To The BeatRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Bill in A Field of CornDocument2 pagesBill in A Field of CornRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Cosy ChicagoDocument1 pageCosy ChicagoRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Nokia Command ListDocument5 pagesNokia Command ListRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- BTS/NodeB Connection Types to BSC/RNCDocument1 pageBTS/NodeB Connection Types to BSC/RNCRustyPrincessNo ratings yet
- Mce BLK Dia - Signal Flow - 1Document1 pageMce BLK Dia - Signal Flow - 1Cardell93No ratings yet
- Advanced Instrumentation and Calibration Assignment 1Document3 pagesAdvanced Instrumentation and Calibration Assignment 1asprillaNo ratings yet
- WSN 2Document81 pagesWSN 2Loya SrijaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication BriefDocument80 pagesMobile Communication BriefNise Mon KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- EST3 Zoned Audio AmplifiersDocument4 pagesEST3 Zoned Audio Amplifierstomjakson333No ratings yet
- Extended BCCH in GSM Technologies To Improve Telecommunications UnderstandingDocument7 pagesExtended BCCH in GSM Technologies To Improve Telecommunications UnderstandingUmar Abbas BabarNo ratings yet
- CN Viva QuestionsDocument18 pagesCN Viva QuestionsSampath Varma67% (3)
- Combimux Line System 8TR695Document6 pagesCombimux Line System 8TR695David TesztNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing and DemultiplexingDocument48 pagesMultiplexing and DemultiplexingAkpevwe IsireNo ratings yet
- IR06121Document42 pagesIR06121prouserdesigner77No ratings yet
- Mux Demux and Oadm Quick Start Guide v3.0Document27 pagesMux Demux and Oadm Quick Start Guide v3.0zarnimaung_ispNo ratings yet
- Channel Multiplexing Bandwidth Data Rateand CapacityDocument9 pagesChannel Multiplexing Bandwidth Data Rateand CapacitysamiNo ratings yet
- Hyung G Myung PHD ThesisDocument150 pagesHyung G Myung PHD ThesisArdhendu TripathyNo ratings yet
- History of Microwave in The California Bay AreaDocument4 pagesHistory of Microwave in The California Bay AreaMaciej JüngstNo ratings yet
- FDMA1Document18 pagesFDMA1Hussain BarwahwalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 DCN Lecture Notes 23 45Document41 pagesUnit 3 DCN Lecture Notes 23 45arun kaushikNo ratings yet
- TPS-NU - Analogue Digital Protection EquipmentDocument4 pagesTPS-NU - Analogue Digital Protection Equipmentarya_85100% (1)
- Priyanka MiniprojectDocument42 pagesPriyanka MiniprojectKiran RazNo ratings yet
- Smartstream Encryptor ModulatorDocument2 pagesSmartstream Encryptor ModulatorRichard LaverianoNo ratings yet
- TD-LTE Basic Technology and Comparison With LTE FDD v1.1 (20110617)Document46 pagesTD-LTE Basic Technology and Comparison With LTE FDD v1.1 (20110617)aminariyahi100% (1)
- cs2402 2 Marks Question Bank-With AnswerDocument26 pagescs2402 2 Marks Question Bank-With AnswerFrousper29No ratings yet
- Forouzan Chp6Document41 pagesForouzan Chp6Aniket MehtaNo ratings yet
- BSC6900 GSM Signal FlowDocument18 pagesBSC6900 GSM Signal FlowPhuong TranNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Lesson Plan and SyllabusDocument10 pagesData Communication Lesson Plan and SyllabusanirudhshekhNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY MANUAL ON Digital COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUESDocument29 pagesLABORATORY MANUAL ON Digital COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUESChandra Mohanty0% (1)
- Ch-3satellite Communications IIDocument36 pagesCh-3satellite Communications IIidrishshaikNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and Computer NetworksDocument38 pagesData Communications and Computer Networkskumararchana0% (1)
- DCS Lab ManualDocument47 pagesDCS Lab ManualharivigneshaNo ratings yet
- RTN 620 Product Description (V100R003 - 07)Document122 pagesRTN 620 Product Description (V100R003 - 07)Jonathan Domingo100% (8)
- Wireless Access Networks Fixed Wireless Access and WLL Networks Design and OperationDocument425 pagesWireless Access Networks Fixed Wireless Access and WLL Networks Design and OperationJuan Dela Cruz0% (1)