Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yearly Lesson Plan Year 6
Uploaded by
muassah_85Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yearly Lesson Plan Year 6
Uploaded by
muassah_85Copyright:
Available Formats
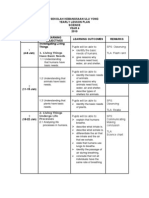
SEKOLAH KEBANGSAAN ULU YONG
YEARLY LESSON PLAN
SCIENCE
YEAR 6
2010
LEARNING
WEEK LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
OBJECTIVES
Pupils will be able to:
state that some
Investigating Living animals live in groups.
Things
state that some SPS: Observing
1 1. Interaction among
animals live in solitary.
(4-8 Jan) living things
give examples of TLA:
1.1 Understanding that
animals that live in Science chart
some animals live in
groups and others groups.
live in solitary. give examples of
animals that live in
solitary.
Pupils will be able to:
explain why animals SPS:
1.1 Understanding that live in groups. Communicating
2 some animals live in
(11-15 Jan) groups and others
explain why animals TLA:
live in solitary. Pictures of
live in solitary
state that cooperation animals
is a form of interaction
among animals.
Pupils will be able to:
state that living things
interact with one SPS:
1.2 Understanding that another in the Observing
3 competition is a form environment.
(18-22 Jan) of interaction among state that competition TLA:
living things is a form of interaction. Pictures of
list the factors that animals
animals compete for.
give reasons why
animals compete.
4 1.2 Understanding that
(25-29 Jan) competition is a form Pupils will be able to: SPS:
of interaction list factors that plants Communicating
among living things compete for.
give reasons why TLA:
plants compete with Science chart
each other.
LEARNING
WEEK LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
OBJECTIVES
Pupils will be able to:
give examples of
extinct animal.
1.3 Understanding the give examples of
responsibility of SPS: Observing
endangered animal.
5 human beings in
(1-5 Feb) give examples of TLA:
protecting
endangered plant. Science chart
endangered species
explain why certain
animals or plants are
facing the threat of
extinction.
1.4 Understanding the
responsibility of Pupils will be able to: SPS:
6
human being in suggest ways to Communicating
(8- 12 Feb)
protecting prevent animals and
endangered species plants from extinction. TLA: Cd
Pupils will be able to:
give examples of SPS:
environmental Observing
1.5 Knowing the impact
7 destruction caused by
of human activities
(17-19 Feb) human. TLA:
on environment
explain how human Picture’s of
activities cause environmental
environmental destruction
destruction.
Pupils will be able to: SPS: Prediction
1.3 Knowing the impact
8 predict what will
of human activities
(22-25 Feb) happen to the Earth if TLA:
on environment
human activities are Science chart
not controlled.
Investigating Force Pupils will be able to:
and Energy SPS:
state that push and
9 1. Force Making
pull are forces.
(1-5 Mar) 1.1 Understanding inferences
that push and pull state that force cannot
are forces be seen but its effects TLA: Realia
can be observed.
Pupils will be able to:
state that a force can SPS:
10 1.2 Understanding the move a stationary Observing
(8-12 Mar) effects of a force object.
state that a force can TLA: Realia
change the motion of
an object.
LEARNING
WEEK LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
OBJECTIVES
SPS:
Pupils will be able to:
Making
11 1.2 Understanding the state that a force can
inferences
(22-26 Mar) effects of a force change the shape of
an object.
TLA: Realia
Pupils will be able to:
12 state that friction is a SPS: Observing
(29 Mar – 1.3 Analysing friction type of force.
2 Apr) describe the effects of TLA: Realia
friction.
Pupils will be able to: SPS:
Making
13 describe ways to
1.3 Analysing friction inferences
(5-9 Apr) reduce friction.
describe ways to TLA:Realia
increase friction.
Pupils will be able to:
state the advantages SPS:
of friction. Making
14 state the inferences
1.3 Analysing friction
(12-16 Apr) disadvantages of
friction. TLA:
conclude that friction Science chart
occurs when two
surfaces are in contact.
15 1.3 Analysing friction SPS:
(19-23 Apr) Pupils will be able to: Experimenting
design a fair test to
find out how different TLA: Realia
types of surfaces
affect the distance a
trolley moves by
deciding what to
change, what to keep
the same and what to
measure.
LEARNING
WEEK LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
OBJECTIVES
Pupils will be able to:
state that an object
which moves faster
SPS:
travels a longer
2. Movement Using space
16 distance in a given
2.1 Understanding time- relationship
(26-30 Apr) time.
speed
state that an object TLA: Realia
which moves faster
takes a shorter time to
travel a given distance.
SPS:
Pupils will be able to:
Measuring and
state what speed is.
17 2.1 Understanding using number
· solve problems using
(3-7 May) speed
the formula.based on
TLA:
the findings.
Science chart
Pupils will be able to: SPS:
Investigating Materials Making
describe what spoilt
18 1. Food preservation inferences
food is.
(10-14 May) 1.1 Understanding
food spoilage. identify characteristics TLA:
of spoilt food. Realia
Pupils will be able to:
SPS:
state that
Observing
19 microorganisms can
1.1 Understanding
(17-21 May) spoil food.
food spoilage. TLA:
state the conditions for Realia
microorganisms to
grow.
Pupils will be able to: SPS:
1.2 Synthesisng the describe ways to Observing
20
concept of food preserve food.
(24-28 May)
preservation. give examples of food TLA:
for each type of food Realia
preservation.
21 1.2 Synthesisng the SPS:
(31 May- concept of food Pupils will be able to: Experimenting
give reasons why each
way of food
preservation is used.
state what food
TLA:
4 June) preservation. preservation is.
Realia
design and carry out a
project to preserve a
given food.
LEARNING
WEEK LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
OBJECTIVES
SPS:
Defining
22 1.3 Realising the Pupils will be able to:
operationally
(21- importance of give reasons why we
25 June) preserving food need to preserve food.
TLA:
Science chart
Pupils will be able to: SPS:
2. Waste management
Classifying
23 2.1 Understanding the identify types of
(28 June- effects of improper waste in the
TLA:
2 July) disposal of waste on environment.
Realia
the environment identify sources of
waste.
Pupils will be able to:
state the improper
ways of waste
disposal.
state the proper
SPS:
2. Waste management ways of waste
Observing
2.1 Understanding the disposal.
24 Communicating
effects of improper describe the harmful
(5-9 July)
disposal of waste on effects of improper
TLA: Realia
the environment waste disposal.
describe how waste is
disposed in a local
area.
suggest ways to
improve waste
disposal.
25 2.2 Understanding SPS: Observing
(12-16 July) that some waste Pupils will be able to:
can decay state that certain waste TLA: Realia
can decay.
give examples of
waste that can decay.
give examples of
waste that do not
decay.
LEARNING
WEEK LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
OBJECTIVES
Pupils will be able to:
state that
microorganisms can
cause waste materials
to decay.
2.2 Understanding state the advantages SPS: Observing
26
that some waste of waste decaying.
(19-23 July)
can decay state the TLA: Realia
disadvantages of
waste decaying.
predict what will
happen to human and
the environment if
waste do not decay.
Pupils will be able to:
Investigating The Earth state what eclipse of
and The Universe the moon is. SPS:
27 1. Eclipses state the position of the Communicating
(26-30 July) Moon, the Earth and
1.1 Understanding the the Sun during the TLA: Realia
eclipse of the moon eclipse of the moon.
explain why eclipse of
the moon occurs
Pupils will be able to:
SPS:
state what eclipse of
Observing
28 1.2 Understanding the the sun is.
(2-6 Aug) eclipse of the sun state the position of the TLA: Realia
Moon, the Earth and
the Sun during the
eclipse of the sun.
29 1.3 Understanding the SPS:
(9-13 Aug) eclipse of the sun Pupils will be able to: Prediction
explain why eclipse of
the sun occurs. TLA:
predict the scenario on Science chart
the Earth during the
eclipse of the sun.
LEARNING
WEEK LEARNING OUTCOMES REMARKS
OBJECTIVES
Pupils will be able to:
explain what simple
Investigating
30 machine is. SPS: Classifying
Technology
(16-20 Aug) state types of simple
1. Machine
machines. TLA: Realia
1.1 Understanding
simple machines give an example for
each type of simple
machine.
Pupils will be able to:
identify simple
machines in a complex SPS:
machine. Making
31 1.2 Analysing a complex
conclude that a conclusion
(23-27 Aug) machine
complex machine is
made up of more than TLA: Realia
one simple machine.
give examples of
complex machines.
Pupils will be able to:
predict how life is
SPS:
1.3 Appreciating the without machines.
32 Experimenting
invention of explain how machines
(30 Aug-
machines that can make our lives
3 Sept) TLA:
make life easier easier.
Realia
design a machine to
solve a problem.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Performance Requirements For Organic Coatings Applied To Under Hood and Chassis ComponentsDocument31 pagesPerformance Requirements For Organic Coatings Applied To Under Hood and Chassis ComponentsIBR100% (2)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Classic Failure FORD EdselDocument4 pagesClassic Failure FORD EdselIliyas Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Treatise On Vocal Performance and Ornamentation by Johann Adam Hiller (Cambridge Musical Texts and Monographs) (2001)Document211 pagesTreatise On Vocal Performance and Ornamentation by Johann Adam Hiller (Cambridge Musical Texts and Monographs) (2001)Lia Pestana RocheNo ratings yet
- PDF. Art Appre - Module 1Document36 pagesPDF. Art Appre - Module 1marvin fajardoNo ratings yet
- Jadual AnaDocument1 pageJadual Anamuassah_85No ratings yet
- This Ruler Is SquareDocument3 pagesThis Ruler Is Squaremuassah_85No ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan Year 2Document8 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Year 2muassah_85100% (1)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Year 4Document13 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Year 4muassah_85No ratings yet
- Evoe Spring Spa Targeting Climbers with Affordable WellnessDocument7 pagesEvoe Spring Spa Targeting Climbers with Affordable WellnessKenny AlphaNo ratings yet
- IAS Exam Optional Books on Philosophy Subject SectionsDocument4 pagesIAS Exam Optional Books on Philosophy Subject SectionsDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4 5895601813654079927 PDFDocument249 pages4 5895601813654079927 PDFqabsNo ratings yet
- Brinker Insider Trading SuitDocument5 pagesBrinker Insider Trading SuitDallasObserverNo ratings yet
- CL Commands IVDocument626 pagesCL Commands IVapi-3800226100% (2)
- Data Report Northside19Document3 pagesData Report Northside19api-456796301No ratings yet
- Motivate! 2 End-Of-Term Test Standard: Units 1-3Document6 pagesMotivate! 2 End-Of-Term Test Standard: Units 1-3Oum Vibol SatyaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Effectiveness of Ware Housing System in Flyton XpressDocument23 pagesA Study On Effectiveness of Ware Housing System in Flyton XpressmaheshNo ratings yet
- Chrome Blue OTRFDocument4 pagesChrome Blue OTRFHarsh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of The 2012 PNLG Forum: General AssemblyDocument64 pagesProceedings of The 2012 PNLG Forum: General AssemblyPEMSEA (Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia)No ratings yet
- ENTH 311 Course Video ReflectionDocument2 pagesENTH 311 Course Video ReflectionJeshua ItemNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Sedimentation TankDocument45 pagesLecture Notes - Sedimentation TankJomer Levi PortuguezNo ratings yet
- Love in Plato's SymposiumDocument31 pagesLove in Plato's Symposiumac12788100% (2)
- Toyota TPMDocument23 pagesToyota TPMchteo1976No ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument56 pagesLinear RegressionRanz CruzNo ratings yet
- Hempel's Curing Agent 95040 PDFDocument12 pagesHempel's Curing Agent 95040 PDFeternalkhut0% (1)
- Aaps Pronouns-ExplainedDocument2 pagesAaps Pronouns-Explainedapi-277377140No ratings yet
- Concept of Intestate SuccessionDocument9 pagesConcept of Intestate SuccessionBodhiratan BartheNo ratings yet
- Theory of Karma ExplainedDocument42 pagesTheory of Karma ExplainedAKASH100% (1)
- Journal Entry DiscussionDocument8 pagesJournal Entry DiscussionAyesha Eunice SalvaleonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mass Communication Solved MCQs (Set-3)Document5 pagesIntroduction To Mass Communication Solved MCQs (Set-3)Abdul karim MagsiNo ratings yet
- Life Stories and Travel UnitDocument3 pagesLife Stories and Travel UnitSamuel MatsinheNo ratings yet
- The Revival Strategies of Vespa Scooter in IndiaDocument4 pagesThe Revival Strategies of Vespa Scooter in IndiaJagatheeswari SelviNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Thin Metal Shells 58Document1 pageBuckling of Thin Metal Shells 58pawkomNo ratings yet
- Understanding electromagnetic waves and radioactivityDocument7 pagesUnderstanding electromagnetic waves and radioactivityJayesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Self Respect MovementDocument2 pagesSelf Respect MovementJananee RajagopalanNo ratings yet