Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DBMS Question and Answer
Uploaded by
Abdirisak MohamudOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DBMS Question and Answer
Uploaded by
Abdirisak MohamudCopyright:
Available Formats
218
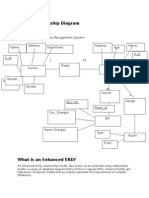
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements:
Conceptual Data Modeling
True-False Questions
1.
The characteristics of data captured during data modeling are crucial in the design of databases,
programs, computer screens, and printed reports.
Answer: True
2.
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 307
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 307
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 307
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 308
A deliverable from conceptual data modeling is a set of entries about data objects to be stored in the
project dictionary or repository
Answer: True
10.
Reference: p. 306
The primary deliverable for the conceptual data modeling step within the analysis phase is an entityrelationship diagram.
Answer: True
9.
Difficulty: Med
A logical data model is prepared during systems analysis.
Answer: False
8.
Reference: p. 306
An enterprise-wide data model is prepared during systems implementation.
Answer: False
7.
Difficulty: Med
During systems design, an entity-relationship diagram with attributes is prepared.
Answer: False
6.
Reference: p. 305
The names of data stores on primitive-level data flow diagrams often correspond to the names of data
entities in entity-relationship diagrams.
Answer: True
5.
Difficulty: Med
The purpose of the conceptual data model is to show as many rules about the meaning and
interrelationships among data as possible.
Answer: True
4.
Reference: p. 305
Processes, rather than data, are the most complex aspects of many modern information systems.
Answer: False
3.
Difficulty: Easy
Difficulty: Easy
Reference: p. 309
When constructing a data model, the analyst needs to know how or when data is processed.
Answer: False
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 309
Chapter 10
11.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
The top-down approach to data modeling derives the business rules for a data model from an intimate
understanding of the nature of the business.
Answer: True
12.
Reference: p. 310
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 310
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
A circle represents a relationship on an entity-relationship diagram.
Answer: False
22.
Difficulty: Hard
Since a name represents a set of entities, it is plural on an entity-relationship diagram.
Answer: False
21.
Reference: p. 310
Book, supplier, and state are entity types.
Answer: True
20.
Difficulty: Hard
Social security number, last name, and first name are entity types.
Answer: False
19.
Reference: p. 310
An entity is a person, place, object, event, or concept in the user environment about which the
organization wishes to maintain data.
Answer: True
18.
Difficulty: Hard
In order to determine the integrity rules, minimum and maximum cardinality, and time dimensions of
data, an analyst might ask, Are values for data characteristics limited in any way?
Answer: True
17.
Reference: p. 310
In order to determine security controls and understand who really knows the meaning of data, an
analyst might ask, What natural activities or transactions of the business involve handling data about
several objects of the same or different type?
Answer: False
16.
Difficulty: Med
In order to determine attributes and secondary keys, an analyst might ask, What characteristics
describe each object?
Answer: True
15.
Reference: p. 309
An analyst would ask What must we know about each object in order to run a business? in order to
determine relationships, their cardinality, and degrees.
Answer: False
14.
Difficulty: Med
The bottom-up approach to data modeling derives a data model by reviewing specific business
documents.
Answer: True
13.
219
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 312
An ellipse represents an entity on an entity-relationship diagram.
Answer: False
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 312
220
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
23.
Use a verb or verb phrase to name an entity.
Answer: False
24.
Reference: p. 315
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 315
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 315
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 315
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 315
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 316
Referencing an employee entity, an employees skills are a multivalued attribute.
Answer: True
35.
Difficulty: Easy
Analysts should substitute single-attribute surrogate keys for large composite keys.
Answer: True
34.
Reference: p. 315
Analysts should use intelligent keys as identifiers.
Answer: False
33.
Difficulty: Med
When selecting an identifier, one should choose a candidate key that will not change its value over the
life of each instance of the entity type.
Answer: True
32.
Reference: p. 314
An identifier is a candidate key that has been selected as the unique, identifying characteristic for an
entity type.
Answer: True
31.
Difficulty: Med
A primary key should be null.
Answer: False
30.
Reference: p. 312
A faculty identification number can serve as an identifier.
Answer: True
29.
Difficulty: Med
An order number is a good example of a candidate key.
Answer: True
28.
Reference: p. 312
Employee identification number, name, address, and skill are attributes.
Answer: True
27.
Difficulty: Med
An entity instance is a single occurrence of an entity type.
Answer: True
26.
Reference: p. 313
A true data entity will have many possible instances, each with a distinguishing characteristic, as well
as one or more other descriptive pieces of data.
Answer: True
25.
Difficulty: Easy
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 316
One way to handle repeating data within an entity is to separate the repeating data into another entity,
called a weak entity.
Answer: True
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 316
Chapter 10
36.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
A multivalued attribute is an attribute that may take on more than one value for each entity instance.
Answer: True
37.
Reference: p. 318
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 318
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 319
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 320
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 320
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 321
A plural relationship is a relationship that the data modeler chooses to model as entity type.
Answer: False
47.
Difficulty: Med
The minimum cardinality of a relationship is the minimum number of instances of entity B that may
be associated with each instance of entity A.
Answer: True
46.
Reference: p. 317
Cardinality is the number of instances of entity B that can (or must) be associated with each instance
of entity A.
Answer: True
45.
Difficulty: Easy
A ternary relationship is the equivalent of three binary relationships.
Answer: False
44.
Reference: p. 317
A unary relationship is the most common type of relationship encountered in data modeling.
Answer: False
43.
Difficulty: Med
A ternary relationship is a relationship between the instances of one entity type.
Answer: False
42.
Reference: p. 316
The goal of conceptual data modeling is to capture as much of the meaning of data as possible.
Answer: True
41.
Difficulty: Med
Relationships are labeled with verb phrases.
Answer: True
40.
Reference: p. 316
A join is an association between the instances of one or more entity types that is of interest to the
organization.
Answer: False
39.
Difficulty: Med
A repeating group is a set of two or more multivalued attributes that are logically related.
Answer: True
38.
221
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 324
A relationship must be turned into an associative entity when the associative entity has other
relationships with entities besides the relationship that caused its creation.
Answer: True
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: pp. 324-325
222
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
48.
On an entity relationship diagram, the U-shaped symbol indicates that the subtype is a subset of the
supertype.
Answer: True
49.
Reference: p. 326
On an entity relationship diagram, total specialization is shown by a single line from the supertype to
the subtype.
Answer: False
50.
Difficulty: Med
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 327
Conceptual data modeling for an Internet-based electronic commerce application differs significantly
from the process followed when analyzing the data needs for other types of applications.
Answer: False
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 335
Multiple Choice Questions
51.
Some systems developers believe that a data model is the most important part of the statement of
information system requirements because:
a.
the characteristics of data captured during data modeling are crucial in the design of databases,
programs, computer screens, and printed reports
b. data rather than processes are the most complex aspects of many modern information systems and
thus require a central role in structuring system requirements
c. the characteristics about data are reasonably permanent
d. all of the above
Answer: d
52.
Reference: p. 305
Each of the following are the focus of current systems development except:
a.
b.
c.
d.
transaction processing systems
management information systems
decision support systems
executive support systems
Answer: a
53.
Difficulty: Med
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 305
Which of the following is a true statement?
a. Data characteristics are dynamic.
b. A data model explains the transient form of an organization.
c. An information system design based on a data orientation, rather than a process or logic
orientation, should have a longer useful life.
d. Data flow paths are permanent.
Answer: c
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 305
Chapter 10
54.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
The most common format used for data modeling is:
a.
b.
c.
d.
state-transition diagramming
entity-relationship diagramming
process modeling
decision table diagramming
Answer: b
55.
223
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 305
During requirements structuring:
a. an E-R model represents conceptual data requirements for a particular system
b. the conceptual E-R data model is refined before it is translated into a logical format from which
database definition and physical database design are done
c. an enterprise-wide data model with very broad categories of data and little detail is prepared
d. a specific E-R model is built to help explain the scope of a particular systems analysis and design
effort
Answer: a
56.
logical design
physical design
analysis
implementation
Answer: c
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 306
Process, logic, and data model descriptions of a system must be consistent and complete since:
a.
b.
c.
d.
they each describe different but complementary views of the same information system
they are prepared during the analysis phase
they are constructed in parallel by separate analyst teams
programming tasks require the integration of the information contained in the diagrams
Answer: a
58.
Reference: p. 305
Conceptual data modeling is typically done in parallel with other requirements analysis and structuring
steps during:
a.
b.
c.
d.
57.
Difficulty: Med
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 306
An E-R model with attributes is prepared during:
a.
b.
c.
d.
design
project identification and selection
analysis
project initiation and planning
Answer: c
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 307
224
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
59.
The primary deliverable from the conceptual modeling step within the analysis phase is a(n):
a.
b.
c.
d.
state-transition diagram
E-R diagram
context data flow diagram
decision tree
Answer: b
60.
top-down approach
bottom-up approach
overview approach
business approach
Answer: a
Reference: p. 309
top-down approach
bottom-up approach
investigative approach
business approach
Answer: b
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 310
The three main constructs of the entity-relationship modeling notation include each of the following
except:
a.
b.
c.
d.
data entities
data flows
relationships
attributes
Answer: b
63.
Difficulty: Med
Gathering the information you need for data modeling by reviewing specific business documents
handled within the system describes the:
a.
b.
c.
d.
62.
Reference: p. 308
The data modeling perspective that derives the business rules for a data model from an intimate
understanding of the nature of the business, rather than from any specific information requirements in
screens, reports, or business forms, is referred to as the:
a.
b.
c.
d.
61.
Difficulty: Med
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
A detailed, logical representation of the entities, associations, and data elements for an organization or
business area defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
entity-relationship diagram
conceptual model
entity-relationship model
data flow diagram
Answer: c
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
Chapter 10
64.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
A graphical representation of an E-R model is a(n):
a.
b.
c.
d.
entity-relationship diagram
relationship diagram
data flow diagram
entity-relationship model
Answer: a
65.
Reference: p. 311
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
data element
attribute
entity
relationship
Answer: c
A collection of entities that share common properties or characteristics defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
entity type
entity instance
entity occurrence
entity collection
Answer: a
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
A single occurrence of an entity type defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
entity instance
entity appearance
attribute
data element
Answer: a
69.
Difficulty: Med
A product is an example of a(n):
a.
b.
c.
d.
68.
Reference: p. 311
attribute
data element
relationship
entity
Answer: d
67.
Difficulty: Med
A person, place, object, event, or concept in the user environment about which the organization wishes
to maintain data refers to a(n):
a.
b.
c.
d.
66.
225
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 312
Which of the following is a true statement?
a.
b.
c.
d.
Data entities correspond to sources/sinks on a data flow diagram.
Relationships correspond to data flows on a data flow diagram.
A data entity will have many possible instances.
Verbs are used to name entity types.
Answer: c
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 312
226
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
70.
A named property or characteristic of an entity that is of interest to the organization defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
attribute
relationship
instance
gerund
Answer: a
71.
Reference: p. 314
An attribute (or combination of attributes) that uniquely identifies each instance of an entity type
defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
data element occurrence
trigger
candidate key
gerund
Answer: c
72.
Difficulty: Med
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 315
When selecting an identifier, one should:
a. use intelligent keys
b. use large composite keys instead of single-attribute surrogate keys
c. choose a candidate key that will not change its value over the life of each instance of the entity
type
d. choose a candidate key such that for each instance of the entity, the attribute is guaranteed to have
valid values or is null
Answer: c
73.
Reference: p. 315
A candidate key that has been selected as the identifier for an entity type is called a(n):
a.
b.
c.
d.
attribute
identifier
secondary key
gerund
Answer: b
74.
Difficulty: Med
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 315
For each entity, the name of the identifier is:
a.
b.
c.
d.
identified by using a double-lined ellipse
underlined on an E-R diagram
bold on an E-R diagram
written in all capital letters on an E-R diagram
Answer: b
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 316
Chapter 10
75.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
An attribute that can have more than one value for each entity instance is referred to as a:
a.
b.
c.
d.
gerund
multivalued attribute
nonexclusive attribute
supertype
Answer: b
76.
Reference: p. 316
relationship
gerund
repeating group
class
Answer: c
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 316
An association between the instances of one or more entity types that is of interest to the organization
best defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
occurrence
relationship
coupling
cardinality
Answer: b
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 317
If STUDENT and COURSE participate in a relationship, their relationship is a(n):
a.
b.
c.
d.
unary relationship
binary relationship
ternary relationship
extraordinary relationship
Answer: b
80.
Difficulty: Med
A set of two or more multivalued attributes that are logically related defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
79.
Reference: p. 316
gerund
multivalued attribute
nonexclusive attribute
repeating attribute
Answer: b
78.
Difficulty: Med
If each employee can have more than one skill, then SKILL is referred to as a:
a.
b.
c.
d.
77.
227
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 319
A relationship between the instances of one entity type is a:
a.
b.
c.
d.
unary relationship
binary relationship
ternary relationship
singular occurrence
Answer: a
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 318
228
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
81.
A simultaneous relationship among instances of three entity types is a:
a.
b.
c.
d.
unary relationship
binary relationship
ternary relationship
multiple occurrence
Answer: c
82.
cardinality
domain
ternary occurrence
participation level
Answer: a
Reference: p. 320
degree of the relationship
minimum cardinality of the relationship
maximum cardinality of the relationship
domain of the relationship
Answer: b
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 321
If entity B is a mandatory participant, then:
a.
b.
c.
d.
the minimum cardinality of the relationship is two
the minimum cardinality of the relationship cannot be defined
the minimum cardinality of the relationship is one
the minimum cardinality of the relationship is optional
Answer: c
85.
Difficulty: Med
The minimum number of instances of entity B that may be associated with each instance of entity A
defines the:
a.
b.
c.
d.
84.
Reference: p. 320
The number of instances of entity B that can (or must) be associated with each instance of entity A
refers to:
a.
b.
c.
d.
83.
Difficulty: Med
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 321
A relationship that the data modeler chooses to model as an entity type best defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
recursive relationship
associative entity
domain
complex relationship
Answer: b
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 324
Chapter 10
86.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
229
Which of the following is not a true statement?
a. An associative entity is represented on an E-R diagram as an ellipse.
b. A relationship must be turned into an associative entity when the associative entity has other
relationships with entities besides the relationship which caused the creation of the associative
entity.
c. A double-lined ellipse indicates a multivalued attribute on an E-R diagram.
d. A diamond represents a relationship on an E-R diagram.
Answer: a
87.
child node
disjoined entity
subtype
supertype
Answer: c
Reference: p. 326
total specialization rule
partial specialization rule
disjoint rule
overlap rule
Answer: a
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 327
Which of the following specifies that an entity instance can simultaneously be a member of two (or
more) subtypes?
a.
b.
c.
d.
total specialization rule
partial specialization rule
disjoint rule
overlap rule
Answer: d
90.
Difficulty: Med
Which of the following specifies that each entity instance of the supertype must be a member of some
subtype in the relationship?
a.
b.
c.
d.
89.
Reference: p. 324
A subgrouping of the entities in an entity type that is meaningful to the organization and that shares
common attributes or relationships distinct from other subgroupings best defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
88.
Difficulty: Med
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 327
Which of the following specifies that an entity instance of the supertype is allowed not to belong to
any subtype?
a.
b.
c.
d.
total specialization rule
partial specialization rule
disjoint rule
overlap rule
Answer: b
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 327
230
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
91.
Which of the following specifies that if an entity instance of the supertype is a member of one subtype
it cannot simultaneously be a member of any other subtype?
a.
b.
c.
d.
total specialization rule
partial specialization rule
disjoint rule
overlap rule
Answer: c
92.
requirements specifications
integrity restrictions
business limitations
business rules
Answer: d
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 328
Which of the following specifies that each instance of an entity type must have a unique identifier that
is not null?
a.
b.
c.
d.
referential integrity constraints
triggering operations
entity integrity
domains
Answer: c
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 328
Which of the following are constraints on valid values for attributes?
a.
b.
c.
d.
referential integrity constraints
triggering operations
entity integrity
domains
Answer: d
96.
Reference: p. 328
referential integrity constraints
triggering operations
entity integrity
domains
Answer: a
95.
Difficulty: Med
Which of the following addresses the rules concerning the relationships between entity types?
a.
b.
c.
d.
94.
Reference: p. 327
Specifications that preserve the integrity of the logical data model are:
a.
b.
c.
d.
93.
Difficulty: Hard
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 328
Which of the following protects the validity of attribute values?
a.
b.
c.
d.
referential integrity constraints
triggering operations
entity integrity
domains
Answer: b
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 328
Chapter 10
97.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
The set of all data types and ranges of values that an attribute can assume defines:
a.
b.
c.
d.
cardinality
constraint set
domain
reference set
Answer: c
98.
Reference: p. 329
triggering operation
entity integrity
referential integrity constraints
domains
Answer: a
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 329
The data manipulation operation (insert, delete, or update) that initiates the operation is called a(n):
a.
b.
c.
d.
condition
action
user rule
event
Answer: d
100.
Difficulty: Med
An assertion or rule that governs the validity of data manipulation operations such as insert, update,
and delete is:
a.
b.
c.
d.
99.
231
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 329
A concise statement of the business rule to be enforced by the triggering operation refers to:
a.
b.
c.
d.
user rule
condition
action
event
Answer: a
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 329
Fill In the Blanks
101.
A conceptual data model is a detailed model that shows the overall structure of organizational data
while being independent of any database management system or other implementation considerations.
Difficulty: Med
102.
Reference: p. 306
An entity-relationship diagram is a detailed, logical, and graphical representation of the entities,
associations, and data elements for an organization or business area.
Difficulty: Med
Reference: p. 311
232
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
103.
An entity-relationship data model is a detailed, logical representation of the entities, associations, and
data elements for an organization or business area.
Difficulty: Med
104.
An entity type is a collection of entities that share common properties or characteristics.
Difficulty: Med
105.
Reference: p. 318
A binary relationship is a relationship between instances of two entity types.
Difficulty: Med
115.
Reference: p. 318
A unary relationship is a relationship between the instances of one entity type.
Difficulty: Hard
114.
Reference: p. 317
Degree refers to the number of entity types that participate in a relationship.
Difficulty: Med
113.
Reference: p. 316
A relationship is an association between the instances of one or more entity types that is of interest to
the organization.
Difficulty: Med
112.
Reference: p. 316
A repeating group is a set of two or more multivalued attributes that are logically related.
Difficulty: Med
111.
Reference: p. 315
A multivalued attribute is an attribute that may take on more than one value for each entity instance.
Difficulty: Med
110.
Reference: p. 315
An identifier is a candidate key that has been selected as the unique, identifying characteristic for an
entity type.
Difficulty: Med
109.
Reference: p. 314
A candidate key is an attribute or combination of attributes that uniquely identifies each instance of an
entity type.
Difficulty: Med
108.
Reference: p. 312
An attribute is a named property or characteristic of an entity that is of interest to the organization.
Difficulty: Med
107.
Reference: p. 311
An entity instance is a single occurrence of an entity type.
Difficulty: Med
106.
Reference: p. 311
Reference: p. 319
A ternary relationship is a simultaneous relationship among instances of three entity types.
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 320
Chapter 10
116.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Cardinality refers to the number of instances of entity B that can (or must) be associated with each
instance of entity A.
Difficulty: Med
117.
Reference: p. 328
A domain is the set of all data types and values that an attribute can assume.
Difficulty: Med
125.
Reference: p. 327
Business rules are specifications that preserve the integrity of a conceptual or logical data model.
Difficulty: Med
124.
Reference: p. 327
The partial specialization rule specifies that an entity instance of the supertype is allowed not to
belong to any subtype.
Difficulty: Hard
123.
Reference: p. 327
The overlap rule specifies that an entity instance can simultaneously be a member of two (or more)
subtypes.
Difficulty: Hard
122.
Reference: p. 326
The disjoint rule specifies that if an entity instance of the supertype is a member of one subtype, it
cannot simultaneously be a member of any other subtype.
Difficulty: Hard
121.
Reference: p. 326
A supertype is a generic entity type that has a relationship with one or more subtypes.
Difficulty: Med
120.
Reference: p. 324
A subtype is a subgrouping of the entities in an entity type that is meaningful to the organization and
that shares common attributes or relationships distinct from other subgroupings.
Difficulty: Med
119.
Reference: p. 320
An associative entity is an entity type that associates the instances of one or more entity types and
contains attributes that are peculiar to the relationship between those entity instances.
Difficulty: Med
118.
233
Reference: p. 329
A triggering operation is an assertion or rule that governs the validity of data manipulation operations
such as insert, update, and delete.
Difficulty: Hard
Reference: p. 330
234
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Matching Questions
Match each of the following terms with its corresponding definition.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
entity
entity type
attribute
multivalued attribute
entity instance
supertype
subtype
126.
A person, place, object, event, or concept in the user environment about which the organization wishes
to maintain data.
Answer: a
Reference: p. 311
127.
A single occurrence of an entity type.
Answer:
128.
Reference: p. 326
Reference: p. 314
A collection of entities that share common properties or characteristics.
Answer:
132.
Reference: p. 326
A named property or characteristic of an entity that is of interest to the organization.
Answer:
131.
A generic entity type that has a relationship with one or more subtypes.
Answer:
130.
Reference: p. 312
A subgrouping of the entities in an entity type that is meaningful to the organization and that shares
common attributes or relationships distinct from other subgroupings.
Answer:
129.
Reference: p. 311
An attribute that can have more than one value for each entity instance.
Answer:
Reference: p. 316
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
235
Match each of the following terms with its corresponding definition.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
133.
unary relationship
ternary relationship
binary relationship
relationship
repeating group
associative entity
disjoint rule
overlap rule
partial specialization rule
total specialization rule
Specifies that if an entity instance of the supertype is a member of one subtype, it cannot
simultaneously be a member of any other subtype.
Answer:
134.
Reference: p. 324
Reference: p. 316
Reference: p. 317
Reference: p. 319
A simultaneous relationship among instances of three entity types.
Answer:
142.
Reference: p. 327
A relationship between instances of two entity types.
Answer:
141.
An association between the instances of one or more entity types that is of interest to the organization.
Answer:
140.
Reference: p. 327
A set of two or more multivalued attributes that are logically related.
Answer:
139.
A many-to-many (or one-to-one) relationship that the data modeler chooses to model as an entity type
with several associated one-to-many relationships with other entity types.
Answer:
138.
Reference: p. 327
Specifies that each entity instance of the supertype must be a member of some subtype in the
relationship.
Answer:
137.
Specifies that an entity instance of the supertype is allowed not to belong to any subtype.
Answer:
136.
Reference: p. 327
Specifies that an entity instance can simultaneously be a member of two (or more) subtypes.
Answer:
135.
Reference: p. 320
A relationship between the instances of one entity type.
Answer:
Reference: p. 318
236
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
For each of the following statements, answer a if it is a true statement, or answer b if the statement is
false.
143.
The name of the identifier of each entity is underlined on an E-R diagram.
Answer:
144.
Reference: p. 317
Reference: p. 318
To illustrate a multivalued attribute, separate the repeating data into another entity, then using a
relationship, link the weak entity to its associated regular entity.
Answer:
148.
Reference: p. 316
The goal of conceptual data modeling is to identify as much of the processing activity as possible.
Answer:
147.
On E-R diagrams, relationships are labeled with verb phrases.
Answer:
146.
Reference: p. 316
To illustrate a multivalued attribute, use a double-lined ellipse.
Answer:
145.
Reference: p. 316
A recursive relationship is a relationship between the instances of two entity types.
Answer:
Reference: pp. 318-319
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
237
For each of the following statements, answer a if it is a true statement, or answer b if the statement is
false.
149.
A singular noun is used to name an entity type.
Answer:
150.
151.
152.
Reference: pp. 311-312
Upper- and lowercase letters are used in naming an entity type.
Answer:
Reference: p. 312
Answer:
Reference: p. 312
A diamond represents an entity.
An entity instance is a single occurrence of an entity type.
Answer:
153.
Reference: p. 312
Many instances of an entity type are represented by data stored in the database.
Answer:
Reference: p. 312
Match each of the following terms with its corresponding definition.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
154.
business rule
disjoint rule
overlap rule
partial specialization rule
total specialization rule
Specifies that if an entity instance of the supertype is a member of one subtype, it cannot
simultaneously be a member of any other subtype.
Answer:
155.
Reference: p. 327
Reference: p. 327
Specifies that each entity instance of the supertype must be a member of some subtype in the
relationship.
Answer:
158.
Specifies that an entity instance of the supertype is allowed not to belong to any subtype.
Answer:
157.
Reference: p. 327
Specifies that an entity instance can simultaneously be a member of two (or more) subtypes.
Answer:
156.
Reference: p. 327
Specifications that preserve the integrity of a conceptual or logical data model.
Answer:
Reference: p. 328
238
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Essay Questions
159.
Define the following key data modeling terms: entity, attribute, relationship, degree, cardinality, and
associative entity.
An entity is a person, place, object, event, or concept in the user environment about which the
organization wishes to collect and maintain data. An attribute is a named property or characteristic of
an entity that is of interest to the organization. A relationship is an association between the instances
of one or more entity types that is of interest to the organization. Degree defines the number of entity
types that participate in a relationship. Cardinality specifies the number of instances of entity B that
can (or must) be associated with each instance of entity A. An associative entity is a many-to-many
(or one-to-one) relationship that the data modeler chooses to model as an entity type with several
associated one-to-many relationships with other entity types.
160.
Discuss unary, binary, and ternary relationships. Provide an example of each.
The number of entity types participating in a relationship defines the degree of the relationship. The
most common relationships are unary, binary, and ternary. A unary relationship is a relationship
between the instances of one entity type. An example of this type of relationship is of the person
entity. One person (or instance) can be married to another person (or instance). The binary
relationship is a relationship between instances of two entity types. An example of this relationship is
of a supplier and part. The binary relationship is the most common type of relationship encountered in
data modeling. The ternary relationship is a simultaneous relationship among instances of three entity
types. An example is a supplier shipping a part to a warehouse.
161.
Contrast data modeling to process modeling and logic modeling.
Data modeling, process modeling, and logic modeling provide complimentary views of the system.
Data modeling focuses on the data that must be stored by the system. Process modeling graphically
represents the processes that capture, distribute, and store data between a system and its environment.
Logic modeling represents the internal structure and functionality of the system.
162.
Briefly identify the four entity-relationship diagrams that are produced and analyzed during
conceptual data modeling.
The four entity-relationship diagrams are: (1) an entity-relationship diagram that illustrates the data
needed in the projects application; (2) an entity-relationship diagram for the system being replaced;
(3) an entity-relationship diagram that illustrates the entire database from which the new applications
data are extracted; and (4) an entity-relationship diagram for the entire database for the existing
application system.
163.
What are multivalued attributes and repeating groups? Provide an example of each.
A multivalued attribute is an attribute that may assume more than one value for each entity instance.
A repeating group is a related set of multivalued attributes. Using a student and the courses she takes
as an example, the course number, name, and grade are multivalued attributes and repeat for each
course that the student takes.
Chapter 10
164.
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
239
What is the role of CASE in conceptual modeling? What information is placed in the CASE repository
during conceptual modeling?
During conceptual modeling, CASE tools maintain E-R diagrams as a visual depiction of structured
data requirements and link objects on E-R diagrams to corresponding descriptions in the CASE
repository. Although the actual list of data elements varies, information about entities, attributes, and
relationships is maintained in the CASE repository.
165.
What is a triggering operation? What components are included? Provide an example.
A triggering operation is an assertion or rule that governs the validity of data manipulation operations
such as insert, update, and delete. A triggering operation includes a user rule, event, entity name,
condition, and action. An example is an attempt to order an item that is not currently in stock.
User rule: ORDER Quantity may not exceed PRODUCT In-Stock-Quantity
Event: Insert
Entity Name: ORDER
Condition: ORDER Quantity > PRODUCT In-Stock-Quantity
Action: Reject the insert transaction
166.
Define domains for the following attributes: GPA, rank, and age.
A students GPA is numeric with two decimal places, ranges and allows values from 0 to 4.00, is not
unique, and allows null values. (An entering freshman would not have a GPA until after her first
semester.) Student rank is a numeric field, does not allow null values, and is not unique. Assuming
all students are undergraduate students, the field contains values, ranging from 1 to 4.
167.
Assume you work for Technology Central, an organization that provides on-site technology seminars
for various companies. Identify at least four entities that your company would track. Build a
conceptual model.
Technology Central tracks information about its courses, staff, locations, and students. The
organization needs to identify which courses are offered at certain locations and which instructors are
teaching these classes. The company also needs to associate students with a particular course offered
at a particular location.
168.
Briefly identify four important business rules for supertype/subtype relationships.
Total specialization, partial specialization, disjoint, and overlap are four business rules for
supertype/subtype relationships. The total specialization rule specifies that each entity instance of the
supertype must be a member of some subtype in the relationship. The partial specialization rule
specifies that an entity instance of the supertype is allowed not to belong to any subtype. The disjoint
rule specifies that if an entity instance of the supertype is a member of one subtype, it cannot
simultaneously be a member of any other subtype. The overlap rule specifies that an entity instance
can simultaneously be a member of two (or more) subtypes.
240
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Some systems developers believe that a data model is the most important part
of the statement of information system requirements because:
A. the characteristics of data captured during data modeling are crucial in the
design of databases, programs, computer screens, and printed reports.
B. data rather than processes are the most complex aspects of many modern
information systems and thus require a central role in structuring system
requirements.
C. the characteristics about data are reasonably permanent.
D. structural information about data is essential to generate programs
automatically.
E. of all of the above.
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 189-190
71
Which of the following is a true statement?
A. Data characteristics are dynamic.
B. A data model explains the transient form of an organization.
C. An information system design based on a data orientation, rather than a
process or logic orientation, should have a longer useful life.
D. Data flow paths are permanent.
E. A data model graphically represents the processes that capture,
manipulate, store, and distribute data between a system and its environment
and among components within a system.
Answer: C
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 190
72
Conceptual data modeling is typically done in parallel with other
requirements analysis and structuring steps during:
A. systems planning and selection.
B. systems design.
C. systems analysis.
D. systems implementation and operation.
E. systems evaluation.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 190
73
Process, logic, and data-model descriptions of a system must be consistent
and complete since:
A. they each describe different but complementary views of the same
information system.
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
B. they are prepared during the analysis phase.
C. they are constructed in parallel by separate analyst teams.
D. a data model indicates when the data are processed.
E. a data model shows how the data are processed.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 191
74
The most common format used for data modeling is:
A. state-transition diagramming.
B. entity-relationship diagramming.
C. process modeling.
D. logic modeling.
E. a flowchart.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 190
75
During systems analysis:
A. a conceptual data model (E-R with attributes) is prepared.
B. a logical model (relational) is prepared.
C. physical files and database designs are prepared.
D. an enterprise-wide data model is prepared.
E. database and file definitions are prepared.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 190
76
During systems planning and selection:
A. a conceptual data model (E-R with attributes) is prepared.
B. a logical model (relational) is prepared.
C. physical files and database designs are prepared.
D. an enterprise-wide data model is prepared.
E. database and file definitions are prepared.
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 192
77
During systems design:
A. a conceptual data model (E-R with attributes is prepared.
B. a logical model (relational is prepared.
C. a conceptual data model (E-R with only entities for the specific project is
prepared.
241
242
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
D. an enterprise-wide data model is prepared.
E. database and file definitions are prepared.
Answer: B
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 192
78
During systems implementation and operation:
A. a conceptual data model (E-R with attributes is prepared.
B. a logical model (relational is prepared.
C. physical files and database designs are prepared.
D. an enterprise-wide data model is prepared.
E. database and file definitions are prepared.
Answer: E
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 192
79
The primary deliverable from the conceptual data-modeling step within the
analysis phase is:
A. a state-transition diagram.
B. an entity-relationship diagram.
C. a context data flow diagram.
D. a decision table.
E. Structured English.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 191-192
80
Which of the following is produced and analyzed during conceptual data
modeling?
A. An entity relationship diagram for the project's application
B. A data dialogue diagram for the project's application
C. A Gantt chart for the whole database from which the new application's data
are extracted
D. A Network diagram for the whole database from which the new
application's data are extracted
E. A data flow diagram that shows how the new system will be physically
implemented
Answer: A
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 193
81
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Which of the following is a true statement?
A. A data model explains what the organization does and what rules govern
how work is done in the organization.
B. To construct a data model, you need to know how data are processed.
C. To construct a data model, you need to know when data are processed.
D. A data flow diagram graphically illustrates the structure and relationships
among data items.
E. During conceptual data modeling, the preparation of a Network diagram is
necessary.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 195
82
The data modeling perspective that derives the business rules for a data
model from an intimate understanding of the nature of the business, rather
than from any specific information requirements in screens, reports, or
business forms, is referred to as the:
A. top-down approach.
B. bottom-up approach.
C. overview approach.
D. business approach.
E. conceptual approach.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 195
83
Gathering the information you need for data modeling by reviewing specific
business documents handled within the system describes the:
A. bottom-up approach.
B. conceptual approach.
C. top-down approach.
D. investigative approach.
E. business approach.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 195
84
Reviewing computer screens, reports, and business forms for the purpose of
gaining an understanding of data is indicative of the:
A. investigative approach.
B. business approach.
C. bottom-up approach.
243
244
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 195
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
D. top-down approach.
E. conceptual approach.
85
Asking system users and business managers "How many instances of each
object might exist?" would help determine:
A. the data entities and their descriptions.
B. the candidate key.
C. attributes and secondary keys.
D. relationships and their cardinality and degrees.
E. integrity rules, minimum and maximum cardinality, and time dimensions
of data.
Answer: A
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 196
86
Asking system users and managers "Who is responsible for establishing
legitimate values for these data?" helps determine:
A. the candidate key.
B. security controls and understanding who really knows the meaning of
data.
C. relationships and their cardinality and degrees.
D. attributes and secondary keys.
E. integrity rules, minimum and maximum cardinality, and time dimensions
of data.
Answer: B
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 196
87
Asking system users and business managers "Is each activity or event always
handled the same way or are there special circumstances?" helps determine:
A. the candidate key.
B. integrity rules, minimum and maximum cardinality, and time dimensions
of data.
C. security controls and understanding who really knows the meaning of
data.
D. attributes and secondary keys.
E. relationships and their cardinality and degrees.
Answer: B
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 196
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
88
A detailed, logical, and graphical representation of the entities, associations,
and data elements for an organization or business area best describes a:
A. logic model.
B. data-flow diagram.
C. entity-relationship diagram or E-R diagram.
D. structure chart.
E. data tree.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 197
89
On an entity-relationship diagram, a rectangle represents a:
A. data flow.
B. entity.
C. multivalued attribute.
D. repeating group.
E. relationship.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 197
90
A person, place, object, event, or concept in the user environment about
which the organization wishes to maintain data refers to a:
A. attribute.
B. data element.
C. relationship.
D. entity.
E. process.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 197
91
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 198
A product is an example of a:
A. data element.
B. attribute.
C. entity.
D. relationship.
E. process.
245
246
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
92
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 198
A renewal is an example of a:
A. data element.
B. attribute.
C. entity.
D. relationship.
E. action stub.
93
A collection of entities that share common properties or characteristics best
defines:
A. entity type.
B. entity instance.
C. entity occurrence.
D. entity collection.
E. data set.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 198
94
A single occurrence of an entity type defines:
A. entity instance.
B. entity appearance.
C. attribute.
D. data element.
E. multivalued attribute.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 198
95
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Which of the following is a true statement?
A. Data entities correspond to sources/sinks on a data flow diagram.
B. Relationships correspond to data flows on a data flow diagram.
C. A data entity will have many possible instances.
D. Verbs are used to name entity types.
E. An entity type is described many times in the data model.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 198
96
A named property or characteristic of an entity that is of interest to the
organization defines:
A. attribute.
B. relationship.
C. instance.
D. associative entity.
E. data flow.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199
97
Vehicle identification number, color, weight, and horsepower best exemplify:
A. entities.
B. entity types.
C. data markers.
D. identifiers.
E. attributes.
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199
98
An attribute (or combination of attributes that uniquely identifies each
instance of an entity type defines:
A. data element occurrence.
B. trigger.
C. candidate key.
D. associative entity.
E. data marker.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199
99
247
248
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
When selecting an identifier, one should:
A. use intelligent keys.
B. use large composite keys instead of single-attribute surrogate keys.
C. choose a candidate key that will not change its value over the life of each
instance of the entity type.
D. choose a candidate key such that for each instance of the entity, the
attribute is guaranteed to have valid values or is null.
E. choose a candidate key that allows for duplicate values.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199
100
A candidate key that has been selected as the unique, identifying
characteristic for an entity type is called a:
A. attribute.
B. identifier.
C. secondary key.
D. gerund.
E. index.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 199
101
On an entity-relationship diagram, the entity's identifier is:
A. identified by using a double-lined ellipse.
B. underlined on an E-R diagram.
C. bold on an E-R diagram.
D. written in all capital letters on an E-R diagram.
E. placed in italics.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 200
102
An attribute that can have more than one value for each entity instance is
referred to as:
A. a gerund.
B. a multivalued attribute.
C. a nonexclusive attribute.
D. a data replica.
E. none of the above.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 200
103
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
If each employee can have more than one skill, then skill is referred to as a:
A. gerund.
B. multivalued attribute.
C. nonexclusive attribute.
D. repeating attribute.
E. data replica.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 200
104
A set of two or more multivalued attributes that are logically related defines:
A. relationship.
B. associative entity.
C. repeating group.
D. class.
E. repeating entity.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 201
105
An association between the instances of one or more entity types that is of
interest to the organization best defines:
A. occurrence.
B. relationship.
C. natural connection.
D. cardinality.
E. entity link.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 201
106
249
250
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Which of the following is a true statement?
A. The goal of conceptual data modeling is to capture as much of the meaning
of data as is possible.
B. The efficiencies gained by maintaining systems at the rule rather than code
level drastically reduce cost.
C. If a thorough repository of data descriptions is kept, the system can be
regenerated as the business rules change.
D. The more details about data that we can model, the better the system we
can design and build.
E. All of the above are true statements.
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 201-202
107
A relationship between the instances of one entity type is a:
A. unary relationship.
B. binary relationship.
C. ternary relationship.
D. singular occurrence.
E. partnership occurrence.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 202
108
The number of entity types that participate in a relationship refers to:
A. cardinality.
B. association.
C. count.
D. degree.
E. normalization.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 202
109
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
If STUDENT and COURSE participate in a relationship, this is an example of
a:
A. unary relationship.
B. coupled relationship.
C. binary relationship.
D. ternary relationship.
E. extraordinary relationship.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 203
110
A ternary relationship occurs when a simultaneous relationship exists among
instances of:
A. the same entity.
B. two entity types.
C. three entity types.
D. four entity types.
E. nine entity types.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 203
111
A relationship between instances of two entity types is a:
A. unary relationship.
B. binary relationship.
C. ternary relationship.
D. multiple occurrence.
E. partnership occurrence.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 203
112
A simultaneous relationship among instances of three entity types is a:
A. unary relationship.
B. binary relationship.
C. ternary relationship.
D. multiple occurrence.
E. recursive join.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 203
113
251
252
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
The number of instances of entity B that can (or must be associated with each
instance of entity A refers to:
A. cardinality.
B. domain.
C. ternary occurrence.
D. participation level.
E. join level.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 203
114
The minimum number of instances of entity B that may be associated with
each instance of entity A defines the:
A. degree of the relationship.
B. minimum cardinality of the relationship.
C. maximum cardinality of the relationship.
D. domain of the relationship.
E. join level.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 203
115
If entity B is a mandatory participant, then:
A. the minimum cardinality of the relationship is two.
B. the minimum cardinality of the relationship cannot be defined.
C. the minimum cardinality of the relationship is one.
D. the minimum cardinality of the relationship is optional.
E. the join level is not null.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 203
116
A "many" maximum cardinality is noted on the E-R diagram by:
A. placing a crow's foot notation near the entity.
B. placing a zero through the line near the entity.
C. using a double ellipse near the entity.
D. placing two slash marks near the entity.
E. using brackets.
Answer: A
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 204
117
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
A relationship that the data modeler chooses to model as an entity type best
defines:
A. recursive relationship.
B. associative entity.
C. domain.
D. complex relationship.
E. complex entity.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 204
118
During which of the following steps will you bring the current phase to a
close, prepare a report and presentation to management concerning
continuation of the project, and get ready to move the project into design?
A. Designing the human interface
B. Requirements determination
C. Project initiation and planning
D. Alternative generation and selection
E. Requirements structuring
Answer: D
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 216
119
Selecting the best alternative system involves:
A. generating a comprehensive set of alternative design strategies.
B. selecting the alternative design strategy that is most likely to result in the
desired information system, given all of the organizational, economic, and
technical constraints that limit what can be done.
C. developing all technology and organizational specifications necessary to
implement the new information system.
D. working with a customer to establish work standards and communication
procedures.
E. both A and B.
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 213
120
253
254
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Which of the following includes statements on the system's functionality,
hardware and system software platform, and method for acquisition?
A. Problem statement
B. Requirements statement
C. Design strategy
D. Systems service request
E. Statement of work
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 213
121
A particular approach to developing an information system best describes:
A. design strategy.
B. problem statement.
C. requirements statement.
D. scope.
E. systems service request.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 213
122
Determining requirements and structuring requirements are associated with:
A. systems selection.
B. systems implementation and operation.
C. systems design.
D. systems planning and selection.
E. systems analysis.
Answer: E
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 213
123
Dividing requirements into different sets of capabilities, ranging from the
bare minimum that users would accept to the most elaborate and advanced
system the company could afford to develop occurs during the:
A. requirements structuring step of the analysis phase.
B. alternative generation and selection step of the analysis phase.
C. testing step of the implementation and operation phase.
D. project initiation and planning step of the planning and selection phase.
E. designing the human interface step of the design phase.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 213
124
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Enumerating different potential implementation environments that could be
used to deliver the different sets of capabilities occurs during the:
A. requirements structuring step of the analysis phase.
B. alternative generation and selection step of the analysis phase.
C. testing step of the implementation and operation phase.
D. project initiation and planning step of the planning and selection phase.
E. designing the human interface step of the design phase.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 213
125
Shaping alternative system design strategies involves:
A. enumerating different potential implementation environments.
B. proposing different ways to source or acquire the various sets of
capabilities for the different implementation environments.
C. dividing requirements into different sets of capabilities.
D. all of the above.
E. none of the above.
Answer: D
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 213
126
In theory, if there are four sources of application software, two
implementation environments, and three sets of requirements, how many
design strategies are possible?
A. 4
B. 24
C. 9
D. 2
E. 27
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 213
127
Which of the following is a true statement regarding midrange alternatives?
A. Midrange alternative design strategies often do not involve computer
technology; instead they focus on making paper flows more efficient or
reducing redundancies in current processes.
B. Midrange alternative design strategies represent compromise solutions.
C. Functionality is the primary focus of midrange alternative design
strategies.
D. Midrange alternative design strategies provide all the required
255
256
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
functionality users demand with a system that is minimally different from the
current system.
E. Midrange alternative design strategies provide all the desired features
using advanced technologies that often allow the system to expand to meet
future requirements.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214
128
Which of the following is a true statement regarding high-end alternatives?
A. High-end alternative design strategies often do not involve computer
technology; instead they focus on making paper flows more efficient or
reducing redundancies in current processes.
B. High-end alternative design strategies represent compromise solutions.
C. Functionality is the primary focus of high-end alternative design
strategies.
D. High-end alternative design strategies provide all the required
functionality users demand with a system that is minimally different from the
current system.
E. None of the above is correct.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214
129
A good number of alternatives to generate is:
A. 3.
B. 2.
C. 4.
D. 5.
E. 7.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214
130
The most conservative solutions in terms of the effort, cost, and technology
involved in developing a new system are the:
A. low-end solutions.
B. high-end solutions.
C. mid-range solutions.
D. constraint-dependent solutions.
E. requirements-dependent solutions.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
131
The alternative that goes beyond simply solving the problem in question and
focuses instead on systems that contain many extra features users may desire
is referred to as a:
A. low-end alternative.
B. high-end alternative.
C. quality-focused alternative.
D. requirements-dependent alternative.
E. constraints-dependent alternative.
Answer: B
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214
132
Which of the following types of alternatives represent compromise solutions?
A. Low-end alternatives
B. High-end alternatives
C. Midrange alternatives
D. Requirements-dependent alternatives
E. Constraints-dependent alternatives
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214
133
The minimum requirements for the new system are called:
A. essential features.
B. desired features.
C. minimum features.
D. mandatory features.
E. designated features.
Answer: D
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214
134
257
258
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
Features that everyone agrees are necessary to solve the problem or meet the
opportunity are called:
A. desired features.
B. essential features.
C. mandatory features.
D. minimum features.
E. requested features.
Answer: C
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214
135
Identifying mandatory features by surveying users and other stakeholders
who have been involved in requirements determination would occur:
A. near the end of the analysis phase, after all requirements have been
structured and analyzed.
B. near the end of the project identification and selection phase, after a formal
request to conduct a project to design and develop an information systems
solution has been approved.
C. during the logical design phase, while detailed function specifications of all
data, forms, reports, screens, and processing rules for all aspects of the
system are prepared.
D. during systems planning and selection.
E. during systems implementation and operation.
Answer: A
Diff: 2 Page Ref: 214-215
136
System features might include:
A. data kept in system files.
B. system outputs.
C. analyses to generate the information in system outputs.
D. expectations on accessibility, response time, or turn-around time for
system functions.
E. all of the above.
Answer: E
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 215
137
Which of the following is a true statement?
A. Mandatory features screen out possible solutions; essential features are the
important capabilities of a system that will serve as the primary basis for
comparison of different design strategies.
B. Essential features screen out possible solutions; mandatory features are
Chapter 10
Structuring System Requirements: Conceptual Data Modeling
259
the important capabilities of a system that will serve as the primary basis for
comparison of different design strategies.
C. Mandatory features screen out possible solutions; essential features are
those that users could live without.
D. Essential features screen out possible solutions; mandatory features are
those that users could live without.
E. Desired features screen out possible solutions; mandatory features are the
important capabilities of a system that will serve as the primary basis for
comparison of different design strategies.
Answer: A
Diff: 3 Page Ref: 215
138
Constraints on systems development may include such factors as:
A. available financial and human resources.
B. elements of the current system that cannot change.
C. legal and contractual restrictions.
D. a date when the current system is needed.
E. all of the above.
Answer: E
Diff: 1 Page Ref: 215
http://wps.pearsoned.co.uk/ema_uk_he_chaffey_bim_1/25/6653/1703289.cw/content/index.html
http://amityonline.com/StudentAssignment/WebForm/StudentPages/StudentAssignmentSubmit.aspx?Form
No=5006702&AID=5&PNAME=MSc+(Information+Technology)&SUB=Database+Management+Syste
m&SEM=1
You might also like
- SQL MCQ - Entity Relationship Model QuestionsDocument7 pagesSQL MCQ - Entity Relationship Model QuestionsWaqar Hassan100% (1)
- JSTLDocument12 pagesJSTLkalpanasripathiNo ratings yet
- DWDM I Mid Objective QBDocument7 pagesDWDM I Mid Objective QBkishore5783100% (1)
- Objective Type Questions Binary Files in PythonDocument3 pagesObjective Type Questions Binary Files in PythonDominic SavioNo ratings yet
- ER DiagramDocument16 pagesER DiagramGanesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 2marks and 16 MarksDocument63 pages2marks and 16 MarksakshayaNo ratings yet
- DBMS Two MarksDocument6 pagesDBMS Two Markssivakami_raja100% (1)
- GRASP Patterns for Responsible Object DesignDocument67 pagesGRASP Patterns for Responsible Object DesignrajafahimNo ratings yet
- Passing Multiple Parameters in SSRSDocument2 pagesPassing Multiple Parameters in SSRSVidya SagarNo ratings yet
- Unit-I PPT DWDMDocument90 pagesUnit-I PPT DWDMGiriDharanNo ratings yet
- Database ProgrammingDocument6 pagesDatabase ProgrammingVon Gary RasNo ratings yet
- GPS Location InformationDocument8 pagesGPS Location Informationbala_07123No ratings yet
- Cloud Quiz Question AnswerDocument12 pagesCloud Quiz Question Answertayyab bsra juttNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer Set of System Analysis andDocument169 pagesQuestion and Answer Set of System Analysis andRishi Kolvekar100% (1)
- Unit 5 Cloud ComputingDocument12 pagesUnit 5 Cloud ComputingvibhamanojNo ratings yet
- MSOffice1 Chapter 8 ArraysDocument34 pagesMSOffice1 Chapter 8 ArraysreachlakshmiNo ratings yet
- DBMS NotesDocument3 pagesDBMS Notesnin culusNo ratings yet
- Company Result - (:companyname) : FreecodecampDocument10 pagesCompany Result - (:companyname) : Freecodecamparavi173No ratings yet
- MIS MCQ SolvedDocument9 pagesMIS MCQ Solvedshamzan100% (1)
- OOP Using C++ Lab Manual 2013Document11 pagesOOP Using C++ Lab Manual 2013abuobidaNo ratings yet
- Domain TestingDocument12 pagesDomain TestingaswanthNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear Regression Part 1Document63 pagesSimple Linear Regression Part 1_vanitykNo ratings yet
- DM Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesDM Important QuestionsSurya Kameswari100% (1)
- Database Normalization Explain 1NF 2NF 3NF BCNF With Examples PDFDocument9 pagesDatabase Normalization Explain 1NF 2NF 3NF BCNF With Examples PDFRiddhi Desai100% (1)
- VB Net DatabaseDocument3 pagesVB Net DatabaseSanjay ManhasNo ratings yet
- The Cloud DatabaseDocument19 pagesThe Cloud DatabaseMèo LườiNo ratings yet
- CST3504 Test #1 - 60 Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesCST3504 Test #1 - 60 Practice QuestionsRandy Naraine100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1Ipsita PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Database RevisionDocument10 pagesDatabase RevisionSergio YazNo ratings yet
- ADT Using VB - Net Lab Mannual July 2011Document22 pagesADT Using VB - Net Lab Mannual July 2011Arjun Taval100% (1)
- CSS3 Skill Test Top 20Document28 pagesCSS3 Skill Test Top 20ShalabhNo ratings yet
- Tableau Desktop Fundamentals: Connect to Data & Create VisualizationsDocument3 pagesTableau Desktop Fundamentals: Connect to Data & Create VisualizationsSelvakumar ArunasalamNo ratings yet
- Ervlets: Abhishek Mane February 8 2013Document54 pagesErvlets: Abhishek Mane February 8 2013Chetan ShindeNo ratings yet
- 6.unit I 2 MarksDocument3 pages6.unit I 2 MarksprasanthprpNo ratings yet
- MVC Design Pattern PPT Presented by QuontraSolutionsDocument35 pagesMVC Design Pattern PPT Presented by QuontraSolutionsQuontraSolutionsNo ratings yet
- DW QuestionsDocument35 pagesDW QuestionsSouvik Banerjee0% (1)
- Developing Ssrs Reports For Dynamics AxDocument23 pagesDeveloping Ssrs Reports For Dynamics AxAhmed Farag IbrahimNo ratings yet
- DBMS QuizDocument2 pagesDBMS QuizSumit Tiwari100% (2)
- Java Assignment-2Document4 pagesJava Assignment-2Mangesh AbnaveNo ratings yet
- Dbms Important Questions and AnswersDocument9 pagesDbms Important Questions and Answerskamalika2005No ratings yet
- Data Mining Introduction and Knowledge Discovery ProcessDocument38 pagesData Mining Introduction and Knowledge Discovery Processchakrika100% (1)
- Introduction To Database Management SystemsDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Database Management Systemsroyce542No ratings yet
- Unit-1 PPT Relational DatabasesDocument63 pagesUnit-1 PPT Relational Databasesnirenjena0% (1)
- Relational Database Design/Modeling/Implementation of a Bank DatabaseDocument80 pagesRelational Database Design/Modeling/Implementation of a Bank DatabaseAnthony BeltranNo ratings yet
- EMPLOYEES WITH PROJECTS IN HOUSTON BUT NO DEPT THEREDocument1 pageEMPLOYEES WITH PROJECTS IN HOUSTON BUT NO DEPT THERERishika VoraNo ratings yet
- Scripting Basics and Web DesignDocument35 pagesScripting Basics and Web DesignHyderabad at QatarNo ratings yet
- DBMS Practical List DDU PDFDocument27 pagesDBMS Practical List DDU PDFAnonymous AMUD9cNo ratings yet
- 2mark With AnswerDocument38 pages2mark With AnswerthulasiramNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Relational Database Part - A (2 Marks) : 1. Define Database Management SystemDocument27 pagesUnit I - Relational Database Part - A (2 Marks) : 1. Define Database Management SystemMohammad Bilal - Asst. Prof, Dept. of CSENo ratings yet
- Tai Lieu On Tap Ly Thuyet PCS 1Document5 pagesTai Lieu On Tap Ly Thuyet PCS 1Tran SonNo ratings yet
- E Notes PDF All UnitsDocument129 pagesE Notes PDF All Unitsshreya sorathiaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual 10 PDFDocument4 pagesLab Manual 10 PDFShahid ZikriaNo ratings yet
- Data Mining-Constraint Based Cluster AnalysisDocument4 pagesData Mining-Constraint Based Cluster AnalysisRaj Endran100% (1)
- Data Analytics Assessment QuestionsDocument11 pagesData Analytics Assessment QuestionsTushar Mani AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence MCQsDocument30 pagesArtificial Intelligence MCQsPusp 220No ratings yet
- Ab Initio OverviewDocument4 pagesAb Initio OverviewKulbir Minhas100% (3)
- Client Server Architecture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandClient Server Architecture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Tif 06Document22 pagesTif 06boblong1911No ratings yet
- Tif 09Document22 pagesTif 09Jamaica MarjadasNo ratings yet
- Modern Systems Analysis and Design 6th Edition Hoffer Test BankDocument23 pagesModern Systems Analysis and Design 6th Edition Hoffer Test Bankodettedieupmx23m100% (27)
- Functions and Subs: UOB Semester FiveDocument11 pagesFunctions and Subs: UOB Semester FiveAbdirisak MohamudNo ratings yet
- Data RecoveryDocument7 pagesData RecoveryAbdirisak MohamudNo ratings yet
- Why formatted disks have less storage than unformattedDocument1 pageWhy formatted disks have less storage than unformattedAbdirisak MohamudNo ratings yet
- Enhanced E-R Model and Business RulesDocument20 pagesEnhanced E-R Model and Business RulesAbdirisak Mohamud0% (1)
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument19 pagesDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureAbdirisak MohamudNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument19 pagesDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureAbdirisak MohamudNo ratings yet
- Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument19 pagesDatabase System Concepts and ArchitectureAbdirisak MohamudNo ratings yet
- Code::Blocks Manual: Version 2.0 BetaDocument140 pagesCode::Blocks Manual: Version 2.0 BetaQuite omiNo ratings yet
- AcunetixDocument13 pagesAcunetixretcalNo ratings yet
- Leading Global Mobility Solutions ProviderDocument3 pagesLeading Global Mobility Solutions ProviderxyzNo ratings yet
- AjaxDocument408 pagesAjaxsivaNo ratings yet
- XML Publisher BrustingDocument13 pagesXML Publisher BrustingKishore KongaraNo ratings yet
- Xmlns Runat: HTML Head Title Title Head Body Form Div H1 H1 Asp Textbox Asp Textbox BRDocument4 pagesXmlns Runat: HTML Head Title Title Head Body Form Div H1 H1 Asp Textbox Asp Textbox BRVidya SagarNo ratings yet
- 105linked Lists Malik Ch05Document77 pages105linked Lists Malik Ch05sachinsr099No ratings yet
- Practice 3Document5 pagesPractice 3Ajoy A GNo ratings yet
- C PreprocessorDocument14 pagesC PreprocessorRAHUL ARORANo ratings yet
- The Bank Management System in VB 6Document32 pagesThe Bank Management System in VB 6sangeetha sNo ratings yet
- Lab - Install Third-Party Software in WindowsDocument2 pagesLab - Install Third-Party Software in WindowsBekalu AndargachewNo ratings yet
- Selenium Webdriver Interview Question PDFDocument24 pagesSelenium Webdriver Interview Question PDFDhanashekhar Jayapal100% (1)
- SOA Unit1Document59 pagesSOA Unit1suganya004No ratings yet
- Harmony Soft. C# Developer Test: We Only Consider Applicants Who Complete The Test!Document5 pagesHarmony Soft. C# Developer Test: We Only Consider Applicants Who Complete The Test!andungtraNo ratings yet
- Microlink Information Technology CollegeDocument43 pagesMicrolink Information Technology CollegeKidus WendesenNo ratings yet
- 10th Class Computer Science Notes in English: CHAPTER NO-1 "Problem Solving"Document3 pages10th Class Computer Science Notes in English: CHAPTER NO-1 "Problem Solving"Hamza NiazNo ratings yet
- Software EngDocument22 pagesSoftware Engnjugunakevin811No ratings yet
- Fuzzing or Fuzz TestingDocument3 pagesFuzzing or Fuzz TestingSHAIRA KAYE CABANTINGNo ratings yet
- Programming: Hardware & SoftwareDocument18 pagesProgramming: Hardware & SoftwarePurushothama ReddyNo ratings yet
- Information Architecture and Web Usability: Course NotesDocument175 pagesInformation Architecture and Web Usability: Course NotesNabila Nailatus SakinaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Data Modeling TechniquesDocument30 pagesConceptual Data Modeling Techniquesschow906291100% (1)
- Prop Fallthrough: Basebutton - VueDocument2 pagesProp Fallthrough: Basebutton - VueRRK 404No ratings yet
- PIVOT and UNPIVOT - Optimization and Execution Strategies in An RDBMSDocument12 pagesPIVOT and UNPIVOT - Optimization and Execution Strategies in An RDBMSvikaulNo ratings yet
- Slide Rekayasa Perangkat LunakDocument25 pagesSlide Rekayasa Perangkat LunakDavid D'bayuNo ratings yet
- Create and Traverse Binary Tree C ProgramDocument23 pagesCreate and Traverse Binary Tree C Programsujal thawareNo ratings yet
- CS1352 Compiler Design Question BankDocument10 pagesCS1352 Compiler Design Question BankSaravanan NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Instrucciones Instalacion WRFDA 4dvarDocument7 pagesInstrucciones Instalacion WRFDA 4dvarD CHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01.1 Welcome To REAL StudioDocument1 pageChapter 01.1 Welcome To REAL StudioEliseo AlatorreNo ratings yet
- Mettl Bulk Upload Template Coding Questions v2Document22 pagesMettl Bulk Upload Template Coding Questions v2gfvfvNo ratings yet
- XPEDITORDocument4 pagesXPEDITORismail4friendsNo ratings yet