Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECE Chemistry Review: Key Concepts
Uploaded by
JohnMarcusOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE Chemistry Review: Key Concepts
Uploaded by
JohnMarcusCopyright:
Available Formats
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
1
CHEMISTRY
Chemistry is a branch of science which deals with the study of matter and the changes it undergoes.
A. Branches of chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
Physical Chemistry
Analytical Chemistry
Biochemistry
I. MATTER
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. It is composed of tiny particles called atoms. There
are presently 106 different kinds of atoms (elements) in which each of these are represented by a symbol.
Law of Conservation of Mass Mass can neither be created nor be
destroyed.
Law of Conservation of Energy Energy can not be created nor
destroyed. It can only be transformed from one form to another.
Law of Definite Composition A pure compound is always made up
of same constituent elements combined in a definite proportion by weight.
Law of Multiple Proportions When two elements react to form more
than one compound, the different weights of one that combine with a fixed weight of the other
are in the ratio of small whole numbers.
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM-CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER
A. Physical States
Solid has definite size and shape
Liquid has definite volume but takes the shape of the container
Gas has neither definite shape nor definite volume
B. Properties
Physical Properties those that can be measured without changing the basic identity of the
substance (e.g. color, density, odor, boiling point).
Chemical Properties those that describe how a substance may react to form other
substances (e.g. flammability, tendency to rust).
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
Intrinsic Properties are properties of the substance that are independent of the shape and
size of the substance. (e.g. temperature, pressure, etc.).
Extrinsic Properties are properties of the substance that are related to its size and shape.
(e.g. volume, mass, weight, etc.)
C. Changes Which Matter Undergoes
Physical Change involves changing one or more physical properties of a sample of matter
without changing its composition (e.g. evaporation, cutting of wire, crystallization, tearing of
paper).
Chemical Change results in the change in composition of matter (e.g. burning of paper,
rusting of iron).
D. Composition
Mixtures
Pure Substance
Heterogeneous Mixtures
marble, concrete, wood
Compounds
salt, water, carbon dioxide gas
Homogeneous Mixtures
sugar solution, pure air, metal alloys
Elements
hydrogen gas, gold, mercury, neon gas
II. CHEMICAL FORMULAS
A. The Atom
Basic building block of the universe; has the following major components:
Subatomic particles
proton
electron
neutron
Charges
positive
negative
neutral
Mass
1.0073 amu
0.00055 amu
1.0087 amu
Electric Charge
-19
1.602x10 C
-1.602x10-19 C
Unit mass in kg
1.673x10-27 kg
9.11x10-31 kg
1.675x10-27 kg
Atomic number equal to the number of protons of an element.
Atomic mass equal to the combined masses of protons and neutrons.
Neutral atom number of protons is equal to the number of electrons.
Positively charged atom if there are more protons than electrons.
Negatively charged atom if there are more electrons than protons.
56
Example:
What is the number of neutron in one atom of 26Fe ?
Answer:
The number of protons is 26. The number of protons and neutrons (mass
number) is 56. Thus, the number of neutrons is 56 26, or 30.
B. Atomic Weight
Equal to the average of the isotopic masses weighted according to the naturally occurring
abundance of the isotopes of the element.
Expressed relative to the value of exactly 12 amu for a carbon-12 atom.
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
Example:
What is the atomic weight of argon (Ar) given the following
percentage of
abundance in nature:
99.60% 40Ar, mass is 39.962 amu
0.337% 36Ar, mass is 35.968 amu
0.063% 38Ar, mass is 37.963 amu.
Answer:
Atomic weight of argon:
= (0.996x39.962) + (0.00337x35.968) +
(0.00063x37.963)
= 39.947 amu
C. Formula Weight
Is used for compounds that are made up of ions and have primarily ionic bonding. Is
convenient as it can be used for both ionic and covalent bonding.
D. Molecular Weight
Is used for compounds that are composed of molecules and have primarily covalent
compound. Will be used only for covalent compounds which consists of molecules like sucrose
C12H22O11, ethyl alcohol C2H5OH, and Carbon Monoxide CO.
Example:
Answer:
Calculate the formula weight of water, H2O.
Since there are 2 atoms of hydrogen and 1 atom of oxygen in a formula unit of
water, then the formula weight is
H=2x1 = 2
O = 1 x 16 = 16
Formula Weight = 18 amu
E. Mole
Amount of a substance which contains 6.022 x 1023 particles (Avogadros number) of matter;
(the world particle can mean atom, molecule, or ion).
Equal to the gram molecular mass of a substance
Example:
Answer:
How many moles and atoms are there in 100 g of argon?
The molecular mass of argon is 39.948 g/mole. The number of moles of argon
in the sample is:
1mol
= 100g
39.948g
= 2.50 mol Ar.
The number of atoms of argon is simply
6.022 1023 atoms
= 2.50 moles
mole
23
=1.51 x 10 atoms
F. Formulas and Formula Masses
A chemical formula indicates the relative number of atoms of each element in a substance.
If the numbers are the smallest possible integral values that express the relative number of
atoms, the formula is called an empirical formula.
The formula mass is the sum of the masses of every atom in a substance as indicated in its
formula.
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
Example:
Answer:
A compound consists of 30.4% nitrogen and the rest oxygen. What is its
empirical formula?
1moleN
mole N = 30.4g N
= 2.17 mole N
14gN
1mol O
= 4.35 mole O
16.0g O
mole O = (100 30.4)g O
The smallest mole ratio of nitrogen to oxygen is 1:2. Thus, the empirical
formula is NO2.
G. Molecular Formulas and Molecular Masses
A molecular formula is similar to the empirical formula expect that it expresses the actual
number of atoms of each element in one molecule of a substance.
If a molecular formula is used, the corresponding formula mass is called a molecular mass.
Example:
Answer:
A compound with molecular mass equal to 60.0 has the following
percent composition: C = 40.0%, H = 6.67%, O = 53.3%. What is its
molecular formula?
Atomic weight of argon:
= (0.996x39.962) + (0.00337x35.968) + (0.00063x37.963)
= 39.947 amu
II. CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS
A. Types of Chemical Compounds
Ionic Compounds metal and nonmetal ions held together by electrostatic forces of
attraction.
Molecular Compounds nonmetal elements held together by covalent bonding.
B. Composition of Chemical Compounds
It is the components of compounds and their relative proportions in a given sample.
Example:
Answer:
What are the masses of carbon and hydrogen in 50.0 g of methane (CH4)?
The molecular mass of methane is (4)1 + (1)12, or 16.
The percentage of C is 12/16 or 75.0%.
The percentage of hydrogen is 4/16 or 25.0%.
For a 50.0g sample the mass of hydrogen is
= 0.25 (50.0g)
= 12.5g
And that of carbon is
= 0.75 (50g)
= 37.5g
C. Oxidation State
It is the number of electron an atom can donate, accept, or share with other atoms to from a
compound.
The common oxidation states of some elements are the following:
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
Elements
F, Cl,
Br, I
O, S
N, P
C, Si
B, Al
Alkali
metals
Alkaline
earth
metals
Oxidation
state
1, -1
-1
-2
-3, +5
-4, +4
+3
+1
+2
D. Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds
Binary compounds (composed of two elements)
Rules for Metals and Nonmetals:
1. The unmodified name of the metal is written followed by the name of the nonmetal, which
ends in ide.
2. For transition metals, a suffix ous is added for the lower state while ic for the higher one.
3. If the Stock System is used, the oxidation number of the metal is written in Roman Numeral
right after the unmodified name of the metal.
Compound
Name
Compound
Name
Fe2S3
ferrous sulfide
AlF3
aluminum fluoride
BaO
barium oxide
Cr2O3
chromium(III) oxide
Cu2O
copper(I) oxide
ZnS
zinc sulfide
CaF2
calcium fluoride
SrO
strontium oxide
Na2S
sodium sulfide
MgCl2
magnesium chloride
Rules for two Nonmetals:
1. Prefixes are written to indicate the relative number of atoms of an element in a compound.
2. A suffix ide is added at the end.
Compound
Name
Compound
Name
BCl3
boron trichloride
SF6
sulfur hexaoxide
CCl4
carbon tetrachloride
PCl3
phosphorus trichloride
CO
carbon monoxide
PCl5
phosphorus pentachloride
NO2
nitrogen dioxide
B2Br4
diboron tetrabromide
N2 O
dinitrogen oxide
SO2
sulfir dioxide
Ternary compounds composed of more than two elements, usually a polyatomic ion and an
element. Naming them is by order: positive first, negative second
Compound
Chemistry
Name
Compound
Name
NH4Cl
ammonium chloride
Na4PO4
sodium phosphate
KC2H3O2
potassium acetate
NaCN
sodium cyanide
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
Mg(NO3)2
magnesium nitrate
BaC2O4
barium oxalate
NaHCC3
sodium bicarbonate
KMnO4
potassium permanganate
K2CrO4
potassium chromate
Na2S2O3
sodium thiosulfate
Binary acids a prefix hydro- and a suffix -ic are added to the base name of the nonmetallic
element, then the word acid.
Name
Formula
Hydrofluoric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrobromic acid
Hydroiodic acid
Hydrosulfuric acid
HF
HCl
HBr
HI
H2S
Ternary acids composed of hydrogen, a nonmetal, and oxygen. Naming them depends on
the of oxygen present in the acid, usually with the lesser number ending with ous and with
the greater number ending in ic; others follow the name of their polyatomic ions.
Name
Formula
Name
Formula
Name
Formula
Nitric acid
HNO3
Hypochloric acid
HClO
Phosphorous acid
H3PO3
Nitrous acid
HNO2
Chlorous acid
HClO2
Phosphoric acid
H3PO4
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
Chloric acid
HClO3
Boric acid
H3BO3
Sulfurous acid
H2SO3
Perchloric acid
HClO4
Carbonic acid
H2CO3
Acetic acid
HC2H3O2
Oxalic acid
H2C2O4
Silicic acid
H2SiO3
III. CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND STOICHIOMETRY
A. Types of Chemical Reactions
Combination/synthesis formation of a compound of complex substance through the
reaction of two elements of simpler substances.
Examples: 2H2 + O2 2H2O + heat
2C7H6O2 + 15O2 14CO2 + 6H2O + heat
CaO + CO2 CaCO3
Decomposition/analysis
Examples: 2H2O
2HgO
CaCO3
breakdown of a compound into other compounds and/or elements.
2H2 + O2
2Hg + O2
CaO + CO2
Single replacement/single displacement the more reactive element replaces the less
reactive element in a compound.
Examples: 2Mg + TiCl4
2MgCl + Ti
Zn + CuSO4
ZnSO4 + Cu
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
Double replacement/double displacement (also called metathesis) exchange of patterns
to form an insoluble salt.
Examples: BaCl2 + NaSO4
2NaCl + BaSO4
Na2CO3 + Ba(OH)2
BaCO3 + 2NaOH
B. Chemical Equation and Stoichiometry
Chemical equation representation of a chemical reaction; reactants are written on the left
side, products at the right side of the arrow.
Law of conservation of matter in a chemical reaction, total mass of reactants equals total
mass of the products.
Stoichiometric coefficients numbers written before a substance in balancing an equation.
C. Limiting Reactant
It is the reactant that restricts or controls the amount of product that will be produced.
D. Percent Yield
Not all reactions proceed to 100% completion, that is not all reactants are consumed to yield
the desired product. Some reactants undergo side-reactions to produce unintended products
(the by-products).
The percent yield is defined as the ratio of the actual yield over the theoretical yield times 100.
IV. GAS LAWS
A. Boyles Law
For a fixed amount of gas at constant temperature, gas volume is inversely proportional to gas
pressure.
v1
v2
Example:
Answer:
P2
P1
A certain was occupying a volume of 10L at 720 mm Hg. At constant
temperature, the gas was compressed resulting to a pressure of 800 mm Hg.
What was the new volume of the gas?
P
720 mm Hg
v 2 1 v1
10 L 9 L
P2
800 mm Hg
B. Charles Law
For a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure the gas volume is directly proportional to the
absolute temperature of the gas (i.e., in Kelvin scale).
v1
v2
Example:
was the
Chemistry
T1
T2
Air inside a 5 L frictionless piston at 25C was heated up to 50C.
new volume of the air?
What
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
Answer:
v2
T2
T1
v1
273 50C
5 L 5.42 L
273 25C
C. Gay-Lussacs Law
For a fixed amount of gas at constant volume, gas pressure is directly proportional to gas
temperature.
P1
P2
Example:
Answer:
T1
T2
Oxygen gas at 30C and 10 atm was further pressurized to 15 atm by
heating
the tank. What was the new temperature of the oxygen gas?
P2
15atm
T2
T
30 273 K 454.5K 181.5C
P1 1 10atm
D. Avogadros Law
At a fixed pressure and temperature, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the amount
of gas.
v1
v2
n1
n2
At STP or standard temperature and pressure (0C and 1 atm) the volume of a mole
gas is 22.4 L.
of
E. The Ideal Gas Law
At low pressure and high temperature, all gases follow the above gas laws. The combination of
all the above laws is called the Ideal Gas Law and it follows the following equation:
L atm
PV = nRT, where R is the ideal gas constant equal to 0.0821
mole K
The equation can also be expressed as:
P1V1
T1
P2 V2
T2
... nR
Example:
moles
to a
Carbon dioxide occupies a volume of 3L at 1.5 atm and 47C. How
many
of carbon dioxide are there? If it is cooled down to 30C
and subjected
pressure of 2 atm, what is the new volume of the
gas?
Answer:
PV = nRT
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
PV
RT
P1V1
P2 V2
T1
(1.5 atm)(3 L)
0.17 mole
Latm
0.0821 moleK (47 273)K
T2
PT
1.5 atm (30 27)K
1 2
3 L
2.13 L
P T
2 atm (47 273)K
2 1
V2 V1
F. Daltons Law of Partial Pressures
The total pressure of a gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressure of the
individual gases that make up the mixture.
The partial pressure of a component gas is simply the pressure that gas is exerting on a
container as if it were alone.
Example:
the partial
Answer:
Air at standard atmospheric pressure is typically 78.084% nitrogen,
20.946%
oxygen, 0.934%?argon, and 0.036% carbon dioxide. What
pressures of each gas in mm HG?
Conversion: 1 atm = 760 mm Hg
Partial pressure of:
Nitrogen:
0.78084 x 760 = 593.44 mm Hg
Oxygen:
0.20946 x 760 = 159.19 mm Hg
Argon:
0.00934 x 760 = 7.10 mm Hg
Carbon Dioxide:
0.00036 x 760 = 0.27 mm Hg
are
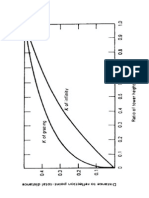
G. Grahams Law of Effusion
Effusion the escape of a gas through an orifice or hole. The rate of effusion of a gas is
inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight.
r1
r2
MW2
MW1
V. THERMOCHEMISTRY
A. Terminology
Heat (q) an energy transfer due to a temperature difference.
Work (w) a form of energy transfer between a system and its surroundings in the form of
compression of expansion of gas.
Internal energy (U) the total energy attributed to the particles of matter and their interactions
within a system; composed of thermal energy (energy associated with random molecular
motion) and chemical energy (energy associated with chemical bonds and intermolecular
forces).
Enthalpy (H) a thermodynamic function defined by H = U + PV. At constant temperature and
pressure, the change in enthalpy, H, is simply the heat of reaction.
Heat reaction (qrxn) heat exchange in a system when theres a chemical reaction at constant
temperature.
Heat capacity (c) the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of an object or
substance by one degree; usually expressed in J/C.
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
10
Specific heat/molar heat capacity (cp) heat capacity per unit mass of a substance at
constant pressure.
Latent heat of fusion (Lf) heat absorbed to melt a substance at constant temperature.
Latent heat of vaporization (Lv) heat required to change a substance from its liquid phase
to its gaseous phase at constant temperature.
B. Calorimetry (heat measurement)
Change in temperature
q = heat capacity x temperature change
= CT
= mass of object x specific heat x temperature change
= mCpT, for water, specific heat is Cp = 1.0 cal/gC
Example:
Answer:
A mass of 50g of copper (specific heat = 0.093 cal/gC) at 30C is heated up
to 100C. How much heat was absorbed by the copper?
q = mCpT
cal
q = 50g 0.093
100C 30C
gC
q = 325.5 cal
Phase change
1. Solid liquid
q = mLv, for water heat of fusion is: Lf = 80 cal/g
2. Liquid gas
q = mLf, for water heat of vaporization is: Lv = 540 cal/g
Example:
is
Answer:
If 100g of ice (Cp = specific heat = 0.5 cal/gC) at -5C is converted to
steam (Cp = specific heat = 0.5 cal/gC) at 110C,
how much heat
required?
heat involved in:
temperature change (-5C to 0C)
q1 = mCpT = 100g (0.5 cal/gC)(5C) = 250 cal
phase change (ice to water)
q2 = mLv = 100g (80 cal/g) = 8000 cal
temperature change (0C to 100C)
q3 = mCpT = 100g (1cal/gC)(100C) = 10,000 cal
phase change (water to steam)
q4 = mLf = 100g(540cal/g) = 54,000 cal
Total heat
= q1 + q2 + q3 + q4
= (250 + 8000 + 10000 + 54000) cal
= 72250 cal
Chemical reaction
1. Endothermic process a reaction wherein heat is absorbed by the system, indicated by a
positive change of enthalpy.
2. Exothermic process a reaction wherein heat is released by the system, indicated by a
negative change of enthalpy.
3. Hess Law states that if a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, the enthalpy of
reaction, H, is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps.
VI. THE ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
11
The Photoelectric Effect discovered by H. Hertz in 1888; described the emission of electrons
from metal surfaces when struck with light of appropriate frequency.
Photon proposed by Einstein in 1905; it means a particle of light consisting a particular amount
(a quantum) of energy. When it collides with an electron, it gives up its entire energy to the electron.
Bohrs Theory of a Hydrogen Atom introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913; states that 1) an electron
in an atom can only be in a certain allowed places, and 2) when it is in one of these allowed places
it possesses a certain amount of energy.
Wave-Particle Duality proposed by Louis de Broglie; states that small particles of matter may at
times display wave-like properties.
The Uncertainty Principle established by Werner Heisenberg; states that it is impossible to know
the precise location and velocity of an electron at the same time.
The Schrdinger Wave Equation formulated by Erwin Schrdinger; describes the wavemechanical model of electrons in an atom.
Orbital a region in an atom where the electron charge density or the probability of finding an
electron is high.
Quantum Numbers the three integral numbers needed to solve the equation of wave mechanics.
1. Principal quantum number (n) refers to the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus.
n = 1, 2, 3
2. Orbital angular quantum number (l) refers to the shape of the orbital. The specific orbital
types are s (sharp), p (principal), d (diffuse), and f (fundamental). Its value depends on the
principal quantum number.
l = 0, 1, 2 (n-1)
3. Magnetic quantum number (ml) refers to the spatial orientation of the
depends on the angular quantum number.
orbital. Its value
4. Spin quantum number (ms) refers to the spin of the electron, sometimes regarded as the
fourth quantum number. The value can be either +1/2 or -1/2.
Rules for Assigning Electrons Orbitals
1. Paulis Exclusion Principle no two electrons in an atom can have the same set
of
quantum numbers.
2. Hunds Rule pf Maximum Multiplicity whenever orbitals of equal energy are available,
electrons occupy these orbitals singly before any pairing of electrons.
The Aufbau Process a method of writing the probable electron configuration of the elements in
the order of increasing atomic number.
Example:
Answer:
VII. THE PERIODIC TABLE
Chemistry
Give the electron configuration of gallium, Ga, with atomic number 31.
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p1
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
12
Periodic table graphical arrangement of the elements in order of increasing atomic numbers such
that elements with similar properties are arranged in vertical columns.
Periodic Law when all the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers,
elements with similar properties will occur at periodic intervals.
Family / Group a vertical columns of elements in the periodic table that provides the number of
valence electrons. e.g., Family 1-A: H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr.
Series / Period horizontal row in the periodic table that provides the number of the last main
energy level. E.g., Series 3: Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar.
A. The Main Groups in the Periodic Table
Group Number
Family Name
Group 1A:
The Alkali Metals
Group 2A:
The Alkaline Earth Metals
Group 3A:
The Aluminum Group
Group 3A:
The Boron Family
Group 4A:
The Tin and Lead Family
Group 4A:
The Carbon and Silicon Family
Group 5A:
The Nitrogen Family
Group 6A:
The Oxygen Family
Group 7A:
The Halogens
Group 8A:
The Noble Gases
Group B:
The Transition Metals
Classifications of Elements
1. Metals good conductors of heat and electricity, ductile, malleable, and shiny. All metals are
solid at room temperature with the exception of liquid mercury. They are the elements, except
Hydrogen, that are on the left side of the border line including the Lanthanide and Actinide
metals.
2. Non-metals poor conductors of heat and electricity, brittle, not shiny, with more varied physical
properties than metals. They are all the elements on the right side of the border line such as S,
Br, and Ar.
3. Metalloids with properties that fall between those of metals and non-metals. They are the
elements that are above and below the borderline plus elements of group 4A such as Al, C, and
As.
Trends in the Periodic Table
1. Electronegativity ability of an atom to attract electron.
2. Ionization energy energy needed to remove an electron from an atom.
3. Electron affinity energy released when an electron is added to an atom.
VIII. CHEMICAL BONDING
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
13
Chemical Bonds forces of attraction that exist between atoms.
Lewis Symbols and Lewis Structures consist of a chemical symbol with dots placed around it to
represent the valence electrons.
Types of Chemical Bonds
1. Ionic or electrovalent bond formed by the transfer of electron from a metallic element to a
non-metallic element.
e.g.
(1) NaCl (2) Fe2O3
2. Covalent bond formed by the sharing of electrons between two or more non-metallic elements.
polar covalent bond unequal sharing of electrons
e.g.
(1) H2O (2) NH3
non-polar covalent bond equal sharing of electrons
e.g.
(1) CH4 (2) O2
(3) N2
dative bond/coordinate covalent bond the pair of electrons shared between atoms is
donated by only one atom.
e.g.
(1) NH3BF3
(2) NH4
3. Metallic bond force of attraction that exists within elemental metals (e.g., all metallic elements).
4. Double-Triple Bond If there are two pairs of electrons between two atoms, it is called a
DOUBLE BOND, and if there are three pairs it is called a TRIPLE BOND.
Resonance the use of two or more Lewis structures to represent a particular molecule.
e.g. (1) SO2 (2) O3
Isomers substances that have the same molecular formulas but differ in their structures and in
their properties.
e.g. Molecular Formula = C2H6O
Ethanol = C2H5OH
dimethyl ether = CH3OCH3
VIII. LIQUIDS, SOLIDS, AND IMF
Comparison of Liquids and Solids
State of
Matter
Volume/Shape
Density
Compressibility
Motion of
Molecules
Liquid
Has a definite
volume; its shape
follows the shape
of its container
High
Only slightly
compressible
The molecules slide
past one another
freely; liquids are
fluid.
Solid
Has a definite
shape and volume
High (generally,
solids are
denser than
liquids)
Incompressible
Vibrate about fixed
positions
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
14
Surface Tension the amount of energy required to increase the surface by unit area. Liquids with
strong intermolecular forces of attraction exhibit greater surface tension.
Viscosity resistance to flow. Liquids which have strong intermolecular forces of attraction are less
fluid than those which have weak forces of attraction. Liquid sugar is thick and flows very slowly.
Intermolecular forces attractive forces that exist between molecules.
Types of IMF
1. Van der Waals Forces very weak intermolecular forces that exist between non-polar
molecules.
e.g.
(1)
CH4
(2)
H2
2. Dipole-Dipole Forces forces that act between polar molecules.
e.g.
(1)
HCl
(2)
H2 O
3. Hydrogen Bonding interaction between the hydrogen atoms bonded to an atom of a very
electronegative element (F, N, O).
e.g.
(1)
H2 O
(2)
NH3
IX. SOLUTIONS AND THEIR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Two components of a solution
1. Solute dissolved substance, present in lesser quantity
2. Solvent dissolved medium, present in greater quantity
Types of solutions according to the solubility of solute
1. Saturated solution a solution containing the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved
by the solvent at a given temperature.
2. Unsaturated solution a solution containing less solute than the solvent can dissolve at a given
temperature.
3. Supersaturated solution a solution containing more solute than the solvent can dissolve.
Factors affecting solubility of solute
1. Nature of solute and solvent
2. Temperature
3. Size of particles, Surface area
4. Pressure (solids and liquids are not affected)
Henrys Law: the solubility of a gas in a liquid is proportional to the pressure of the gas over the
solution.
Expressing Solution Concentration
1. Percent solution
a. % by mass = (mass of solute / mass of solution) x 100%
Example:
Answer:
Chemistry
A sample of 0.892 g of naphthalene (C10H8) is dissolved in 54.6 g of
benzene (C6H6). What is the percent by mass of naphthalene in this
solution?
0.892g
100%
percent by mass
0.892g 54.6g
1.61%
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
15
b. % by volume = (volume of solute/volume of solution) x 100%
c. ppm = (mass of volume of solute/mass or volume of solution) x 1,000,000
d. proof = twice the % of alcohol in solution
2. Mole Fraction (X) the no. of moles of a component divided by the total number of moles of all
components in the solution.
XA
XB
Example:
nA
nA nB
Note:
nB
A = solute
B = solvent
nA nB
Determine the mole fractions of both substances in a solution
containing 26.0 of NaCl and 125.0 g of water.
Answer:
26.0gNaCl
58.5g
/ moleNaCl
XA
26.0gNaCl
125.0gwater
58.5 / moleNaCl 18g / moleH O
XA 0.06
125.0gwater
18g
/
moleH
O
XB
125.0gwater
26.0gNaCl
58.5 / moleNaCl 18g / moleH O
XB 0.94
3. Molarity (M) no. of moles of solute per liter of solution.
M =
Example:
Answer:
Chemistry
moles of solute
liter of solution
What is the molar concentration of a solution containing 16.0g CH3OC in 200
mL of solution?
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
16
16.0g
32.0g/mole
M=
0.2 liter
mole
M=2.5
liter
4. Molarity (m) no. of moles of solute per kg. of solvent.
m =
Example:
number of moles solute
kg solvent
The molarity of a solution of C2H5OH in water is 1.25 mol/kg. How many
grams of alcohol are dissolved in 2.5 kg of water?
Answer:
1.25mole 46g
kg mole
g=2.5kg
g=143.75g
5. Normality (N) no. of equivalent weight of solute per liter of solution.
N =
grams of solute
(eqv wt. of solute) x (liter of soln)
The equivalent weight of solute is determined by its change in valence in the particular
reaction
used. It follows that:
eqv. wt. (g/eqv) =
molecular mass (g/mole)
change in valence (eqv/mole)
Colligative Properties of Solutions
These are properties of solution which depend on the number of solute particles but
not
on the identity of the solute.
1. Vapor Pressure Lowering the addition of a non-volatile solute lowers the vapor pressure of the
liquid because the solute reduces the fraction of solvent present. With relatively fewer solvent
molecules, the rate of their escape from solutions is diminished, resulting in a decreased vapor
pressure.
2. Boling Point Elevation addition of a non-volatile solute lowers the vapor pressure of the
solution. As a result, the boiling point of the solution will be higher than that of the pure liquid.
3. Freezing Point Depression the decrease in freezing point is directly proportional to the
molarity of the solute.
4. Osmotic Pressure pressure needed to prevent osmosis. (Osmosis the net movement of
solvent molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from a more dilute solution to a more
concentrated one.)
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
17
X. CHEMICAL KINETICS
Chemical Kinetics study of rates of chemical reactions, rate laws and reaction mechanisms.
Reaction Rate number of moles of a reactant consumed per unit time. Usually the unit used is
molars per second (M/sec).
Rate Law an equation or mathematical expression showing the relationship between reactant
concentrations and rate of reaction.
Rate Constant an experimentally determined constant of proportionality between the reaction rate
and the concentrations of reactants that appear in the rate law.
Law of Mass Action at constant temperature, the rate of reaction is usually proportional to some
power of concentration of each reactant.
Order of Reaction the sum of the powers of the concentration factors in the rate equation.
Reaction Mechanisms series of successive elementary steps by which reactants are converted
to products.
Factors Affecting Reaction Rate:
Factors
Effect on reaction rate
1. greater frequency of collision
increase
2. higher energy of activation
decrease
3. higher energy of activation
Increase
4. lower temperature
decrease
5. increasing the concentration of reactants
Increase
6. increasing the particle size of reacting molecules
decrease
7. using a catalyst
Increase
Catalyst a substance that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing a
permanent change.
XI. CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
Chemical Equilibrium a state in which two opposing chemicals reactions are proceeding in
opposite directions at the same speed.
Le Chateliers Principle if a system at chemical equilibrium is disturbed by some stress, the
system goes to a new equilibrium condition in such a way as to relieve the stress.
XII. ACIDS AND BASES
Properties of Acids and Bases
Acids
Chemistry
Taste sour
Bases
taste bitter
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
Turn blue litmus red
Electrolytes
React with metal to produce
hydrogen gas
React with carbonates and
bicarbonates to produce CO2 gas
Turn colorless with phenolphthalein
solution
Turn red with methyl orange indicator
pH values less than 7
18
turn red litmus blue
feel slippery
electrolytes
turn pink to violet color with phenolphthalein
solution
turn yellow with methyl orange indicator
pH values greater than 7
Conceptual Definitions of Acids and Bases
Strong Electrolytes all ionic compounds that are dissolved in water (with very few exceptions)
Weak electrolytes compounds with non-metallic cations and anions; their degree of ionization is
lower than those of strong electrolytes.
Non-electrolytes compounds whose solution in water does not conduct electricity.
Neutralization reaction between an acid and a base that produces a salt, a neutral compound.
Hydrolysis a reaction between an ion and water.
Amphoterism property of some compounds to behave both as an acid and as a base.
XIII. ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
Definition Organic chemistry is the chemistry of the compounds of carbon with the exceptions of
carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbonates group, and the cyanide group. Even though these
compounds contain carbon, they were obtained from minerals and are considered to be inorganic
compounds.
General Comparison of Organic and Inorganic Compounds
Property
Organic Compounds
Inorganic Compounds
1. Solubility in water
Insoluble, except those that are
capable of H-bonding
Soluble
2. Solubility in organic
solvents
Soluble
Insoluble
3. Melting point
Low
Very high
4. Boiling point
Low
Very high
5. Electrical conductivity
Non-conductors
Conduct in molten state of
solution
6. Molecular mass
High
Low
7. Structure
Complex
Simple
8. Particles
Molecules
Ions
9. Combustion
Mostly flammable
Usually
10. Isomerism
Common
Rare
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS
Chemistry
19
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
1. The temperature at which mercury starts to
freeze is -35C. What is the temperature, in
degrees Fahrenheit, at which a mercury
thermometer can not be used?
a. -63 F
b. -35 F
c. -31 F
d. -5.4 F
2. A piece of stone weighs 0.05 pounds. When if
is submerged in a graduated cylinder
containing 50 mL of H2O, the level rose to 60
mL. What is the density of the stone in g/mL?
a. 2.27 b. 2.72 c. 7.22 d. 7.27
3. A swimming pool 25m wide, 100m long, and
3m deep is filled with water up to a height of
2m. How many kilograms of water have been
placed inside the pool? (The density of water
is 1000 kg/m3.)
a. 5 million
b. 7.5 million
c. 10 million
d. 12.5 million
4. Which of the following not an example of a
compound?
a. sugar b. salt
c. ash
d. water
5. If two pure substances have different melting
points, then
a. the two substances will surely have
different densities
b. the two samples are certainly different pure
substances
c. the two substances are certain to have
identical chemical formulas
d. the two substances are certain to be
compounds and not elements
6. Which of the following is a compound?
a. water b. wine c. soil
d. mercury
7. Which of the following processes is an
example of a chemical change?
a. evaporation of sea water to form salt
b. melting of an ice cube
c. filtering of paper pulp from a liquid slurry
using a sieve tray
d. rusting of iron
8. We know that air is a homogeneous mixture
and not a compound because
a. it has no definite shape
b. it has no definite volume
c. it ca be compressed
d. its composition can vary
Chemistry
20
9. What do you call a substance that is
composed of two or more elements bonded
chemically?
a. an isotope
b. an element
c. a compound
d. a mixture
10. Which of the following examples is a
physical change?
a. crystallization of sugar from sugar can juice
b. fermenting of ethanol to form wine
c. burning of a piece of candle
d. clotting of blood
11. Which of the following substances cannot be
further decomposed by ordinary chemical
means?
a. water b. sugar c. air
d. silver
12. Which of the following not a manifestation of
a chemical change?
a. reaction of a compound and an element to
form a new compound and an element
b. breaking down of compound into elements
c. combining of atoms of elements to form a
molecule
d. separation of the molecules in a mixture
13. What do you call a nuclear reaction resulting
from the interaction of two nuclei to form a
bigger nucleus and an accompanying release
of energy?
a. nuclear fission
b. alpha emission
c. nuclear fusion
d. natural radioactive decay
14. Which of the following materials cannot be
subjected to carbon dating to determine its
age?
a. a trunk of wood
b. a sword
c. a smear of blood on a piece of cloth
d. an ancient Egyptian scroll
15. What law states that the pressure of a gas is
directly proportional to its absolute
temperature at constant volume?
a. Charles Law b. Gay-Lussacs Law
c. Boyles Law d. Daltons Law
16. To what conditions does a gas behave like
an ideal gas?
a. low temperature and low pressure
b. low temperature and high pressure
c. high temperature and low pressure
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
21
d. high temperature and high pressure
17. What law states that the pressure of gas is
inversely proportional to its volume at
constant temperature?
a. Charles Law
b. Gay-Lussacs Law
c. Boyles Law
d. Daltons Law
18. Which gas diffuses faster?
a. CH4
b. O2
c. CO
d. He
19. Which of the following best describes heat?
a. the capacity to do work
b. forces times distance
c. sum of thermal and chemical energy
d. an energy transfer due to a temperature
difference
20. What happens to water when it begins to
vaporize?
a. it increases in temperature
b. it decreases in temperature
c. no change in temperature
d. no change in thermal energy
21. Burning of gasoline initially requires heat
before it burns spontaneously. Which of the
following does not give a good explanation of
this phenomenon?
a. the initial heat rises the enthalpy of the
reactant
b. the initial heat lowers the activation of
energy of the reactants
c. the enthalpy of the reactants is lower that
the enthalpy of the products
d. the enthalpy of the product is lower than
the enthalpy of the reactant.
22. Which of the following is an endothermic
process?
a. melting of ice
b. burning of paper
c. neutralization of a strong acid and a strong
base
d. violent reaction of sodium metal with water
23. Which of the following events is heat
exchange involved?
a. when there is a phase change
b. when there is a chemical reaction
c. when the gas expands adiabatically
d. when there is difference in temperature
Chemistry
24. Who first predicted the wave-particle dual
property of electrons?
a. Hund
b. Heisenberg
c. De Broglie
d. Schrdinger
25. Who postulated the wave equation that
describes the properties of electrons in an
atom?
a. Bohr
b. Heisenberg
c. Pauli
d. Schrdinger
26. Atoms of nonmetals generally reacts with
atoms of metals by
a. gaining electrons to form ionic compounds
b. gaining electrons to form covalent
compounds
c. sharing electrons to form ionic compounds
d. sharing electrons to form covalent
compounds
27. The addition of a nonvolatile solute to a
solvent will cause
a. the vapor pressure of the solvent to
increase
b. the vapor pressure of the solvent to
decrease
c. the vapor pressure of the solvent to remain
unchanged
d. non of these
28. Which of the following factors does not affect
the rate of reaction?
a. the number of products formed
b. the nature of reactants
c. temperature
d. concentration of reactants
29. Which of the following statements about the
catalyst is not true?
a. they may slow down the reaction
b. they may speed up the reaction
c. they are present in living substances
d. the may become new substances after the
reaction
30. Which of the following statements about
equilibrium is TRUE?
a. it exists in a closed system at varying
temperature
b. it exist in an open system
c. it exists between a liquid and its vapor in a
closed system at uniform temperature.
d. it may exist between a solid and a liquid.
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
31. According to the Bronsted-Lowry theory, an
acid is
a. a proton donor
b. a proton acceptor
c. a proton donor and a proton acceptor
d. neither a proton donor nor a proton
acceptor
32. Which is not true of bases?
a. they always contain OH- ions
b. they neutralize acid
c. the pH of their solution is greater than 7
d. they react with H3O+ ions
33. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of
compounds containing the element
a. hydrogen
b. carbon
c. oxygen
d. nitrogen
34. What is the mass in grams of 1 liter of
carbon
monoxide
(CO)
at
standard
temperature and pressure (STP)? Note: The
molecular weight (MW) of CO is 28 g/mole,
and at STP, 1 mole of any gas occupies a
volume of 22.4 liters.
a. 1.20
b. 1.35
c. 1.45
d. 1.25
35. Two-thirds of the atom in a molecule of water
is hydrogen. What percentage weight of a
water molecule if the weight of two hydrogen
atoms? The atomic weight of hydrogen is
1.008 g/mol and oxygen is 16.00 g/mole.
a. 19.12
b. 11.19
c. 19.11
d. 12.19
36. How many protons (P) and neutrons are
there in the nucleus are present in a Pb
nucleus of atomic mass of 206?
a. P = 92, N = 156
b. P = 85, N = 160
c. P = 82, N = 124
d. P = 90, N = 150
37. A 0.064 kg. of octane vapor (MW = 114) is
mixed with 0.91 kg of air (MW =29.0) in the
manifold of an engine. The total pressure in
the manifold is 86.1 kPa, and a temperature is
290 K. Assume octane behaves ideally. What
is the partial pressure of the air in the mixture
in KPa?
a. 46.8
b. 48.6
c. 84.6
d. 64.8
38. Hydrogen peroxide solution for hair
bleaching is usually prepared mixing 5 grams
of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), Molecular
Chemistry
22
weight = 34 g/mole) per 100 ml of solution.
What is the molarity of this solution?
a. 1.0 M
b. 1.5 M
c. 1.95 M
d. 1.8 M
39. A cylinder contains oxygen at a pressure of
10 atm and a temperature of 300K. The
volume of the cylinder is 10 liters. What is the
mass of oxygen in grams? Molecular weight
(MW) of oxygen is 32 g/mole?
a. 125.02
b. 130.08
c. 135.05
d. 120.04
40. The molecular diameter of CO is 3.19x10 -8 at
300K and pressure of 100 mmHg. What is the
mean free path of the gas in cm?
a. 6.86x10-3
b. 6.86x10-5
c. 2.86x10-4
d. 6.86x10-9
41. How many moles are there in one atom?
a. 3.6x10-23
b. 1.66x10-5
c. 2.86x10-4
d. 6.86x10-9
42. When 0.5g of liquid is completely evaporated
and collected in liter manometer, the pressure
is 0.25 atm and the temperature is 27C.
Assume ideal gas behavior, find the molecular
weight if the gas constant is 0.0821
L.atm/mole.K.
a. 49.2 g/mole
b. 12.3 g/mole
c. 2.2 g/mole
d. 64.0 g/mole
43. If the atomic weight of magnesium is 24.3
g/mol, calculate how many magnesium atoms
does 5g represent?
a. 1.24x1023 atoms
b. 1.76x1023 atoms
c. 3.44x1023 atoms
d. 2.76x1023 atoms
44. How many moles of iron does 25 g of Fe
represent? Note: the atomic weigh of iron (Fe)
is 55.8 g/mol.
a. 0.356 mol
b. 0.564 mol
c. 0.448 mol
d. 0.247 mol
45. How many oxygen atoms are present in 2.00
moles of oxygen molecules considering that is
a diatomic?
a. 2.40 x 1024 atoms
b. 3.43 x 1025 atoms
c. 5.67 x 1026 atoms
d. 1.34 x 1024 atoms
46. if the atomic mass of copper (Cu) if 63.5
g/mol, compute how many grams does 0.252
mole of copper (Cu) has?
a. 16 g
b. 18 g
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
c. 20 g
d. 12 g
23
c. 73.9 g/mol
d. 67.5 g/mol
47. What is the molecular weight of calcium
hydroxide or Ca(OH)2?
a. 74
b. 67
c. 80
d. 44
56. Calculate the specific gravity of Cl 2 at STP.
Note: the molecular weight of Cl2 is 71 g/mol.
a. 3.45
b. 1.23
c. 2.46
d. 1.76
48. How many molecules are there in 25 g of
hydrogen Chloride, HCl?
a. 4.12 x 1023 molecules
b. 4.32 x 1023 molecules
c. 5.34 x 1023 molecules
d. 3.45 x 1023 molecules
57. Compute the volume of oxygen at STP that
can be formed from a 0.75 mole of potassium
chlorate (KClO3).
a. 18.6 liters
b. 16.8 liters
c. 25.2 liters
d. 23.2 liters
49. What is the percentage composition of a
solution in the sodium chloride compound?
a. 60.7%
b. 34.6%
c. 39.3%
d. 50.7%
58. What pressure will be exerted by a 0.50 mol
of gas in a 7 L container at 23C?
a. 1.74 atm
b. 2.05 atm
c. 3.04 atm
d. 1.32 atm
50. What is the composition of oxygen of
potassium sulfate, K2SO4?
a. 53.2%
b. 36.7%
c. 50.4%
d. 43.4%
59. Compute how many moles of oxygen has
are in a 70 L tank at 25C if the pressure is
2000 psi?
a. 389.3 mol
b. 453.4 mol
c. 145.7 mol
d. 247.4 mol
51. A 1.63 g of zinc when heated in air combined
with 0.40 g of oxygen to form oxide of zinc.
What is the percentage composition of Zn in
the compound formed?
a. 80.3%
b. 76.5%
c. 19.7%
d. 53.4%
60. What is the molarity
contains 65 g of sucrose
in 300 g of water?
a. 0.89 mole/kg
c. 0.54 mole/kg
52. Calculate how many moles of ammonia can
be produced from 8 mol of hydrogen reacting
with nitrogen?
a. 4.53 mol NH3
b. 7.76 mol NH3
c. 5.33 mol NH3
d. 4.57 mol NH3
53. How many molecules of water can be
produced by reacting 0.010 mol of oxygen
with hydrogen?
a. 1.20 x 1022 molecules
b. 1.32 x 1022 molecules
c. 2.34 x 1022 molecules
d. 4.15 x 1022 molecules
54. If 2 liters of gas measured at STP weigh
3.23 g, what is the molecular weight of the
gas?
a. 36.2 g/mol
b. 42.3 g/mol
c. 24.7 g/mol
d. 19.4 g/mol
55. An ethyl ether 691 mL weighs 1.65 g
measured at 40C and 630 torr. Compute the
molecular weight of ethyl ether.
a. 34.5 g/mol
b. 43.5 g/mol
Chemistry
of the solution that
(C12H22O11) dissolved
b. 0.78 mole/kg
d. 0.63 mole/kg
61. Calculate the number of moles of an ideal
gas sample at 0.6 atmosphere and 87C
occupies 0.450 liter.
a. 0.0091 mole
b. 0.0087 mole
c. 0.0076 mole
d. 0.0056 mole
62. One gram of hydrogen gas (H 2) is combined
with 10 g of helium (He) gas and confined at
20C and 5 atmospheres. What is the
combined volume in liters?
a. 14.4 liters
b. 17.5 liters
c. 16.4 liters
d. 12.7 liters
63. What is the molarity of the solution if 150 g
of KCl is dissolved in water to make 800 mL
solution?
a. 2.51 moles/L
b. 2.25 moles/L
c. 2.87 moles/L
d. 1.53 moles/L
64. Compute how many grams of KCl must be
dissolved in water so that it can produce a
400 L of 0.6 M (molarity) solution?
a. 17.904 g
b. 14.281 g
c. 11.541 g
d. 12.653 g
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
65. What is the atomic weight of calcium if 2.25
g of pure calcium metal are converted to 3.13
g of pure CaO?
a. 49.8 g/mol
b. 54.3 g/mol
c. 23.7 g/mol
d. 40.9 g/mol
66. What is the equivalent weight of Sulfuric
Acid?
a. 49
b. 98
c. 23
d. 100
67. If 60 g of H2SO4 is dissolved in water to
make a 1.5 L solution, find its normality N?
a. 0.813 equiv/L
b. 0.576 equiv/L
c. 0.871 equiv/L
d. 0.765 equiv/L
68. What is the equivalent weight of Mg(OH)2?
a. 23 g/mol
b. 29 g/mol
c. 58 g/mol
d. 20 g/mol
69. How many grams of H3PO4 are confined in
700 mL container if its normality is 0.5?
a. 11.45 g
b. 12.34 g
c. 10.56 g
d. 9.35 g
70. Which of the following is the simplest
balanced equation of the given reaction?
Na2CO3 + HCl NaCl + H2O + CO2
a. Na2CO3 + 2HCl 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
b. Na2CO3 + 2HCl NaCl + 2H2O + CO2
c. 2Na2CO3 + HCl 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
d. 2Na2CO3 + HCl NaCl + H2O + 2CO2
71. If the molecular formula of water is H 2O, then
what is its molecular mass?
a. 18 amu
b. 19 amu
c. 20 amu
d. 1 amu
72. What is the molecular weight of barium
chloride dehydrate (BaCl22H2O)?
a. 234.4 amu
b. 244.3 amu
c. 270.5 amu
d. 298.5 amu
73. Which of the following is the simplest
balanced equation of the given OxidationReduction Equation?
P + HNO3 + H2O NO + H3PO4
a. 2P + HNO3 + H2O NO + 2H3PO4
b. 3P + HNO3 + H2O NO + 3H3PO4
c. 3P + 5HNO3 + 2H2O 5NO + 3H3PO4
d. 3P + HNO3 + 2H2O 2NO + 3H3PO4
74. What type of bond results in form the sharing
of electrons by two atoms?
a. atomic bond
b. covalent bond
c. metallic bond
d. ionic bond
Chemistry
24
75. Which of the following statements regarding
organic substances is FALSE?
a. Organic substances generally dissolve in high
concentration acids
b. All organic matter contains carbon
c. Organic matter is generally stable at very high
temperatures
d. Organic substances generally do not dissolve
in water
76. What do you call
dissociates in solutions
and negative ions?
a. base
c. electrolyte
a substance that
to produce positive
b. acid
d. solute
77. During a complete or partial neutralization of
acids, what is the ionic compound formed?
a. salt
b. sugar
c. potassium
d. sulfur
78. Which of the following is most likely to prove
that a substance is inorganic?
a. the substance evaporates in room
temperature and pressure
b. the substance is heated together with copper
oxide and the resulting gases are found to
have no effect on limestone
c. analysis shows that the substance contains
hydrogen
d. the substance floats in water
79. Which of the following are found in the
nucleus of an atom?
a. electrons and protons
b. electrons and neutrons
c. protons and neutrons
d. electrons, protons and neutrons
80. Which of the following elements and
compounds is unstable in its pure form?
a. Helium (He)
b. Neon (Ne)
c. Carbon dioxide (CO2)
d. Sodium (Na)
81. What refers to the negatively charge
component of an atom?
a. electron
b. proton
c. neutron
d. ion
82. Which of the following is the simplest type of
reaction where two elements of compounds
combine directly to form a compound?
a. directly combination or synthesis
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
b. decomposition or analysis
c. single displacement
d. double displacement
83. What do you call the bonding that occurs in
inert gases and other elements with full shells,
primarily due to attraction between dipole
structures?
a. ionic
b. metallic
c. covalent
d. van de waals
84. If the heat of a solution is negative, heat is
given off when the solute dissolves in the
solvent. What type of reaction is this?
a. exothermic
b. ideal
c. endothermic
d. efflorescent
85. What do you call materials that do not
conduct electric current?
a. conductor
b. insulator
c. semi conductor
d. intrinsic material
86. What element is known as the lightest
metal?
a. aluminum
b. manganese
c. Magnesium
d. Lithium
87. Which of the following is energy removal
being applied?
a. evaporation of water
b. changing water to steam
c. changing water to ice
d. all of these
88. Halogens fall under what group in the
periodic table?
a. group VIA
b. group VA
c. group IVA
d. group VIIA
89. Which of the following is added to the
drinking water distribution system for
disinfection?
a. Soda ash
b. Chlorine
c. Lime
d. Iodine
90. What refers to the number of gram
equivalent weights of solute per liter of
solution?
a. molarity (M)
b. normality
c. molarity (m)
d. formality
91. Is the attraction between like molecules.
a. absorption
b. diffusion
c. adhesion
d. cohesion
Chemistry
25
92. What do you call a substance that cannot be
decomposed any further by a chemical
reaction?
a. ion
b. element
c. molecule
d. atom
93. One of the following is the standard pressure
and temperature. Which on?
a. 0C and zone atmosphere pressure
b. 0C and zero pressure
c. 0F and one atmosphere
d. 32F and zero pressure
94. Which of the following is the strongest type
of bonds?
a. Van de Waals
b. Metallic
c. Covalent
d. Ionic
95. Sublimation is a direct change from:
a. solid to liquid phase
b. solid to gaseous phase
c. liquid to gaseous phase
d. gaseous phase to liquid phase
96. What do you call hydrocarbons containing
carbon to carbon double bonds?
a. Alkanes
b. Alkenes
c. Alkynes
d. None of these
97. How are materials containing atoms with
less than valence electrons classified?
a. an insulator
b. a semi-conductor
c. a conductor
d. a compound
98. Which of the following has the
characteristics of both metals and nonmetals?
a. conductors
b. insulators
c. metalloids
d. meteors
99. Which are oxidizing and reducing agents in
the following reactions?
2CCl4 + K2CrO4 2Cl2CO + CrO2Cl2 + 2 KCl
a. there are no oxidizing and reducing agents in
this reaction
b. oxidizing agent: chromium; reducing agent:
chlorine
c. oxidizing agent: chlorine; reducing agent:
carbon
d. oxidizing agent: oxygen; reducing agent:
chlorine
100. How are elements numbered 58 to 71 in
the periodic table called?
a. Lanthanons
b. Actinons
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
c. Earth metals
d. Noble gas
101. What type of bonding in which electrostatic
attraction is predominant?
a. Ionic bonding
b. Metallic bonding
c. Covalent bonding
d. Van der Waals bonding
102. What term refers to the passage of an
electric current trough an electrolyte caused
by an external voltage source? Which one?
a. electrolysis
b. electromechanical action
c. electrolyte
d. piezoelectric effect
103. When all of the atoms of a molecule are the
same, the substance is called _____.
a. a compound
b. a chemical
c. an element
d. an ion
104. Which of the following refers to the
measure of the amount of negative ions in the
water?
a. acidity
b. alkalinity
c. turbidity
d. molarity
105. What device produces electrical current by
way of an oxidation-reduction reaction?
a. generator
b. galvanic cell
c. metallic friction
d. all of these
106. What is the maximum number of electrons
that can be accommodated in the valence
shell of an atom?
a. 6
b. 8
c. 10
d. 12
107. Reactions generally proceed faster at high
temperatures because of which of the
following?
a. the molecules are less energetic
b. the molecules collide more frequently
c. the activation energy is less
d. the molecules collide more frequently and the
activation energy is less
108. Which component of an atom has no
electric charge?
a. proton
b. neutron
c. coulomb
d. electron
109. Adding more solute to an already saturated
solution will cause the excess solute to settle
Chemistry
26
to the bottom of the container. What is this
process called?
a. precipitation
b. hydration
c. dehydration
d. saturation
110. What is formed when acids will react with
active metals?
a. sulfur
b. oxygen
c. hydrogen
d. chloride
111. How much is the pH content of an acid?
a. between 4 and 6
b. between 2 and 7
c. between 1 and 5
d. between 0 and 7
112. The condition of a liquid electrolyte is
measured in terms of its:
a. specific gravity
b. acid content
c. voltage output
d. current value
113. What is a substance that speeds up a
chemical reaction without itself undergoing a
chemical change?
a. ingredients
b. reactants
c. solvent
d. catalyst
114. How are elements numbered 90 to 103 in
the periodic table called?
a. alkali
b. actinons
c. earth metals
d. tr ansition elements
115. What is defined as a value equal to the
number of gram moles of solute per 1000
grams of solvent?
a. Molarity (m)
b. Normality
c. Molarity (M)
d. Formality
116. Which of the following is NOT a part of an
atom?
a. electron
b. proton
c. neutron
d. coulomb
117. An element maybe defines as a substance,
all atoms of which have the same:
a. number of neutrons
b. radioactivity
c. atomic weight
d. atomic number
118. How does all B families and group VII in the
periodic table named?
a. light metals
b. rare earth metals
c. non-metals
d. transition metals
119. The device which measures the acid
content of the cell is called _____.
a. acid meter
b. hydrometer
c. hygrometer
d. pyrometer
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
120. The vertical columns in the periodic table
are called:
a. Groups
b. Sections
c. Batches
d. Families
121. What term is used to refer to a negatively
charged ion?
a. Anion
b. Cathode
c. Anode
d. Cation
122. In a copper atom, the valence ring
contains:
a. no electrons
b. one electrons
c. two electrons
d. four electrons
123. The elements along the dark line in the
periodic table are referred to as _____.
a. Light metals
b. Metalloids
c. Non-metals
d. Heavy metals
124. What do you call an atom that loses some
of its electron or accepts extra electrons from
another atom?
a. Intrinsic
b. Mole
c. Neutron
d. Ion
125. A _____ is a cell designed to produce
electric current and can be recharged.
a. Secondary cell
b. electrolytic cell
c. chemical cell
d. battery
126. Which of the following groups in the
periodic
table
the
most
strongly
electronegative elements?
a. Group IV
b. Group V
c. Group VIIA
d. Group VIA
127. Which of the following statement is FALSE?
a. In general, as reaction products are formed,
they react with each other and reform
reactants.
b. At equilibrium, the net reaction rate is zero.
c. The differential rate is the mathematical
expression that shows how the rate of
reaction depends on volume.
d. The net rate at which a reaction proceeds
from left to right is equal to the forward rate
minus the reverse rate.
128. What is the smallest part of matter?
a. molecule
b. element
c. particle
d. atom
129. The opposite of alkali
Chemistry
27
a. acid
c. substance
b. fluid
d. none of these
130. What type of reaction has two compounds
as reactants and two compounds as
products?
a. Direct combination or synthesis
b. Decomposition or synthesis
c. Single displacement
d. Double displacement
131. If the heat of a solution is positive, heat is
absorbed when the solute dissolves in the
solvent. What type of reaction is this?
a. Exothermic
b. Ideal
c. Endothermic
d. Efflorescent
132. The amount of electricity a battery can
produce is controlled by
a. the thickness of the plate
b. the plate surface area
c. the strength of the acid
d. the discharge load
133. What do you call the electrons in the last
orbit or shell of an atom?
a. Bound electrons
b. Free electrons
c. Valence electrons
d. External electrons
134. Which one is the positively charged ion?
a. anion
b. cathode
c. anode
d. cation
135. It is the number of protons in the nucleus of
an atom
a. Molecular number
b. Proton number
c. Mass number
d. Atomic number
136. What do you call the elements in the first
two groups in the periodic table?
a. Light metals
b. Noble gas
c. Non-metals
d. Heavy metals
137. Which one refers to the number of grammoles of solute per liter of solution?
a. Molarity (m)
b. Normality
c. Molarity (M)
d. Formality
138. What type of bonding is electrostatic
attraction most predominant?
a. Ionic
b. Metallic
c. Covalent
d. Van der Waals
139. When the charge of an atom becomes
unbalanced, the charge atom is called _____.
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
a. an ion
c. a proton
b. a neutron
d. an electron
28
a. Group IIA
c. Group IIIA
b. Group IA
d. Group IVA
140. Which of the following type of reactions in
which bonds within a compound are disrupted
by heat or other energy to produce simpler
compounds or elements?
a. direct combination or synthesis
b. decomposition or analysis
c. single displacement
d. double displacement
150. What type of bonding that occurs in metals
when metal atoms lose electrons and the
metallic ions are attracted to a sea of
delocalized electrons?
a. ionic bonding
b. metallic bonding
c. covalent bonding
d. van der waals bonding
141. What do you call hydrocarbons containing
carbon to carbon triple bonds?
a. alkanes
b. alkenes
c. alkynes
d. non of these
151. Which of the following elements is NOT
radioactive?
a. Plutonium
b. Californium
c. Uranium
d. Cobalt
142. If an atom contains more than four valence
electrons, the material is classified as _____.
a. insulator
b. semi-conductor
c. conductor
d. any of these
152. Which of the following refers to a nucleic
acid that stores genetic information?
a. Cellulose
b. Codon
c. DNA
d. Buffer
143. Which of the following refers to a measure
of the quantity of an element or compound?
a. Oxidation number
b. Atomic number
c. Avogadros number
d. Mole
153. During chemical reactions, bonds between
atoms are broken and new bonds are usually
formed. What do you call the starting
substances?
a. Products
b. Reactants
c. Catalyst
d. Ingredients
144. The electrolyte is a solution of water and
_____.
a. sulfuric acid
b. uric acid
c. nitric acid
d. formic acid
145. Acids will turn blue litmus paper to what
color?
a. gray
b. yellow
c. violet
d. red
146. How much is the pH content of a base?
a. between 6 and 10
b. between 2 and 7
c. between 7 and 14
d. between 10 and 16
147. Applying a greater pressure causes pure
solvent to leave the solution. What is the
name of this process?
a. cavitation
b. calcination
c. purification
d. reverse osmosis
148. A deuteron is
a. a neutron plus two protons
b. a nucleus containing a neutron and a proton
c. an electron with a positive change
d. a helium nucleus
149. Which of the following groups in the
periodic table the most weakly electronegative
elements?
Chemistry
154. What do you call solutions having the same
osmotic pressure?
a. Isotonic solutions
b. Monohydroxic solutions
c. Dihydroxic solutions
d. Toxic solutions
155. What is the term used to describe
hydrocarbons containing single covalent
bonds between carbon atoms?
a. alkanes
b. alkenes
c. alkynes
d. allotrope
156. The smallest whole unit of an element like
Uranium is:
a. molecule b. atom
c. ion
d. electron
157. What refers to the formation and collapse
of minute bubbles of vapor in liquid which
caused by a combination of reduced pressure
and increased velocity in the fluid?
a. cavitation
b. stress corrosion
c. fatigue corrosion
d. precipitation
158. The elements in Group 0 in the periodic
table is called_____.
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
a. light metals
b. rare earth metals
c. noble gas
d. heavy metals
159. A pair of electrical conductors of dissimilar
materials so joined as to produce a thermal
emf when the junctions are of different
temperatures.
a. potentiometer
b. piezoelectric
c. thermocouple
d. solar heating
160. Bases will turn red litmus paper to what
color?
a. blue
b. yellow
c. violet d. green
161. Which of the following refers to the diffusion
of a solvent into a stronger solution in an
attempt to equalize the two concentrations?
a. purification
b. electrolysis
c. osmosis
d. hydrolysis
162. The formula for Dinitrogen Pentoxide is:
a. N2O5
b. (NO)5
c. NO
d. none of these
163. Which of the following will occur if a
substance is oxidized?
a. it absorbs energy
b. it loses electrons
c. it becomes more negative
d. it gives off heat
164. What type of reaction has one element and
one compound as reactants?
a. direct combination or synthesis
b. decomposition of analysis
c. single displacement
d. double displacement
165. Which of the following is the atomic number
of silicon?
a. 32
b. 24
c. 14
d. 28
166. Dielectric is another name for _____.
a. a conductor
b. an element
c. an insulator
d. a capacitor
167. Which of the following refers to the change
from gaseous to liquid phase?
a. condensation
b. vaporization
c. sublimation
d. ionization
168. At the same, pressure and temperature,
equal volumes of all gasses contain equal
number of molecules. This is known as
a. Boyles Law
b. Faradays Law
c. Avogadros Law
d. Charles Law
Chemistry
29
169. The galvanic cell is not dependent of which
factor?
a. temperature
b. pressure
c. volume
d. chemical substance
170. Which of the following refers to the number
of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an
atm?
a. atomic weight
b. atomic mass
c. atomic constant
d. atomic number
171. One of the following statements is wrong.
Which one is it?
a. Electron is an elementary quantity of negative
electricity
b. proton is an elementary quantity of positive
electricity
c. an atom is composed of a central nucleus and
orbital electrons
d. the mass of an electron is heavier than that of
a proton
172. During a chemical reactions, bonds
between atoms are broken and new bonds
are usually formed. The ending substance is
called _____.
a. products
b. reactants
c. catalyst
d. ingredients
173. What is the smallest subdivision of an
element of compound that can exist in a
natural state?
a. atom
b. molecule
c. ion
d. element
174. The sharing of one or more electron pairs
between nuclei. It usually occurs when the
electronegativity difference between bonding
species is less than 1.5
a. Bridge Bonding
B. Ionic Bonding
C. Covalent Bonding
D. Valence Bonding
175. The name of this group is the chalcogen
(oxygen) family.
a. Group IIA
b. Group IVA
c. Group VIA
d. Group VIIIA
176. The amount of energy to change 1 g of
liquid to gas at its boiling point.
a. enthalpy of formation
b. enthalpy of fusion
c. enthalpy of reaction
d. enthalpy of vaporization
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
177. The fragmentation of a crystal along a
characteristic
crystallographic
direction,
caused by lines of weakness in constituent
atomic groups.
a. cleavage
b. fracture
c. luster
d. streak
178. A bond formed by the sideways overlap of
two parallel p orbitals.
a. Peptide Bond
b. Pi Bond
c. Saturated Bond
d. Delta Bond
179. This indicator turns into colorless if the
substance is acidic.
a. Phenolphthalein b. Methyl orange
c. Litmus paper
d. Bromthymol blue
180. A chemical structure with definite formula
for which there exists one or more distinct
structures with the sane formula.
a. Isomer
b. Radical
c. Group
d. Colloid
181. A substance that can be decomposed into 2
or more simpler substances by ordinary
chemical means.
a. Element
b. Mixture
c. Compound
d. Solution
182. A theory which treats bonding as an over
lapping of ligand orbitals with those of the
central atom.
a. Ligand Field Theory
b. Crystal Fields Theory
c. Chelate Effect
d. Molecular Orbital Theory
183. Known as fools gold.
a. Quartz
c. Feldspar
b. Cinnabar
d. Pyrite
184. It is the hardest substance known
a. Wad
b. Graphite
c. Diamond
d. Adamantium
185. The splitting of water to form hydrogen and
oxygen
a. reduction
b. electrolysis
c. oxidation
d. hydrolysis
186. Which is not an open chain hydrocarbon
classification?
a. alkenes
b. alkanes
c. cycloalkanes
d. alkynes
Chemistry
30
187. The process of producing ions from neutral
species.
a. Fractional Distillation
b. Hydration
c. Recombination
d. Ionization
188. A chemical bond with sausage roll shape
formed by the sideways overlap of two d
orbitals.
a. Peptide Bond
b. Pi Bond
c. Saturated Bond
d. Delta Bond
189. Multidentate ligands have equal probability
of forming a coordination bond as do
monodentate ions.
a. Ligand Field Theory
b. Paulings Rule
c. Chelate Effect
d. Molecular Orbital Theory
190 It has no definite composition whose
members are composed of two or more
substances, each retaining its own identifying
properties.
a. Homogeneous Mixture
b. Heterogeneous Mixture
c. Aqueous Mixture
d. Ingeneous Mixture
191. A chemical compound having one or more
unpaired electrons which is capable of
bonding with another compound.
a. Labile
b. Resonance Hybrid
c. Free Radical
d. Isodemic Crystal
192. The mineral name for common table salt
a. Halite
b. Cassierite
c. Aragonite
d. Calcite
193. Any process that involves the loss of
electrons.
a. Reduction
b. Exsolution
c. Oxidation
d. Hydrolysis
194. Elements normally found in combination
with iron and nickel.
a. Noble Metals
b. Promethium
c. Tritium
d. Siderophile
195. Any substances that changes the rate of a
reaction without being used up.
a. Catalyst
b. Enztme
c. Reactor
d. Stimulus
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
196. A/An ____ of chemical substances is, by
definition, the number in grams corresponding
to the atomic or molecular mass.
a. atiomic mass
b. atomic weight
c. mole
d. ion
197. A reaction in which an unstable reaction
intermediate is found
a. Coupled Substitution
b. Free Radical Reaction
c. Polar Reaction
d. Concentrated Reaction
198. A reaction for which the difference between
enthalpies of formation between products and
reactants is positive.
a. Intrathermic
b. Exothermic
c. Endothermic
d. Isothermic
199. The _____ is the heat released of absorbed
in a chemical reaction at constant pressure
when simple substances combine into a more
complex substance.
a. enthalpy of formation
b. enthalpy of fusion
c. enthalpy of reaction
d. enthalpy of vaporization
200. Characteristic based upon the reaction of a
substance with other materials.
a. Chemical Property
b. Colligative Property
c. Nuclear Property
d. Physical Property
201. A symmetrical intergrowth of two or more
crystals of the same substance.
a. Twin
b. Isomer
c. Epitaxis
d. Habit
202. A compound which is gaseous at ambient
temperature and pressure and which is easily
melted.
A. Volatile
b. Soluble
c. Liquidus
d. Solidus
203 The energy required to form gaseous
monatomic species.
a. Bond Energy
b. Dissociation Energy
c. Activation Energy
d. Light Energy
204. The amount of energy released as on mole
of a given substance is burned in the
presence of oxygen.
a. Nuclear Energy b. Enthalpy of Reaction
Chemistry
31
c. Trans Effect
d. Heat of Combustion
205. The most diamagnetic naturally occurring
material.
a. Iron
b. Gallium
c. Bismuth
d. Silicon
206. Any Process that involves the gain of
electrons.
a. Reduction
b. Exsolution
c. Oxidation
d. Hydrolysis
207. The change of the thermodynamic state
function enthalpy due to a chemical reaction.
a. enthalpy of formation
b. enthalpy of fusion
c. enthalpy of reaction
d. enthalpy of vaporization
208. A concept invented by Linus Pauling to
measure the tendency for atoms to form ionic
instead of covalent bonds.
a. Electromagnetism
b. Electropositivity
c. Electronegativity
d. Electrodynamism
209. A substance whose particles are strongly
attracted to each other (e.g., gelatin)
a. Colligative
b. Hydrophilic
c. Hydrophobic
d. Cohesive
210. The most common form of calcium
carbonate.
a. Halite
b. Cassierite
c. Aragonite
d. Calcite
211. The substance that undergoes phase
change in the process of dissolving
a. Radical
b. Isomer
c. Solvent
d. Solute
212. A process in which water molecules are
attracted to and form weak bonds with the
solute species.
a. Hydration
b. Oxidation
c. Combustion
d. Reduction
213. The dissociation of a chemical species
resulting from its absorption of a photon.
a. Photosynthesis
b. Photolithography
c. Photosensitization
d. Photodissociation
214. _____ is the mineral name for lead sulfide
(PbS). It is the most important ore of lead.
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
a. Saltpeter
c. Galena
b. Gypsum
d. Silicate
215. A substance that does not undergo
chemical reactions is said to be _____.
a. inert
b. labile
c. alkaline
d. amorphous
32
c. Hunds Rule
224. Elements with the same outermost shell
are said to belong to the same _____.
a. spin
b. period
c. valence
d. slot
225. An alkyl sulfate alkali.
a. Detergent
c. Ethylene
216. Which bond strength is weak?
a. Macromolecular covalent bonds
b. Ionic bonds
c, Hydrogen bonds
d. Van der Waals forces
217. Occurs with the bonding electron pair
remaining intact.
a. Coupled Substitution
b. Free Radical Reaction
c. Polar Reaction
d. Concentrated Reaction
218. A mixture composed of a suspended and a
mobile phase.
a. Isomer
b. Radical
c. Suspension
d. Colloid
219. A/An _____ is a biological catalyst.
a. Amino acids
b. Genes
c. DNA
d. Enzyme
220. The first covalent bond formed between
two nuclei is always a _____. They are
formed when two s orbitals, one s and one p
orbital, two p orbitals, or two d orbitals
overlap.
a. Peptide Bond
b. Pi Bond
c. Sigma Bond
d. Bridge Bond
221. The process by which solutions are
decomposed into their components by using
differences in their boiling points.
a. Fractional Distillation
b. Filtration
c. Recombination
d. Ionization
222. Filtration through a semi-permeable
membrane used to separate colloids.
a. Dialysis
b. Hydrolysis
c. Electrolysis
d. Chromatography
223. In orbitals of identical energy, electrons
remain unpaired if possible in order to
minimize electron-electron repulsion.
a. Spin Multiplicity Rule
b. Selection Rules
Chemistry
d. Paulings Rules
b. Acetone
d. Oil
226. The process whereby an excited species
transfers its energy to another excited species
which subsequently undergoes a reaction
a. Photosynthesis
b. Photolithography
c. Photosensitization
d. Photodissociation
227. _____ is the study of hydrocarbon
compounds, ie., substances consisting of the
elements hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen.
a. Inorganic Chemistry
b. Organic Chemistry
c. Quantum Chemistry
d. Biochemistry
228. _____ displays all chemical elements
systematically in order of increasing atomic
number.
a. Phase Diagram
b. Polarization Spectrum
c. Periodic Table
d. Elements Archive
229. A substance composed of a single type of
atom
a. Atom
b. Compound
c. Solution
d. Colloid
230. A group of elements which are gaseous at
room temperature and pressure, and called
so because they rarely bond with other
elements.
a. Tetratomic Elements
b. Nobel Gases
c. Alkali
d. Lanthanide
231. An element which is not found naturally on
Earth. It has been found in the star HR465 in
Andromeda.
a. Adamantium
b. Promethuim
c. Tritium
d. Adolinium
232. A form of elemental carbon which, because
of its sheet structure, is an excellent lubricant.
a. graphite
b. Carbon
c. Soot
d. Coal
233. Which is not one of the periodic properties?
a. electronegativity
b. electron affinity
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
33
c. radioactive decay coefficient
d. atomic radius
234. The reflection of light beam passing
through a colloid which identifies the presence
of suspended particles.
a. Tyndall Effect
b. Brownian Movement
c. Raoults Law
d. Trans Effect
235. An ionic compound containing a halogen.
a. Halide
b. Lanthanide
c. Alkalide
d. Sulfide
236. A reaction for which the difference between
enthalpies of information between products
and reactants is negative.
a. Intrathermic
b. Exothermic
c. Endothermic
d. Isothermic
244. The _____ is a system of reference
materials against whose hardness a sample is
compared.
a. Richter scale
b. Mohs hardness scale
c. Cavendish balance
d. Brinell hardness model
245. Magma with most of the gas component
escaped.
a. Lava
b. Cinder
c. Sulphur
d. Coal
246. Minerals having high melting temperatures.
a. Endogenic
b. andesitic
c. Granitic
d. Basaltic
237. The quantity of energy released as one
mole of bonds are produced between atoms.
a. Bond Energy
b. Light Energy
c. Activation Energy
d. Atomization Energy
247. _____ minerals are those having low
melting temperatures.
a. Endogenic
b. Andesitic
c. Granitic
d. Basaltic
238. An ion with negative charge
a. Cation
b. Anion
c. Muon
d. Neutrino
248. The transfer of one or more electrons from
a metal to a nonmetal. Electron transfer
usually occurs when the electronegativity
difference between bonding species is 1.5 or
more.
a. Bridge Bonding
b. Ionic Bonding
c. Covalent Bonding
d. Valence Bonding
239. _____ is a measure of the acidity of
alkalinity of a substance.
a. HP
b. dB
c. pH
d. Pro-V
240. Two-phase mixture composed
dispersed and continuous phase.
a. Isomer
b. Radical
c. Suspension
d. Colloid
241. A solvent for atoms.
a. Flux
c. Inert Gases
of
b. Water
d. Kryptonite
242. A class of matter with definite properties
whose members are composed of two or
more substances, each retaining its own
identifying properties.
a. Homogeneous Mixture
b. Heterogeneous Mixture
c. Solid Solution
d. Ingeneous Matter
243. A crystal for which all bonds have the same
electrostatic valency.
a. Labile
b. Resonance Hybrid
c. Free Radical
d. Isodemic Crystal
Chemistry
249. The non-random overgrowth of two
compositionally different crystalline
substances.
a. Twin
b. Isomer
c. Epitaxis
d. Habit
250. The angles between equivalent faces of
crystals of the same substance, measured at
the same temperature, are constant.
a. Bravais Law
b. Hall Effect
c. Tyndall Effect
d. Steno Law
251. The chemical element having the greatest
binding energy per nucleon.
a. Iron
b. Gallium
c. Bismuth
d. Platinum
252. Any type of reaction that involves the
pairing of unpairing of electrons.
a. Coupled Substitution
b. Free Radical Reaction
c. Polar Reaction
d. Concentrated Reaction
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
253. It is the form of oxygen consisting of three
bound oxygen atoms.
a. Halogen
b. Halide
c. Oxide
d. Ozone
254. A group of elements with similar properties
in which the outer-most electron shell is a
partially filled f sublevel.
a. Tetratomic Elements
b. Noble Gases
c. Alkali
d. Lanthanide
255. A substance whose particles are only
weakly attracted to each other (e.g., water)
a. Colligative
b. Hydrophilic
c. Hydrophobic
d. Refractory
256. A class of homogeneous matter which has
a definite composition by weight.
a. compound
b. mixture
c. element
d. substance
257. In the periodic table, Group IA is for the:
a. Halogens
b. Light metals
c. Alkaline metals
d. Alkali metals
258. A covalent bond formed through a
condensation reaction that involves removal
of a water molecule.
a. Peptide Bond
b. Pi Bond
c. Sigma Bond
d. Bridge Bond
259. Which group is the nitrogen family?
a. Group VA
b. Group IVA
c. Group IIIA
d. Group IIA
260. Litmus paper turns into _____ is the
substance is basic.
a. colorless
b. yellow
c. red
d. blue
261. A property which depends only on the
number of particles present, and not their
chemical composition.
a. Chemical Property
b. Colligate Property
c. Nuclear Property
d. Physical Property
262. The amount of energy to change 1g of solid
to liquid at its melting point.
a. enthalpy of formation
b. enthalpy of fusion
c. enthalpy of reaction
d. enthalpy of evaporation
Chemistry
34
263. The process whereby an initially
homogeneous solid solution separates into
two (or more) distinct crystalline minerals
without the addition or removal of materials to
or rom the system.
a. Reduction
b. Exsolution
c. Oxidation
d. Hydrolysis
264. The separation of component particles from
the bulk or mass.
a. Dissociation
b. Atomization
c. Fission
d. Reduction
265. An ion with positive change.
a. Cation
b. Anion
c. Muon
d. Neutrino
266. A cell which uses the flow of electrons from
a spontaneous chemical reaction to do
outside work.
a. Daniel Cell
b. Gravity Cell
c. Concentration Cell
d. Galvanic Cell
267. The anion OH-.
a. Hydride
c. Hydroxide
b. Oxide
d. Nitrate
268. A measure of the tendency of a gas to
escape or expand.
a. Compressibility
b. Fugacity
c. Vaporizability
d. Solubility
269. An ionic theory which is an offshoot of
electrostatic theory. It ignores all covalent
bonding effects.
a. Ligand Field Theory
b. Crystal Fields Theory
c. Chelate Effect
d. Molecular Orbital Theory
270. A purple form of quartz whose color arises
from Fe+4.
a. Amethyst
b. Ruby
c. Topaz
d. Peridot
271. A/An _____ is a hydrocarbon consisting
only of single carbon-carbon bonds
a. Alkyne
b. Alkene
c. Alane
d. Amide
272. A large polypeptide of the kind found in
living organisms.
a. Amino Acid
b. Protein
c. Minerals
d. Fatty Acid
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
273. It is the code in which almost all genetic
information is encoded.
a. Transfer RNA
b. Ribosomal RNA
c. Ribonucleic Acid
d. Deoxyribonucleic Acid
274. A sample of glass is a supercooled liquid
rather than a true solid because it has _____.
a. a definite volume
b. no definite volume
c. a crystalline structure
d. no crystalline structure
275. Two immiscible liquids, when shaken
together, may form a _______.
a. solution
b. sediment
c. hydrated solution d. colloidal dispersion
276. Which of the following is not a pure
substance?
a. water
b. milk
c. hydrogen
d. oxygen
277. Which of the following is not an isotope of
hydrogen?
a. hydrogen
b. deuterium
c. tritium
d. uranium
35
283. Oxidation involves reactions in which
______.
a. a substance gains one or more electrons
b. a substance loses one or more electrons
c. oxygen has been removed from the reactants
d. oxygen is gained by the reactants
284. A bleach may work if it ______.
a. adds hydrogen ions to the stain
b. removes electrons during oxidation
c. adds electrons to reduce coloration
d. moves electrons between energy levels
285. An organic compound ______.
a. contains carbon
b. can be produced synthetically
c. both 1 and 2 are correct
d. neither 1 nor 2 is correct
286. Which of the following can be used to
bombard atoms?
a. protons
b. neutrons
c. electrons
d. all three
287. An atom of which of the following elements
has the greatest ability to attract electrons?
a. silicon
b. bromine
c. sulfur
d. nitrogen
278. Which of the following is formed by the
transfer of electrons from one atom to another?
a. allotrope
b. ion
c. isotope
d. molecule
288. Given the same conditions of temperature,
which nobel gas will diffuse most rapidly?
a. Kr
b. He
c. Ne
d. Ar
279. The modern periodic table is based on
atomic _______.
a. number
b. radius
c. charge
d. mass
289. When most fuels burn, the products include
carbon dioxide and ______,
a. hydrogen
b. hydrocarbons
c. water
d. hydroxide
280. The gram molecular mass for H2SO4 is
______ grams.
a. 7
b. 64
c. 98
d. 196
290. Which type of reaction is occurring when a
metal undergoes corrosion?
a. neutralization
b. polymerization
c. saponification
d. oxidation-reduction
281. The rate of chemical reaction can be
increased by _______.
a. increasing the surface area of the reactants
b. decreasing the reaction temperature
c. decreasing the concentration of the reactants
d. removing the catalyst
282. Which of the following is not a
characteristic of a base?
a. has a bitter taste
b. feels smooth and slippery
c. turns litmus from red to blue
d. typically reacts vigorously with metals
Chemistry
291. Which part of the Periodic Table contains
elements with the strongest metallic properties?
a. upper left
b. lower left
c. upper right
d. lower right
292. A 1 M solution contains 20 grams of solute
in 500 milliliters of solution. What is the mass of
1 mole of the solute?
a. 10 g b. 20 g c. 40 g d. 80 g
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
293. What is the molecular formula of a
compound with an empirical formula of CH and
a molecular mass of 78?
a. C6H6
b. C3H3
c. C4H4
d. C5H5
294. What is the empirical formula of a
compound that contains 85% Ag and 15% F by
mass?
a. Ag2F
b. AgF2
c. Ag2F2
d. AgF
295. A gas has a pressure of 300 torr, a
temperature of 400 K, and a volume of 50.0
milliliters. What volume will the gas have at a
pressure of 150 torr and a temperature of 200
K?
a. 25.0 mL
b. 50.0 mL
c. 75 mL
d. 100 mL
296. How many atoms are present in the
formula KAl(SO4)2?
a. 6
b. 8
c. 10
d. 12
297. How many liters of gas would 1.5 moles
occupy at STP?
a. 15.0
b. 4.5
c. 33.6
d. 44.6
298. If an element has an atomic number of 11,
it will combine most readily with an element that
has an atomic number of _____.
a. 16
b. 17
c. 18
d. 19
299. Which of the following statements is true?
a. chlorine changes in color
b. chlorine changes in density
c. chlorine changes into liquid
d. chlorine reacts explosively to form sodium
chloride
300. Which of the following is a compound?
a. milk
b. gold
c. table salt
d. ink
301. Golds atomic number is 79. How many
protons, neutrons, and electrons are there in 197
Au?
a. 79
b. 118
c. 197
d. 276
302. Which of the following is an element?
a. H2O
b. O3
Chemistry
36
c. CO2
d. C2H4
303. Which of the following is the empirical
formula for glucose, a substance known as
blood sugar, whose molecular formula is
C6H12O6?
a. CH2O
b. CHO
c. C2H4O
d. CHO6
304. Which of the following is the name of the
compound K2SO4?
a. potassium sulfate
b. sulphuric oxide
c. potassium oxide
d. silver nitrate
305. Which of the following balances this
equation: Na(s) + H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H2(g)?
a. Na(s) + 2H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
b. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
c. Na(s) + 2H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
d. Na(s) + 2H2O(l) NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
306. What is the formula weight of
C12H22O11(sucrose)? The atomic weights of
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen are 12.0 amu, 1.0
amu and 16.0 amu, respectively.
a. 29.0 amu
b. 47.0 amu
c. 76.0 amu
d. 342.0 amu
307. What is the mass of 1 mol of glucose,
C6H12O6? The atomic weights of carbon,
hydrogen and oxygen are 12.0 amu, 1.0 amu
and 16.0 amu, respectively.
a. 180.0 amu
b. 360.0 amu
c. 53.0 amu
d. 90.0 amu
308. What is the molarity of a solution made by
dissolving a 23.4 g of sodium sulfate (NaSO4) in
enough water to form 125 mL of solution?
a. 2.12 M
b. 1.32 M
c. 3.33 M
d. 5.34 M
309. What is the kinetic energy in joules and
calories of a 6.0 kg object moving at a speed of
5.0 m/s?
a. 30 cal
b. 18 cal
c. 1.2 cal
d. 0.16 cal
310. What is the formula for a compound formed
between aluminum and oxygen? (The atomic
number of aluminum is 13 while that of oxygen
is 8).
a. Al2O3
b. Al3O5
c. AlO2
d. Al3O4
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
311. What is the volume of exactly 1 mol of gas
at 0C (273.15 K) and exactly 1 atm pressure?
a. 27.31 L
b. 31.32 L
c. 22.41 L
d. 17.42 L
312. Which of the following substances is most
likely to exist as a gas at room temperature and
normal atmospheric pressures?
a. P4O10
b. Cl2
c. AgCl
d. I2
313. Which of the following will happen if a gas
in an enclosed container is heated?
a. pressure increases
b. temperature decreases
c. volume increases
d. volume decreases
314. How can a bigger crystals of table salt be
commercially produced?
a. slow solar evaporation
b. fast solar heating
c. boiling in a cauldron
d. heating over a sand bath
315. The natural fragrance of plants is attributed
to the presence of ______.
a. alkanes
b. esters
c. alcohols
d. acetone
316. A solution is made containing 6.9 g of
NaHCO3 per 100 g of water. What is the weight
percentage of solute in this solution?
a. 93.5%
b. 89.7%
c. 6.5%
d. 10.3%
317. In terms of total mass, carbon monoxide
(CO) is the most abundant of all pollutant gases.
The most serious source of carbon monoxide
poisoning comes from ______.
a. cigarette smoking
b. smoke from factories
c. smoke from vehicles
d. smoke from forest fires
37
b. cohesive force is weaker than adhesive force
c. cohesive and adhesive forces are the same
d. cohesive force is stronger at the bottom
320. Which is a statement of quantitative
description?
a. one bottle holds more liquid than the other
b. the color of one liquid is darker than the other
c. the liquid in one bottle is more cloudy than the
other
d. the liquid in one bottle is 5 mL more than that
in the other
321. The mass number of an element is 16 and
its atomic number is 8. How many neutrons
does it have?
a. 16
b. 8
c. 24
d. 48
322. What kind of substance turns blue litmus
paper into red and is classified as a proton
donor?
a. a salt
b. an acid
c. a base
d. a metal
323. LPG or liquefied petroleum gas is a mixture
of C3H8 and C4H10. This mixture is ______ and
______.
a. propane, butane
b. ethane, methane
c. propane, methane
d. propane, butane
324. Which unit is used t express the amount of
energy absorbed or released during a chemical
reaction?
a. calorie
b. torr
c. degree
d. kilogram
325. A compound with an empirical formula of
CH2 has a molecular mass of 70. What is the
molecular formula?
a. C2H4 b. C4H8 c. CH2
d. C5H10
318. Which of the following is not a non
conventional source of biogas?
a. animal manure b. petroleum
c. ipil-ipil
d. cassava
326. Which are the products of a fermentation
reaction?
a. a soap and a glycerol
b. an alcohol and carbon dioxide
c. an ester and water
d. a salt and water
319. When mercury is placed in a small test
tube, a convex surface may be seen. This
shows that ______.
a. cohesive force is stronger than adhesive force
327. The number of calories per gram required
to melt ice at its melting point is called ______.
a. sublimation
b. heat of fusion
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
38
c. vapor pressure
d. heat of vaporization
a. 10 g
c. 30 g
328. A liquid has one phase, is colorless and
odorless and boils at a temperature range of
110-120C. This liquid is called _____.
a. solution
b. colloid
c. substance
d. heterogenous mixture
337. When a battery is in use, stored chemical
energy is first changed to ______ energy.
a. light
b. electrical
c. mechanical
d. nuclear
329. A white solid that melts sharply was
observed to yield a colorless liquid and a black
solid when burned. Which term best describes
the solid?
a. element
b. mixture
c. substance
d. compound
330. The forces of attraction that exist between
nonpolar molecules are called ____.
a. ionic
b. van der Waals
c. electrovalent
d. atomic
331. Toward which corner of the Periodic Table
are located the elements that have the most
pronounced nonmetallic properties?
a. upper right
b. lower right
c. upper left
d. lower left
332. Which process occurs when dry ice is
changed into carbon dioxide?
a. crystallization
b. sublimation
c. condensation
d. solidification
333. What is the number of an atom which
contains 25 electrons, 25 protons, and 29
neutrons?
a. 50
b. 342.0 amu
c. 25
d. 54
334. Which electron dot formula represents a
nonpolar molecules?
H
H
a. H:C:Cl:
b. H:N:
H
H
H
H
c. H:C:H
d. H:Cl:C
H
H
335. How many moles of water are contained on
0.250 mole of CuSO4 5H2O?
a. 62.5
b. 0.5
c. 1.25
d. 75
336. What is the mass of 3.0 x 1023 atoms of
neon?
Chemistry
b. 7 g
d. 5 g
338. In the reaction Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) + Cu(s), the
reducing agent is _____.
a. Zn(s)
b. Cu(s)
c. Cu2+(aq)
d. Cu2+
339. Which compound contains both covalent
bonds and ionic bonds?
a. HCl(g)
b. N2O5(g)
c. NaCl(s)
d. NaNO3(s)
340. When the pressure exerted on a confined
gas at constant temperature is doubled, the
volume of the gas is _____.
a. constant
b. halved
c. tripled
d. quartered
341. The number of electrons in a neutral atom
of every element is always equal to the atoms
_______.
a. number of nucleons
b. number of neutrons
c. number of positrons
d. number of protons
342. Which is a product of the hydrolysis of an
animal by a strong base?
a. gasoline
b. water
c. kerosene
d. soap
343. The atom of carbon-14 contains _______.
a. 6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 8 electrons
b. 6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 6 electrons
c. 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 8 electrons
d. 8 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons
344. Which formula represents a binary
compound?
a. O2
b. Ne
c. 2C2H5OH
d. C3H8
345. Which temperature represents absolute
zero?
a. 0C
b. 273K
c. 0 K
d. 273C
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
346. When a salt dissolves in water, the water
molecules are attracted by dissolved salt
particles. This attraction is called _______.
a. atom-atom
b. molecule-ion
c. molecule-molecule
d. atom-molecule
347. An example of a heterogamous mixture is
_____.
a. stainless steel
b. soil
c. sugar
d. carbon monoxide
348. Water will boil at temperature of 40C when
the pressure on its surface is ______.
a. 25.5 torr
b. 40 torr
c. 55.3 torr
d. 760 torr
39
14. b.
a sword
15. b.
Gay-Lussacs Law
16. c.
high temperature and low pressure
17. c.
Boyles Law
18. d.
He
19. d.
an energy transfer due to a
temperature difference
20. c.
no change in temperature
21. c.
the enthalpy of the reactants is lower
that the enthalpy of the products
22. a.
melting of ice
23. c.
when the gas expands adiabatically
24. c.
De Broglie
25. d.
Schrdinger
26. a.
gaining electrons to form ionic
compounds
27. b.
the vapor pressure of the solvent to
decrease
1.
c.
Answers &
Solutions
-31 F
2.
a.
2.27
3.
a.
5 million
4.
c.
ash
5.
b.
the two samples are certainly
different pure substances
6.
a.
water
7.
d.
rusting of iron
8.
d.
its composition can vary
9.
c.
a compound
10. a.
crystallization of sugar from sugar can
juice
11. d.
silver
12. d.
separation of the molecules in a
mixture
13. c.
nuclear fusion
Chemistry
28. a.
the number of products formed
29. d.
the may become new substances
after the reaction
30. c.
it exists between a liquid and its vapor
in a closed system at uniform
temperature.
31. a.
a proton donor
32. a.
they always contain OH- ions
33. b.
carbon
34. Solution
Solve for R of CO at the given (22.4 L)
volume and STP;
PV nRT
PV (1 atm)(22.4 L)
nT
(1 mol)(492)R
L atm
R 0.04553
mol R
R
The mass of CO at STP and 1 liter
volume:
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
PV nRT
mRT
PV
MW
PV(MW )
m
RT
(1atm)(1L)(28 g / mol)
L atm
0.04553 mol R (492)R
m 1.25 g
35. Solution
2(Hydrogen)
2(Hydrogen) 1(Oxygen)
2(1.008)
%H
0.1119
2(1.008) 1(16)
%H 11.19%
%H
36. Solution
A
206
P Pb 82 Pb
The number of protons (P) =82
The number of neutrons (N) =20682 =124
P = 82 and N = 124
37. Solution
Daltons Law of Partial Pressures
Ptotal Partial Pr essures
Ptotal Poc tan e Pair
86.1
moc tan e RToc tan e mair RTair
(MW)oc tan e V
(MW )air V
86.1
0.064(8.314)(290) 0.91(8.314)(290)
114 V
29 V
V 0.894 m
Then :
mRTair
(0.91)(8.314)(290)
Pair
(MW )air V
(29)(0.894)
40
PV nRT
mRT
MW
PV(MW )
m
RT
(10 atm 101,325 Pa / atm)
(10li 10 3 m3 / li)(32g / mol)
m
J
8.314 mol K (300)K
m 130 g
PV
40. Solution
The mean free path () of CO:
kT
4 2r 2P
where :
J
8.314
R
mol
K
k
NA 6.023 10 23 molecule / mol
k 1.380 10 23 J / molecule.K
Nm
23
1.38 10 molecule.K (300 K)
4 2 (1/ 2)(3.19 108 ) 2 m2
101,325
N
/
m
100 mmHg
760 mmHg
6.86 10 11m
6.86 10 9 cm
P 84.62 kPa
38. Solution
Moles of Solute
Liters of solution
5 grams
34 gm / mole
Molarity (M)
100 10 3 liters
Molarity (M) 1.47 moles / liters
Molarity (M) 1.5 M
Molarity (M)
39. Solution
The mass of Oxygen (O2):
Chemistry
41. Solution
Using Avogadros Number :
1 mole = 6.023 x 1023 particles
Where :
Particles can be molecules, atoms
or ions
1 mole = 6.023 x 1023 atoms
1
1 atom
moles
6.02 1023
1 atom = 1.66 x 10-24 moles
42. Solution
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
PV nRT
25 g of HCl
mRT
PV
MW
mRT
MW
PV
li atm
(0.5 g) 0.0821
(27 237)K
mol.K
MW
(0.25 atm)(1 li)
MW 49.26 g / mol
43. Solution
1 mol of Mg
6.02 1023 atoms
24.3 g of Mg
mol of Mg
n 1.24 10 23 atoms
44. Solution
1 mol of Fe
25 g of Mg
0.448 mol of Fe
55.8 g of Fe
n 5 g of Mg
45. Solution
2 mol of O2
6.02 10 23 molecules of O 2
1 mol of O2
2 atoms O
1 molecules O2
2.408 1024 atoms of O
0.252 mol Cu
63.5 g Cu
1 mol of Cu
16 g of Cu
47. Solution
1 Ca atom 1 40.1 40.1 amu
2 O atoms 2 16 32 amu
2 H atoms 2 1 2 amu
formula weight 74.1 amu
Chemistry
1 mol of HCl
36.5 g of HCl
6.02 1023 molecules of HCl
1 mol of HCl
4.12 1023 molecules of HCl
49. Solution
Percentage of
total wt. of the element
100%
formula or molecular wt.
Elements
Where : for sodium chloride (NaCl)
1 Na = 23 g
1 Cl = 35.5 g
MW = 58.5 g
23 g
Na
100%
58.5 g
Na 39.3%
50. Solution
Percentage of
total wt. of the element
100%
formula or molecular wt.
Elements
Where : for potassium sulfate (K2SO4)
2 K = 2 x 39.1 = 78.2 g
1 S = 1 x 32.1 = 32.1 g
4 O = 4 x 16 = 34.0 g
MW = 174.3 g
64 g
100%
174.3 g
Na 36.7%
Na
46. Solution
48. Solution
41
51. Solution
The total weight of the product :
Zn = 1.63 g
O = 0.40
Wtotal = 2.03
The percentage of Zn in the 2.30 g weight:
1.63 g
100% 80.3%
2.03 g
Zn 80.3%
Zn
52. Solution
Balance the Equation :
3H2 + N2 2NH3
Based on the balanced equation, the mole
ratio can be computed as:
2 mol NH3
mole ratio
3 mol H2
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
42
Then; the 8 mol of H2:
The density of air at STP:
P
101.325 kN / m2
(Air)
RT (0.287 kJ/ kg.K)(273 K)
2 mol NH3
n 5 mol of NH3
3 mol of H2
n 5.33 mol of NH3
(Air) 1.29 kg / m3 1.29 g / L
53. Solution
The sequence of conversions needed in
the calculations can be written:
moles O2 moles H2O moles of H2O
Balance the Equations:
2H2 + O2 2H2O
Based on the balanced equation, the mole
ratio can be computed as:
2 mol H2O
mole ratio
1 mol O2
The number of moles of the 0.010 mol of
O2 can be computed using the mole-ratio:
6.02 1023 molecules
mol of O2
Nm 0.020 mol of O2
Nm 1.2 1022 molecules of H2O
54. Solution
STP the molar volume to be used is 22.4
Liter/mol
3.23 g 22.4 L
36.2 g / mol
2L
mol
55. Solution
mRT
MW
mRT
MW
PV
PV
MW 73.98 g / mol
56. Solution
The density of Cl2 at STP:
71 g 1 mol
(Cl2 )
3.17 g / L
mol 22.4 li
Chemistry
The number of mol of O2 from the 0.75 mol
of KClO3:
3 mol O2
n (0.75 mol KClO3 )
2 mol KClO3
n 1.125 mol O2
V 25.2 L O2
N
/
m
J
(691 10 3 M3 )
Pa N m
57. Solution
Balance the Equation :
2KclO3 2KCl + 3O2
Based on the balanced equation, the moleratio method:
3 mol O2
Mole ratio
2 mol KClO3
The moles of O2 can be converted to liters
of O2 (at STP);
22.4 L
V (1.125 mol O2 )
mol
MW
(1.65g) 8314
mol.K
(40 273)K
101325 Pa
(630 torr)
760 torr
The specific gravity of a gas can be
calculated by dividing its density by the
density of air and both gases must be of
the same temperature and pressure.
density of CL 2
sp gr(Cl2 )
density of air
3.17 g / L
sp gr(Cl2 )
2.46
1.29 g / L
sp gr(Cl2 ) 2.46
58. Solution
PV nRT
nRT
P
V
L atm
(0.5 mol) 0.0821
(23 273)K
mol K
P
7L
P 1.74 atm
59. Solution
PV nRT
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
n
43
PV
RT
1 atm
(70 L)
14.7 psi
n
L atm
(25 273)K 0.0821
mol K
n 389.3 mol O2
PV nRT
Vtotal
2000psi
60. Solution
The molecular weight of sucrose
(C12H22O11):
MW = 12(12) + (1)(22) + 12(11)
= 342 g/mole
The molarity (m) of the solution with
sucrose as solute :
mass of solute
molarity(m)
kg solvent
65 g
342 g / mol
m
0.63
0.300
m 0.63 mole / kg
61. Solution
PV nRT
PV
n
RT
(0.6 atm)(0.45)L
P
(0.0821 L atm / mol K)(87 273)K
P 0.0091 mole
62. Solution
The total number of moles of the combined
gases:
ntotal nhydrogen nhelium
1 mole H
2
ntotal (1 g H2 )
2 g H2
1 mole H
2
(10 g H2 )
4 g H2
ntotal 3 mole
The total volume can be solved using ideal
gas equation:
Vtotal
Vtotal
(3.0 mol)(20 273)K
0.0821 L atm
mol K
5 atm
14.4 liters
63. Solution
The molecular weight of KCl:
MW = 39.1 + 35.5 = 74.6 g/mol
moles of solute
molarity(M)
L of solution
150 g
74.6 g / mol
M
2.51
0.8 L
M 2.51 mole / L
64. Solution
moles of solute
L of solution
x
0.6 mole 74.6 g / mol
L
0.4 L
molarity(M)
0.6 mole 74.6 g
L
mole
x 17.904 g
x (0.4 L)
65. Solution
The stoichiometry equation is :
Ca + O CaO
The equation shows that one mole of
oxygen and one mole of calcium are
required to make one mole of CaO.
3.13 2.25
nO
0.055 mole
16
nCa 0.055 mole
The atomic weight of Ca:
m
2.25
WCa Ca
nCa 0.055
WCa 40.9 g / mole
66. Solution
Chemistry
ntotal RT
Ptotal
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
The molecular weight of Sulfuric Acid
(H2SO4):
MW = 1(2) + (32)1 + (16)(4) = 98 g/mole
The equivalent Weight of Acid:
molecular weight
Eqivalent Weight
No. of Replacable H
98 g / mole
Equivalent Weight
2
Equivalent Weight 49 g / mol
67. Solution
The molecular weight of (H2SO4):
MW = 1(2) + (32)1 + (16)(4) = 98 g/mole
The Equivalent Weight:
molecular weight
Equivalent Weight
NO. of Replacable H
98 g / mole
Equivalent Weight
49 g / mol
2
The No. of equivalent solute:
gram equiv wt
No. of equiv solute
Equiv Wt
60 g
No. of equiv solute
1.22 equiv.
49 eq wt
The Normality (N) of a solution:
No. of equiv solute
Normality(N)
L of solution
1.22 equiv
N
1.5 L
N 0.813 equiv / L
68. Solution
The molecular weight of Mg (OH)2 :
MW = (24)1 + (16)2 + (1)2 = 58 g/mole
The Equivalent Weight of Base:
molecular wt
Equiv Wt
No. of Replacable OH
58 g / mole
Equiv Wt
2
Equiv Wt 29 g / mol
69. Solution
The molecular weight of (H3PO4):
MW = 1(3) + 31(1) + 16(4) = 98 g/mole
Chemistry
44
The Equivalent Weight:
molecular wt
Equiv Wt
No. of replacable H
Equiv Wt
98 g / mole
32.7 g / mol
2
The Normality (N) of a solution:
no. of equiv solute
Normality(N)
L of solution
x
32.7
0.5
0.700
x 11.45 g
70. Solution
Na2CO3 + HCl NaCl + H2O + CO2
(unbalanced)
By inspection; the balanced equation will
be:
Na2CO3 + 2HCl 2NaCl + H2O + CO2
Na=1(2)=2
C=1
O=1(3)=3
Cl=2(1)=2
Na=1(1)=2
C=1
O=1+1(2)=3
Cl=2(1)=2
71. Solution
The molecular weight of water (H2O):
Where: Hydrogen = 1 and Oxygen = 16
MW = (1)(2)+16(1)
MW = 18 amu (atomic mass unit)
72. Solution
The molecular weight of BaCl22H2O:
1 Ba = 1 x 137.3 = 137.3 amu
2 Cl = 2 x 35.5 = 71.0
2H2O = 2 x 18.00 = 36.0 amu
MW = 244.3 amu
73. Solution
P + HNO3 + H2O NO + H2PO4
(unbalanced)
By inspection; the balanced equation will
be:
3P + 5HNO3 + 2H2O 5NO + 3H2PO4
P=3(1)=3
H=5+(2)(2)=9
O=5(3)+2(1)=17
P=3(1)=3
H=(3)(3)=9
O=5(1)+3(4)=17
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
N=5(1)=5
N=5(1)=5
45
103.
a.
a compound
104.
b.
alkalinity
b.
galvanic cell
74.
b.
covalent bond
105.
75.
c.
Organic matter is generally stable
106.
b.
at very high temperatures
107.
d.
the molecules collide more
76.
c.
electrolyte
77.
a.
salt
78.
b.
frequently and the activation energy
is less
the substance is heated together
108.
b.
neutron
with copper oxide and the resulting
109.
a.
precipitation
gases are found to have no effect
110.
c.
hydrogen
on limestone
111.
d.
between 0 and 7
a.
specific gravity
79.
c.
protons and neutrons
112.
80.
d.
Sodium (Na)
113.
d.
catalyst
b.
actinons
81.
a.
electron
114.
82.
a.
directly combination or synthesis
115.
a.
Molarity (m)
d.
coulomb
83.
d.
van der waals
116.
84.
a.
exothermic
117.
d.
atomic number
insulator
118.
d.
transition metals
b.
hydrometer
85.
b.
86.
d.
Lithium
119.
87.
c.
changing water to ice
120.
a.
Groups
a.
Anion
88.
d.
group VIIA
121.
89.
b.
Chlorine
122.
b.
one electron
b.
Metalloids
90.
b.
normality
123.
91.
d.
cohesion
124.
d.
Ion
a.
Secondary cell
92.
b.
element
125.
93.
a.
0C and zone atmosphere
126.
c.
Group VIIA
pressure
127.
c.
The differential rate is the
94.
c.
Covalent
mathematical expression that
95.
b.
solid to gaseous phase
shows how the rate of reaction
96.
b.
Alkenes
depends on volume.
97.
c.
a conductor
128.
d.
atom
a.
acid
98.
c.
metalloids
129.
99.
a.
there are no oxidizing and reducing
130.
d.
Double displacement
agents in this reaction
131.
c.
Endothermic
Lanthanons
132.
c.
the strength of the acid
c.
Valence electrons
d.
cation
100.
a.
101.
a.
Ionic bonding
133.
102.
a.
electrolysis
134.
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
135.
d.
Atomic number
136.
a.
Light metals
137.
c.
138.
139.
46
171.
d.
Molarity
172.
a.
products
a.
ionic
173.
b.
molecule
a.
an ion
174.
c.
Covalent Bonding
140.
b.
decomposition or analysis
175.
c.
Group VIA
141.
c.
alkynes
176.
d.
enthalpy of vaporization
142.
a.
insulator
177.
a.
cleavage
143.
d.
Mole
178.
b.
Pi Bond
144.
a.
sulfuric acid
179.
a.
Phenolphthalein
145.
d.
red
180.
a.
Isomer
146.
c.
between 7 and 14
181.
c.
Compound
147.
d.
reverse osmosis
182.
d.
Molecular Orbital Theory
148.
b.
a nucleus containing a neutron and
183.
d.
Pyrite
a proton
184.
c.
Diamond
149.
b.
Group IA
185.
d.
hydrolysis
150.
b.
metallic bonding
186.
c.
cycloalkanes
151.
d.
Cobalt
187.
d.
Ionization
152.
c.
DNA
188.
d.
Delta Bond
153.
b.
Reactants
189.
c.
Chelate Effect
154.
a.
Isotonic solutions
190.
b.
Heterogeneous Mixture
155.
a.
alkanes
191.
c.
Free Radical
156.
b.
atom
192.
a.
Halite
157.
a.
cavitation
193.
c.
Oxidation
158.
c.
noble gas
194.
d.
Siderophile
159.
c.
thermocouple
195.
a.
Catalyst
160.
a.
blue
196.
c.
mole
161.
c.
osmosis
197.
d.
Concentrated Reaction
162.
a.
N2O5
198.
c.
Endothermic
163.
b.
it loses electrons
199.
a.
enthalpy of formation
164.
c.
single displacement
200.
a.
Chemical Property
165.
c.
14
201.
a.
Twin
166.
c.
an insulator
202.
a.
Volatile
167.
a.
condensation
203
c.
Activation Energy
168.
c.
Avogadros Law
204.
d.
Heat of Combustion
169.
c.
volume
205.
c.
Bismuth
170.
a.
atomic weight
206.
a.
Reduction
Chemistry
the mass of an electron is heavier
than that of a proton
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
47
207.
c.
enthalpy of reaction
244.
b.
Mohs hardness scale
208.
c.
Electronegativity
245.
a.
Lava
209.
b.
Hydrophilic
246.
d.
Basaltic
210.
d.
Calcite
247.
c.
Granitic
211.
d.
Solute
248.
b.
Ionic Bonding
212.
a.
Hydration
249.
c.
Epitaxis
213.
d.
Photodissociation
250.
d.
Steno Law
214.
c.
Galena
251.
a.
Iron
215.
a.
inert
252.
b.
Free Radical Reaction
216.
d.
Van der Waals forces
253.
d.
Ozone
217.
c.
Polar Reaction
254.
d.
Lanthanide
218.
d.
Colloid
255.
c.
Hydrophobic
219.
d.
Enzyme
256.
d.
substance
220.
c.
Sigma Bond
257.
d.
Alkali metals
221.
a.
Fractional Distillation
258.
a.
Peptide Bond
222.
a.
Dialysis
259.
d.
Group IIA
223.
c.
Hunds Rule
260.
d.
blue
224.
b.
period
261.
b.
Colligate Property
225.
a.
Detergent
262.
b.
enthalpy of fusion
226.
c.
Photosensitization
263.
b.
Exsolution
227.
b.
Organic Chemistry
264.
a.
Dissociation
228.
c.
Periodic Table
265.
a.
Cation
229.
a.
Atom
266.
d.
Galvanic Cell
230.
b.
Nobel Gases
267.
c.
Hydroxide
231.
b.
Promethuim
268.
b.
Fugacity
232.
a.
graphite
269.
b.
Crystal Fields Theory
233.
d.
atomic radius
270.
a.
Amethyst
234.
a.
Tyndall Effect
271.
c.
Alane
235.
a.
Halide
272.
b.
Protein
236.
b.
Exothermic
273.
d.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
237.
a.
Bond Energy
274.
d. no crystalline structure
238.
b.
Anion
275.
d. colloidal dispersion
239.
c.
pH
276.
b. milk
240.
c.
Suspension
277.
d. uranium
241.
a.
Flux
278.
b. ion
242.
a.
Homogeneous Mixture
279.
a. number
243.
d.
Isodemic Crystal
280.
c. 98
Chemistry
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
281.
48
a. increasing the surface area of the
315.
b. esters
reactants
316.
c. 6.5%
282.
d. typically reacts vigorously with metals
317.
a. cigarette smoking
283.
b. a substance loses one or more
318.
b. petroleum
319.
a. cohesive force is stronger than
320.
d. the liquid in one bottle is 5 mL more
electrons
284.
b. removes electrons during oxidation
285.
c. both 1 and 2 are correct
adhesive force
286.
d. all three
287.
d. nitrogen
321.
b. 8
288.
b. He
322.
b. an acid
289.
c. water
323.
a. propane, butane
290.
d. oxidation-reduction
324.
a. calorie
291.
b. lower left
325.
d. C5H10
292.
c. 40 g
326.
b. an alcohol and carbon dioxide
293.
a. C6H6
327.
b. heat of fusion
294.
d. AgF
328.
a. solution
295.
b. 50.0 mL
329.
d. compound
296.
d. 12
330.
b. van der Waals
297.
c. 33.6
331.
a. upper right
298.
b. 17
332.
b. sublimation
299.
d. chlorine reacts explosively to form
333.
d. 54
300.
c. table salt
334.
H
c. H:C:H
H
301.
b. 118
302.
b. O3
335.
c. 1.25
336.
a. 10 g
337.
b. electrical
338.
a. Zn(s)
339.
d. NaNO3(s)
340.
c. tripled
341.
d. number of protons
342.
d. soap
343.
b. 6 protons, 8 neutrons, and 6
344.
d. C3H8
345.
c. 0 K
346.
b. molecule-ion
than that in the other
sodium chloride
303.
a. CH2O
304.
a. potassium sulfate
305.
b. 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
306.
d. 342.0 amu
307.
a. 180.0 amu
308.
b. 1.32 M
309.
c. 1.2 cal
310.
a. Al2O3
311.
c. 22.41 L
312.
b. Cl2
313.
a. pressure increases
314.
a. slow solar evaporation
Chemistry
electrons
EDGE ECE REVIEW SPECIALIST
347.
b. soil
348.
c. 55.3 torr
Chemistry
49
You might also like
- Module 2. Properties and Characteristics of MaterialsDocument28 pagesModule 2. Properties and Characteristics of MaterialsPearl Alexandra FabitoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Electrochemical Energy-1aDocument3 pages1 - Electrochemical Energy-1aMae TadaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials Course OutlineDocument252 pagesMechanics of Materials Course Outlinekhan janNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law Simulation: PV NRTDocument3 pagesIdeal Gas Law Simulation: PV NRTElla GreenNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL ENGINEER’S MANUAL DEFINEDDocument196 pagesMECHANICAL ENGINEER’S MANUAL DEFINEDYURI G. MELLIZANo ratings yet
- MEF 312 - EXAMPLE PROBLEMS SOLUTIONSDocument6 pagesMEF 312 - EXAMPLE PROBLEMS SOLUTIONSAJNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDocument33 pagesHeat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezMark Jake RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ME301 Paper ADocument2 pagesME301 Paper AMitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. MeasurementDocument20 pagesChapter 1. MeasurementCecille Smyers HilariaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids: 1.1. Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsDocument16 pagesProperties of Fluids: 1.1. Fluid Mechanics and HydraulicsJoshua FactorNo ratings yet
- Stresses and Failure Analysis in Mechanical ComponentsDocument38 pagesStresses and Failure Analysis in Mechanical ComponentsNathaniel BaguioNo ratings yet
- Functions and algebraic expressions worksheetDocument16 pagesFunctions and algebraic expressions worksheetZER OKIMNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer (Second Year Plant Ii)Document2 pagesHeat Transfer (Second Year Plant Ii)AdamsNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment Ec41fa2Document22 pagesThermodynamics Assignment Ec41fa2Adrian Dalida Agawin67% (6)
- Redulla Heat Transfer Assignment 4Document8 pagesRedulla Heat Transfer Assignment 4Alan RoyNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transform Part 1Document27 pagesLaplace Transform Part 1clark esteven m. salvador100% (1)
- Unit 1 - IntroductionDocument43 pagesUnit 1 - IntroductionIamzura Abdullah100% (1)
- HW-4-sphere WithoutDocument1 pageHW-4-sphere WithoutSafaa Hameed Al Nasery100% (1)
- BSABE2 - Blasquez - Lab Report 2Document7 pagesBSABE2 - Blasquez - Lab Report 2Lorenzo Niño BlasquezNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer SPDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer SPShamolog100% (1)
- Processes of Ideal GasesDocument28 pagesProcesses of Ideal GasesVincent LagunillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Geothermal Power Plant ReviewerDocument7 pagesChapter 6 - Geothermal Power Plant ReviewerKyle YsitNo ratings yet
- Cc2 ThermodynamicsDocument22 pagesCc2 Thermodynamicsmark anthony tutorNo ratings yet
- Pure Substance 2015Document19 pagesPure Substance 2015Ranel Simon Rey100% (1)
- Exercises: The Probability of ImperfectionsDocument3 pagesExercises: The Probability of ImperfectionsNona FarahdibaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lecture 3 Energy EquationDocument1 pageThermodynamics Lecture 3 Energy EquationGot7100% (1)
- 1 Properties of SteamDocument4 pages1 Properties of Steammark laurence banal33% (3)
- Chapter 5 Eneergy Con 2Document4 pagesChapter 5 Eneergy Con 2LuelsonCordovaDeclaradorNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechDocument10 pagesFluid MechPetForest Ni JohannNo ratings yet
- HMT Unit 1Document9 pagesHMT Unit 1rp0212No ratings yet
- Basic Thermodynamics FundamentalsDocument277 pagesBasic Thermodynamics FundamentalsVinot NathanNo ratings yet
- Bee ProblemDocument17 pagesBee ProblemPabloNo ratings yet
- Merged Refresher MESL Questions OCRDocument22 pagesMerged Refresher MESL Questions OCRBernalynMalinaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3Jerome CansadoNo ratings yet
- FMECH Finals Plate 2018Document1 pageFMECH Finals Plate 2018Jessa San Pedro100% (1)
- HT Solved NumericalsDocument56 pagesHT Solved NumericalsKiran AkkoliNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements Course GuideDocument54 pagesMachine Elements Course GuideLorenzo EstoestaNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument37 pagesModuleAlvin RazoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics FundamentalsDocument20 pagesThermodynamics FundamentalsVaratha Rajan0% (1)
- HjjooDocument28 pagesHjjooJohn Patrick DagleNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry I: Units, Dimensions, Mass, Weight & AccelerationDocument104 pagesPhysical Chemistry I: Units, Dimensions, Mass, Weight & AccelerationDanice LunaNo ratings yet
- HEAT TRANSFER: CONDUCTION, CONVECTION & RADIATIONDocument33 pagesHEAT TRANSFER: CONDUCTION, CONVECTION & RADIATIONAlex Philip0% (1)
- Questions in Strength of MaterialsDocument16 pagesQuestions in Strength of MaterialsRyanNo ratings yet
- Materials and Heat Treatment Course ChapterDocument30 pagesMaterials and Heat Treatment Course ChapterNguyễn Việt TiếnNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Chapter 1 ProblemsDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Chapter 1 ProblemsVon A. Damirez0% (1)
- Heat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezDocument46 pagesHeat Transfer: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezMark Jake Rodriguez0% (1)
- Mechanical Engineering Review 2 Fundamentals ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesMechanical Engineering Review 2 Fundamentals ThermodynamicsIvy Joy UbinaNo ratings yet
- CO Assign#2 BSEE-2ADocument3 pagesCO Assign#2 BSEE-2AEisen JaylordNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document18 pagesChapter 10farah haniNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument5 pagesSampleMark Anthony RazonNo ratings yet
- Enercon-Experiment 1Document10 pagesEnercon-Experiment 1Aldrin QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- HGFHFGHFGDocument24 pagesHGFHFGHFGAljhon BautistaNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument24 pagesHeat ExchangersJade Carlo AntonioNo ratings yet
- AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM Prelim ExamDocument1 pageAIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION SYSTEM Prelim ExamJames Patrick TorresNo ratings yet
- Problist On PPE PDFDocument6 pagesProblist On PPE PDFShumi Nahar67% (3)
- Machine Elements Quiz 1Document17 pagesMachine Elements Quiz 1Quen CuestaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Contuity (Tutorial Part 3)Document13 pagesFluid Flow Contuity (Tutorial Part 3)asapamoreNo ratings yet
- ThermoproblemDocument20 pagesThermoproblemmark anthony tutorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry With Physics Reviewer PDFDocument69 pagesChemistry With Physics Reviewer PDFRJ JRNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer 9th ClassDocument8 pagesQuestion and Answer 9th Class. PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONICS Formulas and ConceptsDocument22 pagesELECTRONICS Formulas and ConceptsHarold Antonio100% (1)
- COMMS 2 - Antenna & Radio Wave AnswersDocument4 pagesCOMMS 2 - Antenna & Radio Wave AnswersVinnie Segovia100% (6)
- Exercise - Basic ConfigurationDocument2 pagesExercise - Basic ConfigurationJohnMarcusNo ratings yet
- COMMS 2 - Antenna & Radio Wave AnswersDocument4 pagesCOMMS 2 - Antenna & Radio Wave AnswersVinnie Segovia100% (6)
- Reviewer Geas ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesReviewer Geas ThermodynamicsJohnMarcusNo ratings yet
- Question Bank in AC Circuits PDFDocument75 pagesQuestion Bank in AC Circuits PDFankit1ksha75% (4)
- Chapter 15Document24 pagesChapter 15Beverly PamanNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document5 pagesHomework 3Rayray MondNo ratings yet
- 1968 - Theory and Problems of Transmission Lines (By PH.D Robert A. Chipman) PDFDocument244 pages1968 - Theory and Problems of Transmission Lines (By PH.D Robert A. Chipman) PDFJohnMarcusNo ratings yet
- Grazing Infinity GraphDocument1 pageGrazing Infinity GraphJohnMarcusNo ratings yet
- Reviewer SitesDocument1 pageReviewer SitesJohnMarcusNo ratings yet
- Reviewer SitesDocument1 pageReviewer SitesJohnMarcusNo ratings yet
- Practiceproblems ChemDocument4 pagesPracticeproblems ChemJohnMarcusNo ratings yet
- Ftir Coffee Okok PDFDocument10 pagesFtir Coffee Okok PDFcentro surcolombiano de investigación en café uscoNo ratings yet
- ChE441 Problem Set 3 PDFDocument6 pagesChE441 Problem Set 3 PDFmelihNo ratings yet
- The Potential of Jackfruit Sap As Alternative GlueDocument6 pagesThe Potential of Jackfruit Sap As Alternative GlueKshiki MikaNo ratings yet
- UV Absorbers / Stabilizers: Uses in The Supply ChainDocument2 pagesUV Absorbers / Stabilizers: Uses in The Supply ChainEMS 4AYDNo ratings yet
- En-10079 Definition of Steel ProductsDocument44 pagesEn-10079 Definition of Steel ProductshugocoimbraNo ratings yet
- CE6101 Behaviour of Cam ClayDocument14 pagesCE6101 Behaviour of Cam ClayGan Chin PhangNo ratings yet
- LSU Protandim StudyDocument8 pagesLSU Protandim StudyLifeVantage™ Protandim®No ratings yet
- World: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadDocument11 pagesWorld: Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadlavanyaNo ratings yet
- Valvula Antirretorno Norgren t60Document1 pageValvula Antirretorno Norgren t60Base SistemasNo ratings yet
- REGULATORYDocument5 pagesREGULATORYyudiar2008No ratings yet
- UST-IACUC Animal Care ReviewDocument8 pagesUST-IACUC Animal Care ReviewKate Montenegro0% (1)
- Chapter10 Entropy 2nd Law STUDDocument27 pagesChapter10 Entropy 2nd Law STUDCristian Menéndez FernándezNo ratings yet
- The Citric Acid CycleDocument27 pagesThe Citric Acid CyclerollyNo ratings yet
- OrificeDocument5 pagesOrificeayesha arshadNo ratings yet
- Autodock2 4 UserguideDocument48 pagesAutodock2 4 UserguidePowellAbogadoNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer MCQs PDFDocument78 pagesMass Transfer MCQs PDFzeeshan33% (3)
- Aits 2223 CRT Ii Jeem OfflineDocument15 pagesAits 2223 CRT Ii Jeem OfflineBHOOMI B100% (1)
- Sigma Marine CoatingsDocument417 pagesSigma Marine CoatingsAhmed Saad80% (5)
- Conplast WLDocument2 pagesConplast WLady999No ratings yet
- Chlorination of HCsDocument186 pagesChlorination of HCsaseptman150% (2)
- Multicam Plastics BrochureDocument2 pagesMulticam Plastics BrochureMoe KimoNo ratings yet
- Chem 110 Highligts 40 43Document28 pagesChem 110 Highligts 40 43dsarathy1No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 KineticDocument11 pagesChapter 6 KineticPHƯƠNG ĐẶNG YẾNNo ratings yet
- BS 7371-1-2009 General RequirementsDocument24 pagesBS 7371-1-2009 General RequirementsmoorthyxNo ratings yet
- Oil-Dri Catalog v.17Document24 pagesOil-Dri Catalog v.17Jelly TepskincareNo ratings yet
- ASME IIA SA29 SA29M Steel Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-Wrought and Cold-FinishedDocument1 pageASME IIA SA29 SA29M Steel Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-Wrought and Cold-FinishedAmanda Ariesta ApriliaNo ratings yet
- CalibrationDocument13 pagesCalibrationAmanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- US Silica White 4070 2Document2 pagesUS Silica White 4070 2Erick Barroso MartinezNo ratings yet
- RAMAN Amplifier Fiber SplicingDocument5 pagesRAMAN Amplifier Fiber SplicingGheePhotobotz100% (1)
- Vda 278 Analysis Using TDDocument2 pagesVda 278 Analysis Using TDWIMX Sales MéxicoNo ratings yet