Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations at
Uploaded by
myiitchemistryOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations at
Uploaded by
myiitchemistryCopyright:
Available Formats
SINHA IIT CHEMISTRY 1
TEST GOC & POC
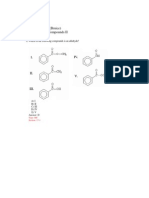
1 : Write the pKa below the phenol to which it corresponds. Briefly explain your reasoning. pKa choices: 7.15,
10.00, 10.46
2: a. Rank the following compounds in order of increasing acidity.
E IT A
Order: (least acidic) < < (most acidic)
b. Provide the structure of a dicarbonyl compound which is clearly more acidic than any of the compounds shown
H I H
Y
above.
N
TR
3 : a. Rank the following phenols in order of acidity.
SI
IS
M
b. Briefly explain your ranking.
4 : Consider the isomeric compounds biphenyl and acenaphthene:
C
a. Identify the more stable isomer: biphenyl acenaphthene
5. Identify the most stable alkene isomer.
A B C.
1-D-10 Talwandi & B-7 JAWAHAR NAGAR,KOTA. 93149-05055
SINHA IIT CHEMISTRY 2
6. Circle the worst nucleophile: HO- CH3CO2- CH3O-
7. Circle the worst leaving group: F- I- CH3-
+
8 Circle the least stable carbocation: CH3 H2COH+ H2CNH2+
9..Circle the compound with the lowest dielectric constant: H2O CH3OH CF3OH
10: Circle the molecule that is less stable and very briefly explain your answer.
11: Circle the most nucleophilic ion or molecule in each set.
b. NH3 H2O CH3OCH3
c. CH3CH2CH2O- CH3CF2CH2O- CF3CH2CH2O-
12-Compound W, C3H8O, reacts with hot concentrated phosphoric acid to give X, C3H6, which rapidly decolourises a
E IT A
solution of bromine in tetrachloromethane. On treatment with ethanoyl chloride, W gives Y, C5H10O2. Oxidation of W
with potassium dichromate in dilute sulphuric acid gives Z, C3H6O, which gives an orange precipitate with 2,4-
H I H
dinitrophenylhydrazine but does not react with an ammoniacal solution of silver nitrate.
Y
Deduce the structures of W, X, Y and Z, explaining carefully what each piece of evidence tells you.
N
TR
13-An oily liquid A is insoluble in water, but on heating with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution for half an hour it
SI
dissolves. From the reaction mixture a liquid B can be distilled, which gives a yellow precipitate with iodine and
sodium hydroxide solution. On careful oxidation B gives an aldehyde, C, which also gives a yellow precipitate with
IS
iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. If sulphuric acid is added to the solution obtained from heating A with sodium
hydroxide solution, a white precipitate D is obtained. D liberates carbon dioxide from sodium hydrogen carbonate
solution, one mole of D reacting with sodium hydrogen carbonate to give one mole of carbon dioxide. Heating D with
M
soda-lime* converts it to benzene.
Find the structures of A, B, C and D, giving your reasoning.
• Soda-lime is calcium oxide that has been slaked with sodium hydroxide solution. Carboxylic acids, on
heating with soda-lime, are decarboxylated, that is the -COOH group is replaced by -H.
•
14-Compound A, C4H8O2, gives an orange precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine reagent, and a silver mirror with
ammoniacal silver nitrate. A is converted to B, C4H6O, on treatment with acid. B may exist as a cis- or trans- isomer; it
C
reacts with hydrogen chloride to give C, C4H7OCl, and with chlorine to give D, C4H6OC12.
Reduction of C gives E, C4H9OCl, which is hydrolysed by dilute alkali to F, C4H10O2. Both A and F give a positive
iodoform (CHI3) test, whereas E does not.
Identify compounds A to F.
15-An alcohol has the molecular formula C4H7OH. Oxidation of this alcohol gives a ketone. Ozonolysis of this alcohol
gives methanal as one of the products.Giving your reasoning in full, deduce the structural formula for this alcohol and
predict whether it will be optically active.
Ozonolysis is a technique for finding the position of C=C double bonds in a molecule. The compound is reacted with
ozone-enriched oxygen in a suitable inert solvent, and the product is hydrolysed with ethanoic acid in the presence of
zinc. This produces a mixture of carbonyl compounds, which may be separated and identified, for example by means of
their 2,4DNP derivatives .
1-D-10 Talwandi & B-7 JAWAHAR NAGAR,KOTA. 93149-05055
SINHA IIT CHEMISTRY 3
16 Iodoethane CH3CH2I reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to give A, with ammonia to give B, and with
potassium cyanide in ethanolic solution to give C, C3H5N. C reacts with lithium aluminium hydride in dry ether
solution to give D. C with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution followed by dilute hydrochloric acid gives E, C3H6O2,
which with phosphorus(V) chloride gives F.
Identify compounds A to F, giving your reasons and equations where appropriate.
17.A, C3H7Cl, reacts with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution to give C, C3H8O. C reacts with phosphorus
pentachloride to give steamy fumes, and can be oxidised with acidified potassium dichromate solution to give D,
C3H6O, and then E, C3H6O2. D reacts with both 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine and ammoniacal silver nitrate. E reacts
with phosphorus pentachloride and with sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, in the latter case giving carbon dioxide.
A will react with benzene in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride to give B, C9H12. The structure of this
compound is not what might have been expected from A. B can be made from benzene and F as the expected product,
however, F being an isomer of A. Sodium hydroxide solution converts F to G, an isomer of C. G can be oxidised with
acidified potassium dichromate solution to H, an isomer of D, but no further. H gives a positive result with the 2,4-
DNP test but not the ammoniacal silver nitrate test; it also gives a positive result in the iodoform reaction.
On heating with alkaline potassium manganate(VII) solution B gives an aqueous solution of I, which on treatment with
E IT A
dilute sulphuric acid gives a white precipitate J.
(a) Identify all of the substances A – J, and explain each of the observations as fully as you can with supporting
H I H
equations.
Y
(b) Suggest why A and F give the same product with benzene.
N
TR
18-A, C2H4, reacts with hydrogen bromide in the gas phase to give B, C2H5Br. This reacts with aqueous sodium
hydroxide solution to give C, C2H6O, which can be oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate solution to give
SI
successively D, C2H4O, and E, C2H4O2. D reacts with both 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine and ammoniacal silver nitrate.
With magnesium in dry ether B gives F, C2H5MgBr; this reagent will react with D to give G, C4H10O. Oxidation of this
IS
compound with acidified potassium dichromate solution gives H, C4H8O. This will also react with F, giving I, C6H14O.
I is not oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate solution.
If A is reacted with bromine in the presence of sodium chloride, two compounds are obtained; J, C2H4Br2, and K,
M
C2H4BrCl. No C2H4Cl2 is formed.
(a) Identify each of the compounds A – K, and explain all the observations as fully as you can.
(b) Why is no C2H4Cl2 formed in the reaction given in the last paragraph?
19-Compound A, C4H8O, reacts with a solution of iodine in sodium hydroxide to give B, C3H5O2Na, and CHI3. A
gives a precipitate with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine but no reaction with ammoniacal silver nitrate.
A can be reduced with lithium aluminium hydride in dry ether to give C, C4H10O, which is chiral. With sodium
chloride in 50% sulphuric acid C gives D, C4H9Cl. With magnesium in dry ether D gives G, C4H9MgCl; G will react
C
with solid carbon dioxide to give an intermediate which when treated with dilute hydrochloric acid gives H, C5H10O2.
If D is heated with potassium hydroxide dissolved in ethanol, three compounds are formed; E is the major product and
has two stereoisomers, and F is the minor product. Both varieties of E, and F, are C4H8.
C reacts with H in the presence of sulphuric acid catalyst to give I, C9H18O2.
1-D-10 Talwandi & B-7 JAWAHAR NAGAR,KOTA. 93149-05055
You might also like
- The Clandestine Chemist's NotebookDocument72 pagesThe Clandestine Chemist's Notebookqwerty789456123100% (6)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Improvised Munitions Black Books Volume 1,2,3Document283 pagesImprovised Munitions Black Books Volume 1,2,3spicychapter32100% (6)
- NMR HandoutDocument23 pagesNMR HandoutVirendra Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- Basic Inorganic Nomenclature FOR IIT-JEE ENTRANCE TEST by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument5 pagesBasic Inorganic Nomenclature FOR IIT-JEE ENTRANCE TEST by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry88% (17)
- Carbocation RearrangementDocument4 pagesCarbocation RearrangementManas J. AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Carbopol MixingDocument3 pagesCarbopol MixingTom JerryNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument29 pagesAldehydes and KetonesJiya singhNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The SDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The Ssweta KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundsDocument34 pagesOrganic Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundsLovely Joysweet100% (2)
- Part - I: Objective Questions: Section A: Geometrical IsomerismDocument10 pagesPart - I: Objective Questions: Section A: Geometrical IsomerismTejas pawarNo ratings yet
- End of Unit Test Higher (H) : © Pearson Education LTD 2019. Copying Permitted ForDocument5 pagesEnd of Unit Test Higher (H) : © Pearson Education LTD 2019. Copying Permitted ForMina Iskander100% (1)
- Chem 206: Introduction to Frontier Molecular Orbital TheoryDocument22 pagesChem 206: Introduction to Frontier Molecular Orbital TheoryeraborNo ratings yet
- How To Find No of Structural Isomers by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations at HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocument2 pagesHow To Find No of Structural Isomers by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations at HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry81% (16)
- IONIC EQUILLIBRIUM FOR IIT-JEE ENTRANCE TEST by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations at Http://openchemistry - inDocument31 pagesIONIC EQUILLIBRIUM FOR IIT-JEE ENTRANCE TEST by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations at Http://openchemistry - inmyiitchemistry100% (7)
- Stoichiometric Relationships in ChemistryDocument42 pagesStoichiometric Relationships in Chemistryma hiuming100% (1)
- Determination of FiberDocument5 pagesDetermination of FiberLaksilu Viduraga Peiris100% (14)
- Geometrical Isomerism (Animated)Document114 pagesGeometrical Isomerism (Animated)myiitchemistry60% (5)
- Resonance and Inductive Effects in Organic ChemistryDocument36 pagesResonance and Inductive Effects in Organic Chemistryeagl33yeNo ratings yet
- NMR 1Document3 pagesNMR 1amitNo ratings yet
- How To Identify Geometrical Isomers by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument4 pagesHow To Identify Geometrical Isomers by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (4)
- Organic Nomenclature HTTPDocument19 pagesOrganic Nomenclature HTTPmyiitchemistry91% (11)
- Production of Pulp 6 PDFDocument17 pagesProduction of Pulp 6 PDFMahalakshmi H MNo ratings yet
- A Mix Design Procedure For Geopolymer Concrete With Fly Ash (21.02.2023)Document10 pagesA Mix Design Procedure For Geopolymer Concrete With Fly Ash (21.02.2023)Velchuri SairamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - HybridizationDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding - HybridizationVarsha YadavNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Structure and BondingDocument13 pagesOrganic Chemistry Structure and BondingHossNo ratings yet
- Some Important Organic Information by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument2 pagesSome Important Organic Information by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry83% (6)
- Neutralization: Prepared by Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Operator Training and Certification UnitDocument44 pagesNeutralization: Prepared by Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Operator Training and Certification UnitKhang TrầnNo ratings yet
- Exercise With Ans FinalDocument24 pagesExercise With Ans Finald anjilappa25% (4)
- Model Questions On U-12, 13 & 14Document12 pagesModel Questions On U-12, 13 & 14kadedoxNo ratings yet
- Class XII Organic Chemistry questionsDocument4 pagesClass XII Organic Chemistry questionsSelcouth elysianNo ratings yet
- NEET - Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Practice PaperDocument3 pagesNEET - Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes Practice PaperGanga DharaNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument16 pagesIsomerismAnusmita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeyDocument3 pagesAlkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs KeySameer HussainNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Practice SheetDocument4 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Practice Sheetsameeryad72No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument20 pagesOrganic ChemistryGirish RaguvirNo ratings yet
- Questions Chapter 1-10 PDFDocument107 pagesQuestions Chapter 1-10 PDFrashidNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Cmpds AnskeyDocument6 pagesAromatic Cmpds AnskeyAaron LeeNo ratings yet
- COORDINATION CHEMISTRY TITLEDocument11 pagesCOORDINATION CHEMISTRY TITLESubhasish Sau100% (2)
- NMR SpectrosDocument29 pagesNMR Spectroshareesh13h100% (1)
- Carbonyl Compounds 12thDocument24 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 12thRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table IPEDocument15 pagesPeriodic Table IPEAdiChemAdi100% (4)
- CSIR UGC NET Model Question Papers Chemical SciencesDocument32 pagesCSIR UGC NET Model Question Papers Chemical SciencesShiksha PortalNo ratings yet
- Dipole Moments in Organic CHEMISTRYDocument18 pagesDipole Moments in Organic CHEMISTRYBalraj Dhillon100% (2)
- Set of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocument6 pagesSet of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry50% (4)
- Solid State-1Document31 pagesSolid State-1ChirAgNo ratings yet
- Conformations and Stereochemistry QuizDocument8 pagesConformations and Stereochemistry QuizrameshiitNo ratings yet
- 10.true False (D and F Block Elements)Document11 pages10.true False (D and F Block Elements)rajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1Document195 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1aditya kumar Agarwal100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - MCQSDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes - MCQSDivyam GargNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Nucleophilic Substitution: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanDocument16 pagesChapter 8 Nucleophilic Substitution: Answers Prof. Sivaguru JayaramanRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure ChemistryDocument143 pagesAtomic Structure ChemistryYoshitha Kuntumalla100% (1)
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen NEET MCQsDocument2 pagesOrganic Compounds Containing Nitrogen NEET MCQs2003vinay0% (1)
- Unit 16 Electrochemistry Revision AnswersDocument16 pagesUnit 16 Electrochemistry Revision Answersckwmciwem100% (1)
- Problems On Named ReactionsDocument103 pagesProblems On Named ReactionsBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- Alkene DPPDocument20 pagesAlkene DPPKalyan ReddtNo ratings yet
- Benzene Derivatives: Key Concepts and ReactionsDocument14 pagesBenzene Derivatives: Key Concepts and ReactionsRaj ModiNo ratings yet
- Organic chemistry principles & techniquesDocument3 pagesOrganic chemistry principles & techniquesHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questio10Document21 pagesMultiple Choice Questio10Achiket Anand DesaiNo ratings yet
- 10+2 Chem P-Block ElementsDocument44 pages10+2 Chem P-Block ElementsArjun PasrichaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Organic Chemistry by Eyes of Ajnish Kumar Gupta (AKG)Document24 pagesIntroduction of Organic Chemistry by Eyes of Ajnish Kumar Gupta (AKG)ajju_208180% (5)
- Model Answer: The Following Questions Answer Choose The Correct Answer: (20Document4 pagesModel Answer: The Following Questions Answer Choose The Correct Answer: (20Khalid AbeedNo ratings yet
- TEST 2 GOC & POC Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 pagesTEST 2 GOC & POC Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistryNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Anti Aromatic Non AromaticDocument2 pagesAromatic Anti Aromatic Non AromaticRitesh SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chemistry 12Document5 pagesWorksheet Chemistry 12mohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry II (100 Items)Document11 pagesInorganic Chemistry II (100 Items)maria jeusa matiasNo ratings yet
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 pagesPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- LS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024b00625d276-Statistical ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesLS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024b00625d276-Statistical ThermodynamicsHamit RanaNo ratings yet
- 01 Solid State EDocument1 page01 Solid State EKunalSinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Acid and BaseDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Acid and BaseKelsi Kyla PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry - MCQsDocument11 pagesSurface Chemistry - MCQsHumaira RazzaqNo ratings yet
- CAREER POINT PRE-MEDICAL ISOMERISM MCQDocument20 pagesCAREER POINT PRE-MEDICAL ISOMERISM MCQSanjay Mani TripathiNo ratings yet
- Module8 PDFDocument40 pagesModule8 PDFFaizan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions 40-CFrom EverandNuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions 40-CJoseph CernyNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions 40-BFrom EverandNuclear Spectroscopy and Reactions 40-BJoseph CernyNo ratings yet
- Solid State / Crystalline State ChemistryDocument26 pagesSolid State / Crystalline State ChemistrymyiitchemistryNo ratings yet
- Unique Approach of Problem Solving in Isomerism by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocument6 pagesUnique Approach of Problem Solving in Isomerism by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry100% (3)
- Set of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocument6 pagesSet of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry50% (4)
- Mole Concept Solution Practice Set 1 Objective by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument2 pagesMole Concept Solution Practice Set 1 Objective by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (4)
- JEE - Similar Test Paper Goc & Alkane by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument4 pagesJEE - Similar Test Paper Goc & Alkane by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (9)
- Mole Concept Empirical & Molecular Formula by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 pagesMole Concept Empirical & Molecular Formula by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (5)
- Mole Concept Solution Practice Set Objective by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument1 pageMole Concept Solution Practice Set Objective by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry50% (2)
- Mole & Stoichiometry by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 pagesMole & Stoichiometry by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry50% (2)
- UNSTABLE FUNCTIONAL GROUPS IN ORGANIC by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument1 pageUNSTABLE FUNCTIONAL GROUPS IN ORGANIC by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (2)
- Test Goc 3 by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument6 pagesTest Goc 3 by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistryNo ratings yet
- TEST 2 GOC & POC Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 pagesTEST 2 GOC & POC Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistryNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR IIT-JEE ENTRANCE TEST by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument2 pagesPRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY FOR IIT-JEE ENTRANCE TEST by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (10)
- TEST 2 GOC & POC Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 pagesTEST 2 GOC & POC Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistryNo ratings yet
- Making Salts Revision Task: AcidsDocument4 pagesMaking Salts Revision Task: AcidsJu MaiaNo ratings yet
- S Block Ncert SolutionsDocument32 pagesS Block Ncert SolutionsManish ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - Chapter 07 (SOLUTION AND SUSPENSION)Document2 pagesWorksheet 2 - Chapter 07 (SOLUTION AND SUSPENSION)Aisha AnwarNo ratings yet
- EFEMA Index of Food EmulsifiersDocument150 pagesEFEMA Index of Food EmulsifiersPhạm Trung HiếuNo ratings yet
- Chemical Calculations Involving SolutionsDocument13 pagesChemical Calculations Involving SolutionsPhi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric and Thermometric Determination of Boric AcidDocument5 pagesPotentiometric and Thermometric Determination of Boric AcidBenjamin Gelmo RoqueNo ratings yet
- CVBG Tip Of The Month: Robb Gunter's Super Quench FormulaDocument1 pageCVBG Tip Of The Month: Robb Gunter's Super Quench Formulaguytr2No ratings yet
- Astm C497Document12 pagesAstm C497FrengkiNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory Ion TestDocument50 pagesInorganic Chemistry Laboratory Ion TestTrescia Mae EstilloreNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document5 pagesExp 221413温邦宏No ratings yet
- 5 Solution Stoichiometry (S)Document11 pages5 Solution Stoichiometry (S)Mr TanNo ratings yet
- Testing Eksternal LabDocument12 pagesTesting Eksternal LabRaficaNo ratings yet
- Guide to Preparing and Identifying SaltsDocument63 pagesGuide to Preparing and Identifying Saltsabdullah khalilNo ratings yet
- ChemCollective Autograded Labs PDFDocument13 pagesChemCollective Autograded Labs PDFYuri M. BandaNo ratings yet
- Des 6651Document27 pagesDes 6651biniNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Chemical Analytical Study of Mercuric Chloride (Veeram) On Before and After PurificationDocument7 pagesA Comparative Chemical Analytical Study of Mercuric Chloride (Veeram) On Before and After Purificationjmanuel108yahoo.co.ukNo ratings yet
- Valorizacion Del Desecho de Aguas Residuales Del Prosamiento de AceitunasDocument11 pagesValorizacion Del Desecho de Aguas Residuales Del Prosamiento de AceitunasJalcamNo ratings yet
- NSCI6103 - Course Project.Document9 pagesNSCI6103 - Course Project.Devon JayNo ratings yet
- Grade Xii Practical ContentDocument7 pagesGrade Xii Practical ContentAvi ANo ratings yet
- Indian Rayon Summer Project ReportDocument98 pagesIndian Rayon Summer Project Reportankit3688% (8)
- Inorganic Chem 11Document68 pagesInorganic Chem 11hisrom286No ratings yet