Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review 1101
Uploaded by
becca1987Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review 1101
Uploaded by
becca1987Copyright:
Available Formats
Physics 1101
Final Examination Review Problems
You should attempt the problems below prior to coming to class for the final lab. In fact, your instructor may
ask you to solve the problems on the board during the review session. There is no substitute for your diligence
and participation in this process. If you do nothing but watch someone else solve the problems, you will not
learn much from the review. If you at least seriously attempt the problems, you will learn something.
As you know, one problem on the final examination concerns graphical analysis of data. Here are some
equations for you to practice putting in the proper form to make a straight line graph. For each equation, show
how to rewrite the equation to make a straight line graph of some function of y versus some function of x.
Identify what represents the slope and what represents the vertical intercept.
EXAMPLE: y2 - a = bx(1/2); Rewrite as y2 = a + bx(1/2). Plot y2 on the vertical axis and x(1/2) on the horizontal
axis. The slope is then b and the vertical intercept is a. Review the introduction in the PHYS 1101 manual for
help.
TRY THESE: (1) y = [c + dx(1/3)]2; (2) y = ae(kx) (3) y= kxn (determine k and n)
(4) (y2 + b)(1/2) = ax
1. As an object is heated, it normally expands, thereby increasing its volume V. Since its mass m remains
constant, its density d usually decreases. A physics student measured this effect by measuring the density of a
material as a function of temperature T. She found the results shown below.
T (oC)
50.0
100.0
150.0
200.0
250.0
d (g/cm3)
4.975
4.935
4.913
4.878
4.853
The equation that she knows properly describes the effect is d = d o(1- T), where do and are constants. Plot a
straight-line graph of the appropriate variables and use it to find values (with units) for do and .
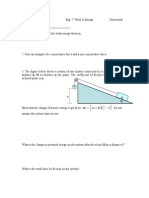
2. In an experiment using an inclined track with a dynamics cart, the computer failed, and the student had to
record the distance the cart traveled in a certain time interval. If the cart traveled 35.0 cm in 3.5 s, find its
acceleration and the tension in the string connecting the cart to the accelerating (hanging) mass.
3. Two cubes having identical volumes are cemented together to form a composite material. Each cube is 2.60
cm on a side. If the total mass of the composite material is determined to be 152.6 grams and one of the cubes is
made from a material whose density is 2.70 g/cm 3, find the density of the other material. Neglect the mass of the
cement.
4. Two-dimensional collisions may be studied by using an air table (similar to an air hockey game)
instead of the method we used. Suppose a 40-gram air puck traveling to the east with speed 10 cm/s
collides with and sticks to a 60-gram air puck traveling south with speed 15 cm/s. Find the velocity
(magnitude and direction with respect to east) of the combined mass after the collision.
5. In the computer-based experiment concerning rotational motion, the acceleration of a point on the rim of the
large steel disk, is 8.0 cm/s2. What is the angular acceleration of the pulley about which the string is wound?
The radius of the pulley is 1.25 cm and the radius of the steel disk is 6.0 cm.
You might also like
- Review 1102Document1 pageReview 1102becca1987100% (1)
- 1102 Exp09 Lenz LawDocument9 pages1102 Exp09 Lenz Lawbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 13 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 13 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 6 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 6 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 3 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 3 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 12 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 12 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 11 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 11 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 7 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 7 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 9 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 9 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 8 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 8 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 2 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 2 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 5 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 5 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 6 HW PDFDocument1 page1101 Exp 6 HW PDFbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 12 HWDocument1 page1101 Exp 12 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 4 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 4 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 2 HWDocument1 page1101 Exp 2 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1102 Exp 1 HWDocument1 page1102 Exp 1 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 10 HW PDFDocument1 page1101 Exp 10 HW PDFbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 5 HW PDFDocument1 page1101 Exp 5 HW PDFbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 9 HW PDFDocument1 page1101 Exp 9 HW PDFbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 7 HW PDFDocument1 page1101 Exp 7 HW PDFbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 11 HW PDFDocument1 page1101 Exp 11 HW PDFbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 8 HW PDFDocument1 page1101 Exp 8 HW PDFbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 3 HWDocument1 page1101 Exp 3 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 4 HW PDFDocument1 page1101 Exp 4 HW PDFbecca1987No ratings yet
- The Ethics of Ambiguity by SimoneDocument7 pagesThe Ethics of Ambiguity by Simonebecca1987No ratings yet
- 1101 Exp 1 HWDocument1 page1101 Exp 1 HWbecca1987No ratings yet
- ELET 4300 Lesson 01 Intro To Modern OS Fall 08292013Document28 pagesELET 4300 Lesson 01 Intro To Modern OS Fall 08292013becca1987No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Tutor 1Document4 pagesTutor 1kamal_ismethNo ratings yet
- Free Fall Using Light GatesDocument2 pagesFree Fall Using Light GatesIbrahim BtNo ratings yet
- Dynamic of IC EnginesDocument21 pagesDynamic of IC EnginesMohit DadarwalNo ratings yet
- 9th Physics Revision Work-Sheets 2023-24-095745Document6 pages9th Physics Revision Work-Sheets 2023-24-095745Sidhant LodhiNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper - M2 PDFDocument18 pagesPractice Paper - M2 PDFfuaadhNo ratings yet
- Geometric Flow Equations for Schwarzschild-AdS Space-time and Hawking-Page Phase TransitionDocument35 pagesGeometric Flow Equations for Schwarzschild-AdS Space-time and Hawking-Page Phase Transitionmichael pasquiNo ratings yet
- 6 DynamicsDocument93 pages6 Dynamicsmurada_7No ratings yet
- Biomechanics: KinematicsDocument6 pagesBiomechanics: KinematicsNadziran EzizNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Unit 3 Kinematics in One Dimension Cheat Sheet/Study GuideDocument2 pagesAP Physics Unit 3 Kinematics in One Dimension Cheat Sheet/Study GuideSandy SandriNo ratings yet
- فيزياء تجربة البندول البسيطDocument6 pagesفيزياء تجربة البندول البسيطنعمه الشمريNo ratings yet
- Physics 1101 task solutions in A4 paper with units conversionDocument2 pagesPhysics 1101 task solutions in A4 paper with units conversionWenn Mark BurerosNo ratings yet
- Traffic Flow Theory PDFDocument33 pagesTraffic Flow Theory PDFPaolo Angelo GutierrezNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document55 pagesCH 11Mega LialitaNo ratings yet
- GED Physics Motion ForcesDocument4 pagesGED Physics Motion ForcesShahadat Hussain Parvez100% (2)
- Ex.1:Find The Average of All Prime Numbers Between 30 andDocument3 pagesEx.1:Find The Average of All Prime Numbers Between 30 andz1y280% (5)
- FDDocument7 pagesFDharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For College Physics 1st Edition by EtkinaDocument46 pagesSolution Manual For College Physics 1st Edition by Etkinaa190286885100% (2)
- Self-Check 1-1: Submitted by On 3/9/2012 5:21:18 PMDocument219 pagesSelf-Check 1-1: Submitted by On 3/9/2012 5:21:18 PMblue4882No ratings yet
- Dynamics - Solutions Chapter R2Document40 pagesDynamics - Solutions Chapter R2holverson2No ratings yet
- NK C SI R: Rigid Body Dynamics, Home Work Sheet-7Document2 pagesNK C SI R: Rigid Body Dynamics, Home Work Sheet-7Nilakantha PradhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Schwarzschild MetricDocument4 pages1 Schwarzschild MetricMatejaBoskovicNo ratings yet
- Eastern Mediterranean University Homework #1Document4 pagesEastern Mediterranean University Homework #1casaberoNo ratings yet
- Goran Marjanovic Pyramids Guardians of Primary Cosmic Vibration of The Local DensitiesDocument12 pagesGoran Marjanovic Pyramids Guardians of Primary Cosmic Vibration of The Local DensitiesSadegh SimorghNo ratings yet
- Speed, Time and DistanceDocument33 pagesSpeed, Time and DistanceFahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanics (B.SC) Engineering Mechanics Ch06 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Mechanics (B.SC) Engineering Mechanics Ch06 Simple Harmonic MotionSaher100% (1)
- SQ NP LQ From Chapter KinematicsDocument8 pagesSQ NP LQ From Chapter KinematicsSupreme PhuyalNo ratings yet
- 01 06 2021++Kinematics+Introduction+Vinay+Sir+Physics+11th+Elite+Live+VJEEDocument131 pages01 06 2021++Kinematics+Introduction+Vinay+Sir+Physics+11th+Elite+Live+VJEEsanju kumariNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Graph MatchingDocument3 pagesLab 1 - Graph Matchingkitsune-nildeNo ratings yet
- Sample ProblemsDocument36 pagesSample ProblemsLovely Joy GumbaNo ratings yet
- General Theory of RelativityDocument31 pagesGeneral Theory of Relativityneo0000No ratings yet