Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulas for Math Units
Uploaded by
Ismael RocaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas for Math Units
Uploaded by
Ismael RocaCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics: Units 2A and 2B
Formula Sheet
Number and algebra
Equation of a line: y = mx + c, where m = gradient; c = yintercept
Space and measurement
In a right triangle:
sin
opposite
hypotenuse
cos
adjacent
hypotenuse
tan
opposite
adjacent
Pythagoras Theorem :
In a right triangle ABC , where a, b are the short sides and c is the hypotenuse
Circle :
c2 a 2 b2
C 2 r D, where C is the circumference, r is the radius and D is the diameter
A r 2 , where A is the area
1
Triangle:
Parallelogram:
A bh
Trapezium :
1
2
b h, where b is the base and h is the perpendicular height
( a b) h, where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides
and h is the perpendicular height
Prism:
V Ah, where V is the volume, A is the area of the base and
h is the perpendicular height
Pyramid:
1
V Ah
3
Cylinder :
S 2 r h 2 r 2 , where S is the total surface area
V r 2h
Cone :
S r s r 2 , where s is the slant height
V
Sphere :
1
3
r 2h
S 4 r 2
V
4
3
r3
Gradient of line, m, through the points ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) is given by m
y2 y1
x2 x1
Distance, d , between the points ( x1, y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) is given by d ( y2 y1 ) 2 ( x2 x1 ) 2
Note: Any additional formulas identified by the examination panel as necessary will be
included in the body of the particular question
Mathematics: Units 2C and 2D
Formula Sheet
Number and algebra
Index laws:
For any numerical value a 0 and integers m and n,
am an am n
am an am n
Simple interest :
I P r t , where P is the principal, r is the rate per year and t is the time in years
Space and measurement
In a right triangle:
sin
opposite
cos
hypotenuse
adjacent
hypotenuse
tan
opposite
adjacent
Pythagoras Theorem:
In right triangle ABC , where a, b are the short sides and c is the hypotenuse
c2 a 2 b2
In any triangle ABC :
a
sin A
b
sin B
c
sin C
a 2 b 2 c 2 2 b c cos A
A
Circle :
1
2
cos A
b2 c2 a2
2bc
a b sin C , where A is the area
C 2 r D, where C is the circumference, r is the radius and D is the diameter
A r 2 , where A is the area
1
Triangle:
Parallelogram:
A bh
Trapezium :
1
2
b h, where b is the base and h is the perpendicular height
( a b) h, where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides
and h is the perpendicular height
Prism:
V Ah, where V is the volume, A is the area of the base and
h is the perpendicular height
Pyramid:
1
V Ah
3
Cylinder :
S 2 r h 2 r 2 , where S is the total surface area
V r 2h
Cone :
S r s r 2 , where s is the slant height
V
Sphere :
1
3
r 2h
S 4 r 2
V
4
3
r3
Space and measurement
Gradient of line, m, through the points ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) is given by m
y2 y1
x2 x1
Distance d , between the points ( x1 , y1 ) and ( x2 , y2 ) is given by d ( y2 y1 ) 2 ( x2 x1 ) 2
Lines are perpendicular if m1 m2 1
Chance and Data
P ( A) P ( A) 1
Note: Any additional formulas identified by the examination panel as necessary will be
included in the body of the particular question.
Mathematics: Units 3A and 3B
Formula Sheet
Number and algebra
Index laws:
For a , b 0 and m ,n real,
a m b m ( a b) m
a
Simple interest :
Compound interest :
am
am n
n
a
1
m
a
an
am an am n
am
a
n
(a m )n a m n
a0 1
for m an integer and n a positive integer
I P r t , where P is the principal, r is the rate per year and t is the time in years
A P 1 r compounded annually
t
A P (1 ) nt compounded n times a year
n
dy
Differentiation:
If f ( x) y, then f ( x)
Powers:
If f ( x) x n , then f ( x) n x n 1
or
If y x n , then
Product rule:
If y f ( x) g ( x)
or
If y uv
dy du
dv
then
vu
dx
dx dx
dx
y f ( x) g ( x) f ( x) g ( x)
then
x n 1
Integration :
Antiderivative:
dy
x n 1
n
Given
x then y =
c, n 1
dx
n 1
x n dx
n 1
c, n 1
Space and measurement
In any triangle ABC :
a
sin A
b
sin B
c
sin C
a 2 b2 c 2 2 b c cos A
A
Space and measurement
1
2
a b sin C , where A is the area
cos A
b2 c2 a2
2bc
dy
dx
n x n 1
Circle :
C 2 r D, where C is the circumference, r is the radius and D is the diameter
A r 2 , where A is the area
1
Triangle:
Parallelogram:
A bh
Trapezium :
1
2
b h, where b is the base and h is the perpendicular height
( a b) h, where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides
and h is the perpendicular height
Prism:
V Ah, where V is the volume, A is the area of the base and
h is the perpendicular height
Pyramid:
1
V Ah
3
Cylinder :
S 2 r h 2 r 2 , where S is the total surface area
V r 2h
Cone :
S r s r 2 , where s is the slant height
V
Sphere :
1
3
r 2h
S 4 r 2
V
4
3
r3
Chance and data
P ( A) P( A) 1
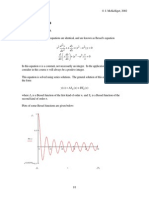
In a normal distribution approximately:
68% of values lie within one (1) standard deviation of the mean
95% of values lie within two (2) standard deviations of the mean
99.7% of values lie within three (3) standard deviations of the mean.
Note: Any additional formulas identified by the examination panel as necessary will be
included in the body of the particular question.
Mathematics: Units 3C and 3D
Formula sheet
Number and algebra
dy
dx
then f ( x) e x
then f ( x)
If f ( x) y
If f ( x) e x
If f ( x) x n
Product rule:
If
y f ( x) g ( x)
then
y uv
dy du
dv
then
vu
dx
dx dx
or
If
or
If
y f ( x) g ( x) f ( x) g ( x)
then f ( x) n x n 1
Quotient rule:
f ( x)
If
g ( x)
then y
u
v
du
dv
vu
dy
dx
then
dx
2
f ( x) g ( x) f ( x ) g ( x )
( g ( x)) 2
dx
Chain rule:
y f ( g ( x))
If
or
then y f ( g ( x)) g ( x)
Powers:
x dx
then
n 1
c, n 1
Incremental formula : y
dy
dx
Exponential growth and decay :
dy
dt
y f (u ) and u =g x
dy dy du
dx du dx
n 1
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus :
d x
f t dt f x
and
dx a
If
If
ky , then y Ae kt
Space and measurement
Exponentials: e dx e x c
x
a f x dx f b f a
Circle :
C 2 r D, where C is the circumference, r is the radius and D is the diameter
A r 2 , where A is the area
1
Triangle:
Parallelogram:
A bh
Trapezium :
1
2
b h, where b is the base and h is the perpendicular height
( a b)h, where a and b are the lengths of the parallel sides
and h is the perpendicular height
Prism:
V Ah, where V is the volume, A is the area of the base and
h is the perpendicular height
Pyramid:
1
V Ah
3
Cylinder :
S 2 r h 2 r 2 , where S is the total surface area
V r 2h
Cone :
S r s r 2 , where s is the slant height
V
Sphere :
1
3
r 2h
S 4 r 2
V
4
3
r3
Volume of solids of revolution :
V y 2 dx rotated about the x axis
V x 2 dy , rotated about the y axis
Chance and data
Probability laws:
P ( A) P( A) 1
P ( A B ) P ( A) P( B ) P ( A B )
P ( A B ) P ( A) P ( B / A) P ( B ) P ( A / B )
Binomial distributions :
Mean : np
and
standard deviation :
np (1 p )
A confidence interval for the mean of a population is :
x z
x z
where is the population mean, is the population standard deviation and
where x is the sample mean, n is the sample size and
z is the cut off value on the standard normal distribution corresponding to the confidence level.
Note: Any additional formulas identified by the examination panel will be included in the body
of the particular question.
You might also like
- Amino Acid FormulasDocument2 pagesAmino Acid FormulasIsmael RocaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Formulas For Statistics 1Document7 pagesStatistical Formulas For Statistics 1Ismael RocaNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasIsmael RocaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet and List of Symbols, Basic Statistical InferenceDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet and List of Symbols, Basic Statistical InferenceManuel RivasNo ratings yet
- Akypo Household LeafletDocument11 pagesAkypo Household LeafletIsmael Roca100% (1)
- Akypo Household LeafletDocument11 pagesAkypo Household LeafletIsmael Roca100% (1)
- Biocide FormulDocument3 pagesBiocide FormulIsmael RocaNo ratings yet
- Corrosivity Vs NIK Acids (R)Document3 pagesCorrosivity Vs NIK Acids (R)Ismael RocaNo ratings yet
- Lutensol TO Types: Technical InformationDocument15 pagesLutensol TO Types: Technical InformationLjupco AleksovNo ratings yet
- SEO-optimized document titleDocument9 pagesSEO-optimized document titleIsmael RocaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Narrative Report in Homeroom Guidance Q2 2021 2022Document5 pagesNarrative Report in Homeroom Guidance Q2 2021 2022Charles Carl GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lists of IntegralsDocument10 pagesLists of IntegralsAnu RadhaNo ratings yet
- IntegersDocument16 pagesIntegerssanttoNo ratings yet
- Solve equations and logarithmsDocument34 pagesSolve equations and logarithmsJojobaby5171467% (3)
- Angles Year 7 ExerciseDocument15 pagesAngles Year 7 ExerciseAlexaNo ratings yet
- 2012 2013RCcatalogDocument60 pages2012 2013RCcatalogsoumendranath_deNo ratings yet
- WriteyourownwordproblemDocument3 pagesWriteyourownwordproblemapi-273064494No ratings yet
- Master Quantitative Aptitude with tips & tricksDocument24 pagesMaster Quantitative Aptitude with tips & tricksSankar Adhikari0% (1)
- Fractions and Decimals ScholasticDocument49 pagesFractions and Decimals ScholastichusseinNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Term 2 AnalysisDocument94 pagesLecture Notes Term 2 AnalysispipNo ratings yet
- SSLC Maths Question Bank & Solution All ChaptersDocument70 pagesSSLC Maths Question Bank & Solution All ChaptersSubhash S78% (59)
- Homework Opoly For YouDocument34 pagesHomework Opoly For YouHenrique MouraNo ratings yet
- Plotting Multiple Spheres in MatlabDocument5 pagesPlotting Multiple Spheres in MatlabDrSaurabh TewariNo ratings yet
- Stokes Resume Final W-O Personel InfoDocument2 pagesStokes Resume Final W-O Personel Infoapi-248885941No ratings yet
- Add MathDocument16 pagesAdd MathIEyra ShaHeraNo ratings yet
- Review Module 13 Route Surveying Part 1Document1 pageReview Module 13 Route Surveying Part 1YeddaMIlagan100% (1)
- 3D GeometryDocument13 pages3D GeometryRoshan RajNo ratings yet
- Csse Guidance Sheet 3-10-12Document2 pagesCsse Guidance Sheet 3-10-12ath01No ratings yet
- Bessel Functions PDFDocument6 pagesBessel Functions PDFchrischovNo ratings yet
- SBI Clerk Practice Set - BSCDocument9 pagesSBI Clerk Practice Set - BSCSiva BantuNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/12Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/12YoviNo ratings yet
- 0580 w16 Ms 32Document6 pages0580 w16 Ms 32Aroon ChangNo ratings yet
- Geometry JeopardyDocument54 pagesGeometry Jeopardyapi-689431578No ratings yet
- 24940Document2 pages24940api-285165211No ratings yet
- PLG518 - Semester 1 2013-14Document5 pagesPLG518 - Semester 1 2013-14Suzanne BellNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic DifferentiationDocument11 pagesLogarithmic DifferentiationAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Problems Set 3 MathDocument36 pagesMechanical Engineering Problems Set 3 MathAizNo ratings yet
- Use Equals Sign To Determine Missing Numbers Algebra Level 3 Worksheet - Ver - 3Document13 pagesUse Equals Sign To Determine Missing Numbers Algebra Level 3 Worksheet - Ver - 3Fatima AliuNo ratings yet
- The LATEX Mathematics CompanionDocument80 pagesThe LATEX Mathematics CompanionGiulio Bertellini100% (2)
- JMU Elementary Education Program: Lesson Plan OutlineDocument6 pagesJMU Elementary Education Program: Lesson Plan Outlineapi-298389125No ratings yet