Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Star Map Feb 2016
Uploaded by
Powerhouse MuseumCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Star Map Feb 2016
Uploaded by
Powerhouse MuseumCopyright:
Available Formats
TheSky (c) Astronomy Software 1984-1998
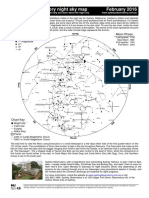
Sydney Observatory night sky map
February 2016
A map for each month of the year, to help you learn about the night sky
www.sydneyobservatory.com.au
The star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide
CAMELOPARDALIS
for February
2015 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and
at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For
URSA MAJOR
Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while extra stars will be
CASSIOPEIA
visible to the north. Stars down to a brightness or magnitude limit of 4.5 are shown on the
star chart. To use this star chart,
rotate the chart so that the direction you are facing (north, south, east or west) is shown at the bottom. The centre of the chart
represents the point directly above your head, called the zenith point, and the outer circular edge represents the horizon.
North
Star Brightness
Zero or brighter
1st magnitude
2nd
3rd
4th
Moon Phase
Last quarter:
New Moon:
First quarter:
Full Moon:
LYNX
Capella
AURIGA
NE
PERSEUS
NW
Gemini (the Twins)
01st
09th
15th
23rd
ANDROMEDA
TRIANGULUM
Pleiades
First quarter Moon
on the 23rd
Pollux
GEMINI
M44
CANCER
TAURUS
Aldebaran
Hyades
ARIES
Betelgeuse
ORION
CANIS MINOR
Regulus
PISCES
Procyon
M42
Orion (the Hunter)
MONOCEROS
Rigel
HYDRA
ERIDANUS
Sirius
Canis Major
(the Great Dog)
Sirius
LEPUS
CETUS
East
CANIS MAJOR
Adhara
West
SEXTANS
FORNAX
COLUMBA
CAELUM
PYXIS
HYDRA
PUPPIS
ERIDANUS
PICTOR
CRATER
HOROLOGIUM
RETICULUM
DORADO
ANTLIA
VELA
PHOENIX
Achernar
LMC
CARINA
FALSE CROSS
VOLANS
HYDRUS
MENSA
PISCIS AUSTRINUS
TUCANA
SMC
SOUTHERN CROSS
AQUARIUS
SCULPTOR
Canopus
CHAMAELEON
GRUS
South Celestial Pole
OCTANS
MUSCA
CRUX
Chart Key
INDUS
Mimosa
SE
Bright star
CENTAURUS
Faint star
Ecliptic
Milky Way
P Planet
LMC or Large Magellanic Cloud
SMC or Small Magellanic Cloud
POINTERS
MICROSCOPIUM
APUS
PAVO
SW
Hadar
TRIANGULUM AUSTRALE
Alpha Centauri
CIRCINUS
South
TELESCOPIUM
ARA
NORMA
CORONA AUSTRALIS
The best time to view the Moon using binoculars
or a small telescope is a few days either side of the first quarter Moon on the
LUPUS
15th of this month. The constellation of Orion (the Hunter) is high in the sky throughout February. The three
stars that make up
SAGITTARIUS
the belt of Orion form the base and the dagger hanging from Orions belt forms the handle, of an asterism that is colloquially
known as The Saucepan. The v-shaped head of Taurus (the Bull) can be seen further to the west of Orion, while the
companions of this hunter are found further to the east, in Canis Major (the Great Dog) and Canis Minor (the Little Dog). Crux,
(the Southern Cross) is low in the south east.
SCORPIUS
Zubenelgenubi
Sydney Observatory, with a magnificent view overlooking Sydney Harbour, is open 10am to
Centre
of theand
GalaxyBoxing Day, and open 10am to
5pm daily except closed Good Friday, Christmas
Day
noon on New Years Eve. Open Monday to Saturday for night sessions (times vary depending
on the season) for sky viewing through one of our telescopes (cosy planetarium session if
cloudy), and 3D movies about the Universe. Bookings are essential for night programs.
For more information, check the website at www.sydneyobservatory.com.au or call
(02) 9921 3485. Sydney Observatory is at 1003 Upper Fort Street, Observatory Hill, in the
historic Rocks area of Sydney.
Sydney Observatory is part of the Museum of Applied Arts and Sciences. The Sydney Observatory night sky map was created by Dr. M Anderson using the
TheSky software. This months edition was prepared by Brenan Dew 2016 Museum of Applied Arts and Sciences, Sydney.
You might also like
- Signs Symbols of The World - DR McElroyDocument658 pagesSigns Symbols of The World - DR McElroyClip ClapsNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 Sky ScienceDocument16 pagesGrade 6 Sky ScienceHarish MathiazhahanNo ratings yet
- All Fixed StarsDocument4 pagesAll Fixed StarsJayshree Borkar75% (4)
- Night Sky: A Field Guide to the ConstellationsFrom EverandNight Sky: A Field Guide to the ConstellationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- ConstellationDocument7 pagesConstellationAnonymous xMXvFtNo ratings yet
- 100 Things to See in the Night Sky: From Planets and Satellites to Meteors and Constellations, Your Guide to StargazingFrom Everand100 Things to See in the Night Sky: From Planets and Satellites to Meteors and Constellations, Your Guide to StargazingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Science 5 Q4-Module 6Document17 pagesScience 5 Q4-Module 6Yanyan Alfante100% (1)
- Bright Star AtlasDocument1 pageBright Star AtlasDiego de BastianiNo ratings yet
- Wepik Doodle Sketchnotes Lesson General Presentation 20230831123933htyaDocument23 pagesWepik Doodle Sketchnotes Lesson General Presentation 20230831123933htyaRexxy AnjmNo ratings yet
- Star Map Jan 2016Document1 pageStar Map Jan 2016Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map Aug 2015Document1 pageStar Map Aug 2015Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map Dec 2015Document1 pageStar Map Dec 2015Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map Nov 2015Document1 pageStar Map Nov 2015Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map June 2015Document1 pageStar Map June 2015Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- December 2013 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageDecember 2013 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- May 2013 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageMay 2013 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Taurus Leads A Starry Stampede: Stars & PlanetsDocument4 pagesTaurus Leads A Starry Stampede: Stars & PlanetsbirbiburbiNo ratings yet
- Starry Trails July 2017Document2 pagesStarry Trails July 2017shindudevilNo ratings yet
- Quarter III Lesson on ConstellationsDocument37 pagesQuarter III Lesson on ConstellationsSia AlarieNo ratings yet
- Starry Trails April 2017Document2 pagesStarry Trails April 2017shindudevilNo ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2015 03Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2015 033582No ratings yet
- Starrt Trails August 2016Document2 pagesStarrt Trails August 2016shindudevilNo ratings yet
- Learn About Constellations and AsterismsDocument89 pagesLearn About Constellations and AsterismsChelleNo ratings yet
- 100 Things to See in the Night Sky, Expanded Edition: Your Illustrated Guide to the Planets, Satellites, Constellations, and MoreFrom Everand100 Things to See in the Night Sky, Expanded Edition: Your Illustrated Guide to the Planets, Satellites, Constellations, and MoreNo ratings yet
- What can you see from the Isle of Man’s dark sky locations? (38Document5 pagesWhat can you see from the Isle of Man’s dark sky locations? (38FilthyNo ratings yet
- Starry Trails Sept 2015Document2 pagesStarry Trails Sept 2015shindudevilNo ratings yet
- SCI9 Q3 L5Document39 pagesSCI9 Q3 L5alvin taganasNo ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2014 08Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2014 083582No ratings yet
- Binoculars March 2024Document12 pagesBinoculars March 2024ageluz00No ratings yet
- The Solar SystemDocument16 pagesThe Solar SystemPriya SegaranNo ratings yet
- Tour of The Milky WayDocument71 pagesTour of The Milky WaygayNo ratings yet
- Stars and Constellations GuideDocument29 pagesStars and Constellations GuidevrihadNo ratings yet
- Constellations Stars SummaryDocument67 pagesConstellations Stars SummaryJayru RemillosaNo ratings yet
- AY Honor Stars Answer Key Used by General ConferenceDocument11 pagesAY Honor Stars Answer Key Used by General ConferenceAbelNo ratings yet
- July 2014 Night Skies Over TanzaniaDocument3 pagesJuly 2014 Night Skies Over TanzaniaOthman MichuziNo ratings yet
- 100 Things to See in the Southern Night Sky: From Planets and Satellites to Meteors and Constellations, Your Guide to StargazingFrom Everand100 Things to See in the Southern Night Sky: From Planets and Satellites to Meteors and Constellations, Your Guide to StargazingNo ratings yet
- Skymaps Com 2014 04Document2 pagesSkymaps Com 2014 043582No ratings yet
- Cardinal DirectionDocument48 pagesCardinal DirectionPrapti NayakNo ratings yet
- 18 THE UNIVERSE ScsDocument19 pages18 THE UNIVERSE ScshelenaNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Q3 Module6Document7 pagesSci9 Q3 Module6Kirsten Angela VirtudazoNo ratings yet
- Trip Through Our Solar SystemDocument4 pagesTrip Through Our Solar SystemHirenkumarNo ratings yet
- Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto This YearDocument2 pagesUranus, Neptune, and Pluto This YearbirbiburbiNo ratings yet
- The Book of Stars: Being a Simple Explanation of the Stars and Their Uses to Boy LifeFrom EverandThe Book of Stars: Being a Simple Explanation of the Stars and Their Uses to Boy LifeNo ratings yet
- Evidence that alien life exists on Saturn's moon TitanDocument3 pagesEvidence that alien life exists on Saturn's moon TitanSandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Astronomy 5 Section 4046 Usc - Lattc Program Lab 1Document8 pagesAstronomy 5 Section 4046 Usc - Lattc Program Lab 1Gre MatrNo ratings yet
- Stargazing101 North Ebook v2Document35 pagesStargazing101 North Ebook v2Sambhav AcharyaNo ratings yet
- The Evening Sky Map: JANUARY 2014Document2 pagesThe Evening Sky Map: JANUARY 20143582No ratings yet
- Sky MapsDocument2 pagesSky MapsPatrick SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Constellations Through the SeasonsDocument5 pagesConstellations Through the SeasonsLeah CasanoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 STARS and CONSTELLATIONSDocument7 pagesLESSON 6 STARS and CONSTELLATIONSiem.mei0424No ratings yet
- Constallation English SpeechDocument2 pagesConstallation English SpeechfranNo ratings yet
- Different Patterns Throughout The YearDocument29 pagesDifferent Patterns Throughout The YearEllyssa Kate LazaroNo ratings yet
- ABCs of Political EconomyDocument15 pagesABCs of Political EconomyVilhelmo De OkcidentoNo ratings yet
- Constellations 1Document16 pagesConstellations 1Althea ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Section 1a - The Night Sky - Our Place and Time - StudentDocument31 pagesSection 1a - The Night Sky - Our Place and Time - StudentDeon SmithNo ratings yet
- ConstellationsDocument16 pagesConstellationsKhalid RedzaNo ratings yet
- Autumn Night SkyDocument1 pageAutumn Night SkyHartford CourantNo ratings yet
- Stargazing101 South EBook v1p1Document36 pagesStargazing101 South EBook v1p1jbosukleeNo ratings yet
- The Solar System GuideDocument36 pagesThe Solar System GuideEshaan SanalNo ratings yet
- How To Use The Sun and StarDocument7 pagesHow To Use The Sun and StarCondor7tNo ratings yet
- ConstellationsDocument51 pagesConstellationsaranasprincess88No ratings yet
- ConstellationsDocument51 pagesConstellationsaranasprincess88No ratings yet
- The Seasons Constellations ActivitiesDocument7 pagesThe Seasons Constellations Activitiesfatin nasuhaNo ratings yet
- Star Map Mar 2016Document1 pageStar Map Mar 2016Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map Feb 2016Document1 pageStar Map Feb 2016Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map April 2016Document1 pageStar Map April 2016Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map Sep 2015Document1 pageStar Map Sep 2015Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map May 2015Document1 pageStar Map May 2015Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map For July 2015Document1 pageStar Map For July 2015Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map Mar 2015Document1 pageStar Map Mar 2015Powerhouse Museum100% (1)
- December 2014 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageDecember 2014 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- January 2015 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageJanuary 2015 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Commemorative AerogrammeDocument2 pagesCommemorative AerogrammePowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- May 2013 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageMay 2013 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Star Map Feb 2015Document1 pageStar Map Feb 2015Powerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Aerofoil WingDocument3 pagesAerofoil WingPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- May 2013 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageMay 2013 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- November 2014 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageNovember 2014 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Strictly Ballroom Paper DollsDocument7 pagesStrictly Ballroom Paper DollsPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- June 2014 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageJune 2014 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- September 2014 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageSeptember 2014 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Paper Helicopter: Time: 15 Minutes Difficulty: HintDocument3 pagesPaper Helicopter: Time: 15 Minutes Difficulty: HintPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- August 2014 Night Sky ChartDocument1 pageAugust 2014 Night Sky ChartPowerhouse Museum100% (1)
- 2 Ringed FlyerDocument3 pages2 Ringed FlyerPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Bunnykins Matching CardsDocument10 pagesBunnykins Matching CardsPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Green Dyed Flower ExperimentDocument2 pagesGreen Dyed Flower ExperimentPowerhouse MuseumNo ratings yet
- Major Star Constellation: Fact CardsDocument4 pagesMajor Star Constellation: Fact CardsSeemaNoorNo ratings yet
- Carolingian Planetary Observations The C PDFDocument14 pagesCarolingian Planetary Observations The C PDFJefferson de AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- Book-Jesus Teachings - Base On The Zodiac.Document42 pagesBook-Jesus Teachings - Base On The Zodiac.mindbodystorm_283273No ratings yet
- 6.4.5 SD.7.AfricanMythologyDocument28 pages6.4.5 SD.7.AfricanMythologyVostjeNo ratings yet
- Star Map Feb 2016Document1 pageStar Map Feb 2016Powerhouse Museum100% (1)
- Monoceros Week 3Document7 pagesMonoceros Week 3Lizzy CovingtonNo ratings yet
- Stargazing 101 - Whirlwind Tour of Night SkyDocument36 pagesStargazing 101 - Whirlwind Tour of Night Skygeoholub100% (1)
- Zodiac Sign IN Astronomy: Presented byDocument30 pagesZodiac Sign IN Astronomy: Presented byRaj BarmanNo ratings yet
- Zodiac Model Descriptions FinalDocument14 pagesZodiac Model Descriptions FinalMikes JetiganNo ratings yet
- The Meaning of the Signs of the Zodiac According to the Milky WayDocument9 pagesThe Meaning of the Signs of the Zodiac According to the Milky Wayhscottarmstrong3302No ratings yet
- Astronomy Merit Badge Pamphlet 35859Document84 pagesAstronomy Merit Badge Pamphlet 35859Mark QuinNo ratings yet
- Stars and Constellations - Print - QuizizzDocument5 pagesStars and Constellations - Print - QuizizzTashi OngNo ratings yet
- Constellations and PatternsDocument76 pagesConstellations and PatternsGrace Jem Villacorta EjadaNo ratings yet
- NSO 2022 Intermediate Level Reference Book Super Senior CategoryDocument117 pagesNSO 2022 Intermediate Level Reference Book Super Senior CategoryManav KumarNo ratings yet
- Mullaney Deep Sky 111Document6 pagesMullaney Deep Sky 111Daniel BernardesNo ratings yet
- ConstellationDocument29 pagesConstellationChonama FetalcoNo ratings yet
- Activity - Seasonal Stars - Submit Your Answers Here! - 2021FL-AST-101-01Document5 pagesActivity - Seasonal Stars - Submit Your Answers Here! - 2021FL-AST-101-01TriciaNo ratings yet
- The Milky Way and The Cosmic Soma PDFDocument9 pagesThe Milky Way and The Cosmic Soma PDFAnil DNo ratings yet
- 7 - Purnavasu MytologyDocument20 pages7 - Purnavasu Mytologyshunmugathason100% (4)
- 12 Principle ConstellationsDocument2 pages12 Principle ConstellationscharlsNo ratings yet
- Winter Guide To The Constellations: What Is A Star?Document18 pagesWinter Guide To The Constellations: What Is A Star?ManimekalaiNo ratings yet
- The Gemini PrinciplesDocument15 pagesThe Gemini Principlesbemxgm-1No ratings yet
- Fixed Stars Have Awakened AstrologersDocument10 pagesFixed Stars Have Awakened Astrologersaiavenue100% (1)
- Twin FlameDocument11 pagesTwin FlameManu MihaiNo ratings yet
- Pattern of The Constellation: Group 3 PresentationDocument19 pagesPattern of The Constellation: Group 3 Presentationalraffie gubatNo ratings yet
- SRICFDocument14 pagesSRICFRon David SmithNo ratings yet