Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydrocortisone
Uploaded by
timie_reyesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydrocortisone
Uploaded by
timie_reyesCopyright:
Available Formats
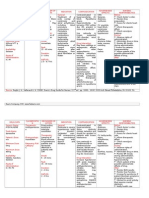
Hydrocortisone is a corticosteroid.
It works by decreasing or preventing tissues from responding
to inflammation. It also modifies the body's response to certain immune stimulation.
Indications
Replacement therapy in adrenal cortical insufficiency
Allergic statessevere or incapacitating allergic conditions
Hypercalcemia associated with cancer
Short-term inflammatory and allergic disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, collagen
diseases (SLE), dermatologic diseases (pemphigus), status asthmaticus, and autoimmune
disorders
Hematologic disordersthrombocytopenic purpura, erythroblastopenia
Trichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement
Ulcerative colitis, acute exacerbations of MS, and palliation in some leukemias and
lymphomas
Intra-articular or soft-tissue administration: Arthritis, psoriatic plaques
Retention enema: For ulcerative colitis, proctitis
Dermatologic preparations: To relieve inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of
dermatoses that are steroid responsive
Anorectal cream, suppositories: To relieve discomfort of hemorrhoids and perianal
itching or irritation
Interventions
Systemic administration
WARNING: Give daily before 9 AM to mimic normal peak diurnal corticosteroid levels
and minimize HPA suppression.
Space multiple doses evenly throughout the day.
Do not give IM injections if patient has thrombocytopenic purpura.
Rotate sites of IM repository injections to avoid local atrophy.
Use minimal doses for minimal duration to minimize adverse effects.
Taper doses when discontinuing high-dose or long-term therapy.
Arrange for increased dosage when patient is subject to unusual stress.
Ensure that adequate amount of Ca2+ is taken if prolonged administration of steroids.
Use alternate-day maintenance therapy with short-acting corticosteroids whenever
possible.
WARNING: Do not give live virus vaccines with immunosuppressive doses of
hydrocortisone.
Provide antacids between meals to help avoid peptic ulcer.
Topical dermatologic administration
Use caution with occlusive dressings; tight or plastic diapers over affected area can
increase systemic absorption.
Avoid prolonged use, especially near eyes, in genital and rectal areas, on face, and in skin
creases.
Teaching points
Systemic administration
Take this drug exactly as prescribed. Do not stop taking this drug without notifying your
health care provider; slowly taper dosage to avoid problems.
Dosage reductions may create adrenal insufficiency. Report any fatigue, muscle and joint
pains, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, weakness, dizziness, or low
blood sugar (if you monitor blood sugar).
Take with meals or snacks if GI upset occurs.
Take single daily or alternate-day doses before 9 AM; mark calendar or use other
measures as reminder of treatment days.
Do not overuse joint after intra-articular injections, even if pain is gone.
Frequent follow-up visits to your health care provider are needed to monitor drug
response and adjust dosage.
Wear a medical alert ID (if you ae using long-term therapy) so that any emergency
medical personnel will know that you are taking this drug.
You may experience these side effects: Increase in appetite, weight gain (some of gain
may be fluid retention; monitor intake); heartburn, indigestion (eat frequent small meals;
use of antacids may help); increased susceptibility to infection (avoid crowds during peak
cold or flu seasons, and avoid anyone with a known infection); poor wound healing (if
injured or wounded, consult health care provider); muscle weakness, fatigue (frequent
rest periods may help).
Report unusual weight gain, swelling of lower extremities, muscle weakness, black or
tarry stools, vomiting of blood, epigastric burning, puffing of face, menstrual
irregularities, fever, prolonged sore throat, cold or other infection, worsening of
symptoms.
Intra-articular, intralesional administration
Do not overuse the injected joint even if the pain is gone. Adhere to rules of proper rest
and exercise.
Topical dermatologic administration
Apply sparingly, and rub in lightly
Avoid contacting your eye with the medication.
Report burning, irritation, or infection of the site, worsening of the condition.
Avoid prolonged use.
Anorectal preparations
Maintain normal bowel function with proper diet, adequate fluid intake, and regular
exercise.
Use stool softeners or bulk laxatives if needed.
Notify your health care provider if symptoms do not improve in 7 days or if bleeding,
protrusion, or seepage occurs.
You might also like
- PALS Provider Manual PDFDocument57 pagesPALS Provider Manual PDFtimie_reyes90% (21)
- Rib Retractions Nasal Flaring Use of Accessory Muscles CyanosisDocument2 pagesRib Retractions Nasal Flaring Use of Accessory Muscles CyanosisTimie Navarro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cue Card AsthmaDocument2 pagesCue Card Asthmatimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Cues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective DataDocument5 pagesCues/Data Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Datatimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Cue Card AsthmaDocument2 pagesCue Card Asthmatimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Define AsthmaDocument5 pagesDefine Asthmatimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- PediatricDocument1 pagePediatrictimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- NecessitiesDocument2 pagesNecessitiestimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Drugs for Cardiac Arrest and ArrhythmiasDocument2 pagesDrugs for Cardiac Arrest and Arrhythmiastimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- aEmergency-Drugs XDocument12 pagesaEmergency-Drugs Xtimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Risk For Injury NCP SeizuresDocument2 pagesRisk For Injury NCP Seizurestimie_reyes88% (8)
- Emergency Drugs XDocument4 pagesEmergency Drugs Xtimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- DX StdieDocument22 pagesDX Stdietimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Revised Seizure Disorder CaseDocument4 pagesRevised Seizure Disorder Casetimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Seizuretimie_reyes100% (1)
- Drugs for Cardiac Arrest and ArrhythmiasDocument2 pagesDrugs for Cardiac Arrest and Arrhythmiastimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Acs Hne NTHN 170706Document6 pagesAcs Hne NTHN 170706timie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Ed Drugs Ongoing RevisionDocument3 pagesEd Drugs Ongoing Revisiontimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Acs StrokeDocument7 pagesAcs Stroketimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY CARDIAC DRUGSDocument21 pagesEMERGENCY CARDIAC DRUGSdrsabuegNo ratings yet
- Acs Hne NTHN 170706Document6 pagesAcs Hne NTHN 170706timie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Ed Drugs Ongoing RevisionDocument3 pagesEd Drugs Ongoing Revisiontimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY CARDIAC DRUGSDocument21 pagesEMERGENCY CARDIAC DRUGSdrsabuegNo ratings yet
- Emergency Room DrugsDocument3 pagesEmergency Room DrugsKrisia CastucianoNo ratings yet
- Acs Hne NTHN 170706Document6 pagesAcs Hne NTHN 170706timie_reyesNo ratings yet
- AMC Terminal Layout and Emergency ProceduresDocument2 pagesAMC Terminal Layout and Emergency Procedurestimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- AMC Fire ExtinguishersDocument3 pagesAMC Fire Extinguisherstimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- Ed Drugs Ongoing RevisionDocument3 pagesEd Drugs Ongoing Revisiontimie_reyesNo ratings yet
- AMC Reviewer 1Document5 pagesAMC Reviewer 1timie_reyesNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Dopamine Agonists: Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, Arizona, U.S.ADocument17 pagesDopamine Agonists: Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, Arizona, U.S.Aelenac67No ratings yet
- Cancers Natural Enemy 06!01!2013Document252 pagesCancers Natural Enemy 06!01!2013straw man100% (3)
- Module 8 - Group 3Document16 pagesModule 8 - Group 3MEDECIELO MELONo ratings yet
- Actilyse ® 50 MG Actilyse ® 20 MG: Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument13 pagesActilyse ® 50 MG Actilyse ® 20 MG: Acute Myocardial InfarctionmasterNo ratings yet
- Managing Medication SafelyDocument30 pagesManaging Medication Safelyshubham solankiNo ratings yet
- Market SizeDocument4 pagesMarket SizeUbair HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Beta Glucans May Interact With Medications For High Blood Pressure, Immune Suppression Or IndomethacinDocument2 pagesBeta Glucans May Interact With Medications For High Blood Pressure, Immune Suppression Or IndomethacinSASA100% (1)
- RabeprazoleDocument4 pagesRabeprazoleBhaskar SenguptaNo ratings yet
- EGBS4 KolchinskyDocument98 pagesEGBS4 Kolchinskyswapnil_sahoo_1No ratings yet
- Preliminary Screening of Antimicrobial and Phytochemical Studies of Jatropha Gossypifolia LinnDocument5 pagesPreliminary Screening of Antimicrobial and Phytochemical Studies of Jatropha Gossypifolia LinnNarendra MNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicsDocument19 pagesAnalgesicsRogelio Junior RiveraNo ratings yet
- Export of Indian Pharmaceuticals To NamibiaDocument58 pagesExport of Indian Pharmaceuticals To NamibiahabeebsheriffNo ratings yet
- CHT DMARDDocument3 pagesCHT DMARDkoolaberNo ratings yet
- Water ValidationDocument6 pagesWater ValidationNaveenKumar100% (1)
- Daftar Obat Pengobatan MassalDocument7 pagesDaftar Obat Pengobatan MassalChristian Hasudungan NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Hold Time Study For Cleaned FBD BagsDocument6 pagesHold Time Study For Cleaned FBD BagsDevendra Dwivedi100% (1)
- Omsite 2005 PDFDocument180 pagesOmsite 2005 PDFJulie100% (2)
- Intro Letter For Chemietron For Aristo Pharma MumbaiDocument2 pagesIntro Letter For Chemietron For Aristo Pharma MumbaiOm Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Industry of PakistanDocument20 pagesPharmaceutical Industry of PakistanAli UsamaNo ratings yet
- Initial Patient Assessment FormDocument3 pagesInitial Patient Assessment FormFrederickKalangieNo ratings yet
- Joseph P. Goldberg & Carrie L. Ernst & Stephen M. Stahl - Managing The Side Effects of Psychotropic Medications-American Psychiatric Publishing (2012) PDFDocument533 pagesJoseph P. Goldberg & Carrie L. Ernst & Stephen M. Stahl - Managing The Side Effects of Psychotropic Medications-American Psychiatric Publishing (2012) PDFbabyjesus1100% (3)
- Scope of Pharmacy Services To The Emergency DepartmentDocument5 pagesScope of Pharmacy Services To The Emergency DepartmentalfinadyaNo ratings yet
- Interpretative ReadingDocument11 pagesInterpretative Readingtanty_ukNo ratings yet
- Medication20quizzes 12028429Document2 pagesMedication20quizzes 12028429DurgaNadellaNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR HARGA JUAL BARANG PT. DHAINAKO PUTRA SEJATI 05/07/2021Document16 pagesDAFTAR HARGA JUAL BARANG PT. DHAINAKO PUTRA SEJATI 05/07/2021Bambang TriyonoNo ratings yet
- New Drug Application (NDA)Document13 pagesNew Drug Application (NDA)Dipak ShindeNo ratings yet
- 260002-Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology-IIDocument2 pages260002-Pharmaceutical Microbiology and Biotechnology-IIchintoo4696No ratings yet
- DrugBank - Erythromycin (DB00199)Document18 pagesDrugBank - Erythromycin (DB00199)Nuril FahmiNo ratings yet
- Statement of Purpose for Pharmacy Technician ProgramDocument3 pagesStatement of Purpose for Pharmacy Technician ProgramEminence SOP Writers100% (1)