Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Battery Management Manual FPRA D01 PDF
Uploaded by
maximoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Battery Management Manual FPRA D01 PDF
Uploaded by
maximoCopyright:
Available Formats
Battery Management Manual
Revision D01
FPRA
Flexi Power Rectifier
Battery Management Manual
Revision D01
Page 1 of 9
1/23/2009
Battery Management Manual
Revision D01
History:
Date
Version
Author
Change Notes
23.01.09
D01
Daniel Kreuzer
Creation of document
Authors:
Daniel Kreuzer
daniel.kreuzer@emerson.com
Abbreviations:
tbd
GUI
DDU
PDA
MAC
IP
LCD
CU
PID
VPN
to be done
Web-based User Interface
DC Distribution Unit
Power Distribution Assembly
Media Access Control
Internet Protocol
Liquid Crystal Display
Control
Product Information Data
Virtual Private Network
Related Documents:
User Manual FPRA D02 by Daniel Kreuzer: how to use for the Web-based User Interface and for
the LCD Front-Panel Display of the FPRA system
Page 2 of 9
1/23/2009
Battery Management Manual
Revision D01
Content
1
Overview .................................................................................................................................. 4
Battery Charge/Discharge/Recharge Concept .................................................................. 5
The Example System .............................................................................................................. 7
3.1
Start-up ............................................................................................................................... 7
3.2
Idle/Charge Off.................................................................................................................. 7
3.3
Discharge/Boost Discharge ............................................................................................. 8
3.4
Charge/Boost Charge........................................................................................................ 8
3.5
Battery Test ........................................................................................................................ 9
Page 3 of 9
1/23/2009
Battery Management Manual
Revision D01
1 Overview
This document is a how to use and how it works for the battery management of the FPRA
system.
Page 4 of 9
1/23/2009
Battery Management Manual
Revision D01
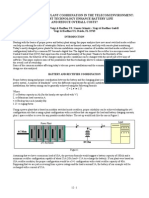
2 Battery Charge/Discharge/Recharge Concept
First Battery detected
Ubat > Nominal Set Volt
System Charge
Init
System Charge
Start
System Charge
Start Timeout
NO Discharge
Discharge > 1%
Discharge > 1%
Manual Boost Charge Request
System
Discharge Start
Time out initial Charge
Manual Boost Charge Request
Initial
Charge
Manual Boost
Charge Request
Manual Boost
Charge
Battery Test Request
System Charge
Off
Battery Test
Discharge > 1%
Idle
Discharge
Time out Boost Charge
Discharge > 10%
System
Discharge
System Boost
Discharge
Time out Charge
NO Discharge
NO discharge
Discharge > 1%
Discharge > 1%
System Charge
(const. I)
Discharge > 1% Discharge > 1%
System Charge
(const V)
System Boost
Charge (const I)
Ubat > Nominal Set Volt
Manual Boost
Charge Request
System Boost
Charge (const V)
Ubat > (Nominal Set Volt + Boost Volt Offset)
Manual Boost
Charge
Manual Boost Charge Request
Recharge
Page 5 of 9
1/23/2009
Battery Management Manual
Revision D01
The Battery state machine mainly consists of five different parts:
1. Initial Charge/Charge Start: after start-up the system is in initial charge state. This
state guarantees fully charged batteries before changing to the default operational
state. During this time it is not possible to start a battery test. The duration for the
initial charge time is user settable and can be changed under System Related
Settings Start Charge Time. It is not possible to stop the initial charge cycle in
order to start a battery test, but it is possible to schedule a battery test, which starts
directly after the initial charge.
2. Charge Off State/Idle State: this is the default operational state. This is the only
state, which allows starting a battery test.
3. Battery Test: battery test is a simulated AC-Fail/Discharge State. After a battery test
the system will change to discharge state in order to recharge the batteries.
4. Discharge State: Discharging more than 1% and less than 10% of total battery
capacity will result in the Discharge State. If AC is back before discharging more than
10% of total capacity the batteries will be recharged without boost voltage. The
duration for the recharge is user settable and can be changed under System Related
Settings Charge Time.
5. Boost Discharge State: Discharging more than 10% of total battery capacity will
result in the Boost Discharge State. After AC is back the batteries will be recharged
with boost voltage. The duration for the boost recharge is user settable and can be
changed under System Related Settings Boost Charge Time Manual Boost
Charge State: A manual started Boost Charge can be performed during a normal
charge or during Charge Off State.
Page 6 of 9
State changes from Charging States or Charge Off State requires a discharge of
more than 1% of overall battery capacity. Depending on the overall battery capacity
this may take several minutes.
1/23/2009
Battery Management Manual
Revision D01
3 The Example System
For a better understanding of the overall battery handling the complete process will be
discussed with the help of an example system:
3.1
200Ah Battery Block 50% charged at start up
-54.5V set Voltage
20A charge limit
20A load
no battery test scheduled
2h initial charge time
2h recharge time
3h Boost charge time
Start-up
During start-up the System operates in the initial charge (also called start charge) cycle:
1. Lowers the System Voltage down to 44V
2. Increase Voltage until the Battery Voltage is reached
3. Increase Voltage until the charge limit is reached This state is called constant
current
4. During charging batteries the voltage is raising until the set Voltage of 54.5V is
reached (without violating the charge limit) changing to state constant voltage
5. Stay for 2 hours (initial charge time) in constant Voltage
6. Switch to Idle (also called Charge Off) state
The initial charge guarantees fully charged batteries before switching to the normal operation
state. This allows a much more accurate handling of batteries during the normal system
operation. During start up/initial charge it is not possible to start a battery test. It is also not
possible to cancel or stop the initial charge.
3.2
Idle/Charge Off
The normal operation state is called Idle or Charge Off State. This is the only state, which
allows battery tests.
Page 7 of 9
1/23/2009
Battery Management Manual
3.3
Revision D01
Discharge/Boost Discharge
If the AC fails and the batteries are discharge for more than 1% of their capacity (2Ah for the
example system) the system switches its state to Discharge:
1. AC-Fail
2. Discharge Batteries for more than 1% of their capacity
3. Switch to Discharge State
4. 30min discharge (5Ah discharge)
4. 3hours discharge (60Ah discharge)
system Voltage follows the battery Voltage
system Voltage follows the battery Voltage
5. Stay in discharge state
5. Switch to boost discharge state
If the discharge is greater than 10% of the overall capacity of the batteries the system will
switch to boost discharge state.
3.4
Charge/Boost Charge
On AC back, the system will switch to the charge or boost charge state. This depends on the
state reached within discharge cycle.
1. AC back switch to charge state
2. Increase Voltage until charge limit
reached constant current
3. During charging batteries the voltage
raising until the set Voltage of 54.5V
reached (without violating the charge limit)
changing to state constant voltage
is
is
is
4. Stay for 2 hours (charge time) in constant
Voltage
5. Switch to Idle (also called Charge Off)
state
1. AC back switch to boost charge state
2. Increase Voltage until charge limit is
reached constant current
3. During charging batteries the voltage is
raising until the Boost set Voltage of 54.5V
plus Boost Offset (user settable) is reached
(without violating the charge limit)
changing to state constant voltage
4. Stay for 3 hours (boost charge time) in
constant Voltage
5. Switch to Idle (also called Charge Off)
state
If not required, the complete boost discharge and charge handling can be disabled. If
disabled, only the normal discharge and charge handling is used.
Page 8 of 9
1/23/2009
Battery Management Manual
3.5
Revision D01
Battery Test
A Battery Test simulates an AC fail and measures the related data:
Test Start Time
Test Duration
Average Current
Average Temperature
Discharged Ah
Test End-Voltage
With the measured data and the user provided test thresholds (Duration, Ah to discharge, Fail
Voltage, Warning Voltage) a result is calculated.
1. Start Battery Test
2. Rectifier Voltage is decreased down to -40V simulates an AC fail
3. From now on the handling (discharge and charge) is completely the same as if a real
AC fail occurs.
Since there is no difference in battery handling between a Battery Test and a real AC fail,
each AC fail triggers a Battery Test, a so-called AC-Fail Test. There is only one difference
between a real Battery Test and an AC-Fail Test: if the AC supply is back during an AC-Fail
Test, the test is countered as stopped with no valid result.
Page 9 of 9
1/23/2009
You might also like
- Battery Management Manual FPRA D01Document9 pagesBattery Management Manual FPRA D01Fuerza GarciaNo ratings yet
- Battery Management Manual For Flexi Power Rectifier Rev AADocument9 pagesBattery Management Manual For Flexi Power Rectifier Rev AAEduardoUruetaNo ratings yet
- Battery Management Manual For Flexi Power Rectifier Rev ABDocument9 pagesBattery Management Manual For Flexi Power Rectifier Rev ABGömbicz GergelyNo ratings yet
- Sect 1Document30 pagesSect 1Sry SantosNo ratings yet
- 7S To 16S ANT BMS - NewDocument11 pages7S To 16S ANT BMS - Newjuut kluwutNo ratings yet
- Manual Td2310tu, Td2410tuDocument12 pagesManual Td2310tu, Td2410tujnsosa3No ratings yet
- Spec Rfnt3Document12 pagesSpec Rfnt3mimikajaNo ratings yet
- Ecco LD2420C Solar Controller ManualDocument26 pagesEcco LD2420C Solar Controller ManualpillaydanNo ratings yet
- Thyrotronic 07-02Document8 pagesThyrotronic 07-02Hillary Mcgowan100% (1)
- Edoc-Experiences Battery Capacity TestingDocument6 pagesEdoc-Experiences Battery Capacity TestingEl Comedor BenedictNo ratings yet
- Battery Charger Termination Issues With System Load Applied Across Battery While ChargingDocument5 pagesBattery Charger Termination Issues With System Load Applied Across Battery While ChargingBOLFRANo ratings yet
- Dead Ship Start-Up and Black Out Re-Start Procedures 4059-KA-00289231 - D - 02 Docx IMAM REVDocument16 pagesDead Ship Start-Up and Black Out Re-Start Procedures 4059-KA-00289231 - D - 02 Docx IMAM REVarviel_lea3150% (2)
- Starting Solutions: Solid-State Controllers vs. Electromechanical StartersDocument10 pagesStarting Solutions: Solid-State Controllers vs. Electromechanical StartersDavid PovedaNo ratings yet
- Provozní Mody - Guidance For Operation Modes of The SPH Series InverterDocument9 pagesProvozní Mody - Guidance For Operation Modes of The SPH Series InverterLadislav BreckaNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: Intelligent Solar Charge ControllerDocument12 pagesUser's Manual: Intelligent Solar Charge Controllerjean1884No ratings yet
- Ec 2Document20 pagesEc 2susmitamandali100% (1)
- USB Intelligent Electronic Load Tester: . IntroductionDocument13 pagesUSB Intelligent Electronic Load Tester: . IntroductionRakan HijazeenNo ratings yet
- Designing An Excitation System: Example #1 - A Simple Standby GeneratorDocument25 pagesDesigning An Excitation System: Example #1 - A Simple Standby Generatorparatonerq0% (1)
- HZFD 400 Battery Charge and Discharge TesterDocument17 pagesHZFD 400 Battery Charge and Discharge TesterMohammed A. AliNo ratings yet
- Designing An Excitation SystemDocument24 pagesDesigning An Excitation SystemMohamed RashidNo ratings yet
- Electrical Enclosures ClassDocument6 pagesElectrical Enclosures ClassFahmy FaizalNo ratings yet
- Operation & Maintenance Manual: For Khartoum North Power Station-Phase Iii (2×100Mw) ProjectDocument33 pagesOperation & Maintenance Manual: For Khartoum North Power Station-Phase Iii (2×100Mw) Projectمحمد خالدNo ratings yet
- Generator, Starter, Battery and Spark Plug Repair InstructionsDocument10 pagesGenerator, Starter, Battery and Spark Plug Repair InstructionsSoporte Tecnico AutoMotrixNo ratings yet
- Load Shedding Philosophy ExplainedDocument35 pagesLoad Shedding Philosophy Explainedchinnarao100% (1)
- Enhanced Blackout Recovery TestingDocument15 pagesEnhanced Blackout Recovery TestingXa MauNo ratings yet
- BCSW ChargerDocument12 pagesBCSW ChargermatoyNo ratings yet
- 4 - 5 1553 BMP 903051 DirectionsForUse Uen BDocument18 pages4 - 5 1553 BMP 903051 DirectionsForUse Uen BDmitrij sovetowNo ratings yet
- Ups Testing ReportDocument3 pagesUps Testing Reportharigopalk12No ratings yet
- TWM Basic Steps To Acquire Power and AMPS DataDocument35 pagesTWM Basic Steps To Acquire Power and AMPS DataVahidNo ratings yet
- 10.chapter 2Document14 pages10.chapter 2hsushweyi tint28No ratings yet
- Cruise Control System Software DevelopmentDocument14 pagesCruise Control System Software DevelopmentMinh-Ha LeNo ratings yet
- RD510 Battery Tester User ManualDocument18 pagesRD510 Battery Tester User ManualZeckNo ratings yet
- Pump Performance Test Procedure Sheet 3Document4 pagesPump Performance Test Procedure Sheet 3renjithv_4No ratings yet
- Manual For Model Mp300 To Mp700 Electric Motor Driven Fire Pump ControllersDocument25 pagesManual For Model Mp300 To Mp700 Electric Motor Driven Fire Pump ControllersJoel CarranzaNo ratings yet
- Testing and Commissioning of Substation DC SystemDocument4 pagesTesting and Commissioning of Substation DC Systemjob_pNo ratings yet
- Manual CMP45Document10 pagesManual CMP45Mickael SoaresNo ratings yet
- QPS Battery Rejuvenator BattReLIFEDocument5 pagesQPS Battery Rejuvenator BattReLIFEFrazer TownNo ratings yet
- Diesel Electric Drives GuidelineDocument6 pagesDiesel Electric Drives GuidelineSegneanu Marinica-iulianNo ratings yet
- Boiler Light UpDocument86 pagesBoiler Light Upmoovendan pNo ratings yet
- Charging System Troubleshooting (1406) : Instrucción EspecialDocument16 pagesCharging System Troubleshooting (1406) : Instrucción EspecialMiguel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Testing of Emergency Generator: Procedure For Battery StartDocument5 pagesTesting of Emergency Generator: Procedure For Battery Startმარიამ აბაშიძეNo ratings yet
- Testing of Emergency Generator: Procedure For Battery StartDocument5 pagesTesting of Emergency Generator: Procedure For Battery Startმარიამ აბაშიძეNo ratings yet
- Relay Protection DataDocument14 pagesRelay Protection DataNaveen GuptaNo ratings yet
- Blue Smart IP22 Charger-EnDocument30 pagesBlue Smart IP22 Charger-EnnereoreiserNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual for dc Brake UnitsDocument11 pagesInstallation Manual for dc Brake Unitsprasiva@04No ratings yet
- Chrysler Dakota Part7Document24 pagesChrysler Dakota Part7Sašo Brunšek-BrunoNo ratings yet
- Parallel OperatingDocument10 pagesParallel Operatinglinkangjun0621No ratings yet
- C653/C653A and C625 Alternator Troubleshooting GuideDocument12 pagesC653/C653A and C625 Alternator Troubleshooting GuideAldo CuadraNo ratings yet
- Profitec 2000 S Battery Charger For Secured DC Power SuppliesDocument36 pagesProfitec 2000 S Battery Charger For Secured DC Power SuppliesdinkoheNo ratings yet
- Power and Battery Plant CoordinationDocument6 pagesPower and Battery Plant Coordinationdeepthik27No ratings yet
- Cruze Charging System GuideDocument8 pagesCruze Charging System Guidelibardo hurtadoNo ratings yet
- SEBU7789-00 - Operation & Maintenance, Service InformationDocument5 pagesSEBU7789-00 - Operation & Maintenance, Service InformationSayed Younis SadaatNo ratings yet
- Motor Protective RelaysDocument26 pagesMotor Protective RelayssrindiraNo ratings yet
- Fluke Battery BankDocument4 pagesFluke Battery BankEdmund Yoong100% (1)
- 500 Series Troubleshooting GuideDocument8 pages500 Series Troubleshooting Guideengineassembly100% (1)
- Q6 Pro: Smart Charger Operating InstructionsDocument18 pagesQ6 Pro: Smart Charger Operating InstructionsDeen OsmNo ratings yet
- Battery Charger Testing MethodsDocument6 pagesBattery Charger Testing Methodsmathew_john0077393No ratings yet
- Practical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsFrom EverandPractical Guides to Testing and Commissioning of Mechanical, Electrical and Plumbing (Mep) InstallationsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Upgrade RadioDocument1 pageUpgrade RadiomaximoNo ratings yet
- 500 DS3 - DSheet Flatpack2 Rectifier - 48 4000W Dual - v3 PDFDocument2 pages500 DS3 - DSheet Flatpack2 Rectifier - 48 4000W Dual - v3 PDFmaximoNo ratings yet
- Smartpack (DS-242100.100.DS3-1-7) .APR.09Document2 pagesSmartpack (DS-242100.100.DS3-1-7) .APR.09samsungaceplusNo ratings yet
- Flatpack2 Cabinetized 96kwDocument2 pagesFlatpack2 Cabinetized 96kwKelvinVelasquezPascualNo ratings yet
- FPRA Site Star Installation Guide NokiaDocument94 pagesFPRA Site Star Installation Guide NokiamaximoNo ratings yet
- Flatpack 2 Integrated SystemsDocument2 pagesFlatpack 2 Integrated SystemsNdambuki DicksonNo ratings yet
- 100 DS3 - DSheet Flatpack2 Rectifier - 48 3kW - v2Document2 pages100 DS3 - DSheet Flatpack2 Rectifier - 48 3kW - v2Raul Guevara AscanNo ratings yet
- Sral XD 1292918Document10 pagesSral XD 1292918Bader NammurNo ratings yet
- Product Sheet & Instruction Manual: Cimmic™ Cdi 0.1 Ml Disk (Carbonyldiimidazole) (2 Μm Channels) - Pack Of 3Document5 pagesProduct Sheet & Instruction Manual: Cimmic™ Cdi 0.1 Ml Disk (Carbonyldiimidazole) (2 Μm Channels) - Pack Of 3Antonio MoncayoNo ratings yet
- Control Aveo1Document42 pagesControl Aveo1carlosNo ratings yet
- Kampus Merdeka BelajarDocument17 pagesKampus Merdeka BelajarmartinNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Devices at Home: Science 8Document5 pagesElectrical Safety Devices at Home: Science 8John Mark PrestozaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Waste Management ArticleDocument5 pagesHospital Waste Management ArticleFarrukh AzizNo ratings yet
- International Humanitarian Law - Atty. Mercado (July 2016)Document77 pagesInternational Humanitarian Law - Atty. Mercado (July 2016)MiroNo ratings yet
- ISI Statistical Data PurchaseDocument2 pagesISI Statistical Data Purchasevishal_mtoNo ratings yet
- Mcgee-Vodou and Voodoo in SR PDFDocument28 pagesMcgee-Vodou and Voodoo in SR PDFtakne_007No ratings yet
- Conceptual SellingDocument53 pagesConceptual SellingshrundNo ratings yet
- Pearson Magazine Mysterious MummyDocument16 pagesPearson Magazine Mysterious Mummymark_schwartz_41No ratings yet
- Fatimah Az-ZahraDocument10 pagesFatimah Az-ZahraYahya AliNo ratings yet
- Zabbix Manual 1.8.1Document143 pagesZabbix Manual 1.8.1fjrialNo ratings yet
- Architecture: By: Kristanto (170406146) Dosen: Ir. Rudolf Sitorus, MlaDocument15 pagesArchitecture: By: Kristanto (170406146) Dosen: Ir. Rudolf Sitorus, MlakristantoNo ratings yet
- Lower Fungi ClassificationDocument40 pagesLower Fungi ClassificationAsfi Raian OmeNo ratings yet
- Vezo Knowledge: Traditional Ecological Knowledge in Andavadoaka, Southwest Madagascar - 2006Document73 pagesVezo Knowledge: Traditional Ecological Knowledge in Andavadoaka, Southwest Madagascar - 2006HayZara MadagascarNo ratings yet
- 2012 11 Fluoropolymers_Safe_Hand_ENDocument29 pages2012 11 Fluoropolymers_Safe_Hand_ENsamNo ratings yet
- Removal of Sulfide and COD From A Crude Oil Wastewater Model by Aluminum and Iron ElectrocoagulationDocument4 pagesRemoval of Sulfide and COD From A Crude Oil Wastewater Model by Aluminum and Iron ElectrocoagulationEhab DheyaaNo ratings yet
- Reverse Logistics Implementation in The Construction Industry: Paper Waste FocusDocument9 pagesReverse Logistics Implementation in The Construction Industry: Paper Waste FocusSamuel YuliusNo ratings yet
- Leadership Styles of ManagersDocument16 pagesLeadership Styles of ManagersmuzammelNo ratings yet
- Chapter3-Registration of Business EntitiesDocument28 pagesChapter3-Registration of Business EntitiesEncik ComotNo ratings yet
- David Mind DARK PSYCHOLOGY MASTERY - 3 Books in 1 - Dark Psychology How To Analyze People The Art of MDocument581 pagesDavid Mind DARK PSYCHOLOGY MASTERY - 3 Books in 1 - Dark Psychology How To Analyze People The Art of Mmonikaxd100% (1)
- 004 September 5, 2023 ARTS Q1 W1aDocument3 pages004 September 5, 2023 ARTS Q1 W1aJullene TunguiaNo ratings yet
- Cello BachDocument3 pagesCello BachPera PericNo ratings yet
- Bbg3 AnswersDocument123 pagesBbg3 AnswersAbraham Castro JuarezNo ratings yet
- Landscape WHLP in AP June 2021 1st WeekDocument1 pageLandscape WHLP in AP June 2021 1st WeekVERONICA SINGSONNo ratings yet
- Language styles in movie scriptsDocument13 pagesLanguage styles in movie scriptsVebriati Lelyana ManurungNo ratings yet
- Soal BHS Dan Sastra Inggris - Xii 2020Document9 pagesSoal BHS Dan Sastra Inggris - Xii 2020laroibafiNo ratings yet
- Shona Made Easy: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument25 pagesShona Made Easy: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleInnocent Clifford Marandu100% (1)
- La Moneda y Papel Moneda en Los Campos de ConcentraciónDocument68 pagesLa Moneda y Papel Moneda en Los Campos de ConcentraciónGildardo Adolfo TovarNo ratings yet
- CAF (ICAP) Daniyal Agha resumeDocument2 pagesCAF (ICAP) Daniyal Agha resumeDaniyal AghaNo ratings yet