Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GGGGGGGGGGGGG Noo
Uploaded by
Bahi Al BossOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GGGGGGGGGGGGG Noo
Uploaded by
Bahi Al BossCopyright:
Available Formats
No.
of Pages: (A)
No. of Questions:
8
38
EC1001 A
vv
MIDSUMMER EXAMINATIONS 2008
Subject
ECONOMICS
Title of Paper
EC1001 MACROECONOMICS
Time Allowed
Two Hours (2 Hours)
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Instructions to candidates
This paper is in two sections. Students should attempt ALL the questions in Section A and ONE in Section
B. The maximum mark awarded for Section A is 69 marks. The maximum mark awarded for Section B is 33
marks. The maximum mark for the entire paper is 100 (any marks over 100 are disregarded).
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
SECTION A: Multiple Choice
All questions should be attempted. Use the answer sheet provided to record the one response you believe to
be the most appropriate for each question.
The marking scheme is the following. 3/(1.35) marks (this is 3 divided by 1.35) for each
right answer, -1/(1.35) marks (this is 1 negative mark divided by 1.35) for each wrong
answer, and Zero mark if no answer is given.
1. The 2002 CPI was 177 and the 1982 CPI was 96.5. If your parents put aside 1,000 for you in 1982, how
much would you have needed in 2002 in order to buy what you could have with the 1,000 in 1982?
a. 1,834.20
b. 1,777.77
c. 1,714.81
d. None of the above are correct.
2. A difference in wages that offsets differences in the nonpay features of two jobs is called
a. a compensating differential.
b. a wage adjustment.
c. an efficiency wage.
d. a minimum wage.
EC1001 A - Macroeconomics I
EC1001 A
Use the figure below for the following questions.
Figure 17-1
3. Refer to Figure 17-1. If the money supply is MS2 and the value of money is 2, there is excess
a. demand equal to the distance between A and C.
b. demand equal to the distance between A and B.
c. supply equal to the distance between A and C.
d. supply equal to the distance between A and B.
4. If the Bank of England decides to sell 10 million in securities and the Paris National Bank writes out a
10 million check to purchase these securities, then the
a. Paris National Bank now has 10 million more of excess reserves at the Bank of England.
b. Paris National Bank now has 10 million fewer reserves at the Bank of England.
c. Bank of England has increased its asset position by 20 million.
d. money supply has increased.
5. Which of the following is the most liquid asset?
a. capital goods
b. stocks and bonds with a low risk
c. stocks and bonds with a high risk
d. funds in a checking account
6. You want to have $100,000 in five years. If the interest rate is 8 percent, about how much do you need to
save today?
a. $66,225.25
b. $67,556.42
c. $68,058.32
d. $71,428.57
7. An open market purchase occurs when
a. the Bank of England buys government securities from a bank.
b. a bank buys government securities from the Bank of England.
c. a securities dealer buys shards of stock from the Bank of England.
d. the Treasury buys government securities from the Bank of England.
EC1001 A - Macroeconomics I
EC1001 A
8. Suppose the real exchange rate is 1/2 gallon of Canadian gasoline per gallon of U.S. gasoline, a gallon of
U.S. gasoline costs $1.50 U.S., and a gallon of Canadian gas costs $3.90 Canadian. What is the nominal
exchange rate?
a. .385 Canadian dollars per U.S. dollar
b. .65 Canadian dollars per U.S. dollar
c. 1.30 Canadian dollars per U.S. dollar
d. None of the above is correct.
9. A high proportion of the population under the age of 15 undermines economic growth because
a. the young require more infrastructure than older people.
b. the young require more capital goods than older people.
c. they present such a huge increase in human capital.
d. the young consume but they do not produce.
10. The country of Hykania does not trade with any other country. Its GDP is $20 billion. Its government
purchases $3 billion worth of goods and services each year, collects $3 billion in taxes, and provides $2
billion in transfer payments to households. Private saving in Hyrkania is $4 billion. What is investment in
Hyrkania?
a. $4 billion
b. $3 billion
c. $2 billion
d. There is not enough information to answer the question.
11. Suppose that the price of a bond is equal to the sum of the present value of its payments. Suppose further
that the bond pays $50 today and $1,050 one year from today. What is the price of this bond if the interest
rate is 5 percent?
a. $1,100.00
b. $1,050.00
c. $1,047.62
d. $945.35
12. Which of the following shifts short-run, but not long-run aggregate supply right?
a. a decrease in the price level
b. a decrease in the expected price level
c. a decrease in the capital stock
d. an increase in the money supply
13. In the long run when money is neutral, which of the following increases when the money supply growth
rate increases?
a. real output growth
b. real interest rates
c. nominal interest rates
d. the money supply divided by the price level
EC1001 A - Macroeconomics I
EC1001 A
14. You put money in an account and earn a real interest rate of 6 percent, inflation is 2 percent, and your
marginal tax rate is 20 percent. What is your after-tax real rate of interest?
a. 4.8 percent
b. 3.2 percent
c. 2.8 percent
d. None of the above is correct.
15. The wealth effect, interest rate effect, and foreign trade effect all explain why the aggregate
a. supply curve is horizontal.
b. supply curve is vertical.
c. supply curve is upward sloping.
d. demand curve is downward sloping.
16. In the 1800s, Europeans purchased stock in American companies who used the funds to build railroads
and factories. The Europeans made
a. foreign portfolio investments.
b. indirect domestic investments.
c. foreign direct investments.
d. foreign indirect investments.
17. Which of the following is correct?
a. Stocks, bonds, and deposits are all similar in that each provides a medium of exchange
b. Banks lend mostly to large and familiar companies rather than smaller local firms.
c. Banks charge borrowers a slightly lower interest rate than they pay to depositors.
d. None of the above are correct.
18. The multiplier effect is the multiplied impact on
a. the money supply of a given increase in government purchases.
b. tax revenues of a given increase in government purchases.
c. investment of a given increase in interest rates.
d. aggregate demand of a given increase in government purchases.
19. Suppose that France imposed an import quota on beef. Sales of French beef producers would
a. rise and exports of other industries would increase.
b. rise and exports of other industries would decline.
c. not change, exports of other industries would increase.
d. not change, exports of other industries would decline.
EC1001 A - Macroeconomics I
EC1001 A
Figure 19-2
20. Refer to Figure 19-2. This figure depicts labor demand and supply in a nonunionized labor market. The
original equilibrium is at point A. If a labor union subsequently establishes a union shop and negotiates an
hourly wage of $20, then there will be an excess
a. supply of 3,000 workers.
b. demand of 7,000 workers.
c. supply of 4,000 workers.
d. supply of 7,000 workers.
21. The idea of paying workers an efficiency wage is that
a. doing so is more efficient than paying them the market wage.
b. paying workers less gives them the incentive to work harder.
c. workers and management gain at the expense of the stockholders of the company.
d. workers have the incentive to do high-quality work.
22. Ruth collected Social Security payments of $220 a month in 1985. If the price index rose from 90 to 105
during 1985 her Social Security payments for 1986 should have been about
a. $252.43.
b. $253.00.
c. $256.67.
d. None of the above are correct.
EC1001 A - Macroeconomics I
EC1001 A
Use the pair of diagrams below to answer the following questions.
Figure 22-1
23. Refer to Figure 22-1. If the economy starts at c and 1, then in the short run, a decrease in the money
supply growth rate moves the economy to
a. e and 1.
b. d and 2.
c. d and 3.
d. None of the above is correct.
24. At which interest rate is the present value of $360 three years from today equal to about $320 today?
a. 4 percent
b. 4.5 percent
c. 5 percent
d. 5.5 percent
25. Jack and Jill are co-owners of the U.S. firm Wells Petroleum. Jack borrows money to build an oil well in
Texas. Jill borrows money to build an oil well in Venezuela.
a. Both Jack and Jill's purchase of capital count as demand for loanable funds in the U.S.
market.
b. Neither Jack nor Jill's purchase of capital count as demand for loanable funds in the U.S.
market.
c. Jack's purchase of capital counts as demand for loanable funds in the U.S. market; Jill's
purchase does not.
d. Jill's purchase of capital counts as demand for loanable funds in the U.S. market; Jack's
purchase does not.
26. Aggregate demand would shift right if either
a. the price level decreased, or government expenditures increased.
b. the price level decreased, or the government instituted an investment tax credit.
c. government expenditures or the money supply increased.
d. All of the above are correct.
27. The national debt
a. can be paid off without major economic effects.
b. need never be paid off.
c. is no more serious a problem than is a corporation's debt.
d. should not exist during a period of economic prosperity.
6
EC1001 A - Macroeconomics I
EC1001 A
28. Ceteris paribus, as the price level falls, a country's exchange rate
a. and interest rates rise.
b. and interest rates fall.
c. fall and interest rates rise.
d. rise and interest rates fall.
29. Vertical equity in taxation refers to the idea that people
a. in unequal conditions should be treated differently.
b. in equal conditions should pay equal taxes.
c. should be taxed according to their age and experience.
d. should receive government benefits according to how much they have been taxed.
30. The exchange rate is about 153 Kazakhstan tenge per dollar. According to purchasing-power parity, this
exchange rate would rise if
a. the price level in either the United States or Kazakhstan rose.
b. the price level in either the United States or Kazakhstan fell.
c. the price level in the United States rose or the price level in Kasakhstan fell.
d. the price level in the United States fell or the price level in Kasakhstan rose.
31. According to purchasing-power parity theory, if a McDonald's Big Mac cost $2.50 in the United States
and 5 euros in France, then the nominal exchange rate should be
a. 2 euros per dollar.
b. 1euro per dollar.
c. 1/2 euro per dollar.
d. None of the above is correct.
32. Kramer's Frozen Sandwiches is thinking of building a new warehouse. They believe that this will given
them $50,000 of additional revenue at the end of one year, $60,000 additional revenue at the end of two
years, and $70,000 in additional revenue at the end of three years. If the interest rate is 5 percent, they
would be willing to pay
a. $140,000, but not $150,000.
b. $150,000, but not $160,000.
c. $160,000, but not $170,000.
d. $170,000, but not $180,000.
33. Which of the following shifts aggregate demand right?
a. The price level rises.
b. The price level falls.
c. The money supply falls.
d. None of the above is correct.
34. Which list contains only actions that increase the money supply?
a. raise the discount rate, make open market purchases
b. raise the discount rate, make open market sales
c. lower the discount rate, make open market purchases
d. lower the discount rate, make open market sales
EC1001 A - Macroeconomics I
EC1001 A
SECTION B
Answer one and only one of the questions numbered 35 to 38. The maximum number of marks awarded for
this Section is 33.
35. Answer both (a) and (b)
(a) Demonstrate that whether you would prefer to have $225 today or wait five years for $300 depends on
the interest rate. Show your work.
(b) As the interest rate increases, what happens to the present value of a future payment? Explain why
changes in the interest rate will lead to changes in the quantity of loanable funds demanded and
investment spending.
36. Answer both (a) and (b).
(a) Suppose that velocity and output are constant and that the quantity theory and the Fisher effect both
hold. What happens to inflation, real interest rates, and nominal interest rates when the money supply
growth rate increases from 5 percent to 10 percent?
(b) Suppose that a country has $120 billion of national savings, and $80 billion of domestic investment. Is
this possible? Where did the other $40 billion of national savings go?
37. Suppose the UK independence party wins a general election and institutes a "Buy British" campaign, in
order to encourage spending on domestic goods. What effect will this have on the UK trade balance?
Describe carefully your argument.
38. GDP is defined as the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given
period of time. In spite of this definition, some production is left out of GDP. Give some examples of such
goods; explain why some final goods and services are not included, and carefully consider the difficulties
in including them.
ID: A
vv
Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
29.
30.
31.
32.
33.
34.
A
A
D
B
D
C
A
C
D
C
B
B
C
D
D
A
D
D
B
D
D
C
C
A
A
C
B
B
A
D
A
C
D
C
ID: A
SHORT ANSWER
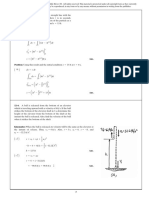
35. (a) For example at 3 percent the present value of $300 in five years is $300/(1.03) 5 = $258.78 but at 7
percent the present value of $300 in five years is $300/(1.07) 5 = $213.90.
(b) An increase in the interest rate reduces the present value of future payments. Investment spending is
the purchasing of capital goods that are expected to raise future revenues. When interest rates rise, the
present value of these future revenues decline so that fewer capital expenditures are likely to generate
enough revenue to justify their price.
36.
(a) Inflation and nominal interest rates each increase by 5 percent points. There is no change in the real
interest rate or any other real variable.
(b) This is possible for an open economy. The remaining $40 billion is for net capital outflow in the form
of purchases of foreign assets by U.S. residents. U.S. citizens can saving by buying U.S. assets or by
buying foreign assets.
37. Such a campaign will increase the demand for domestically produced goods and hence decrease the
demand for imports. This increases the demand for dollars in the market for foreign currency. The real
exchange rate of the U.S. dollar will appreciate, and the net effect will be no change in the trade balance.
The level of net exports ultimately depends upon domestic saving and investment, neither of which are
affected by the campaign.
38. GDP excludes some products because they are so difficult to measure. These products include services
performed by individuals for themselves and their families, and most goods that are produced and
consumed at home and, therefore, never enter the marketplace. In addition, illegal products are not
included in GDP even if they can be measured because, by society's definition, they are bads, not goods.
You might also like
- Dessler Hrm13 Inppt01 GeDocument31 pagesDessler Hrm13 Inppt01 GeBahi Al BossNo ratings yet
- Dessler Hrm13 Inppt06 GeDocument34 pagesDessler Hrm13 Inppt06 GeBahi Al BossNo ratings yet
- The Secret To Employee Motivation: Done By: Mishal Alsaud Id: 210110235Document13 pagesThe Secret To Employee Motivation: Done By: Mishal Alsaud Id: 210110235Bahi Al BossNo ratings yet
- AVM 430 - Semester 152 - 2nd Midterm SlidesDocument38 pagesAVM 430 - Semester 152 - 2nd Midterm SlidesBahi Al BossNo ratings yet
- AVM 370 - Chapter 1Document33 pagesAVM 370 - Chapter 1Bahi Al BossNo ratings yet
- Dessler HRMDocument42 pagesDessler HRMNisaNabilaRiadiniNo ratings yet
- Sect 40Document1 pageSect 40Bahi Al BossNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- VISIONARCHDocument3 pagesVISIONARCHJHON YDUR REMEGIONo ratings yet
- Practical Approach To Practice 5SDocument4 pagesPractical Approach To Practice 5SNikola DjorovicNo ratings yet
- Factors for Marketing Success in Housing SectorDocument56 pagesFactors for Marketing Success in Housing SectorNhyiraba Okodie AdamsNo ratings yet
- Presentacion ISA Graphic Febrero 2015Document28 pagesPresentacion ISA Graphic Febrero 2015Ileana ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Science Room Rules Teaching PlanDocument1 pageScience Room Rules Teaching PlanraqibsheenaNo ratings yet
- Manual Filmadora Panasonic Dvc20pDocument42 pagesManual Filmadora Panasonic Dvc20pWilhan Jose GomesNo ratings yet
- Emergency Incidents AssignmentDocument4 pagesEmergency Incidents Assignmentnickoh28No ratings yet
- Uuee 17-2020Document135 pagesUuee 17-2020Tweed3ANo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Water Supply SchemeDocument126 pagesDesign and Construction of Water Supply SchemeShreyansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Software Process & Quality Management: Six SigmaDocument26 pagesSoftware Process & Quality Management: Six SigmaPhu Phan ThanhNo ratings yet
- Valve Position Monitors: APL 5 Series CSA Approved Type 4X/6Document12 pagesValve Position Monitors: APL 5 Series CSA Approved Type 4X/6Torres Toledo JttNo ratings yet
- Shear Stress ProblemsDocument5 pagesShear Stress ProblemsNoven VillaberNo ratings yet
- Service Level ManagementDocument8 pagesService Level Managementrashmib1980No ratings yet
- Essay 5 Practice Activities - DBS IntroductionsDocument6 pagesEssay 5 Practice Activities - DBS IntroductionsLeyla IsayevaNo ratings yet
- MAINTENANCE AND RELIABILITY ENGINEERING - Lecture 1Document24 pagesMAINTENANCE AND RELIABILITY ENGINEERING - Lecture 1K ULAGANATHANNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Global Business 2nd Edition Gaspar Test BankDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Global Business 2nd Edition Gaspar Test BankJerryGarrettmwsi100% (56)
- Project Report On PepsiDocument87 pagesProject Report On PepsiPawan MeenaNo ratings yet
- SMB GistDocument7 pagesSMB GistN. R. BhartiNo ratings yet
- Dyna PDFDocument12 pagesDyna PDFVernadette VenturaNo ratings yet
- TOTO Indonesia Sanitary CatalogDocument40 pagesTOTO Indonesia Sanitary CatalogiaqistiNo ratings yet
- QUIZ - FinalsDocument5 pagesQUIZ - FinalsFelsie Jane PenasoNo ratings yet
- 4563Document58 pages4563nikosNo ratings yet
- Comparison Between India and ChinaDocument92 pagesComparison Between India and Chinaapi-3710029100% (3)
- Why Delegate Authority and Empower EmployeesDocument5 pagesWhy Delegate Authority and Empower EmployeesHarold MaribojocNo ratings yet
- Vda. de Villanueva vs. JuicoDocument3 pagesVda. de Villanueva vs. JuicoLucas Gabriel Johnson100% (1)
- Design of Masonary Retaining Wall - SteppedDocument3 pagesDesign of Masonary Retaining Wall - Steppedmeenu100% (1)
- Motor Protection and Monitoring Catalog Ca08100006eDocument116 pagesMotor Protection and Monitoring Catalog Ca08100006eraniaNo ratings yet
- AcctIS10E - Ch04 - CE - PART 1 - FOR CLASSDocument32 pagesAcctIS10E - Ch04 - CE - PART 1 - FOR CLASSLance CaveNo ratings yet
- Specifications For Metro Ethernet 13-Sdms-10Document30 pagesSpecifications For Metro Ethernet 13-Sdms-10ashrafNo ratings yet
- Prova ScrumDocument11 pagesProva ScrumJoanna de Cassia ValadaresNo ratings yet