Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ansi ST Entrance Syllabus
Uploaded by
Shoaib Shaikh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesNSI kanpur entrance syllabus for chemical engineers
Original Title
Ansi St Entrance Syllabus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNSI kanpur entrance syllabus for chemical engineers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views4 pagesAnsi ST Entrance Syllabus
Uploaded by
Shoaib ShaikhNSI kanpur entrance syllabus for chemical engineers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
SYLLABUS FOR ENTRANCE EXAMINATION
A.N.S.I. (SUGAR TECHNOLOGY) COURSE-2016 MATHEMATICS SECTION A
1 ALGEBRA AND TRIGONOMETRY Group, Permutation groups , Subgroups, Centre and
Normalizer, Cyclic groups, Coset decomposition, Lagranges theorem, Homomorphism and
Isomorphism, Cayleys theorem , Normal Subgroups, Quotint group, Fundamental theorem of
Homomorphism, Sequence and its convergence, Convergence of infinite series, Comparison test,
Ratio test, Root test, Raabes test, Logarithmic test. Alternating series, Leivnitz test, Absolute and
conditional convergence.
Complex functions, Seperation into real and imaginary parts, Exponential, Direct and inverse
trigonometric and Hyperbolic functions, Logarithmic functions.
2 MATRICES- Addition and multiplications, elementary row and column operations, rank
determination, solution of system of linear equations, Eigen values and Eigen vectors, CayleyHamilton theorem.
3 CALCULUS- Standard functions, limits. Continuity, properties of continuous functions in closed
intervals, differentiability. Mean Value theorem, Taylors theorem. Maxima and Minima, properties
of tangent and normal, curvature, asymptotes, double points, points of inflexion and tracing,
Fundamental theorem of integral calculus, method of integration, Rectification, Quadrature, volume
and surface of solids of revolution. Partial differentiation and its application. Double and Triple
integration, Application of area, volume, centre of mass, moments of inertia etc. Simple test of
convergence of series of positive term, alternating series and absolute convergence.
4 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS-Ordinary differential equations of first order, singular solutions,
geometrical interpretations, linear differential equations with constant coefficients.
5 GEOMETRY-Analytical Geometry of straight lines and conics referred to Cartesian and Polar
coordinates. Three dimensional geometry for planes, straight lines.
6 MECHANICS- Velocity and acceleration along radial and transverse direction and along
tangential and normal directions. Simple Harmonic Motion, Inverse Square Law, Projectiles
.Common centenary and centre of Gravity.
7 MATHEMATICAL STATISTICS- Discrete and continuous distributions (Binomial, Poissons
and Normal Distributions), Moments, Correlation and simple linear Regression.
8. VECTOR ALGEBRA AND VECTOR CALCULUS- Vector addition, scalar multiplication and
vector multiplication (multiplication of three and four vectors also), applications in geometry, vector
Differentiation, Gradient, Divergence and curl and their applications.
CHEMISTRY SECTION- B GENERAL & PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY
1. Chemical equilibrium- Homogeneous and heterogeneous system, equilibrium constant, effect of
temperature on equilibrium constant; Law of mass action ; definition, verification and its application
to simple homogeneous and heterogeneous systems. Le Chateleir & Brauns Principle, its
application.
2. Colloids General method of preparation, properties and uses of colloids; Lyophillic and
Lyophobic sol, charge on colloidal particles; Stability, protection and coagulation of colloids; Gold
number and its application, Tyndall effect, Brownian Movement.
3. Electrochemistry- Specific, Equivalent and Molar conductivities. Ionic conductance, ionic
mobility, Kohlrausch Law. Transport number and its determination. Solubility of sparingly soluble
salts. Electrode potential and Nernst equation, Reference electrodes, Description and working of
hydrogen and glass electrodes and their use in pH determination. Common ion effect, solubility
product and its application.
4. Chemical Kinetics- Molecularity and order of a reaction, Derivation of rate constant of first and
second order reaction.
5. Catalysis, characteristics, classification, homogeneous, heterogeneous catalysis, enzyme catalysis
and miscellaneous examples.
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
1. Optical and Geometrical isomerism, asymmetric carbon atom, racemisation and resolution of
racemic mixtures, resonance and its application in organic chemistry.
2. Methods of preparation, properties and uses of alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, esters, ethers, amines,
amides, amino acids and proteins.
3. Carbohydrates- Classification, structure of D-glucose and fructose (open and ring structure), interconversion of monosaccharides: aldose to ketose, ketose to aldose, pentose to hexose, hexose to
pentose, Killianis synthesis, Wohls degradation, epimerization. Disaccharides-manufacture of
sucrose, structure and their common reaction, Polysaccharides.
4. Benzene and its structure. Simple reactions of benzene, toluene, phenols, nitro and amino
compounds, benzoic, salicylic, cinnamic & sulphonic acids, aromatic aldehydes and ketones, diazo,
azo compounds, naphthalene, pyridine, thiophene and furan.
5. Orientation and structure of Benzene.
INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
1. Periodic properties- Ionization potential, Electron Affinity, Electro Negativity, Atomic and Ionicradii, hybridization, Polarization.
2. Oxidation states and oxidation number, common oxidizing and reducing agents, ionic equations
and balancing of chemical reactions by oxidation- reduction method.
3. Coordination compounds-double and complex salts, Definition: complex-ion coordination number,
nomenclature. Werners theory of complexes, effective atomic number, stability of complexions,
Stability constant, factors affecting stability, valence bond theory, crystal field theory of complex
compounds, methods of study of complexes.
4. Principles of inorganic chemical analysis.
5. Study of d-Block elements and little bit about Lanthanoid-contraction.
6. Metal Carbonyl and idea of Balk bending.
PHYSICS - SECTION- C 1. MECHANICS and WAVE MOTION:Dynamics of particle in
rectilinear and Circular Motion, Linear and angular momentum. Moment of inertia, theorem of
parallel and perpendicular axes, Rotation energy and rotation inertia for simple bodies, combined
translational and rotational motion of rigid body on horizontal and inclined planes, Relations between
elastic constants, Bending of beam, Torsion of cylinder, Law of gravitation, Keplers laws, Geostationary satellites. Differential equation of Simple harmonic motion, Damped and forced
vibrations,Composition of S.H.M., stationary waves, Phase and group velocity.
2.THERMODYNAMICS:-Equipartition of energy, specific heat of mono-atomic, diatomic and
triatomic gases, adiabatic expansion, Vander Waals gas equation of state, critical constants, JouleThomson expansion, principle of re-generative cooling. Laws of thermodynamics, Carnot cycle,
Carnot theorem, Entropy, thermodynamical scale of temperature, Clausius- Cleyperon equation,
Adiabatic demagnetization, Black body. Stefan-Bolzman Law, Kirchoffs Law, planks law.
3. OPTICS & LASERS: Principle of superposition, Interference, Coherence, Lateral shift of fringes,
localized fringes, thin films. Michelson interferometer, Determination of wave length, Fresnel half
period zones, Straight Edge, Diffraction Grating, Rayleigh criterion of resolution, Polarization,
Double refraction in uniaxial crystals, Nicol Prism, Retardation Plates, Optical Activity, Polarimeter,
its principle and applications, Laser action, population inversion, application of Lasers.
4. Electricity of Magnitism: Growth and decay of current through inductive resistances, charging
and discharging & R-C & RLC circuits, Time constant,Coulombs Law, Electric field and potential
due to uniform charged sphere, Gauss law and its applications, Electric dipole energy of a condenser,
Magnetic field, Magnetic force of a current, Laws of Induction, Faraday and Lenzs Law, Bio-savart
Law, Lorentz force, Mutual and self-induction, Moving Coil Ballistic Galvanometer, Dielectric
constant, Polarization Properties of dia, para and ferromagnetic materials, curie temperature,
Hysteresis.
5. QUANTUM MECHANICS: Photo-electric phenomenon, Compton effect, wave particle duality,
de Broglie matter wave, Heisenberg Uncertainty principle, Schrodinger wave equation, interpretation
of wave function, spectra of hydrogen, continuous x-ray, Mosley Law, X-ray absorption spectra
,Discrete set of electronic energies of molecules.
6. RELATIVITY: Reference systems, Inertial frames, Galilean invariance and conservation laws,
Propagation of light, Michelson-Morley Expt. Lorentz transformation, length contraction, time
dilation, variation of mass with velocity, mass energy equivalence.
7. STATISTICAL PHYSICS: Probability and thermodynamic Probability, Probability and Entropy,
Boltzman Entropy relation, statistical interpretation of second Law of thermodynamic, Bose-Einstein
and Fermi-Dirac distribution.
8. NUCLEAR PHYSICS: Atomic Nuclear and its properties, mass deflect and binding energy,
structure of nuclear, Fission and Fusion.
9. SOLID STATE ELECTRONICS: Semi conductor, p-n junction diode and its characteristics,
Avalanche and zener break down, Rectifier, LED, p-n-p and n-p-n transistors and their
characteristics, curves , Hall effect, Amplifiers, R-C coupled amplifier, common ammeter amplifier,
common-base amplifier and common collector amplifier. Transistor as an oscillator, Hardley
oscillator, FET and MOSFET . Motion of a charged particle in electric and magnetic field, cathode
ray oscillograph.
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING SECTION D
(1) Process Calculation: Law of conservation of mass and energy, Recycle, by pass and purge, its
calculation, degree of freedom analysis. Ideal gas law, Daltons law, Amagats law, Average
molecular weight of gaseous mixture, Vapour pressure, Raoults law and Henrys law.
(2) Thermodynamics: First and second Law of thermodynamics and their application. Equation of
state and thermodynamic properties of ideal Gases and Real system, phase equilibria, fugacity,
mixture properties, chemical reaction equilibria. Maxwell relations, Thermodymic relations, Gibbs
phase rule, Carnot cycle, Enthalpy and Entropy.
(3) Fluid Mechanics and Mechanical Operation: Fluid statics, Newtonian and Non-Newtonian
fluids, Bernoulli equation, flow through pipe line system. Flow meters, Pump and compressors, Flow
through packed and fluidized bed. Size reduction and size reparation filtration, mixing and
agitation.Entrance and exit losses in flow process, Rayleighs method of dimensional analysis,
Buckingham pi theorem.
(4) Heat Transfer: Conduction, convection and radiation, Heat transfer coefficient including
boiling, condensation and evaporation systems , type of heat exchangers and evaporators and their
design, Radiation, Basic laws, Black body and Grey body concepts, Furnaces, their classification,
principle and design criteria.
(5) Mass Transfer and Transport Phenomenon: Ficks Law, Film Penetration and Surface renewal
theories. Momentum heat and mass transfer analogies, distillation, absorption leaching, liquid-liquid
extraction, crystallization, drying, adsorption,
(6) Chemical Reaction Engineering: Theories of reaction rates, single and multiple reactions in
ideal reactors, kinetics of homogeneous reactions, Interpretation of kinetic data.Catalysis and enzyme
catalysis, Transport number, Kohlrauschs law, solubility product, redox reaction. Electrochemical &
concentration cell.
Question paper will consist of Four sections i.e. Mathematics, (weightage 20%), Chemistry
(weightage 40%) & Physics (weightage 20%) & Chemical Engineering (weightage 20%). Each
section will be of equal marks. In each section questions shall be of objective, short answer and
long answer type. Candidates may attempt all the sections.
You might also like
- 40+ law students profilesDocument5 pages40+ law students profilesShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 101 EligDocument36 pages101 EligShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Financial Management of Tamilnadu Water Supply Program - : A Contrarian ExperienceDocument21 pagesFinancial Management of Tamilnadu Water Supply Program - : A Contrarian ExperienceShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Young Professional Policy PDFDocument3 pagesYoung Professional Policy PDFShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Admin - Asst - OBC - 01 - 01 - 19 PDFDocument3 pagesAdmin - Asst - OBC - 01 - 01 - 19 PDFShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Swachch Bharat AbhiyanDocument6 pagesSwachch Bharat AbhiyanShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- BCCL Director Technical PositionDocument4 pagesBCCL Director Technical PositionShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Rejection List IC 08 17915 PDFDocument29 pagesRejection List IC 08 17915 PDFShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Rejection List IC 08 17915 PDFDocument29 pagesRejection List IC 08 17915 PDFShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Proposed Project For Livestock Production - 6Document2 pagesProposed Project For Livestock Production - 6Anonymous yIlaBBQQNo ratings yet
- Asset Register OlichakDocument1 pageAsset Register OlichakShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MGNREGA data availability status for Danapur block in Patna district of BiharDocument1 pageMGNREGA data availability status for Danapur block in Patna district of BiharShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2: Remedial Education in India: Povertyactionlab ORGDocument13 pagesCase Study 2: Remedial Education in India: Povertyactionlab ORGShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Data Tools Participatory Rural Appraisal TechniquesDocument45 pagesData Tools Participatory Rural Appraisal TechniquesShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- IIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATDocument8 pagesIIST PROJECT REPORT FORMATLee SweeneyNo ratings yet
- Rural Self Employment Training InstitutesDocument2 pagesRural Self Employment Training InstitutesShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Growing Opportunities in Dairy FarmingDocument4 pagesGrowing Opportunities in Dairy FarmingShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MPSRLM Report on Poverty AlleviationDocument22 pagesMPSRLM Report on Poverty AlleviationShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- F4 Another Fake DocumentDocument1 pageF4 Another Fake DocumentShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- F3 Another Fake DocumentDocument1 pageF3 Another Fake DocumentShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Baseline Study Interim Report for WCLDocument312 pagesBaseline Study Interim Report for WCLShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- F2 Another Fake DocumentDocument1 pageF2 Another Fake DocumentShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Mandi PresentationDocument12 pagesMandi PresentationShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- NSQFDocument2 pagesNSQFShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Maq Spring04 Calccostofcapital PDFDocument8 pagesMaq Spring04 Calccostofcapital PDFShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Thinking About Poverty: Phase I: Income and Expenditure Based ThinkingDocument9 pagesEvolution of Thinking About Poverty: Phase I: Income and Expenditure Based ThinkingShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Report - Working Group On Institutional Financing WorkingDocument30 pagesReport - Working Group On Institutional Financing WorkingShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Farm Income Statistics in India-RASDocument23 pagesFarm Income Statistics in India-RASShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Business Plan ComparisonDocument1 pageBusiness Plan ComparisonShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Organization Structure & TheoriesDocument18 pagesUnit 1 - Organization Structure & TheoriesShoaib ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Oct. 2, 1962 J. W. M. Steeman 3,056,837: Process For Preparing HexamethylenediamineDocument3 pagesOct. 2, 1962 J. W. M. Steeman 3,056,837: Process For Preparing HexamethylenediaminezibaNo ratings yet
- Patterns of DisruptionDocument34 pagesPatterns of DisruptionFred Nijland0% (1)
- Hydrodesulfurization of Dibenzothiophene On A Como/Al O Catalyst: Reaction Network and KineticsDocument8 pagesHydrodesulfurization of Dibenzothiophene On A Como/Al O Catalyst: Reaction Network and KineticsGrupo de Investigaciones en CatalisisNo ratings yet
- De Sulfur IzationDocument2 pagesDe Sulfur IzationngotrongthucNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Unit Processes and Unit OperationsDocument19 pagesBasic Principles of Unit Processes and Unit OperationsAisyah Murti Condro100% (2)
- Cell Chemistry QuestionsDocument2 pagesCell Chemistry QuestionskevinNo ratings yet
- Effect of H2O2 Concentration on Catalase Reaction RateDocument8 pagesEffect of H2O2 Concentration on Catalase Reaction RateKim-Bảng PhạmNo ratings yet
- M. Curini, F. Epifano, S. Genovese, M.C. Marcotullio, O. Rosati. Ytterbium Triflate-Promoted TandemDocument3 pagesM. Curini, F. Epifano, S. Genovese, M.C. Marcotullio, O. Rosati. Ytterbium Triflate-Promoted TandemMariel MedinaNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic ChamberDocument24 pagesAnaerobic ChamberDip MajumderNo ratings yet
- Ageless Apples (Reaction Rates & Catalysts)Document5 pagesAgeless Apples (Reaction Rates & Catalysts)NihalAbou-GhalyNo ratings yet
- 2nd PU Chemistry Model QP 1Document9 pages2nd PU Chemistry Model QP 1Prasad C M100% (2)
- Chemistry in Everyday Life: 1. DrugsDocument9 pagesChemistry in Everyday Life: 1. DrugsArya StarkNo ratings yet
- HR500 BrochureDocument6 pagesHR500 BrochureBrian VasquezNo ratings yet
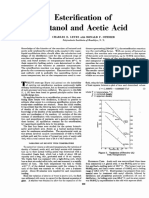
- Esterification of Butanol Acid: AceticDocument10 pagesEsterification of Butanol Acid: AceticCeciNo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter 9 MergedDocument569 pages14 Chapter 9 MergedSil Franciley QuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Ethanol Steam Reforming For Hydrogen Production - Latest and Effective Catalyst Modification Strategies To Minimize Carbonaceous DeactivationDocument15 pagesEthanol Steam Reforming For Hydrogen Production - Latest and Effective Catalyst Modification Strategies To Minimize Carbonaceous DeactivationCristian BurgosNo ratings yet
- Ai - Preparation of Hydrogenated Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber (H-NBR) With Controllable Molecular Weight, 2017 +Document5 pagesAi - Preparation of Hydrogenated Nitrile-Butadiene Rubber (H-NBR) With Controllable Molecular Weight, 2017 +oreamigNo ratings yet
- The Production of Cumene Using Zeolite Catalyst Aspen Model DocumentationDocument16 pagesThe Production of Cumene Using Zeolite Catalyst Aspen Model Documentationديانا محمدNo ratings yet
- Facility Inspection Report for 500 TPD Nitric Acid PlantDocument8 pagesFacility Inspection Report for 500 TPD Nitric Acid Plantlaoy aolNo ratings yet
- PharmaceuticsDocument38 pagesPharmaceuticsVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Q4 - 3rd SummativeDocument2 pagesQ4 - 3rd SummativeRowenickNo ratings yet
- 1126pm - 47.epra Journals 5023Document3 pages1126pm - 47.epra Journals 5023No NameNo ratings yet
- Acs Iecr 0c05041rtyDocument25 pagesAcs Iecr 0c05041rtyAmir HassanNo ratings yet
- Buchner LectureDocument18 pagesBuchner LectureAmr GamalNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS For JEE (Main) PrintDocument2 pagesSYLLABUS For JEE (Main) PrintShubham DauleNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Isoamyl AcetateDocument3 pagesSynthesis of Isoamyl AcetateClaire TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Direct DME Synthesis from Natural GasDocument9 pagesDirect DME Synthesis from Natural GasM Alim Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Journal: AicheDocument1 pageJournal: AicheJohn AnthoniNo ratings yet
- Doc15 - 06GaseousHydrogenStations Best PracticeDocument34 pagesDoc15 - 06GaseousHydrogenStations Best PracticeSundaram KanagarajNo ratings yet