Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 5 - Trees
Uploaded by
trevorsum123Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 5 - Trees
Uploaded by
trevorsum123Copyright:
Available Formats
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
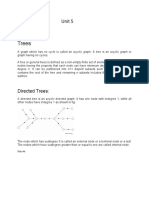
Chapter 5
TREES
5.1 Introduction
Trees are particularly useful in computer science, where
they are employed in a wide range of algorithms.
Defination 1:
A tree is a connected undirected graph with no simple
circuit / without any circles.
A graph with n vertices is a tree if and only if it has n 1
edges and no cycles.
Example 1
Which of the graphs shown in figure 2 are trees? (Susanna,
705)
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
Example 2
Determine whether a graph G has ten vertices and twelve
edges is a tree or not?
Definition 2
Let T be a tree. If T has only one or two vertices, then each
is called a terminal vertex. If T has at least three vertices,
then a vertex of degree 1 in T is called a terminal vertex
(leaf) and a vertex of degree greater 1 in T is called an
internal vertex (branch vertex).
Example 3
Find all terminal vertices and all internal vertices in the
following tree.
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
Definition 3
A rooted tree is a tree in which one vertex is distinguished
from the others and it is called the root. The level of a
vertex is the number of edges along the unique path
between it and the root. The height of a rooted tree is the
maximum level to any vertex of the tree. Given any root of
any internal vertex v of a rooted tree, the children of v are
all those vertices that are adjacent to v. If w is a child of v,
then v is called parent of w, two vertices that are both
children of the same parent are called siblings. Given
vertices v and w, if v lies on the unique path between w and
the root, the v is an ancestor of w and w is a descendant of
v.
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
Example 4
(a) Consider the tree shown below with root a:
a
i.
What is the level of n?
ii.
What is the height of this rooted tree?
iii.
What are the children of n?
iv.
What is the parent of g?
v.
What are the siblings of j?
vi.
What are the descendants of f?
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
Definition 4
A binary tree is a rooted tree in which every parent has at
most two children. Each child in a binary tree is designed
either a left child or a right child (but not both), and every
parent has at most one left child and one right child. A full
binary tree is a binary tree in which each parent has
exactly two children.
Example 5
Draw a binary
a b c d / e 2 .
tree
to
represent
the
expression
Example 6
Construct a binary search tree for the strings math,
computer, power, north, zoo, donkey, and book
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
5.2 Applications of Trees
There are numerous important applications trees included:
Network optimization with minimum spinning tree.
Problem solving with backtracking in decision
trees.
Data compression with prefix codes in Huffman
coding trees.
5.3 Spanning Trees
Definition 5
A tree T is a spanning tree of a graph G if T is a subgraph
of G that contains all of the vertices of G.
Example 7
(a)
Find all spanning trees for the graph below:
v5
v4
v3
v0
v1
v2
6
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
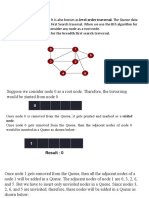
5.4 Minimal Spanning Trees
Definition 6
Let G be a weighted graph. A minimal spanning tree of G
is a spanning tree of G with minimum weight that is has the
smallest possible sum weights of its edges.
How can we find a minimum spanning tree?
8
b
9
e
3
f
10
7
12
6
9
h
g
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
The algorithm to find a minimal spanning tree is known
as Prims Algorithm.
This algorithm builds tree by iteratively adding edges
until a minimal spanning tree is obtained.
The algorithm begins with a single vertex. Then at each
iteration, it adds to the current tree a minimum-weight
edges that does not complete a cycle.
Prims Algorithm
This algorithm finds a minimal spanning tree in a
connected, weighted graph.
Begin by choosing any edges with smallest weight
and putting it into the spanning tree,
Successively add to the tree edges of minimum
weight that are incident to a vertex already in the tree
and not forming a simple circuit with those edges
already in the tree,
Stop when (n-1) edges have been added.
QM1063 CHAPTER 5
Kruskals Algorithm
Kruskals algorithm is identical to Prims algorithm, except
that it does not demand new edges to be incident to a vertex
already in the tree.
Both algorithm are guaranteed to produce a minimum
spanning tree of a connected weighted graph.
You might also like
- TreesDocument4 pagesTreessuneel4tuNo ratings yet
- Class of Problems Where There Is No Efficient Algorithm To SolveDocument5 pagesClass of Problems Where There Is No Efficient Algorithm To Solvegoflux pwnsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 17 - Minimum Spanning Tree PDFDocument16 pagesLecture 17 - Minimum Spanning Tree PDFshubhamgupta007No ratings yet
- TreesDocument44 pagesTreesHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- W4203 Lec4Document28 pagesW4203 Lec4Manoj Kumar GNo ratings yet
- TreesDocument15 pagesTreesSarah FergusonNo ratings yet
- Trees: Lecturer. Ahmed Hadi Al-ShamaryDocument21 pagesTrees: Lecturer. Ahmed Hadi Al-ShamaryAhmed HussainNo ratings yet
- Unit V: Trees (Refer T-1)Document28 pagesUnit V: Trees (Refer T-1)Bum TumNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 LastDocument49 pagesAssignment2 LastLegesse SamuelNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory 3Document14 pagesGraph Theory 3ThuThao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Saidur Sir BookDocument44 pagesSolution Manual For Saidur Sir BookFabiha TasneemNo ratings yet
- 12 Trees, models and properties (Дрва)Document9 pages12 Trees, models and properties (Дрва)Филип ЏуклевскиNo ratings yet
- A Study On Focus Arithmetics Labeling of GraphsDocument57 pagesA Study On Focus Arithmetics Labeling of GraphsGanesan KandasamyNo ratings yet
- EppDM5eMetric 10 04Document31 pagesEppDM5eMetric 10 04Hitesh NaikNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics: TreesDocument36 pagesDiscrete Mathematics: TreesSahithi AthkuriNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document32 pagesUnit 5Dinesh TripathiNo ratings yet
- Graph Theory AlgorithmsDocument19 pagesGraph Theory AlgorithmsLn Amitav BiswasNo ratings yet
- Chapter11 Tree Dan Spanning TreeDocument43 pagesChapter11 Tree Dan Spanning TreeKurnia AjiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 TREESDocument37 pagesModule 5 TREESNitin AbrolNo ratings yet
- Graph: By: Deepak Kumar SinghDocument55 pagesGraph: By: Deepak Kumar Singhसुरज पौडेलNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - FinalDocument22 pagesUnit 3 - Finalanoopsingh1744No ratings yet
- PF: No Need To Consider Any Trees On Fewer Than 3 Vertices (WHY?) - If The Radius of TheDocument6 pagesPF: No Need To Consider Any Trees On Fewer Than 3 Vertices (WHY?) - If The Radius of TheAllan Ayala BalcenaNo ratings yet
- Wa0009.Document17 pagesWa0009.aayush waghereNo ratings yet
- 35 Spanning TreesDocument13 pages35 Spanning TreesrwrtgrerhrNo ratings yet
- Department of Sciences and Humanities 4 Semester B.E. Programme (IT)Document11 pagesDepartment of Sciences and Humanities 4 Semester B.E. Programme (IT)Rutvik SakhavalaNo ratings yet
- TreesDocument107 pagesTreesjungjeyoo300No ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics: Chapter 10.4-10.5Document17 pagesDiscrete Mathematics: Chapter 10.4-10.5Nguyen Dinh Minh (K15 HL)No ratings yet
- 11 W11 DMDocument47 pages11 W11 DMHaseeb ZahidNo ratings yet
- DMGT-module6 and 7Document50 pagesDMGT-module6 and 7manish 2003No ratings yet
- Variation in Terminology: Rosen BryanDocument55 pagesVariation in Terminology: Rosen BryanSameOldHatNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Minimum Spanning TreeDocument5 pagesTerm Paper On Minimum Spanning Treeafdtakoea100% (1)
- DMS Unit-4 NotesDocument12 pagesDMS Unit-4 Notesj79494793No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document47 pagesChapter 11kabir cs - 21-04No ratings yet
- Algorithms and Data StructuresDocument161 pagesAlgorithms and Data StructuresAnil Kumar0% (1)
- TJUSAMO 2014-15 Graph TheoryDocument5 pagesTJUSAMO 2014-15 Graph TheoryWithoon ChinchalongpornNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document43 pagesModule 7Kshitiz GoyalNo ratings yet
- Graph AlgorithmsDocument45 pagesGraph AlgorithmsSrinivas ANo ratings yet
- 10 Unit10Document29 pages10 Unit10nikhil02008No ratings yet
- Project Title: Minimal Spanning Tree: Batch: ADocument6 pagesProject Title: Minimal Spanning Tree: Batch: Asamruta21No ratings yet
- Cs - 502 F-T Subjective by Vu - ToperDocument18 pagesCs - 502 F-T Subjective by Vu - Topermirza adeelNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 2019 v2Document28 pagesUnit-4 2019 v2Sathwick HkNo ratings yet
- GeorgiaTech CS-6515: Graduate Algorithms: CS6515 - Exam2 Flashcards by Daniel Barker - BrainscapeDocument89 pagesGeorgiaTech CS-6515: Graduate Algorithms: CS6515 - Exam2 Flashcards by Daniel Barker - BrainscapeJan_SuNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics: H. Turgut Uyar Ay Seg Ul Gen Cata Emre HarmancıDocument22 pagesDiscrete Mathematics: H. Turgut Uyar Ay Seg Ul Gen Cata Emre Harmancıसुरेश राणेNo ratings yet
- Week 12 - TreesDocument10 pagesWeek 12 - TreesEmmanuel GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual To Chapter 05Document13 pagesSolution Manual To Chapter 05Vimox S Shah100% (1)
- Analisa Algoritma: Graph AlgorithmsDocument42 pagesAnalisa Algoritma: Graph AlgorithmsAbdul HamidNo ratings yet
- Play With Trees SolutionDocument33 pagesPlay With Trees SolutionDanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- DMGT Module 6 TreesDocument53 pagesDMGT Module 6 TreesteeshtakparmarNo ratings yet
- TD SpanningtreeDocument4 pagesTD SpanningtreeKarine DeschinkelNo ratings yet
- TreesDocument30 pagesTreessorouts441No ratings yet
- Tree ADT: November 1, 2004Document13 pagesTree ADT: November 1, 2004Jenner Patrick Lopes BrasilNo ratings yet
- My TreeeeeDocument7 pagesMy TreeeeetuktukNo ratings yet
- D.Math 7nd ChapterDocument14 pagesD.Math 7nd ChapterSajjad ShamimNo ratings yet
- Lec7 Dynamictrees 1Document5 pagesLec7 Dynamictrees 1Chandra MouliNo ratings yet
- On Total Domination in GraphsDocument40 pagesOn Total Domination in GraphsJayagopal Research GroupNo ratings yet
- Daa Mod - 3-1Document14 pagesDaa Mod - 3-1Disha GudigarNo ratings yet
- And The Traveling Salesman Problem: On The Shortest Spanning Subtree of A GraphDocument3 pagesAnd The Traveling Salesman Problem: On The Shortest Spanning Subtree of A GraphadrinkpleaseNo ratings yet
- 10 Trees (SF)Document72 pages10 Trees (SF)trung phanNo ratings yet
- TreesDocument6 pagesTreesRajendranbehappyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Family PAMM IB PlanDocument4 pagesCloud Family PAMM IB Plantrevorsum123No ratings yet
- 8.2g Where Can I Find Other WalletsDocument1 page8.2g Where Can I Find Other Walletstrevorsum123No ratings yet
- 1.03 Welcome To The $100 A Day Investment CourseDocument1 page1.03 Welcome To The $100 A Day Investment Coursetrevorsum123No ratings yet
- 1) MS Excel - Training GuideDocument26 pages1) MS Excel - Training Guidetrevorsum123No ratings yet
- Getting Started With Excel: ComprehensiveDocument10 pagesGetting Started With Excel: Comprehensivetrevorsum123No ratings yet
- Microsoft ExcelDocument32 pagesMicrosoft Exceltrevorsum123No ratings yet
- 1 Ahmad 2 Ahmad 3 Ahmad 4 Ahmad 5 Ahmad: 8) Fill HandleDocument35 pages1 Ahmad 2 Ahmad 3 Ahmad 4 Ahmad 5 Ahmad: 8) Fill Handletrevorsum123No ratings yet
- SignageDocument2 pagesSignagetrevorsum123No ratings yet
- The Important of Insurance: Why Choose Great Eastern?Document17 pagesThe Important of Insurance: Why Choose Great Eastern?trevorsum123No ratings yet
- SPJKCJDDFSDNKLNKLDocument18 pagesSPJKCJDDFSDNKLNKLtrevorsum123No ratings yet
- SignageDocument2 pagesSignagetrevorsum123No ratings yet
- Social Network Analysis - AA - Article - Session 12Document56 pagesSocial Network Analysis - AA - Article - Session 12VINDHYA MYADAMNo ratings yet
- SPOJ TutorialDocument297 pagesSPOJ TutorialRitu Raj100% (1)
- Chap 7Document35 pagesChap 7Emanuella GomesNo ratings yet
- Information & Management: Jiexun Li, Xin Li, Bin ZhuDocument10 pagesInformation & Management: Jiexun Li, Xin Li, Bin ZhuTechnos_IncNo ratings yet
- Bhat, S. P., & Bernstein, D. S. (2000) - Finite-Time Stability of Continuous Autonomous SystemDocument8 pagesBhat, S. P., & Bernstein, D. S. (2000) - Finite-Time Stability of Continuous Autonomous SystemLegis FloyenNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6: Course TextbookDocument3 pagesProblem Set 6: Course TextbookDevendraReddyPoreddyNo ratings yet
- Data Structures and Algorithms AssignmentDocument25 pagesData Structures and Algorithms Assignmentعلی احمد100% (1)
- Mad111 Chap 5Document115 pagesMad111 Chap 5Minh VuNo ratings yet
- What Is BFS?: Let's Consider The Below Graph For The Breadth First Search TraversalDocument13 pagesWhat Is BFS?: Let's Consider The Below Graph For The Breadth First Search TraversalAyush PathakNo ratings yet
- HATS: A Hierarchical Graph Attention Network For Stock Movement PredictionDocument16 pagesHATS: A Hierarchical Graph Attention Network For Stock Movement PredictionNguyen Xuan MaoNo ratings yet
- A. 2451 B. 4950 C. 4851 D. 9900Document48 pagesA. 2451 B. 4950 C. 4851 D. 9900Abhijit routNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Graphs: Module OverviewDocument16 pagesMathematics of Graphs: Module Overviewbianca mabalotNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Declarative Programming in CLIPS and PROLOGDocument8 pagesAn Introduction To Declarative Programming in CLIPS and PROLOGMadhusoodan ShanbhagNo ratings yet
- Nrltutorial Part2 Gnns PDFDocument66 pagesNrltutorial Part2 Gnns PDFRafael Lima0% (1)
- ADA Assignment 2 PDFDocument5 pagesADA Assignment 2 PDFMudit GargNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document46 pagesCH 02Tấn PhátNo ratings yet
- 2015BCC Grade 7 - 8 (Solutions)Document37 pages2015BCC Grade 7 - 8 (Solutions)pjNo ratings yet
- Joyner Python-Notes PDFDocument115 pagesJoyner Python-Notes PDFIgor RajićNo ratings yet
- Graph TheoryDocument22 pagesGraph TheoryCamille Angeles BonitoNo ratings yet
- 41 Undirected GraphsDocument73 pages41 Undirected GraphsMarcus Barros BragaNo ratings yet
- Graphs Algorithms OptimizationDocument305 pagesGraphs Algorithms OptimizationYoussefi AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Programme - MCA Course Name - Discrete Mathematics Course Code - MCA104 (Semester - 1)Document5 pagesProgramme - MCA Course Name - Discrete Mathematics Course Code - MCA104 (Semester - 1)BWUMCA21078 SOUVIK SARKARNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math ProblemsDocument50 pagesDiscrete Math ProblemsMike PosktovaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math: Rohit Mandal Section FDocument36 pagesDiscrete Math: Rohit Mandal Section Fसुबास अधिकारीNo ratings yet
- Application of Graph Coloring in Map Coloring and GSM Mobile Phone NetworksDocument2 pagesApplication of Graph Coloring in Map Coloring and GSM Mobile Phone NetworksPunya Nayak50% (4)
- Graph Cycles and Olympiad Problems: Mathematics MagazineDocument5 pagesGraph Cycles and Olympiad Problems: Mathematics MagazinePQH CuberNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2tishizzleNo ratings yet
- Articulation Points and Bridges Tutorials & Notes - Algorithms - HackerEarthDocument9 pagesArticulation Points and Bridges Tutorials & Notes - Algorithms - HackerEarthKolaparthi DeepakNo ratings yet
- Some New Kinds of Connected Domination in Fuzzy GraphsDocument11 pagesSome New Kinds of Connected Domination in Fuzzy GraphsIOSRjournal100% (1)
- Parabola Review Worksheet AnswersDocument1 pageParabola Review Worksheet Answersbriandmcneill0% (1)