Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Iso TC 174 SC N 235
Uploaded by
Miruna PetriaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Iso TC 174 SC N 235
Uploaded by
Miruna PetriaCopyright:
Available Formats
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
ISO/TC 174
N 235
Date: 2010-10-21
ISO/CD 13756
ISO/TC 174/WG 1
Secretariat: DIN
Jewellery Determination of silver in silver jewellery alloys
Volumetric (potentiometric) method using sodium chloride or potassium
chloride
Joaillerie, bijouterie Dosage de l'argent dans les alliages d'argent pour la bijouterie-joaillerie Mthode
volumtrique (potentiomtrique) utilisant le chlorure de sodium ou le chlorure de potassium
Warning
This document is not an ISO International Standard. It is distributed for review and comment. It is subject to
change without notice and may not be referred to as an International Standard.
Recipients of this draft are invited to submit, with their comments, notification of any relevant patent rights of
which they are aware and to provide supporting documentation.
Document type: International Standard
Document subtype:
Document stage: (30) Committee
Document language: E
X:\TA1\TG1-2\NA027\ISO\TC_174\Dokumente\Verteilt in 2010\0235_ISO_CD_13756_(E).doc STD Version
2.4a
ISO/CD 13756
Copyright notice
This ISO document is a working draft or committee draft and is copyright-protected by ISO. While the
reproduction of working drafts or committee drafts in any form for use by participants in the ISO standards
development process is permitted without prior permission from ISO, neither this document nor any extract
from it may be reproduced, stored or transmitted in any form for any other purpose without prior written
permission from ISO.
Requests for permission to reproduce this document for the purpose of selling it should be addressed as
shown below or to ISO's member body in the country of the requester:
[Indicate the full address, telephone number, fax number, telex number, and electronic mail address, as
appropriate, of the Copyright Manager of the ISO member body responsible for the secretariat of the TC or
SC within the framework of which the working document has been prepared.]
Reproduction for sales purposes may be subject to royalty payments or a licensing agreement.
Violators may be prosecuted.
ii
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
ISO/CD 13756
Contents
Page
Foreword ............................................................................................................................................................iv
1
Scope ......................................................................................................................................................1
Normative references............................................................................................................................1
Principle..................................................................................................................................................1
Reagents.................................................................................................................................................1
Apparatus ...............................................................................................................................................2
Sampling.................................................................................................................................................2
7
7.1
7.1.1
7.1.2
7.1.3
7.2
7.2.1
7.2.2
7.2.3
Procedure ...............................................................................................................................................2
Determination of sodium chloride or potassium chloride standard solution factor......................2
Preparation of silver standards ...........................................................................................................2
Titration of standard silver solution ....................................................................................................2
Calculation of sodium chloride or potassium chloride standard solution factor...........................2
Determination ........................................................................................................................................3
Preparation of the sample solutions ...................................................................................................3
Elimination of palladium .......................................................................................................................3
Titration of the sample solution ...........................................................................................................3
8
8.1
Method of calculation and expression of results...............................................................................3
Repeatability ..........................................................................................................................................4
Test report ..............................................................................................................................................4
Bibliography........................................................................................................................................................5
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
iii
ISO/CD 13756
Foreword
ISO (the International Organization for Standardization) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies
(ISO member bodies). The work of preparing International Standards is normally carried out through ISO
technical committees. Each member body interested in a subject for which a technical committee has been
established has the right to be represented on that committee. International organizations, governmental and
non-governmental, in liaison with ISO, also take part in the work. ISO collaborates closely with the
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) on all matters of electrotechnical standardization.
International Standards are drafted in accordance with the rules given in the ISO/IEC Directives, Part 2.
The main task of technical committees is to prepare International Standards. Draft International Standards
adopted by the technical committees are circulated to the member bodies for voting. Publication as an
International Standard requires approval by at least 75 % of the member bodies casting a vote.
Attention is drawn to the possibility that some of the elements of this document may be the subject of patent
rights. ISO shall not be held responsible for identifying any or all such patent rights.
ISO 13756 was prepared by Technical Committee ISO/TC 174, Jewellery.
This second edition cancels and replaces the first edition (ISO 13756:1997), which has been technically
revised.
iv
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
COMMITTEE DRAFT
ISO/CD 13756
Jewellery Determination of silver in silver jewellery alloys
Volumetric (potentiometric) method using sodium chloride or
potassium chloride
Scope
This International Standard specifies a volumetric method for the determination of silver in silver jewellery
alloys, preferably within the range of fineness stated in ISO 9202. These alloys may contain copper, zinc,
cadmium and palladium. Apart from palladium, which must be precipitated before commencing titration, these
elements do not interfere with this method of determination.
NOTE
This method is an alternative method to ISO 11427, see reference [2], which has been identified as the
reference method.
Normative references
The following referenced documents are indispensable for the application of this document. For dated
references, only the edition cited applies. For undated references, the latest edition of the referenced
document (including any amendments) applies.
ISO 11596, Sampling of the precious metal alloys in jewellery and associated products
Principle
The sample is dissolved in dilute nitric acid. The silver content of the resulting solution is determined by
titration with standard sodium chloride or potassium chloride solution using a potentiometric indication of the
equivalence point.
Reagents
During the analysis, unless otherwise stated, use only reagents of recognised analytical grade and only
distilled water or water of equivalent purity.
4.1 Nitric acid (HNO3); 20 = 1,20 g/cm3, 33 % HNO3 (mass fraction)., with a halide content of less than
5 ppm.
4.2
Sodium chloride solution, c (NaCL)= 0,1 mol/l.
Dissolve 5,84 g of sodium chloride (dried at 105 C) in water and dilute to 1 000 ml.
4.3
Potassium chloride solution, c (KBr)= 0,1 mol/l.
Dissolve 7,44 g of potassium chloride (dried at 105 C) in water and dilute to 1 000 ml.
4.4
Disodium dimethylglyoxime octahydrate solution.
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
ISO/CD 13756
Dissolve 10 g of disodium dimethylglyoxime octahydrate in 1 000 ml of water.
4.5
Silver, minimum purity 999,9 parts per thousand () by mass.
Apparatus
Ordinary laboratory apparatus and the following.
5.1 Motor-driven plunger or piston-type burette, linked to potentiometer or automatic titrator and capable
of delivering increments of 0,05 ml at the equivalence point.
5.2 Titration apparatus, with combination silver electrode or silver chloride coated silver electrode and
Hg/Hg2SO4 electrode or other suitable reference electrode.
NOTE
A silver chloride coating can be obtained by electrolysis, branching a silver electrode as anode in a dilute
hydrochloric acid solution c(HCl)=0,1 mol/l. After suitable surface preparation, apply an anodic current density of 1 mA/cm2
for approximately one hour, until the silver surface is completely covered with silver chloride.
5.3
Analytical balance, with a reading accuracy of 0,01 mg.
Sampling
The sampling procedure for silver and silver alloys shall be performed in accordance with ISO 11596.
Procedure
7.1
7.1.1
Determination of sodium chloride or potassium chloride standard solution factor
Preparation of silver standards
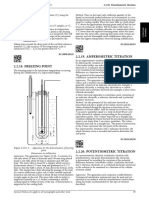
Weigh, to the nearest 0,01 mg, three samples, each of 300 mg to 500 mg of silver (4.5), and transfer them to
glass beakers. Add 5 ml of nitric acid (4.1) to each, and warm gently to dissolve the silver. Keep the tops of
the beakers covered with watch glasses. Heat until evolution of nitrogen oxides ceases. Allow to cool. Rinse
the watch glasses into beakers. Transfer to the titration apparatus (5.2). Add the minimum volume of water,
within the range of about 20 ml to 60 ml, to satisfy the requirements of the titration apparatus (5.2) with
respect to measurement and stirring.
The mass of the standard silver samples should lie within 20 mg of the mass of silver in the sample portion.
7.1.2
Titration of standard silver solution
Add, via the plunger-burette (5.1) under continuous stirring, sufficient sodium chloride standard solution (4.2)
or potassium chloride standard solution (4.4) to precipitate about 95 % of the silver in the solution. Titrate the
remaining silver in such a manner that the equivalence point can be interpolated from 0,05 ml additions of the
sodium chloride or potassium chloride standard solution.
NOTE
This split titration approach can be effected automatically using an automatic titrator with so called dynamic
volume dosing based on the measured potential difference across the electrodes in the titration vessel (5.2).
7.1.3
Calculation of sodium chloride or potassium chloride standard solution factor
The sodium chloride or potassium chloride standard solution factor F is calculated using Equation (1)
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
ISO/CD 13756
F=
mAg
Vs
(1)
where
mAg
is the mass of silver, in milligrams;
Vs
is the volume, in millilitres, of sodium chloride or potassium chloride solution at equivalence
point.
The factor determinations shall not differ from each other by more than 0,05 % , relative value. The mean
value, F, shall be used in subsequent calculations for maximum accuracy. The sodium chloride or potassium
chloride standard solution factor shall be determined immediately before analysis of the sample portions. mAg.
7.2
Determination
7.2.1
Preparation of the sample solutions
Weigh, to the nearest 0,01 mg, two sample portion, each containing between 300 mg and 500 mg of silver,
and transfer them to glass beakers. Add 5 ml of nitric acid (4.1) to each and warm gently to dissolve the alloy.
Keep the tops of the beakers covered with watch glasses. Heat until evolution of nitrogen oxides ceases.
Allow to cool. Rinse the watch glasses into beakers. Transfer to the titration apparatus (5.2). Add water as for
7.2.1.
7.2.2
Elimination of palladium
Palladium, if present, shall be eliminated by addition of an aqueous solution of disodium dimethylglyoxime
octahydrate (4.4). For each 100 mg of palladium, add 50 ml of this solution before commencing titration.
7.2.3
Titration of the sample solution
Proceed exactly as for the standard solution. It may be necessary to carry out a pilot determination to obtain
an approximate value of the silver content.
Method of calculation and expression of results
8.1.1
The mass mAg in milligrams of silver in the sample portion is calculated using Equation (2):
m AG = F Vs
(2)
where
F
is the sodium chloride or potassium chloride standard solution factor expressed in milligrams of silver
for each millilitre of solution;
Vs
is the volume, in millilitres, of sodium chloride or potassium chloride at equivalence point
8.1.2
(3)
The silver content of the sample WAg in parts by mass per thousand () is calculated using Equation
WAg =
mAg
103
ms
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
(3)
ISO/CD 13756
where
ms is the mass, in milligrams, of the sample.
8.1
Repeatability
The results of duplicate determinations shall correspond to better than 1 part per thousand () by mass of
silver. If the variation is greater than this, the assay shall be repeated.
Test report
The test report shall include the following information:
a)
identification of the sample including source, date of receipt, form of sample;
b)
sampling procedure;
c)
the method used by reference to this International Standard;
d)
silver content of the sample, in parts by mass per thousand () as single values and mean values;
e)
if relevant, any deviations from the method specified in this International Standard;
f)
any unusual features observed during the determination;
g)
date of test;
h)
identification of laboratory carrying out this analysis;
i)
signature of laboratory manager and operator.
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
ISO/CD 13756
Bibliography
[1]
ISO 9202, Jewellery Fineness of precious metal alloys
[2]
ISO 11427, Determination of silver in silver jewellery alloys Volumetric (potentiometric) method
using potassium bromide
ISO 2010 All rights reserved
You might also like
- E1-240-2014 - Foundation Engineering II Introduction To Building FoundationsDocument21 pagesE1-240-2014 - Foundation Engineering II Introduction To Building FoundationsEfraim HaifekeNo ratings yet
- JIG AND FIXTURE DESIGN MANUL Eric K HenriksenDocument160 pagesJIG AND FIXTURE DESIGN MANUL Eric K HenriksenPrakashmech4028No ratings yet
- ISO-8589-2007 - Orientações Sobre o Design Da SalaDocument11 pagesISO-8589-2007 - Orientações Sobre o Design Da Salaananda.gouveaNo ratings yet
- Iso 05815-1-20031547185181297Document22 pagesIso 05815-1-20031547185181297Hakeem Shahzad100% (1)
- ANSI/AIHA Ventilation Standards - " A Consensus ApproachDocument132 pagesANSI/AIHA Ventilation Standards - " A Consensus ApproachSamiYousifNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Quality TestingDocument5 pagesChocolate Quality TestingMiruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- Board Exam SeminarDocument37 pagesBoard Exam SeminarNikko D. InacayNo ratings yet
- Advances in Estimation NavigationDocument545 pagesAdvances in Estimation NavigationyeopdidiNo ratings yet
- Until Thermal Equilibrium Is Obtained.: Loss GainDocument5 pagesUntil Thermal Equilibrium Is Obtained.: Loss GainCharls DeimoyNo ratings yet
- BS en 13037-2011Document12 pagesBS en 13037-2011Doiciel100% (1)
- DIN Metallurgy CollectionDocument3 pagesDIN Metallurgy CollectionAkbar ShaikNo ratings yet
- Iso 16948 2015Document9 pagesIso 16948 2015Fernando Grajeda CruzNo ratings yet
- Iso/Np 13534Document18 pagesIso/Np 13534Boris ZaslichkoNo ratings yet
- Boiler Feed Pump KSBDocument9 pagesBoiler Feed Pump KSByogacruiseNo ratings yet
- 0000 Pi SPC 004Document18 pages0000 Pi SPC 004zsmithNo ratings yet
- Environmental Balance of Salt Production Speaks in Favour of Solar SaltworksDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Balance of Salt Production Speaks in Favour of Solar SaltworksminingnovaNo ratings yet
- Flash Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester: Standard Test Methods ForDocument18 pagesFlash Point by Pensky-Martens Closed Cup Tester: Standard Test Methods ForGildardo Mujica HerreraNo ratings yet
- Fuel Ethanol Industry Guidelines Specifications 2018 PDFDocument58 pagesFuel Ethanol Industry Guidelines Specifications 2018 PDFMary Joy DalisayNo ratings yet
- ISO 9912-1-2004 Agricultural Irrigation Equipment. Filters For Micro-Irrigation. Terms, Definitions and ClassificationDocument16 pagesISO 9912-1-2004 Agricultural Irrigation Equipment. Filters For Micro-Irrigation. Terms, Definitions and ClassificationAbdou BouzianeNo ratings yet
- COD - Digestie Rapida PDFDocument2 pagesCOD - Digestie Rapida PDFCorina StanculescuNo ratings yet
- Coal Analysis + Price AdjusmentDocument46 pagesCoal Analysis + Price AdjusmentWahyoedyNo ratings yet
- ApplicationBrochure 2 BOD 30247570Document52 pagesApplicationBrochure 2 BOD 30247570Jose AparcanaNo ratings yet
- Sist en 15414 3 2011Document9 pagesSist en 15414 3 2011Rawa NawzadNo ratings yet
- EN 12255-6-2002 - enDocument3 pagesEN 12255-6-2002 - enSolid Vanadium50% (2)
- Hach TKN Method 10242 Final 01102013Document10 pagesHach TKN Method 10242 Final 01102013Oudah AliNo ratings yet
- ISO 29541-2010 Solid Mineral Fuels - Determination Total Carbon Hydrogen NitrogDocument18 pagesISO 29541-2010 Solid Mineral Fuels - Determination Total Carbon Hydrogen NitrogWinnjone YinNo ratings yet
- Iteh Standard Preview (Standards - Iteh.ai) : SIST EN 15403:2011 Slovenski StandardDocument9 pagesIteh Standard Preview (Standards - Iteh.ai) : SIST EN 15403:2011 Slovenski StandardmohammadNo ratings yet
- PD Cen TR 15310-4-2006Document24 pagesPD Cen TR 15310-4-2006Jorge SalasënNo ratings yet
- Is 15705Document10 pagesIs 15705Amandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Measurement in Organic Solvents: PH of Non-Aqueous SamplesDocument12 pagesMeasurement in Organic Solvents: PH of Non-Aqueous Samplesveneta gizdakova100% (1)
- Is 11255 4 2006Document8 pagesIs 11255 4 2006VinodVaghaniNo ratings yet
- BS en 881-2004Document22 pagesBS en 881-2004Abu Alhassan A.100% (1)
- Iso 8833-1989Document16 pagesIso 8833-1989mohamed guedichiNo ratings yet
- Iso TR 00945-2-2011Document22 pagesIso TR 00945-2-2011htrg jhNo ratings yet
- Iso 11254-1 - 2000 PD Sudan 42 PDFDocument30 pagesIso 11254-1 - 2000 PD Sudan 42 PDFEgemet SatisNo ratings yet
- As 4156.3-2008 Coal Preparation Magnetite For Coal Preparation Plant Use - Test MethodsDocument8 pagesAs 4156.3-2008 Coal Preparation Magnetite For Coal Preparation Plant Use - Test MethodsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- BS en 12393-2-2013Document46 pagesBS en 12393-2-2013DoicielNo ratings yet
- Iso Dis 18218-1 Iuc-28-1 Apeo Direct-MethodDocument11 pagesIso Dis 18218-1 Iuc-28-1 Apeo Direct-MethodNguyen Trung HuyNo ratings yet
- BS EN 1775-2007 Gas Supply - Gas Pipework For Buildings - Maximum Operating Pressure Less Than or Equal To 5 Bar - Functional RecommendationsDocument48 pagesBS EN 1775-2007 Gas Supply - Gas Pipework For Buildings - Maximum Operating Pressure Less Than or Equal To 5 Bar - Functional RecommendationsevgenyNo ratings yet
- BS en 16079-2011Document34 pagesBS en 16079-2011laythNo ratings yet
- C1111-10 (Reapproved 2015)Document6 pagesC1111-10 (Reapproved 2015)Mohamad ZandiNo ratings yet
- Iso 8288 1986Document9 pagesIso 8288 1986Jim FrenkenNo ratings yet
- Iso-5074-1994 HgiDocument12 pagesIso-5074-1994 Hgifatmachemist1No ratings yet
- Iso 19114Document70 pagesIso 19114Ximena Garcia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Metz Lab Presentation: First Floor, Thangavel Nagar, Walajabad Main Road, Mannivakkam-600048Document20 pagesMetz Lab Presentation: First Floor, Thangavel Nagar, Walajabad Main Road, Mannivakkam-600048sevugarajanNo ratings yet
- Iso7359 1985 PDFDocument5 pagesIso7359 1985 PDFJust4545No ratings yet
- BS Iso 20280-2007Document22 pagesBS Iso 20280-2007ngobaochanNo ratings yet
- 2.2.20. Titrare PotentiometricaDocument2 pages2.2.20. Titrare Potentiometricaclaudia100% (1)
- Zooplancton Calidad de AguaDocument26 pagesZooplancton Calidad de AguaLady Johanna Cely CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Standard Terminology Relating To Water D 1129 - 03Document4 pagesStandard Terminology Relating To Water D 1129 - 03stevgonNo ratings yet
- Iso 749 1977Document4 pagesIso 749 1977laboratorium operasionalNo ratings yet
- IEC - 60155 Glow Lamparas IncandecentesDocument29 pagesIEC - 60155 Glow Lamparas IncandecentesAlex A. Siles QuirogaNo ratings yet
- BS en 1254-6Document52 pagesBS en 1254-6cancan25No ratings yet
- ISO 7886-4 (Auto Disable Syringes) PDFDocument20 pagesISO 7886-4 (Auto Disable Syringes) PDFJahanzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Astm C471MDocument18 pagesAstm C471MJaime Andrés Cardona DíazNo ratings yet
- Iso TTR 18931 2001 (E)Document14 pagesIso TTR 18931 2001 (E)marco9991No ratings yet
- Automated Determination of The Hydroxyl Number (HN) According To ASTM E 1899-08 and DIN 53240-2Document13 pagesAutomated Determination of The Hydroxyl Number (HN) According To ASTM E 1899-08 and DIN 53240-2DIENLUU150489100% (1)
- Et Iso 5270 Ds 2012Document13 pagesEt Iso 5270 Ds 2012Jocilene DantasNo ratings yet
- Information - Roofing SheetDocument5 pagesInformation - Roofing SheetRajeev RanjanNo ratings yet
- Method For Mercurous Nitrate Test For Copper I and Copper Alloys (Document4 pagesMethod For Mercurous Nitrate Test For Copper I and Copper Alloys (Mukesh kumarNo ratings yet
- December 06Document36 pagesDecember 06Quy DangNo ratings yet
- Iso 2406-1974 PDFDocument5 pagesIso 2406-1974 PDFmarcos crisostoNo ratings yet
- BS Iso TR 05925-2-1997 (1999)Document16 pagesBS Iso TR 05925-2-1997 (1999)Олег СоловьевNo ratings yet
- IecDocument24 pagesIecMuhammad SameerNo ratings yet
- Iso 05350-2-2006Document18 pagesIso 05350-2-2006DavidNo ratings yet
- Salt Codex AlimentariaDocument5 pagesSalt Codex AlimentariaMindy GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Sist Iso 15249 2000Document11 pagesSist Iso 15249 2000Mai PhuNo ratings yet
- Iso 15249 en PDFDocument8 pagesIso 15249 en PDFAli HaduNo ratings yet
- Iso 8402-1994Document23 pagesIso 8402-1994Davood OkhovatNo ratings yet
- Inspect F50: Everything Needed For Conventional High Resolution Sample InvestigationDocument4 pagesInspect F50: Everything Needed For Conventional High Resolution Sample InvestigationMiruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Oxidation Resistance and Degradation of CR AlC Coating On M38G Superalloy at 900-1100 C 2Document8 pagesShort-Term Oxidation Resistance and Degradation of CR AlC Coating On M38G Superalloy at 900-1100 C 2Miruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- H-Cube Mini Application OverviewDocument2 pagesH-Cube Mini Application OverviewMiruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- Precipitation TitrationsDocument44 pagesPrecipitation TitrationsMiruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- RM180 Users Manual Maple VersionDocument35 pagesRM180 Users Manual Maple VersionMiruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- PharmaID - SciAps LiteratureDocument4 pagesPharmaID - SciAps LiteratureMiruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- Ab-135 2 enDocument8 pagesAb-135 2 enMiruna Petria100% (1)
- Etd Chapt 6Document69 pagesEtd Chapt 6Miruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- TN680 MHTC 96 Drop CalorimetryDocument9 pagesTN680 MHTC 96 Drop CalorimetryMiruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- Etd Chapt 6Document69 pagesEtd Chapt 6Miruna PetriaNo ratings yet
- Phreeqc 3 2013 ManualDocument519 pagesPhreeqc 3 2013 ManualpauloalpeNo ratings yet
- Stream, Streak, PathlinesDocument4 pagesStream, Streak, PathlineschauguleNo ratings yet
- Determination of Elastic Constants of Additive Manufactured Inconel 625 Specimens Using An Ultrasonic TechniqueDocument11 pagesDetermination of Elastic Constants of Additive Manufactured Inconel 625 Specimens Using An Ultrasonic TechniqueHamidreza JavidradNo ratings yet
- AC Servo Spindle System (V2.5) - UDocument79 pagesAC Servo Spindle System (V2.5) - UDmytroKrNo ratings yet
- Práctica GrafcetDocument11 pagesPráctica GrafcetJaimeNo ratings yet
- SS Skyfr 000819 - 2Document3 pagesSS Skyfr 000819 - 2Anonymous HfsLqoWlNo ratings yet
- Civil GeomechanicsAndStructuresDocument64 pagesCivil GeomechanicsAndStructuresJOE G PHILIP CENo ratings yet
- Evs 1Document76 pagesEvs 1AbhishekSinghNo ratings yet
- 11th - STD - Physics - Volume II - EM - WWW - Tntextbooks.in PDFDocument328 pages11th - STD - Physics - Volume II - EM - WWW - Tntextbooks.in PDFTheresaNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph'S College of EngineeringDocument2 pagesSt. Joseph'S College of Engineeringfaizu35No ratings yet
- A S C D W V S: Pplication OF Tatistical Oncepts IN THE Etermination OF Eight Ariation IN AmplesDocument7 pagesA S C D W V S: Pplication OF Tatistical Oncepts IN THE Etermination OF Eight Ariation IN AmplesElaine Nicole CanebaNo ratings yet
- Gel ElectrophoresisDocument13 pagesGel ElectrophoresisVishnu Reddy Vardhan PulimiNo ratings yet
- Survey II NotesDocument95 pagesSurvey II NotesJoshua KiptooNo ratings yet
- Kaleay Hagos 2018Document34 pagesKaleay Hagos 2018ghouti ghoutiNo ratings yet
- Intro To PhysicsDocument3 pagesIntro To PhysicsB.VNo ratings yet
- Cromax 4140 PDFDocument2 pagesCromax 4140 PDFDidik PrihantoroNo ratings yet
- Adv Funct Materials - 2023 - Zhang - Water Adsorption in MOFs Structures and ApplicationsDocument32 pagesAdv Funct Materials - 2023 - Zhang - Water Adsorption in MOFs Structures and ApplicationsnemaderakeshNo ratings yet
- Radiation QuestionsDocument27 pagesRadiation QuestionsSteve BishopNo ratings yet
- Sucrose SolutionDocument2 pagesSucrose Solutionrosangela_darcNo ratings yet
- Phenol Vs Alcohol PDFDocument18 pagesPhenol Vs Alcohol PDFSonNo ratings yet
- Specification of Ground AnchorDocument15 pagesSpecification of Ground AnchordonnyNo ratings yet
- Water Testing Lab ReportDocument8 pagesWater Testing Lab ReportJacqueline WongNo ratings yet