Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neces Math 215 Finals Reviewer (A.y. 2014-2015)
Uploaded by
John Francis DizonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Neces Math 215 Finals Reviewer (A.y. 2014-2015)
Uploaded by
John Francis DizonCopyright:
Available Formats
NECES- MATH 215 (Finals) Reviewer A.Y.
2014-2015
POLYHEDRA
Total Surface Area of a Regular Polyhedron
If s is the measure of one edge of a regular polyhedron,
then the total surface area TSA is given by:
nps 2
TSA =
180
4 tan
n
where p is the number of polygons enclosing the
polyhedron and n is the number of sides in each polygon.
Volume of a Regular Polyhedron
In any regular polyhedron, where d denotes the dihedral
angle between any two adjacent faces, f the number of
faces at one vertex, and n the number of sides in each
polygon,
180 0
cos
0
-1
180
d= 2sin
sin n
Volume of a Prism
V = Bh
where B is the area of the base and h is the height of the
prism.
Volume of an Oblique Prism
V=Bh=Re
Where R is the area of a right section and e is the length
of a lateral edge with the inclination measured with
respect to plane B. Since Bh=Re and h=e sin, then R=B
sin.
II, PARALLELEPIPED
Lateral Surface Area of a Rectangular Solid
- Is the sum of the four side faces of the solid and is
determined by the formula:
LSA = 2lh + 2wh
Total Surface Area
TSA = 2lw + 2lh + 2wh
The volume is given by
d
nps 3 tan
2
V=
180 0
24 tan 2
n
where p denotes the number of polygons, and s the length
of an edge.
PRISMS and CYLINDERS
I .PRISMS
Lateral Surface Area of a Prism
- The product of the perimeter of a right section and
the length of a lateral edge
Volume of a Rectangular Solid
V = lwh
III. CUBES
Diagonal Length of a Cube
d=s 3
Surface Area of a Cube
LSA = 4s2
Total Surface Area: TSA = 6s2
Lateral Surface Area:
Volume of a Cube
LSA = Pe
where LSA is the lateral surface area, P is the perimeter
of a right section, and e is the length of a lateral edge.
Total Surface Area: TSA = LSA + 2B
where B is the area of one base.
Mark Stephen Mata | NECES ACADEMICS TEAM
V = s3
NECES- MATH 215 (Finals) Reviewer A.Y. 2014-2015
IV. CYLINDER
II.CONES
Lateral Surface Area of the right circular cylinder:
LSA =
2rh
Lateral Surface Area
LSA =
Total Surface Area of the cylinder
TSA = 2 r2 + 2 rh
= 2 r(r + h)
= C (r + h)
Where C is the circumference of the base, r is the radius
of the base, and h is the height of the cylinder.
Volume of a Cylinder
V = Bh = r2h
1
l 2r
2
rl
Total Surface Area
TSA = r 2 r l
= r (r + l)
Volume of a Cone
V=
1
r 2 h
3
For oblique prism where R = B sin ,
V = Bh = Re
PYRAMIDS AND CONES
I. PYRAMID
Total Surface Area of the Pyramid
TSA = B + LSA
Area of a Triangular Face of a Pyramid
A=
1
bl
2
Lateral Surface Area of a Regular Pyramid
LSA =
1
Pl
2
Volume of a Pyramid
1
V = Bh
3
SAMPLE PROBLEMS:
1. A solid cube of metal whose edges are 22cm is
melted and recase into rectangular solid whose base
is 18cm x 15cm. How high is the solid?
Solution:
To solve for the volume
V = e3 = 10,648cu.cm
To solve for the height of the solid
V = lwh
10,648 = 18 x 15 x h
h=
10,648
= 39.43cm
270
2. Building bricks are closely stacked in a pile 2.5m high,
12m long and 5m wide. If the bricks are 4cm by 8cm
by 16cm, how many bricks are in the pile?
Solution:
To solve for the space where the bricks are stacked
V = hlw = 2.5 x 12 x 5 = 150cu.m.
where B is the base area and h is the height.
To solve for the volume of the brick in meters
V = 0.04 x 0.8 x .16 = 0.000512cu.m.
To solve for the number of bricks in the stack
Mark Stephen Mata | NECES ACADEMICS TEAM
NECES- MATH 215 (Finals) Reviewer A.Y. 2014-2015
150
292,969 bricks
0.000512
3. Find the volume of an oblique triangular prism whose
base is an equilateral triangle, the side of which is 4
cm., the lateral edge of the prism is equal to the side
of the base and inclined to the base plane at an angle
of 60.
Solution:
To solve the area of the triangle
s 2 3 42 3
4 3 sq. cm.
4
4
To solve for the altitude
h cos 60 4 3 2 3
0
6. Find the radius of the cylindrical pail 20 in. high that
will hold exactly 5 cubic feet?
Solution:
V=
r2h
3
12in
= r2(20in.)
1 ft
( 5 ft3)
r2=
r=
8640in 3
20in
12 3
in.
To solve for the volume of the prism
V Ah 4 3 2 3 24 cu. cm.
4. Find the volume of a pyramid whose base contains
60 sq. m if one edge is 5 m and the angle formed by
this edge and the plane is 30.
7. A stalactite which may be seen hanging in the
underground river of Palawan is approximately in the
form of a cone 3 ft. long with a base 16 in. in diameter.
The calcium carbonate of which it is formed weighs
131 lb. per cu.ft. Find the weight of the stalactite.
Solution:
Solution:
To solve for the height of the pyramid
h = sin30 x 5m = 2.5m
To solve for the volume of the pyramid
1
1
V Bh 60sq.m.2.5m 50 cu. m.
3
3
5. A cylindrical container whose radius is 2 inches holds
pint. Find its height in inches.
Solution:
The radius in feet is
The area of the base is
H=
693
in.
128
Mark Stephen Mata | NECES ACADEMICS TEAM
2 4
sq. ft.
r 2 = =
9
3
2
A=
The volume of the conical stalactite is
V=
V r2h
3 28.875in 3
2
x
2 h
4
1
16 1 2
x
12 2 3
1
1 4
Bh 3 21.40 cu. ft.
3
3 9
The weight of the stalactite is
W = 1.40 x 131 = 183.4 lbs.
You might also like
- Course Title (Course Code) : Fluid Flow MeasurementDocument9 pagesCourse Title (Course Code) : Fluid Flow MeasurementJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument176 pagesGeometryJan Martin Scarella0% (1)
- Midterm Quiz 1 Solution Manual Pce414Document13 pagesMidterm Quiz 1 Solution Manual Pce414manalorommel77No ratings yet
- CE142P-2 / E01 Engr. Edward Monjardin 01-09-21 01-12-21: Jingona, Fatimah Rahima TDocument6 pagesCE142P-2 / E01 Engr. Edward Monjardin 01-09-21 01-12-21: Jingona, Fatimah Rahima TFatimah Rahima Jingona100% (1)
- Curvature and RefractionDocument3 pagesCurvature and RefractionRussel LiwagNo ratings yet
- Bce 211F - Angles and DirectionsDocument31 pagesBce 211F - Angles and DirectionsJan FroydNo ratings yet
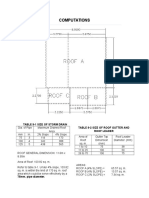
- Computations: Table 9-1 Size of Storm Drain Table 9-2 Size of Roof Gutter and Roof LeaderDocument12 pagesComputations: Table 9-1 Size of Storm Drain Table 9-2 Size of Roof Gutter and Roof LeaderZedrickTrinidadNo ratings yet
- GEAS - Problems 2Document10 pagesGEAS - Problems 2Jonar MarieNo ratings yet
- Zonal CavityDocument32 pagesZonal CavityarkidechNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument19 pagesDifferential EquationsDinah Jane MartinezNo ratings yet
- 5-Curvilinear Motion (Normal and Tangential Components)Document7 pages5-Curvilinear Motion (Normal and Tangential Components)Percival ArcherNo ratings yet
- Topographic SurveyingDocument33 pagesTopographic Surveyingkevin bryanNo ratings yet
- Basic Engineering Correlation Admath X de 001Document6 pagesBasic Engineering Correlation Admath X de 001Ska dooshNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - Curvature and Refraction, Measuring Vertical DistancesDocument11 pagesLesson 9 - Curvature and Refraction, Measuring Vertical DistancesJohn Andrei PorrasNo ratings yet
- Exp 4-Manning's Rugosity CoefficientDocument2 pagesExp 4-Manning's Rugosity Coefficientadityain2003No ratings yet
- Fieldwork 6Document5 pagesFieldwork 6MonicaShayneVillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Unit Exam 1Document7 pagesUnit Exam 1Emmanuel San Miguel0% (1)
- Handouts - Trigonometry and GeometryDocument5 pagesHandouts - Trigonometry and GeometryTrisha RañadaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Survey 1Document27 pagesEngineering Survey 1Ralph MarronNo ratings yet
- Measure Distance Fundamentals SurveyDocument29 pagesMeasure Distance Fundamentals SurveyNick Robinsons100% (1)
- Chapter6-Force System in Space PDFDocument25 pagesChapter6-Force System in Space PDFBejong Boy0% (1)
- TrigonometryDocument2 pagesTrigonometryRennel MallariNo ratings yet
- Particle Size Distribution AnalysisDocument5 pagesParticle Size Distribution AnalysisNely ZulfatnNo ratings yet
- LevelingDocument4 pagesLevelingChester Allan Clavero100% (2)
- Surveying Elem HigherDocument14 pagesSurveying Elem HigherNeilCyrus RamirezNo ratings yet
- Forces in SpaceDocument64 pagesForces in SpaceKellie BrownNo ratings yet
- Cee 109 - First ExamDocument43 pagesCee 109 - First ExamRonald Renon QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Exercise - AlgebraDocument6 pagesExercise - AlgebraRoxan Bueno Mora100% (1)
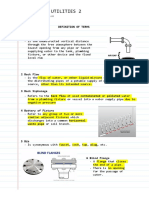
- Engineering Utilities 2 Definition of TermsDocument8 pagesEngineering Utilities 2 Definition of TermsDum AccountNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying / Engr. Romel N. VinguaDocument32 pagesQuantity Surveying / Engr. Romel N. VinguaBG GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Man owns two unequal square lots totaling 15,025 sqmDocument90 pagesMan owns two unequal square lots totaling 15,025 sqmNeilyn BongalanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Physics ModuleDocument96 pagesThermal Physics Module3334333No ratings yet
- Module 3 (H.R Alignment 2) Different Methods in Laying A Simple CurveDocument7 pagesModule 3 (H.R Alignment 2) Different Methods in Laying A Simple CurveOwene Miles AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Surveying Lab ReportDocument14 pagesSurveying Lab Reportapi-385520144No ratings yet
- CE141-2 M3 Exam Part 1Document1 pageCE141-2 M3 Exam Part 1Jemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- FS7 Lesson 7 - Missing Data and Subdivision of LotDocument31 pagesFS7 Lesson 7 - Missing Data and Subdivision of LotJames harvyNo ratings yet
- Fieldwork 1Document13 pagesFieldwork 1Hazel CordanoNo ratings yet
- D-EU1-Plateno.3-Pita Andrae Kate SandaeDocument5 pagesD-EU1-Plateno.3-Pita Andrae Kate SandaeShaft SandaeNo ratings yet
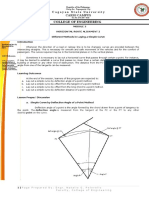
- Given: Chord length = 2/3 radiusLet the central angle be θUsing the theorem: Chord length = 2r sin(θ/2)2/3r = 2r sin(θ/2)1/3 = sin(θ/2)θ = 2 * sin^-1(1/3) = 39.9°The central angle is 39.9 degreesDocument51 pagesGiven: Chord length = 2/3 radiusLet the central angle be θUsing the theorem: Chord length = 2r sin(θ/2)2/3r = 2r sin(θ/2)1/3 = sin(θ/2)θ = 2 * sin^-1(1/3) = 39.9°The central angle is 39.9 degreesFree student100% (1)
- Energy ConversionDocument98 pagesEnergy ConversionLouise UmaliNo ratings yet
- Probable Error MeasurementsDocument7 pagesProbable Error MeasurementsElyse LedesmaNo ratings yet
- A Closed Cylindrical Tank With Axis VerticalDocument8 pagesA Closed Cylindrical Tank With Axis VerticalVini Marie MadrigalNo ratings yet
- May 2005 Board ExamDocument6 pagesMay 2005 Board ExamAndrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- Reflection in PrelimDocument2 pagesReflection in PrelimRichelle TanNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: The Respondent's Email Address (1503438@ub - Edu.ph) Was Recorded On Submission of This FormDocument12 pagesDifferential Calculus: The Respondent's Email Address (1503438@ub - Edu.ph) Was Recorded On Submission of This FormJoseph LantoNo ratings yet
- B. Electricity - Basic PrinciplesDocument4 pagesB. Electricity - Basic PrinciplesXyxy LofrancoNo ratings yet
- I. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.Document11 pagesI. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.jclou0211No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Chapter 5 - Types of Const. - Req. of Fire Zones - Building DesignDocument60 pagesChapter 4 - Chapter 5 - Types of Const. - Req. of Fire Zones - Building DesignMark Ryan Nagales100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Surveying CorrectionsDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Surveying CorrectionsAngelie Tugadi Dingle100% (1)
- Differential Leveling: Reference: Elementary Surveying 3 Edition by Juny Pilapil La PuttDocument10 pagesDifferential Leveling: Reference: Elementary Surveying 3 Edition by Juny Pilapil La PuttKevinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document9 pagesExperiment 2Narry StrummerNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies LecturesDocument17 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies LecturesEri EliNo ratings yet
- TasadayDocument1 pageTasadayMark Eugene DollanoNo ratings yet
- (Updated File) Job # 5. To Find The Area of Traverse by Triangulation MethodDocument9 pages(Updated File) Job # 5. To Find The Area of Traverse by Triangulation MethodUsama Bin YousufNo ratings yet
- Conical FrustumDocument11 pagesConical FrustumRajaKuppanNo ratings yet
- Solid MensurationDocument44 pagesSolid MensurationKay PorrasNo ratings yet
- Mensuration Tricks, Formulas & Examples: Add CommentDocument19 pagesMensuration Tricks, Formulas & Examples: Add CommentGirdhar GopalNo ratings yet
- Geometry & TrigonometryDocument104 pagesGeometry & Trigonometrycherry agaNo ratings yet
- Volumes, Surface Areas and Radian Measure: Review of Areas and Perimeters of Planar FiguresDocument15 pagesVolumes, Surface Areas and Radian Measure: Review of Areas and Perimeters of Planar Figuresmasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Geometry and Volume Word ProblemsDocument62 pagesGeometry and Volume Word ProblemsMichael Damian60% (5)
- Force: Mikee Vhie D. CaronanDocument24 pagesForce: Mikee Vhie D. CaronanJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Signals Spectra Processing PowerPoint PresentationDocument8 pagesSignals Spectra Processing PowerPoint PresentationJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Basag FDDocument58 pagesBasag FDJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- JersonDocument1 pageJersonJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Basag FDDocument58 pagesBasag FDJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - ResistorsDocument8 pagesLesson 4 - ResistorsJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Collective ECE ReviewersDocument8 pagesCollective ECE ReviewersLorenz ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Answer Key (Profed)Document11 pagesAnswer Key (Profed)John Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Class C Requirement Endorsement CertificateDocument1 pageClass C Requirement Endorsement CertificateJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- LET Practice Test 2-Professional EducationDocument5 pagesLET Practice Test 2-Professional EducationCrisencio M. Paner100% (2)
- General Education - Social Studies ANSWER KEYDocument1 pageGeneral Education - Social Studies ANSWER KEYJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- To Pass The Examination, An Examinee Must Obtain An Average Rating of Not Less Than 75% and Must Have No Rating Lower ThanDocument1 pageTo Pass The Examination, An Examinee Must Obtain An Average Rating of Not Less Than 75% and Must Have No Rating Lower ThanJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Professional Education - Napulot 3 (WALANG ANSWER KEY)Document26 pagesProfessional Education - Napulot 3 (WALANG ANSWER KEY)John Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER - Philosophical Foundation of EducationDocument9 pagesREVIEWER - Philosophical Foundation of EducationJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Professional Education Set 3Document5 pagesProfessional Education Set 3John Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Professional Education Set 3Document5 pagesProfessional Education Set 3John Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- To Pass The Examination, An Examinee Must Obtain An Average Rating of Not Less Than 75% and Must Have No Rating Lower ThanDocument1 pageTo Pass The Examination, An Examinee Must Obtain An Average Rating of Not Less Than 75% and Must Have No Rating Lower ThanJohn Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Professional Education Set 1Document5 pagesProfessional Education Set 1John Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- Professional Education Set 2Document5 pagesProfessional Education Set 2John Francis DizonNo ratings yet
- KENWOOD TK 7302 Manual - ADocument2 pagesKENWOOD TK 7302 Manual - AMas IvanNo ratings yet
- QFD PresentationDocument75 pagesQFD PresentationBhushan Verma100% (3)
- Particle Size Reduction TechniquesDocument10 pagesParticle Size Reduction TechniquesJay ShahNo ratings yet
- Carbon FibreDocument25 pagesCarbon Fibrejagadish.kvNo ratings yet
- Mole Conversions Extra Practice Answer KeyDocument1 pageMole Conversions Extra Practice Answer Keyapi-376281962No ratings yet
- Common MisconceptionsDocument7 pagesCommon MisconceptionsBoazz750No ratings yet
- Homework ClassDocument11 pagesHomework ClassHossain100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5bhavyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3Spring RollsNo ratings yet
- SECTION 2-07 Fire Protection: Airplane Operations ManualDocument26 pagesSECTION 2-07 Fire Protection: Airplane Operations ManualAnish ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Hikmayanto Hartawan PurchDocument12 pagesHikmayanto Hartawan PurchelinNo ratings yet
- Dev - Mag - 09Document26 pagesDev - Mag - 09georgpiorczynskiNo ratings yet
- PDF Ecs h81h3 Ad DDDocument37 pagesPDF Ecs h81h3 Ad DDsanak tiuhNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics (046) Marking Scheme: Sample Question Paper (2017-18)Document8 pagesEngineering Graphics (046) Marking Scheme: Sample Question Paper (2017-18)RaghuSrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 - Friction Losses in PipesDocument34 pagesExperiment 1 - Friction Losses in PipesKhairil Ikram33% (3)
- Sandvik DL311Document4 pagesSandvik DL311Anonymous Dm7iMmtNo ratings yet
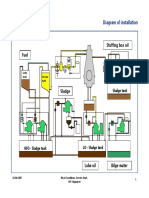
- Westfalia Separator Installation DiagramDocument68 pagesWestfalia Separator Installation DiagramOno Jr Araza100% (3)
- Open Problems in The Mathematics of Data ScienceDocument152 pagesOpen Problems in The Mathematics of Data Sciencecan dagidirNo ratings yet
- EC424 Monetary Economics (Michaelmas Term) Additional QuestionsDocument5 pagesEC424 Monetary Economics (Michaelmas Term) Additional QuestionsSteamPunkNo ratings yet
- Junction boxes gas group IIC selectionDocument16 pagesJunction boxes gas group IIC selectionkskadryNo ratings yet
- EE6010-High Voltage Direct Current TransmissionDocument12 pagesEE6010-High Voltage Direct Current Transmissionabish abish0% (1)
- Effects of Nimodipine, Vinpocetine and Their Combination On Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction in RatsDocument9 pagesEffects of Nimodipine, Vinpocetine and Their Combination On Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction in RatsBilal AbbasNo ratings yet
- TIPS ON MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTIESDocument2 pagesTIPS ON MEASUREMENT UNCERTAINTIESrahmaNo ratings yet
- Product Information: Introducing The Machine Information Center (MIC) MiningDocument44 pagesProduct Information: Introducing The Machine Information Center (MIC) MiningKolo BenduNo ratings yet
- SUMMATIVE EXAM (G11) 2023 ExamDocument3 pagesSUMMATIVE EXAM (G11) 2023 ExamDens Lister Mahilum100% (1)
- Image ReconstructionDocument28 pagesImage ReconstructionRahul PaulNo ratings yet
- E8244 Ahu Catalogue 2014 PDFDocument174 pagesE8244 Ahu Catalogue 2014 PDFmurugesanNo ratings yet
- 913-2174-01 - Ibypass VHD User Guide Version 1.5 - Revh - VanphDocument218 pages913-2174-01 - Ibypass VHD User Guide Version 1.5 - Revh - Vanphpham hai van100% (1)
- Clustering Methods for Data MiningDocument60 pagesClustering Methods for Data MiningSuchithra SalilanNo ratings yet
- 3D Reinforcement of Stiffener-To-Skin T-Joints by Z-Pinning and TuftingDocument9 pages3D Reinforcement of Stiffener-To-Skin T-Joints by Z-Pinning and TuftingLouis GrouNo ratings yet