Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tutorial No.5-Midterm Revision
Uploaded by
waleedkhalillahmedCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial No.5-Midterm Revision
Uploaded by
waleedkhalillahmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Mechanics of Materials Lab Sections: L-11, L-12, L-61, L62, L63
Midterm Revision
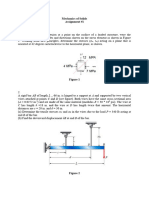
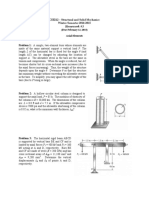
1.8-8 A cable and pulley
system at D is used to bring a
230-kg pole (ACB) to a
vertical position as shown in
the figure part (a). The cable
has tensile force T and is
attached at C. The length L of
the pole is 6.0 m, the outer
diameter is d =140 mm, and
the wall thickness t=12 mm.
The pole pivots about a pin at
A in figure part (b). The
allowable shear stress in the
pin is 60 MPa and the
allowable bearing stress is 90
MPa. Find the minimum
diameter of the pin at A in
order to support the weight of
the pole in the position shown
in the figure part (a).
Mechanics of Materials Lab Sections: L-11, L-12, L-61, L62, L63
Midterm Revision
Mechanics of Materials Lab Sections: L-11, L-12, L-61, L62, L63
Midterm Revision
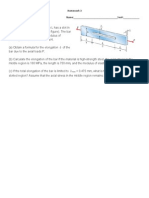
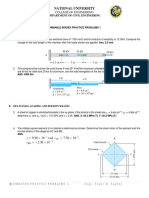
2.3-4 A rectangular bar of length L has a slot in the middle half of its length (see figure). The bar
has width b, thickness t, and modulus of elasticity E. The slot has width b/4.
(a) Obtain a formula for the elongation d of the bar due to the axial loads P.
(b) Calculate the elongation of the bar if the material is high-strength steel, the axial stress in the
middle region is 160 MPa, the length is 750 mm, and the modulus of elasticity is 210 GPa.
Mechanics of Materials Lab Sections: L-11, L-12, L-61, L62, L63
Midterm Revision
2.4-9 The aluminum and steel pipes shown in the figure are
fastened to rigid supports at ends A and B and to a rigid plate
C at their junction. The aluminum pipe is twice as long as the
steel pipe. Two equal and symmetrically placed loads P act on
the plate at C.
(a) Obtain formulas for the axial stresses a and s in the
aluminum and steel pipes, respectively.
(b) Calculate the stresses for the following data: P= 50 kN,
cross-sectional area of aluminum pipe Aa=6000 mm2, crosssectional area of steel pipe As= 600 mm2, modulus of
elasticity of aluminum Ea =70 GPa, and modulus of elasticity
of steel Es =200 GPa.
Mechanics of Materials Lab Sections: L-11, L-12, L-61, L62, L63
Midterm Revision
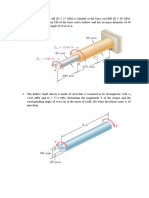
2.10-4 A round brass bar of diameter d1=20 mm has upset ends of diameter d2=26 mm (see figure).
The lengths of the segments of the bar are L1 =0.3 m and L2= 0.1 m. Quarter-circular
fillets are used at the shoulders of the bar, and the modulus of elasticity of the brass is E=100 GPa.
If the bar lengthens by 0.12 mm under a tensile load P, what is the maximum stress
bar?
max in the
Mechanics of Materials Lab Sections: L-11, L-12, L-61, L62, L63
Midterm Revision
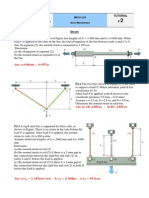
3.4-3 A stepped shaft ABCD consisting of solid circular segments is subjected to three torques, as
shown in the figure. The torques have magnitudes 3000 N.m, 2000 N.m, and 800 N.m. The length
of each segment is 0.5 m and the diameters of the segments are 80 mm, 60 mm, and 40 mm. The
material is steel with shear modulus of elasticity G=80 GPa.
(a) Calculate the maximum shear stress max in the shaft.
(b) Calculate the angle of twist D (in degrees) at end D.
You might also like
- Problem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarDocument7 pagesProblem Sheet # 2: and R at The Ends of The BarYatharth KhicharNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainDocument4 pagesMechanics of Solid Problems On Stress and StrainYogeswaranNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Homework 3Document9 pagesStrength of Materials Homework 3felipe GNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsYan NieNo ratings yet
- HW#02Document8 pagesHW#02tozandehjaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesAssignment Strength of MaterialsVinay Korukonda0% (1)
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsYan NieNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsIsabelle LunaNo ratings yet
- Special Assignment Mekanik PepejalDocument15 pagesSpecial Assignment Mekanik PepejalIsmail IbrahimNo ratings yet
- MEC103 Mechanics of Deformable BodiesDocument24 pagesMEC103 Mechanics of Deformable BodiesLorene Ropeta.No ratings yet
- HW1Document2 pagesHW1gas58No ratings yet
- HW1Document2 pagesHW1Amir NourNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1TanmayNo ratings yet
- Score 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerDocument5 pagesScore 1265 HPS 1716 X 70 %: Final AnswerChristian M. MortelNo ratings yet
- Exercises of TorsionDocument3 pagesExercises of TorsionPham CongNo ratings yet
- First Project ExamplesDocument49 pagesFirst Project ExamplesMeleti Meleti MeletiouNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials 1 PDFDocument2 pagesMechanics of Materials 1 PDFEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Document4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 2.Jesus RodeloNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1jermainpeart4No ratings yet
- MOM Assignment IDocument3 pagesMOM Assignment IAll_regNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document7 pagesCH 4Irem Dolek0% (1)
- Mechanics of MaterialDocument3 pagesMechanics of MaterialChhaya Sharma100% (1)
- IINEEA1 Tutorial 1Document6 pagesIINEEA1 Tutorial 1michaeljxmesNo ratings yet
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pages9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- ES 64 - EXAM 2 FiNALDocument5 pagesES 64 - EXAM 2 FiNALGlimmer Dawn Loredo OrdanielNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 FinalDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 FinalshishirNo ratings yet
- StrengthDocument2 pagesStrengthAmmar Bany AtaNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics QuestionsDocument3 pagesSolid Mechanics QuestionsUnknownNo ratings yet
- Determine stress in steel rod with turnbuckle due to temperature changeDocument10 pagesDetermine stress in steel rod with turnbuckle due to temperature changeDon MatiasNo ratings yet
- Mech 223 - Tutorial 02Document2 pagesMech 223 - Tutorial 02Abdullrahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Homework #3: CEE212 - Structural and Solid Mechanics Winter Semester 2014-2015Document2 pagesHomework #3: CEE212 - Structural and Solid Mechanics Winter Semester 2014-2015MaimaiFabilonaDumalaogNo ratings yet
- Statically IndeterminateDocument3 pagesStatically IndeterminateRhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- SOMDocument14 pagesSOMAditya ojhaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document4 pagesProblem Set 2anonymouscheNo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses and Strains PDFDocument2 pagesSimple Stresses and Strains PDFSai Krishna SK100% (1)
- Axial LoadingDocument4 pagesAxial LoadingAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- National University civil engineering practice problems on mechanics of deformable bodiesDocument2 pagesNational University civil engineering practice problems on mechanics of deformable bodiesEldridge EastNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI GIỮA HỌC KỲ CTTT ME2101Document2 pagesĐỀ THI GIỮA HỌC KỲ CTTT ME2101xmenpro006No ratings yet
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 pagesAssignment For IPEAbirHasanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document3 pagesProblem Set 2Jeff BayedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- MMDocument2 pagesMMAccount PhoneNo ratings yet
- Taller No 2 Resistencia I 2013BDocument4 pagesTaller No 2 Resistencia I 2013BAsep Bin UjangNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1Document2 pagesSheet - 1Abdel Hamied EbrahemNo ratings yet
- Simple StrainDocument36 pagesSimple StrainMartina CelsoNo ratings yet
- Me218 Fa15 W3 HoDocument10 pagesMe218 Fa15 W3 HonhiuNo ratings yet
- SOM AssignmentDocument6 pagesSOM Assignmentshreyas shahNo ratings yet
- Problems On StrainDocument16 pagesProblems On StrainRalph Evidente33% (3)
- Axial stress problemsDocument2 pagesAxial stress problemsPsyco BejaouiNo ratings yet
- Assignment04 (2:11:14)Document2 pagesAssignment04 (2:11:14)Gabriel SmithNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsDocument3 pagesSheet 3 Stress and Strain-Axial Loading - Statically Indeterminate - MechatronicsAhmed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Prob SheetDocument20 pagesProb SheetAditya ShuklaNo ratings yet
- CCB 241 - Assignment 1 - Due On 21 Feb. 2023Document7 pagesCCB 241 - Assignment 1 - Due On 21 Feb. 2023aaschlysebakisoNo ratings yet
- 121 - Pdfsam - 1mechanics of Materials (3 Ed) (Team Nanban) TMRGDocument20 pages121 - Pdfsam - 1mechanics of Materials (3 Ed) (Team Nanban) TMRGEugenio DerbesNo ratings yet
- Strain and stress measurement conceptsDocument17 pagesStrain and stress measurement conceptsRasheed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-2Document4 pagesTutorial 2-2nageshNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document7 pagesTutorial 5A SкNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Laboratory Stirrer GuideDocument8 pagesLaboratory Stirrer GuidewaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Polymers 12 02579Document19 pagesPolymers 12 02579waleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Polymers-13-02423 2Document25 pagesPolymers-13-02423 2waleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Secrets of Success PDFDocument7 pagesSecrets of Success PDFdeveshwerNo ratings yet
- JBCPR 2015090213523808Document10 pagesJBCPR 2015090213523808waleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Polymers 13 01523 3Document19 pagesPolymers 13 01523 3waleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 14 10458Document13 pagesSustainability 14 10458waleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Stress Transformation 2Document19 pagesStress Transformation 2waleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Cracked Microparticles On The Mechanical and The Fracture Behavior of Particulate CompositeDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Cracked Microparticles On The Mechanical and The Fracture Behavior of Particulate CompositewaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- D792-13 Standard Test Methods For Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by DisplacementDocument6 pagesD792-13 Standard Test Methods For Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by DisplacementHussein Beqai100% (1)
- JBCPR 2015090213523808Document10 pagesJBCPR 2015090213523808waleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Relative Importance IndexDocument5 pagesRelative Importance IndexwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Villanova Torsion Test ReportDocument19 pagesVillanova Torsion Test ReportwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial No 4 TorsionDocument7 pagesTutorial No 4 TorsionwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics and Strength of Materials LabDocument78 pagesStructural Mechanics and Strength of Materials Labwaleedkhalillahmed100% (1)
- The Influence of Debonding On The Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Nanocomposites Waleed K. AhmedDocument90 pagesThe Influence of Debonding On The Mechanical Properties of Hybrid Nanocomposites Waleed K. AhmedwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Compression Testing WoododDocument2 pagesCompression Testing WoododsivaeinfoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial No. 2-Normal Stresses & Mechanical PropertiesDocument5 pagesTutorial No. 2-Normal Stresses & Mechanical PropertieswaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- BucklingDocument3 pagesBucklingwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Lab 4torsion EngDocument17 pagesLab 4torsion EngJuan RestrepoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial No. 1-ReviewDocument7 pagesTutorial No. 1-ReviewwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Torsion Tutorial - L51 PDFDocument10 pagesTorsion Tutorial - L51 PDFwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- ModeModelling Compressive Strength of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using Neural Networks and Regressionlling Compressive Strength of RecycledDocument11 pagesModeModelling Compressive Strength of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Using Neural Networks and Regressionlling Compressive Strength of RecycledwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial de Mecánica de La Fractura (Ansys APDL)Document14 pagesTutorial de Mecánica de La Fractura (Ansys APDL)omarihuanoNo ratings yet
- ICMCM2012 Conference ScheduleDocument19 pagesICMCM2012 Conference SchedulewaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Determine Polymer Melt Flow IndexDocument3 pagesDetermine Polymer Melt Flow IndexwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Spacecraft and Mission DesignDocument10 pagesSpacecraft and Mission DesignluciopatricioNo ratings yet
- 01 AutoPIPE Vessel Fundamentals Introduction PPTDocument10 pages01 AutoPIPE Vessel Fundamentals Introduction PPTInamullah KhanNo ratings yet
- EBS e PDFDocument92 pagesEBS e PDFRowan Cornelius100% (2)
- Evolution of Mobile Base Station ArchitecturesDocument6 pagesEvolution of Mobile Base Station ArchitecturesShivganesh SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- Glencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Answer KeyDocument8 pagesGlencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Answer Keybodinetuzas2100% (1)
- Experiment 6Document7 pagesExperiment 6sajithNo ratings yet
- Ericsson Training PDFDocument118 pagesEricsson Training PDFNuwan100% (1)
- Color TheorypdfDocument99 pagesColor TheorypdfNews OffbeatNo ratings yet
- Types of distributed computing in 40 charactersDocument8 pagesTypes of distributed computing in 40 charactersAiman FatimaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Solutions Week 10Document3 pagesTutorial Solutions Week 10Jaden EuNo ratings yet
- Bengali Ebook 191011Document3 pagesBengali Ebook 191011bhaskar2000_inNo ratings yet
- Mobile Equipment: Components, Systems and SolutionsDocument8 pagesMobile Equipment: Components, Systems and SolutionsJobiar HossainNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Image Processing Toolbox Basic IntroductionDocument10 pagesMATLAB Image Processing Toolbox Basic IntroductionHilbertNo ratings yet
- 505s PDFDocument20 pages505s PDFArfan AliNo ratings yet
- Quectel WCDMA<E Linux USB Driver User Guide V1.9 Preliminary 20190325 PDFDocument50 pagesQuectel WCDMA<E Linux USB Driver User Guide V1.9 Preliminary 20190325 PDFVassileios VelaorasNo ratings yet
- Linux Optical Disk How ToDocument36 pagesLinux Optical Disk How ToBenjamin GonzalezNo ratings yet
- FP35 Hearing Aid Analyzer TrainingDocument85 pagesFP35 Hearing Aid Analyzer TrainingPamela Tamara Fernández EscobarNo ratings yet
- Sweater Consumption CostingDocument2 pagesSweater Consumption Costingapi-214283679No ratings yet
- Experiments On Partial Replacement of Coconut Shell As Coarse Aggregate in ConcreteDocument10 pagesExperiments On Partial Replacement of Coconut Shell As Coarse Aggregate in ConcreteIJIRSTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Review: 1 Writing Linear Equations: Slope-Intercept FormDocument2 pagesChapter 5 Review: 1 Writing Linear Equations: Slope-Intercept FormmeanprNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing ScalesDocument18 pagesEngineering Drawing ScalesShadabNo ratings yet
- Master'S Thesis: Simulation of An Underground Haulage System, Renström Mine, Boliden MineralDocument76 pagesMaster'S Thesis: Simulation of An Underground Haulage System, Renström Mine, Boliden MineralJosé Carlos Bustamante MoralesNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Advance Database Concepts-Lesson 2Document5 pagesModule 3 - Advance Database Concepts-Lesson 2jjNo ratings yet
- CH-7 System of Particles and Rotaional MotionDocument9 pagesCH-7 System of Particles and Rotaional MotionMithul VPNo ratings yet
- Excel Session - Final - For - AttendeesDocument156 pagesExcel Session - Final - For - AttendeesLakshmiReddyKNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4Document2 pagesProblem Set 4chrisray39No ratings yet
- Introduction and operating system structure syllabusDocument29 pagesIntroduction and operating system structure syllabusRadhika BadbadeNo ratings yet
- IR LM100A Crawlair Drill PDFDocument8 pagesIR LM100A Crawlair Drill PDFAnonymous 8yIptglHhNo ratings yet
- Electron Configurations and PropertiesDocument28 pagesElectron Configurations and PropertiesAinthu IbrahymNo ratings yet
- Discretization Methods of Fractional Parallel PIDDocument4 pagesDiscretization Methods of Fractional Parallel PIDBaherNo ratings yet