Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alyssa
Uploaded by
Sudipto Kundu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesMacroeconomics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMacroeconomics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views2 pagesAlyssa
Uploaded by
Sudipto KunduMacroeconomics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1.
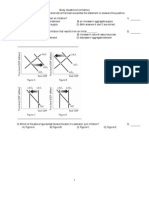
For movements along the long-run aggregate supply curve:
A. The prices of goods and services change while the input prices
remain fix
B. Potential GDP is dependent on the price level
C. The inflation rate and the money wage rate (input prices) change by
the same percentage
D. All of the above
7. Prior to the Great Depression in 1929, the dominate macro-economic
theory was:
A. Keynesian
B. Classical
C. supply-side economics
D. real business cycle theory
8. Both the original classical school and the modern real business cycle
theory hold:
A. actual GDP and potential GDP can diverge creating temporary
involuntary unemployment and recession
B. actual GDP is always equal to potential GDP so all unemployment is
voluntary and
Government macroeconomic policy actions cannot influence the
economy
C. only fiscal policy can reduce the impacts of recession
D. political activism is necessary to fight recessions
9. Which will increase (shift) the short-run aggregate supply rightward?
A. an increase in the money supply
B. a favorable price shock (i.e. a fall in oil prices) or an decrease in
inflationary expectations
C. an increase in inflationary expectations and a negative price shock
(i.e. a rise in oil prices)
D. An increase in investment spending
13. The classical economists conclusion that nominal income is determined
by movements in the money supply rested on their belief that ____ could be
treated as ____ in the short run.
A. velocity; constant
B. money; variable
C. money; constant
D. velocity; variable
14. The classical economists believed that if the quantity of money doubled
A. prices would fall
B. output would double
C. prices would double
D. prices would remain constant
15. The speculative motive for holding money is closely tied to what function
of money?
A. medium of exchange
B. standard of deferred payment
C. store of wealth
D. unit of account
16. Keynes hypothesized that the transactions component of money demand
was primarily determined by the level of
A. velocity
B. stock market prices
C. income
D. interest rates
17. According to the real business cycle (RBC) theory, recessions are the
result of
A. an increase in investment
B. an increase in growth rate of the quantity of money
C. a fall in growth rate of productivity
D. a decrease in growth rate of the quantity of money
20. The U.S. exchange rate rises. As a result, there is a
A. rightward shift in the long run US aggregate supply curve
B. leftward shift in the US aggregate demand curve
C. leftward shift in the long run US aggregate supply curve
D. rightward shift in the US aggregate demand curve
21. A major technological advance shifts the
A. short run aggregate supply curve rightward but does not shift the
long run aggregate supply curve
B. long run aggregate supply curve rightward but does not shift the
short run aggregate supply curve
C. long run and short run aggregate supple curves rightward
D. long run aggregate supply curve rightward and the short run
aggregate supply curve leftward
36. According to the original Keynesian school, the primary source of the
business cycle is:
A. from unexpected fluctuations in aggregate demand and the fact that
todays money wage rates were negotiated at past datesthus past
rational expectations of the current price level influence the current
wage rate
B. supply side shocks from technological change
C. from unexpected fluctuations in aggregate demand in a rare
divergence from normal rational expectations
D. the instability of investment and consumption spending by investors
and consumers
E. FED policy with regards to monetary policy (money supply changes)
and its effect on aggregate demand
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing CalculationsDocument4 pagesConfidence Intervals and Hypothesis Testing CalculationsSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- TaylorDocument3 pagesTaylorSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- Explanations: Solution For The First ProblemDocument3 pagesExplanations: Solution For The First ProblemSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- Explanations: Solution For The First ProblemDocument3 pagesExplanations: Solution For The First ProblemSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- AshDocument1 pageAshSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- TateDocument1 pageTateSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- TarasDocument3 pagesTarasSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- AliDocument5 pagesAliSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- Production (Q) : GraphforqvslDocument1 pageProduction (Q) : GraphforqvslSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- ShazeenDocument1 pageShazeenSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- RachelDocument1 pageRachelSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- Defining SCM PaperDocument41 pagesDefining SCM PaperSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- Reair Time Probability 3 3 0.1 5.1 4 0.2 5 0.3 6 0.3 7 0.1 0.1 3 7 0.2 4 0.3 5 0.3 6 0.1 7Document1 pageReair Time Probability 3 3 0.1 5.1 4 0.2 5 0.3 6 0.3 7 0.1 0.1 3 7 0.2 4 0.3 5 0.3 6 0.1 7Sudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- ArielDocument1 pageArielSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- AndrewDocument8 pagesAndrewSudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- AmyDocument1 pageAmySudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- MAGGIEDocument298 pagesMAGGIESudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- Tottenham CaseDocument19 pagesTottenham Casekranilrai75% (8)
- StrategyDocument1 pageStrategySudipto KunduNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Law of Variable ProportionsDocument6 pagesLaw of Variable ProportionsDeepashikhaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Marketing CompetitionDocument4 pagesAssignment Marketing Competitionzouz3000No ratings yet
- Economics of Regulation Mid-Term 2010-11Document2 pagesEconomics of Regulation Mid-Term 2010-11Saurav DuttNo ratings yet
- Midterm SampleDocument8 pagesMidterm SampleHussein EssaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document2 pagesQuiz 2hrshtkatwala100% (1)
- Capitalism: 'From Each According To Their Ability, To Each According To Their Needs'' LeninDocument1 pageCapitalism: 'From Each According To Their Ability, To Each According To Their Needs'' LeninValeria SirețanuNo ratings yet
- Gali and Blanchard Divine Coincidence PaperDocument37 pagesGali and Blanchard Divine Coincidence PaperNiall DavisonNo ratings yet
- Ecn 502Document20 pagesEcn 502biodun oNo ratings yet
- Study Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Document8 pagesStudy Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Kiran KachhawahaNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument33 pagesConsumer Behaviortracylr87_528841394No ratings yet
- The Basic New Keynesian Model ExplainedDocument29 pagesThe Basic New Keynesian Model ExplainedTiago MatosNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet - FinalDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet - FinalAhmedAlhosaniNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document4 pagesQuiz 1soldiersmithNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Individual AssignmentDocument5 pagesMicroeconomics Individual AssignmentYuenJinNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Answer Key - Rutabaga Old WordDocument2 pagesPractice Problems Answer Key - Rutabaga Old WordsdNo ratings yet
- StagflationDocument6 pagesStagflationRoshan Raj RegmiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Practice Problems:: B) Greater LowerDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Practice Problems:: B) Greater Lowerkayti1211No ratings yet
- Assignment 1-QuestionDocument8 pagesAssignment 1-QuestionFreesyria Campaign56% (9)
- Assumptions and Definitions: Microeconomics (From Greek Prefix Mikro-Meaning "Small" and Economics) Is A BranchDocument2 pagesAssumptions and Definitions: Microeconomics (From Greek Prefix Mikro-Meaning "Small" and Economics) Is A BranchKeerthiraj PoojaryNo ratings yet
- MCQ Economics Revision GuideDocument11 pagesMCQ Economics Revision GuidejancyNo ratings yet
- Production Possibilities CurveDocument34 pagesProduction Possibilities CurveavijitkumaraichNo ratings yet
- Twelve: Monopolistic Competition: The Competitive Model in A More Realistic SettingDocument21 pagesTwelve: Monopolistic Competition: The Competitive Model in A More Realistic SettingAmit BhattacherjiNo ratings yet
- Bernheim Calculus FinalDocument122 pagesBernheim Calculus Finalsrinjoy100% (1)
- Question Slow LearnersDocument18 pagesQuestion Slow Learnersapi-348687812No ratings yet
- Ekonomi Manajerial: Dalam Perekonomian GlobalDocument30 pagesEkonomi Manajerial: Dalam Perekonomian GlobalMaryam BurhanuddinNo ratings yet
- Introduction to MicroeconomicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction to MicroeconomicsJp Kafle100% (1)
- Principles of Micro EconomicsDocument275 pagesPrinciples of Micro Economicsashairways67% (3)
- Indifference CurveDocument29 pagesIndifference CurveLalit KalraNo ratings yet
- Monopolistic CompetitionDocument13 pagesMonopolistic CompetitionAnonymous KvNac2YIkNo ratings yet
- Econ130 14-2 Tutorial QuestionsDocument19 pagesEcon130 14-2 Tutorial QuestionsCharlene LeongNo ratings yet