Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Secure Data in Public Clouds Using Mediated Certificate-Less Public-Key Encryption
Uploaded by
IJSTEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Secure Data in Public Clouds Using Mediated Certificate-Less Public-Key Encryption
Uploaded by
IJSTECopyright:
Available Formats
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering | Volume 2 | Issue 11 | May 2016
ISSN (online): 2349-784X
Secure Data in Public Clouds using Mediated
Certificate-Less Public-Key Encryption
A. Gandhimathi
Department of Information Technology
Anna University Regional Campus Coimbatore, India
Mr. J. Mannar mannan
Department of Information Technology
Anna University Regional Campus Coimbatore, India
Abstract
Cloud is a new growing field in the present information age used in internet that provides computing resources as a service over
online. The third generation network move towards Big data, Semantic web and Cloud technology. Cloud provides various services
over online where people can store, process and retrieve data from it. During the data transmission via public cloud, security is the
most important concern. Security using certificate is a cost effective and time consuming task in the cloud environment. To address
the limitations, a mediated certificate-less encryption scheme without pairing operation is proposed for securely sharing sensitive
information in public clouds using RSA algorithm. In this approach multiple users can access the information at the same time.
Here, the encrypted file send to client and the client will decrypt the encrypted file using file key. The proposed method performs
better compared with existing certificate based security algorithms.
Keywords: Cloud Computing, Aneka tool, Public Cloud, Certificate-less Encryption
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
I.
INTRODUCTION
In the present information age, cloud computing is new murmuring word of software engineers and hot topic of research in
distributed, on-demand computing technology.
Cloud Computing:
Cloud computing is Internet-based computing that providing shared processing resources and data to computers and other devices
on demand. In this model is used to enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable
computing resources that can be abruptly provisioned and released with minimal management effort and high efficient manner.
Networks, servers, storage, applications and services are the examples for this model. The users can use the services provided by
the service provider without troubles planning, procuring, building, configuring and maintaining the infrastructure. For a real world
example, if you need to travel from one city to another you dont buy a train.The person Only buy a ticket and he pay the money
for the distance he going to be cover. And train service provider will take care of maintaining trains and rail-treks and manpower.
Cloud computing also using computing resources managed by provider and the provider will take care of infrastructure
management and user they need to pay only for services used.In cloud computing the Organizations use a variety of different
service models as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS and deployment models are Private, Public, Hybrid, and Community. Public cloud is an
extension of private cloud along with the additional cost-benefit due to service provider adapts low cost cloud storage to enterprise.
Public Cloud provides the benefit of shared infrastructure and automation in term of low-cost.
Secure Cloud Storage:
Cloud computing and storage solutions provide user and enterprise with various capabilities to store and process their data in thirdparty data centers. The number of security issues/concerns associated with cloud computing but these issues falls into two broad
categories: First the security issues faced by cloud providers such as software, platform, or infrastructure-as-a-service via the cloud.
The next one is security issues faced by their customers such as companies or organizations who host applications or store data on
the cloud.
Aneka Tool:
Aneka is a market oriented Cloud development and management platform with rapid application development and workload
distribution capabilities it allows to build, schedule, provision and monitor results using pricing, accounting, and QoS/SLA services
in private and/or public network environments. And also integrated with middle ware package which allows you to seamlessly
frame and operate an interconnected network in addition to accelerating development, deployment and management of distributed
applications that will be used to Microsoft .NET frameworks on these networks. Aneka plays the major role of Application Platform
as a Service for Cloud Computing. Aneka supports various programming models they are Task Programming, Thread
Programming and MapReduce Programming and tools are used for rapid creation of applications and their logical deployment on
private or public Clouds to distribute applications.
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org
101
Secure Data in Public Clouds using Mediated Certificate-Less Public-Key Encryption
(IJSTE/ Volume 2 / Issue 11 / 015)
XenServer:
XenServer is the leading open source virtualization platform, powered by the Xen Project hypervisor and the XAPI tool stack. This
is used in the worlds largest clouds and enterprises. XenServer is a virtualization platform which gives critical features for any
server or data center,
Management Capabilities includes the following features,
1) Multi-Server Management.
2) Role Based Administration.
3) Performance Alerting and Reporting.
Scalable Virtual Infrastructure includes the following,
1) Live VM Migration
2) Live Storage Migration
3) Host Failure Protection
4) Host Power Management
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Sensitive data transmission requires privacy and security to ensure confidentiality. This type of security for data stored in private
or public cloud needs additional security to ensure confidentiality and also should not take time cost. To address this limitation, S.
Yu, 2010 et al [1] proposed a new cryptosystem for fine-grained sharing of encrypted data named as Key-Policy Attribute-Based
Encryption. In their work, the authors construct sharing of audit log information and broadcast encryption. It supports delegation
of private keys which subsumes Hierarchical Identity Based Encryption.
Meanwhile Dan Boneh and Brent waters [2007], present a general framework for analyzing and constructing searchable public
key systems for various families that will declare. Then construct public key systems that support comparison queries and general
subset queries and it also support conjunctions. On the other hand, Scott Coull et al., [2009] presented a model to support a wide
range of access control policies, it includes efficient and private realization of the Chinese Wall and Bell-LaPudulla policies, which
is used for financial and defense applications, and each transaction requires only constant time.
Dan Boneh, Xuhua Ding, Gene Tsudik [2004] presents a new approach for fine grained control over user security. Privileges
centered on the concept of an online SEM. Use of SEM are conjunction with simple threshold of the RSA cryptosystem offer
number of practical advantages over current revocation technique.
Jan Camenisch, Maria Dubovitskaya and Gregory Newen [2009], present a protocol for anonymous access to a database where
the different records have different access control permission, the protocol offers maximal security guarantees for both database
and users.
Xiaoxin Wu, Lei Xu and Xinwen Zhang [2012], propose certificate-less proxy re encryption scheme for data sharing with cloud.
It is used to reduce the computing and communication cost for data owner.
M. Bellare, A. Desai, D. Pointcheval, P. Rogawayet al, says to compare the relative strength of popular notions of security for
public key encryption scheme. In additional which belive simpler contribution is a new definition of non-malleability compare
than previous one.
AmitSahai and Brent water [2005], presents two constructions of fuzzy Identity-Based Encryption (IBE) schemes. It can be
viewed as IBE of messages under fuzzy, and these IBE schemes are both error-tolerant and secure against collusion attack and
prove selective ID security model.
David PointCheval and Jacques stern [2000], presents security arguments for a large class of known signature schemes. Provides
Elgamal signature scheme, and also provides existential forgeries even against an adaptively chosen-message attack.
Sherman S.M, Chow, Colin Boyd and Juan Manual Gonzalez Nieto [2006] et al, introduce the notion of SMC, which allows
more lightweight versions of mediated cryptography while maintaining the ability for instantaneous revocation of keys, which is
used to avoid key escrow.
III. CERTIFICATELESS PUBLIC-KEY ENCRYPTION
Providing security to data using various algorithms has their pros and cons. Hackers always try to hack our privacy data over online and secure data from various hackers and malwares is a time and cost consuming task. Data security over cloud is additional
burden to service providers and users. Multiple encryption and decryption, certificates and other security issues make more costly
for data security in the cloud. To address these limitations, The Mediated Certificate-less public key encryption scheme is proposed.
In this method, the data security is as equal to the certificated encryption techniques. This scheme does not depend on the pairingbased operation. It reduces the computational overhead and to efficiently encrypt for multiple users. The novel approach of mclPKE scheme is to share secure data in public clouds. It does not suffer from the key escrow problem. The RSA Asymmetric key
approach used for performing double encryption for multiple users. The RSA algorithm is efficiently encrypt and decrypt the file
using file key. It also be used for performing digital signature and it will be helpful for improving the security.
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org
102
Secure Data in Public Clouds using Mediated Certificate-Less Public-Key Encryption
(IJSTE/ Volume 2 / Issue 11 / 015)
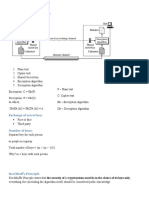
System Architecture:
Fig. 1: System architecture
The figure1 shows the overall system architecture. During the data encryption and download phases, the data owner downloads
the public keys of users to generate the intermediate keys as shown above. The data owner encrypts each data item only once using
a random symmetric key K and then mCL-PKE encrypts K using its public key. The data owner uploads the encrypted data along
with the intermediate keys to the cloud. The encrypted data is stored in the storage service in the cloud and the intermediate keys
are stored at the SEM in the cloud. Users can download and decrypt the data using SEM key.
IV. IMPLEMENTATION
RSA:
The algorithm used for modern computers to encrypt and decrypt messages. It is an asymmetric cryptographic algorithm.
Asymmetric algorithm uses two different keys such as Public and private key. Public key is given to everyone used to encrypt
messages. The private key must be kept private used to decrypt the messages. Steps to generate the keys:
1) Prime numbers p and q.
2) Calculate n=pq
3) Calculate the totient (n)=(p-1)(q-1).
4) Choose an integer such that1<e< (n) and
its co prime to (n). And gcd(e,(n))=1.
5) Compute the congruence relation de=1(mod(n)). ie.de=1+k(n).
Encrypting messages
Decrypting messages
V. RESULT ANALYSIS
In this section, present the performance results for our mediated certificate-less public key encryption scheme is discussed. The
proposed encryption algorithm is more efficient than their existing algorithm for message size above 16K bytes.
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org
103
Secure Data in Public Clouds using Mediated Certificate-Less Public-Key Encryption
(IJSTE/ Volume 2 / Issue 11 / 015)
Fig. 5.1: Comparison of encryption
A similar observation is made for decryption algorithm; this observation is consistent with the fact that our scheme uses an
efficient hash function and XOR operations to perform encryption and decryption whereas their scheme uses more expensive
constructs.
Fig. 5.2: Comparison Decryption
Hence our proposed pairing free mediated certificate-less public key encryption scheme is secure against the partial decryption
attack.
VI. CONCLUSION
In this paper proposed the mediated certificate-less public key encryption scheme without pairing operations and provide formal
security. It also solves the key escrow problem and revocation problem. The improved approach to satisfying multiple users can
access the same access control policies and this approach performs double encryption of each data item used to reduce the overall
overhead. Finally using RSA Asymmetric key approach to provide high security of the data and very easy in key distribution.
REFERENCES
V. Goyal, O. Pandey, A. Sahai, and B.Waters, Attribute-based encryption for ne-grained access control of encrypted data, in Proc. 13th ACM Conf. CCS,
New York, NY, USA, 2006, pp. 8998.
[2] D. Boneh and B. Waters, Conjunctive, subset, and range queries on encrypted data, in Proc. 4th TCC, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007, pp. 535554.
[3] S. Coull, M. Green, and S. Hohenberger, Controlling access to an oblivious database using stateful anonymous credentials, in Irvine: Proc. 12th Int. Conf.
Practice and Theory in PKC, Chicago, IL, USA, 2009, pp. 501520.
[4] D.Boneh, X. Ding, and G. Tsudik,Fine-grained control of security capabilities, ACM Trans. Internet Technol., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 6082, Feb. 2004.
[5] J. Camenisch, M. Dubovitskaya, and G. Neven, Oblivious trans- fer with access control, in Proc. 16th ACM Conf. CCS, New York, NY, USA, 2009, pp.
131140.
[6] X. W. Lei Xu and X. Zhang, CL-PKE: A certicate-less proxy re- encryption scheme for secure data sharing with public cloud, in ACM Symp. Inform.
Comput. Commun. Security, 2012.
[7] M. Bellare, A. Desai, D. Pointcheval, and P. Rogaway, Relations among notions of security for public-key encryption schemes, in Proc. Crypto 98, H.
Krawczyk Ed. Springer-Verlag, LNCS 1462.
[8] A. Sahai and B. Waters, Fuzzy identity-based encryption, LNCS 3494 in Proc. EUROCRYPT, Aarhus, Denmark, 2005, pp. 457473.
[9] D. Pointcheval and J. Stern, Security arguments for digital signatures and blind signatures, J. Cryptology, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 361396, 2000.
[10] S. S. M. Chow, C. Boyd, and J. M. G.Nieto, Security- mediated certicate-less cryptography, in Proc. 9th Int. Conf. Theory Practice PKC, New York, NY,
USA, 2006, pp. 508524.
[1]
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org
104
You might also like
- Optimization of Overall Efficiency Using Facilities Planning in Ropp Cap Making IndustryDocument8 pagesOptimization of Overall Efficiency Using Facilities Planning in Ropp Cap Making IndustryIJSTENo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Magneto Repulsive Wind TurbineDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Magneto Repulsive Wind TurbineIJSTENo ratings yet
- FPGA Implementation of High Speed Floating Point Mutliplier Using Log Based DesignDocument4 pagesFPGA Implementation of High Speed Floating Point Mutliplier Using Log Based DesignIJSTENo ratings yet
- Development of Relationship Between Saturation Flow and Capacity of Mid Block Section of Urban Road - A Case Study of Ahmedabad CityDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Relationship Between Saturation Flow and Capacity of Mid Block Section of Urban Road - A Case Study of Ahmedabad CityIJSTENo ratings yet
- A Cloud Based Healthcare Services For Remote PlacesDocument4 pagesA Cloud Based Healthcare Services For Remote PlacesIJSTENo ratings yet
- Automatic Generation Control in Three-Area Power System Operation by Using "Particle Swarm Optimization Technique"Document8 pagesAutomatic Generation Control in Three-Area Power System Operation by Using "Particle Swarm Optimization Technique"IJSTENo ratings yet
- Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Iron Ore Tailings and Glass PowderDocument7 pagesPartial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Iron Ore Tailings and Glass PowderIJSTENo ratings yet
- Effect of RIB Orientation in Isogrid Structures: Aerospace ApplicationsDocument9 pagesEffect of RIB Orientation in Isogrid Structures: Aerospace ApplicationsIJSTENo ratings yet
- Multipurpose Scheme of Workshop Exhaust System For Ventilation and Electrical Power GenerationDocument9 pagesMultipurpose Scheme of Workshop Exhaust System For Ventilation and Electrical Power GenerationIJSTENo ratings yet
- RFID Based Toll Gate AccessDocument5 pagesRFID Based Toll Gate AccessIJSTENo ratings yet
- Optimization of Treatability by FACCO For Treatment of Chemical Industry EffluentDocument9 pagesOptimization of Treatability by FACCO For Treatment of Chemical Industry EffluentIJSTENo ratings yet
- A Mixture of Experts Model For ExtubationDocument4 pagesA Mixture of Experts Model For ExtubationIJSTENo ratings yet
- Comparative Study and Analysis of PCC Beam and Reinforced Concrete Beam Using GeogridDocument7 pagesComparative Study and Analysis of PCC Beam and Reinforced Concrete Beam Using GeogridIJSTENo ratings yet
- Enriching Gum Disease Prediction Using Machine LearningDocument6 pagesEnriching Gum Disease Prediction Using Machine LearningIJSTENo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Survey of Techniques/Methods For Content Based Image Retrieval SystemDocument6 pagesA Comprehensive Survey of Techniques/Methods For Content Based Image Retrieval SystemIJSTENo ratings yet
- Optimizing Turning Process For EN43 by Taguchi Method Under Various Machining ParametersDocument4 pagesOptimizing Turning Process For EN43 by Taguchi Method Under Various Machining ParametersIJSTENo ratings yet
- The Bicycle As A Mode Choice - A Gendered ApproachDocument4 pagesThe Bicycle As A Mode Choice - A Gendered ApproachIJSTENo ratings yet
- Optimum Placement of DG Units Using CPF MethodDocument6 pagesOptimum Placement of DG Units Using CPF MethodIJSTENo ratings yet
- Interstage Construction Techniques For Mass Gain: An OverviewDocument5 pagesInterstage Construction Techniques For Mass Gain: An OverviewIJSTENo ratings yet
- An Implementation and Design A Customized Advanced Image Editor Using Image Processing in MatlabDocument5 pagesAn Implementation and Design A Customized Advanced Image Editor Using Image Processing in MatlabIJSTENo ratings yet
- Onerider The Bike TaxiDocument3 pagesOnerider The Bike TaxiIJSTENo ratings yet
- A Radar Target Generator For Airborne TargetsDocument8 pagesA Radar Target Generator For Airborne TargetsIJSTENo ratings yet
- App-Based Water Tanker Booking, Monitoring & Controlling SystemDocument6 pagesApp-Based Water Tanker Booking, Monitoring & Controlling SystemIJSTENo ratings yet
- Using The Touch-Screen Images For Password-Based Authentication of IlliteratesDocument6 pagesUsing The Touch-Screen Images For Password-Based Authentication of IlliteratesIJSTENo ratings yet
- Research On Storage Privacy Via Black Box and Sanitizable SignatureDocument6 pagesResearch On Storage Privacy Via Black Box and Sanitizable SignatureIJSTENo ratings yet
- Wireless Information Process and Power Transfer in Single-User OFDM SystemDocument6 pagesWireless Information Process and Power Transfer in Single-User OFDM SystemIJSTENo ratings yet
- Duplicate Detection Using AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesDuplicate Detection Using AlgorithmsIJSTENo ratings yet
- Technology Advancement For Abled PersonDocument9 pagesTechnology Advancement For Abled PersonIJSTENo ratings yet
- An Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithms For Photovoltaic Systems Using Matlab and Arduino Based RTOS SystemDocument5 pagesAn Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithms For Photovoltaic Systems Using Matlab and Arduino Based RTOS SystemIJSTENo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Bulk Encryption On GPUs - AMDDocument25 pagesBulk Encryption On GPUs - AMDjhty2112No ratings yet
- Stream Ciphers - Andreas KleinDocument399 pagesStream Ciphers - Andreas KleinLeonard2311No ratings yet
- 220 Cipher TechniqueDocument10 pages220 Cipher Techniquecagedraptor100% (1)
- Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument11 pagesCryptography and Network SecurityRaymondNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CryptographyDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Cryptographyachuu1987No ratings yet
- Sudha Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSudha Seminar ReportPrathik KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document22 pagesChapter 01Aryan JuyalNo ratings yet
- Cryptography in Context: Nathaniel KarstDocument15 pagesCryptography in Context: Nathaniel Karstapi-278392608No ratings yet
- An Efficient Hardware Model For RSA Encryption System Using Vedic MathematicsDocument5 pagesAn Efficient Hardware Model For RSA Encryption System Using Vedic Mathematicserparveenkaur86No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Symmetric KeyDocument60 pagesUnit 2 Symmetric KeyAniket ChandaNo ratings yet
- Security and Cryptography: OrganizationDocument27 pagesSecurity and Cryptography: OrganizationkitoNo ratings yet
- 21.0.3 Class Activity - Creating CodesDocument3 pages21.0.3 Class Activity - Creating Codesbui lamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cryptography: Zahra Sadat Bahri Student No. 98110232 Homework 1 October 8, 2021Document7 pagesIntroduction To Cryptography: Zahra Sadat Bahri Student No. 98110232 Homework 1 October 8, 2021Baran BahriNo ratings yet
- 04 Using Block v2 AnnotatedDocument54 pages04 Using Block v2 AnnotatedbodokidNo ratings yet
- Understanding WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK AuthenticationDocument2 pagesUnderstanding WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK AuthenticationLe ProfessionistNo ratings yet
- Steganography Powerpoint Presentation by Papan SarkarDocument11 pagesSteganography Powerpoint Presentation by Papan SarkarPapan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Number Theory - Presentation - MARSDocument21 pagesCryptography and Number Theory - Presentation - MARSsunil_38No ratings yet
- CS6701 CNS-Lesson Plan-Regulation - 2013Document5 pagesCS6701 CNS-Lesson Plan-Regulation - 2013addssdfaNo ratings yet
- Viber Encryption OverviewDocument6 pagesViber Encryption OverviewBakir ŠiljakNo ratings yet
- Calculos PropostaDocument4 pagesCalculos PropostaMiguel CavacoNo ratings yet
- Columnar Transposition CipherDocument3 pagesColumnar Transposition CipherViraliDoshi50% (4)
- Traditional Symmetric Key CiphersDocument9 pagesTraditional Symmetric Key CiphersSamsung A30No ratings yet
- Quiz4 PDFDocument8 pagesQuiz4 PDFЮлия Котяй100% (1)
- ENISA Report - Post-Quantum Cryptography Current State and Quantum MitigationDocument37 pagesENISA Report - Post-Quantum Cryptography Current State and Quantum Mitigationjohn woolisNo ratings yet
- SRS for Cryptography SoftwareDocument11 pagesSRS for Cryptography SoftwareRaj Sharma0% (1)
- Chapter Two Number Theory and CryptographyDocument40 pagesChapter Two Number Theory and CryptographyMihretu BekeleNo ratings yet
- Mysterious Messages Comprehension MADocument5 pagesMysterious Messages Comprehension MAximena ferdinandNo ratings yet
- Digital SignatureDocument19 pagesDigital SignatureRanu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2022-23 VAPT ReportDocument17 pages2022-23 VAPT ReportMovies 4 U khanNo ratings yet
- Caesar Cipher Using Java - Crypto LabDocument4 pagesCaesar Cipher Using Java - Crypto LabNaveen KumarNo ratings yet