Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 2C Financial Statements & Transaction Analysis 2016
Uploaded by
leCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 2C Financial Statements & Transaction Analysis 2016
Uploaded by
leCopyright:
Available Formats
HC1011(BPA & Bbus) and HF1008(BoF)
HC1011/HF1008
Topic 2
Financial Statements and
Transactions Analysis
Types of Business Entities
Introduction
This week we will cover the following:
Types of Business Entities
Basic financial statements
Assumptions made and characteristics
of information
Basic effects of transactions on the
accounting equation and financial
statements
Single proprietorship or sole trader
Owned by one person
Partnership
Owned by two or more partners
Company of corporation
Owned by shareholders
Separate legal entity
Simple Balance Sheets
Basic Financial Statements
Financial performance
Operating efficiency
Financial position
Economic condition
Cash flows
Operating activities
Investing activities
Financing activities
Statement of Changes in Equity
Balance Sheets consist of
Assets (current and non-current),
Liabilities (current and non-current) and
Equity (capital, retained earnings and
reserves).
Assets and Liabilities are those items which
belong to the entity, equity belongs to the owners.
Holmes Ins*tute 2016
Simple Balance Sheets
The Balance Sheet
Marianas GEN Y Fashions
Balance Sheet
It is structured around the accounting equation:
as at 30 June 2015
ASSETS
LIABILITIES
Cash at Bank
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY
Or
$ 50,340 Accounts payable
$ 20,760
Accounts receivable
17,790 Mortgage payable
201,000
Inventory
14,610
221,760
Dressmaking Equipment
110,700
Land
ASSETS LIABILITIES = EQUITY
Building
60,000 EQUITY
255,000 Marianas, Capital
$508,440
286,680
$508,440
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY
7
The Balance Sheet (cont.)
The Balance Sheet (cont.)
ASSETS
Cash at Bank
Accounts receivable
Inventory
What is Asset? What are the common asset
accounts?
$ 50,340
17,790
14,610
Dressmaking equipment
Land
110,700
What is liability? What are the common liability
accounts?
60,000
Building
255,000
$508,440
Less: LIABILITIES
Accounts payable
$ 20,760
Mortgage payable
201,000
ASSETS
LIABILITIES
= EQUITY
What is Owners Equity (Shareholders
Equity)?
221,760
NET ASSETS
$286,680
EQUITY
Marianas, Capital
286,680
9
$286,680
Balance Sheet Accounts
The Balance Sheet (cont.)
Assets
Asset Accounts
Resources controlled by the entity as a result of past
transactions or events from which future economic
benefits are expected to flow to the entity
Liabilities
Present obligations of an entity arising from past
transactions or events, the settlement of which is
expected to result in an outflow of resources from the
entity
Equity
The residual interest of the owner/s in the assets
(less liabilities) of the entity
11
Holmes Ins*tute 2016
10
Cash at bank (current)
Accounts receivable (current)
Bills receivable (either current or non-current)
Other receivables or debtors (usually current)
Prepaid expenses (usually current)
Land (non-current, fixed)
Buildings (non-current, fixed)
Plant and equipment (non-current, fixed)
Copyright, patents, etc. (non-current, intangible)
12
Balance Sheet Accounts (cont.)
Balance Sheet Accounts (cont.)
Liability accounts
Equity accounts
Accounts payable (current)
Bills payable (either current or non-current)
Unearned income (usually current)
Other current liabilities
GST collections and outlays (current)
Mortgage payable (non-current)
Bonds and debentures (non-current)
Four main types of transactions
Investment of assets by owner
Withdrawal of assets by owner
Income derived
Expenses incurred
Types of accounts
Capital
Drawings or withdrawals
13
14
The Income Statement
The Income Statement
Marianas GEN Y Fashions
The income statement, also referred to as the
Statement of Financial Performance (or a Profit
& Loss Statement), presents the financial
efforts of an entity for a given period (generally
one year).
Income Statement
For the year ended 30 June 2015
INCOME
Dress making revenue
$442,500
EXPENSES
Advertising expense
It presents information on Revenue and
Expenses, the outcome being either a Profit or
a Loss .
$ 20,250
Materials expense
91,710
Salaries & wages expense
127,800
Rent expense
40,260
Telephone expense
20,190
Light & Power expense
47,940
PROFIT
348,150
$ 94,350
15
The Income Statement (cont.)
16
The Statement of Changes in Equity
Income
Marianas GEN Y Fashions
Statement of Changes in Equity
For the year ended 30 June 2015
Inflows of or savings in outflows of economic
benefits that result in an increase in equity during
the reporting period
Marianas, Capital - 1 July 2014
Expenses
Decreases in equity representing the consumption or
loss of economic benefits in the form of reductions
in assets or increases in liabilities other than
distributions to owners
Net profit for the year
Holmes Ins*tute 2016
94,350
$ 331,680
Less: Drawings
Mariana, Capital - 30 June 2014
17
$ 237,330
45,000
$ 286,680
18
The Statement of Cash Flows
The Statement of Changes in Equity (cont.)
Balance sheet
Income statement
Balance sheet
as at beginning of year
for the period
as at beginning of year
A1 L1 = E1
I E = Profit
A2 L2 = E2
Statement of owners equity
Income and expenses do not necessarily
represent cash.
Income & Expenses result in Profit/Loss. It
represents recognition of earnings as well as
expenses that can be accrued as well as some
non-cash expenses such as depreciation
Statement of cash flows reports
Cash in
Cash out
By activity type
for the period
E1 + Profit Drawings = E2
3
19
20
In class exercise 1
The Statement of Cash Flows (cont.)
Consider the list of accounts given and categorise them as an asset, liability or
shareholders equity item that would appear on the balance sheet or a revenue or expense
that would appear on the income statement by ticking the appropriate column.
Marianas GEN Y Fashions
Statement of Cash Flows
For the year ended 30 June 2015
Asset
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES
Cash received from customers
$424,710
Cash paid to suppliers and employees
(342,000)
Net cash from operating activities
Cost of goods sold
Loan
Purchase of land and buildings
(315,000)
Purchase of dress-making equipment
(110,700)
Net cash used in investing activities
Equipment
Wages
expense
Wages
payable
(425,700)
Retained prots
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES
Amount borrowed under mortgage
201,000
Investment by owner
237,330
Drawings by owner
(45,000)
Accounts
receivable
Accounts
payable
Prepaid
insurance
Net cash from financing activities
393,330
Net increase (decrease) in cash held
50,340
Cash at beginning of year
Unearned
revenue
Accrued
wages
Inventory
Cash at end of year
Deprecia*on
$ 50,340
21
22
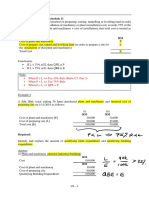
In class exercise 2
Answer:
Liability
Share capital
Shareholders
Equity
Sales
Accounts
payable
14,000
Capital
Inventory
31,000
Unearned revenue
9000
Account payable
19,000
Prepaid insurance
6000
Wages expenses
13,000
Sales revenue
58,000
insurance expenses
3,000
Plant & Equipment
110,000
Loan
25,000
Cash
20,000
REQUIRED:
Accrued wages
1.Prepare an income statement for the period between Jan to 30 June 2013.
2.Whats the amount of the initial capital that Peter invested in his business?
3.Prepare balance sheet at 30 June 2013.
23
Holmes Ins*tute 2016
Account receivable
Unearned revenue
Deprecia*on
Information:
Retained prots
Inventory
financial year, 30 June 2013. The business has the following account
Wages payable
Prepaid insurance
Peter started his small retail business in January 2013. At the end of the
Wages expense
Accounts receivable
Expense
Cost of goods sold
Equipment
Revenue
Loan
Shareholders Revenue Expense
Equity
Sales
$ 82,710
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES
Asset
Liability
Share capital
24
Answer: Income Statement
Answer: Balance Sheet
Peters
Retail
Income
Statement
for
the
year
ended
at
30
June
2013
Sales
Expenses:
Wages
Insurance
13,000
3,000
Net Prot
$
58,000
16,000
42,000
Assets
Cash
Accounts
Receivable
Inventory
Prepaid
Insurance
Peters
Retail
Balance
Sheet
as
at
30
June
2013
$
Liabili;es
20,000
Accounts
Payable
Unearned
revenue
14,000
31,000
Loan
6,000
Plant & Equipment
110,000
Total Assets
181,000
Equity
Capital
Total
L
+
E
$
19,000
9,000
25,000
53,000
128,000
128,000
181,000
As the total L+E = A = 181,00. Equity is then 181,000-53,000 = 128,000
25
26
Assumptions Made & Characteristics of Information (cont.)
Assumptions Made & Characteristics of Information
Financial Statement Assumptions
Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Information
Accounting entity assumption
Need to identify boundaries
Accrual basis assumption
Transactions and events recorded when they
occur
Going concern assumption
Entity will continue indefinitely
Accounting period assumption
Profit determined for a period of time
Monetary assumption
Relevance
Materiality
Comparability and consistency
Understandability
Reliability
Faithful representation
Substance over form
Neutrality
Prudence
Completeness
27
Effects of Transactions on the Accounting Equation &
Financial Statements
28
Example
Transactions result in changes in assets,
liabilities and equity
Every transaction affects at least
2 components of the accounting equation
After each transaction is recorded the equation
is still in balance
1. Gracie Jones deposits $35,000 in a business
bank account.
Assets
Cash at bank
(1) $35,000
=
=
Liabilities
Equity
Gracie Jones, Capital
$35 000
ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY
29
Holmes Ins*tute 2016
30
Example (cont.)
Example (cont.)
3. Gracie purchases inventory for $2,500 on
credit
2. Gracie purchases a Vehicle & some Shopfittings in cash
Assets
=
Cash at bank Shop-fittings Vehicle
(1) $35,000
=
(2) -30,000 + 9,000
+ 21,000
5,000 + 9,000
+ 21,000 =
Liabilities
+
Equity
Gracie Jones, Capital
$35,000
35,000
Assets
Cash at bank Shop-fittings
(1) $35,000
(2) -30,000 + 9,000 +
5,000 + 9,000 +
(3)
5,000 + 9,000 +
35,000
=
Vehicle Inventory
21,000
21,000
+ 2,500
21,000 + 2 500
Liabilities
+
Equity
Accounts payable
Gracie Jones, Capital
=
$35,000
=
=
=
35,000
+2,500
2,500
$37,500
35,000
$37,500
31
32
Transaction Analysis
In class exercise 3
Jeffs Pool Repairs began operations on 1 August 2013 and completed the following
transactions during the first month.
1.Jeff Drain deposited $50,000 of his personal funds in a current account at a bank
opened in the name of the business
2.Pool repair equipment was purchased at a cost of $30,000, of which $20,000 was
paid in cash. A loan payable was given for the remainder of $10,000
3.Jeff collected $6000 from customers for repair services performed.
4.Rent was paid for the month of August, $2400.
5.Supplies amounting to $2740 were purchased on credit
6.Wages of $1000 were paid as well as an account for electricity, $540.
7.Jeff paid for the supplies purchased in (5) above
8.Supplies used during August amounted to $1280
Required:
a) Prepare transaction analysis and show the effects of each of the transactions on the
accounts listed. Indicate totals after each transaction
b) Prepare an income statement and a statement of changes in equity for the month
ended 31 Aug, and a balance sheet as at 31 Aug 2013.
33
Answer:
Answer
35
Holmes Ins*tute 2016
34
36
Answer
Answer
37
38
Basic Rules of double entry
For every DR there
must be an equal CR
When to increase &
when to decrease
DR
Tutorial
Reading: Chapter 1, 2 & 3
Tutorial:
Chapter 1
CR
Asset
Discussion Questions: 15, 16,
Problems: 1.3, 1.19, 1.22
Expense
Chapter 2
Liability
Discussion questions: 1, 7,
Problems: 2.1, 2.11,
Equity
Chapter 3
Discussion questions: 1, 3
Problem 3.1, 3.5, 3.7 & 3.15 pp. 131-140
Revenue
This will be further discussed in next weeks lecture
39
Holmes Ins*tute 2016
40
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 2015 04 28 - Endurance International Group: A Web of DeceitDocument61 pages2015 04 28 - Endurance International Group: A Web of DeceitgothamcityresearchNo ratings yet
- Audit of Cash ProblemsDocument23 pagesAudit of Cash ProblemsReign Ashley RamizaresNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Contemporary Accounting A Strategic Approach For Users 9th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Contemporary Accounting A Strategic Approach For Users 9th Edition PDFpeggy.mulvey478100% (33)
- Internal Audit Tapestry EY ACLN InSights Apr11Document16 pagesInternal Audit Tapestry EY ACLN InSights Apr11Veena HingarhNo ratings yet
- Lone Pine Cafe Case SolutionDocument5 pagesLone Pine Cafe Case SolutionShammika Krishna75% (4)
- SOP-General Office ExpensesDocument1 pageSOP-General Office ExpensesMohammad Amir HamzaNo ratings yet
- Bsac 306 - Govacc Seatwork 1 Overview of Govt Acctg-Student Copy - RoldanDocument6 pagesBsac 306 - Govacc Seatwork 1 Overview of Govt Acctg-Student Copy - RoldanJheraldinemae RoldanNo ratings yet
- Chap 7+ 8 Documents+Daybook - SolutionDocument8 pagesChap 7+ 8 Documents+Daybook - SolutionBilal GouriNo ratings yet
- Substantive Procedures - Class of Transactions: Sales and Sales ReturnDocument16 pagesSubstantive Procedures - Class of Transactions: Sales and Sales ReturnCyrra BalignasayNo ratings yet
- Group Activity 1Document10 pagesGroup Activity 1Winshei Cagulada0% (1)
- Account Determination MM en inDocument146 pagesAccount Determination MM en inlitu84No ratings yet
- Single Entry Accounting RecordsDocument8 pagesSingle Entry Accounting RecordsPARAG BHAWANINo ratings yet
- SCM Discussion1Document18 pagesSCM Discussion1David GuevarraNo ratings yet
- 75% RuleDocument2 pages75% RuleKAM JIA LINGNo ratings yet
- Psa 230Document20 pagesPsa 230Joanna Caballero100% (2)
- Acma M1Document6 pagesAcma M1Mohammed Shaff AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Accounting - 1st Quiz Cash and Cash Equivalent 2011Document2 pagesAccounting - 1st Quiz Cash and Cash Equivalent 2011Louie De La Torre40% (5)
- National Municipal Asset Valuation ManualDocument86 pagesNational Municipal Asset Valuation Manualkhan_sadi0% (1)
- Penn Foster 06101501 Financial Accounting Exam Parts 1 and 2 Manville and Coleman-FooseDocument3 pagesPenn Foster 06101501 Financial Accounting Exam Parts 1 and 2 Manville and Coleman-FooseMike RussellNo ratings yet
- Laporan Keuangan 31 Desember 2016Document78 pagesLaporan Keuangan 31 Desember 2016Nova Dwi LestariNo ratings yet
- Identifying Manufacturing Overhead CostsDocument2 pagesIdentifying Manufacturing Overhead CostsSnapShop by AJNo ratings yet
- Analyze financial statements and calculate ratiosDocument11 pagesAnalyze financial statements and calculate ratiosFaria AlamNo ratings yet
- 2016 06 04 - Eap - 04 Jun - 1Document13 pages2016 06 04 - Eap - 04 Jun - 1janastarr99No ratings yet
- Competency Based Learning MaterialsDocument29 pagesCompetency Based Learning MaterialsAlexandra Sarmuyan100% (2)
- Toronto Chapter: Strengthening Relationships Through PartnershipsDocument44 pagesToronto Chapter: Strengthening Relationships Through PartnershipssunilNo ratings yet
- Income Statement TemplateDocument6 pagesIncome Statement TemplateAziz MalikNo ratings yet
- 4AC0 01 Que 20150107Document20 pages4AC0 01 Que 20150107anupama dissanaykeNo ratings yet
- Latihan MatrikulasiDocument4 pagesLatihan MatrikulasiD Ayu Hamama PitraNo ratings yet
- Accelerapro CPD coursesDocument2 pagesAccelerapro CPD coursesMiecoMoralesNo ratings yet
- MACC7001 Course OutlineDocument5 pagesMACC7001 Course Outline南玖No ratings yet