Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jjo
Uploaded by
Anonymous DJuu65GOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jjo
Uploaded by
Anonymous DJuu65GCopyright:
Available Formats
SITUATION:
Part I.
A truck traveling along a straight road at speed v1 = 20 km/hr, increase
s its speed to v2 = 120 km/hrin time t = 15 s. If its acceleration is constant,
determine the distance traveled.
A car starts from rest and reaches a speed v = 80 ft/s after traveling a
distance d = 500 ftalong a straight road. Determine its constant acceleration a
nd the time of travel.
A particle is moving with velocity v0 when s = 0 and t = 0. If it is sub
jected to a deceleration of a = -k v3, where k is a constant, determine its velo
city as functions of time.
A baseball is thrown downward from a tower of height h = 50 ftwith an in
itial speed v0 = 18 ft/s. Determine the speed at which it hits the ground and th
e time of travel.
Starting from rest, a particle moving in a straight line has an accelera
tion of a = (2t - 6). Whatis the particle s velocity at 6 s and what is its positi
on at 11 s?
Traveling with an initial speed 70 kpha car accelerates at rate 6000 km/
hr2along a straight road. How long will it take to reach a speed 120 kph? Also,
through what distance does the car travel during this time?
A freight train travels at v = 60(1 - e- b t) where tis the elapsed time
. Determine the distance traveled in time 3 s, and the acceleration at this time
. (where: b = 1/s)
A particle has an initial speed v0 = 27 m/s. If it experiences a deceler
ation a = -6t, determine thedistance traveled before it stops.
A particle is moving with velocity v0 when s = 0 and t = 0. If it is sub
jected to a deceleration of a = -k v3, where k is a constant, determine its velo
city as functions of time.
The car is travelling at 30 mi/h when the traffic light 295ft ahead turn
s yellow. The driver takes 1s to react before he applies the brakes. A) After he
applies the brakes, what constant rate of deceleration will cause the car to co
me to a stop just as it reaches the light? B) How long does it take the car to t
ravel the 295ft to the light.
The airplane releases its drag parachute at time t=0. Its velocity is gi
ven as a function of time by,
v =
80/(1+0.32t )m/s. What is the airplane s acceleratio
n at t = 3seconds,
SITUATION:
PART II.
The pitcher throws the baseball horizontally with a speed of 140ft/s fro
m a height of 5 ft. If the batter is 60 ft away, determine the time for the ball
to arrive at the batter and the height h at which it passes the batter.
Determine the horizontal velocity VA of a tennis ball at A so that it ju
st clears the net at B. Also, find the distance s where the ball strikes the gro
und.
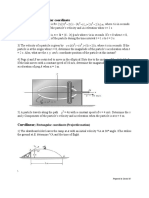
Determine the smallest angle ?, measured above the horizontal, that the
hose should be directed so that the water stream strikes the bottom of the wall
at B. The speed of the water at the nozzle is VC.
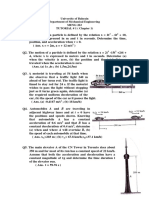
(4) When the athlete releases the shot, it is 7ft above the ground. The horizont
al distance the shot travels from the point of release to the point where it hit
s the ground is 60ft. What was the initial velocity v of the shot?
(5) Measurements of a shot recorded on a videotape during a basketball
shown. The ball passed through the hoop even though it barely cleared
of the player B who attempted to block it.
Neglecting the size of
determine the magnitude vAof its initial velocity and the height h of
ball when it passes over player B.
game are
the hands
the ball,
the
(6) A projectile is launched from the ground level with an initial velocity v =
20 m/s. What initial angle above the horizontal causes the range R to be maximum
, and what is the maximum range?
(7) The skier in
Fig. 13.21 leaves the 200 surface at
10m/s.
a.) Dete
rmine the distance d to the point where
he lands
.
b.) What
are the magnitudes of his components
parallel
and perpendicular to the 450 surface just
before h
e lands?
You might also like
- Chapter 2 - WorksheetDocument11 pagesChapter 2 - WorksheetHenokNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document3 pagesAssignment 5Garvit GargNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-IDocument12 pagesWorksheet-IHabtie WalleNo ratings yet
- Quest-Ed - Copy - Google DriveDocument6 pagesQuest-Ed - Copy - Google DriveShukla Manish100% (1)
- Problem Set On DynamicsDocument40 pagesProblem Set On DynamicsMa. Socorro Angela LlavoresNo ratings yet
- CE261 DYNAMICS-Problems Fall 09Document24 pagesCE261 DYNAMICS-Problems Fall 09Kevin MedinaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Rectilinear and Curvilinear Motion ProblemsDocument4 pagesUnit I Rectilinear and Curvilinear Motion ProblemsmanojNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of particles and motionDocument23 pagesDynamics of particles and motionVisminda Sebastian0% (1)
- 3 Rectilinear ProblemsDocument8 pages3 Rectilinear ProblemsmohamedalfatihNo ratings yet
- Ce261 Dynamics-Problems Fall 2011Document23 pagesCe261 Dynamics-Problems Fall 2011Ankur SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Problems On DynamicsDocument37 pagesLecture Problems On DynamicsCha Castillo100% (1)
- Work Sheet I & IIDocument17 pagesWork Sheet I & IIeyobNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Worksheet One: Bililign FDocument3 pagesDynamics Worksheet One: Bililign FFootkball 1No ratings yet
- Taller I-Repaso CinemáticaDocument3 pagesTaller I-Repaso CinemáticaEmmanuel Gómez LosadaNo ratings yet
- Curvilinear Rectangular Coordinate: T J+ K M, Where T Is in SecondsDocument4 pagesCurvilinear Rectangular Coordinate: T J+ K M, Where T Is in Secondsdaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Kinematics) : X 4t+5t MetreDocument1 pageAssignment (Kinematics) : X 4t+5t MetreGurleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies ProblemsDocument5 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies ProblemsRuel B. Ramos Jr.No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Eso209 SummerDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 Eso209 SummerDinesh Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Take Home Exam InstructionsDocument3 pagesTake Home Exam InstructionsHeiro KeystrifeNo ratings yet
- PSET DRB FRDocument8 pagesPSET DRB FRKATHLEEN JOY DE CASTRONo ratings yet
- Problem-Set-Part-1-AnswerDocument17 pagesProblem-Set-Part-1-AnswerVince MarananNo ratings yet
- Newton 2Document4 pagesNewton 2Tsedeke YeteshaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet I - Kinematics of ParticlesDocument7 pagesWorksheet I - Kinematics of ParticlesAdnan ShafiNo ratings yet
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 1 (Chapter 1)Document3 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 1 (Chapter 1)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- 3-Homeworks Examples ProblemsDocument53 pages3-Homeworks Examples ProblemsCafer BalNo ratings yet
- MEC31Document3 pagesMEC31DiannaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document5 pagesTutorial 2Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On DynamicsDocument7 pagesWorksheet On DynamicsfieraminaNo ratings yet
- Cinematica ParticulaDocument20 pagesCinematica ParticulaGeovanny OrtegaNo ratings yet
- MCHE-213 Assignment IDocument8 pagesMCHE-213 Assignment IAbed BaalbakiNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreDocument5 pagesExtra Exercise Chapter One: System of Units: - BT, Where T Refers To Time. What AreAina AdamNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM SET KinematicsDocument1 pagePROBLEM SET KinematicsRykell FloresNo ratings yet
- MECDYNAMICSDocument15 pagesMECDYNAMICSMark Asesor CalonzoNo ratings yet
- Border BetchDocument25 pagesBorder Betchjmaf mafNo ratings yet
- Enphys30 - As1.1 1Document1 pageEnphys30 - As1.1 1Lawrence Angelo Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Motion Along A Line: StudentDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Motion Along A Line: StudentQassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Dynamics in MotionDocument34 pagesDynamics in Motiond jay mereculoNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Prob SetDocument29 pagesDynamics Prob Setrammable0% (2)
- ENGN 37 HomeworkDocument25 pagesENGN 37 HomeworkLucia AntoniusNo ratings yet
- XI Ch-3 Motion in A Straight Line 0Document36 pagesXI Ch-3 Motion in A Straight Line 0sunildhanwanNo ratings yet
- Variable acceleration and motion curve problemsDocument2 pagesVariable acceleration and motion curve problemsKent Edve Neil Rabe0% (2)
- Kinema TicsDocument7 pagesKinema Ticsapcc1No ratings yet
- Review Module - Classical PhysicsDocument2 pagesReview Module - Classical PhysicsTatingJainarNo ratings yet
- MCE 111 Mechanics Dynamics - Assignment 1Document2 pagesMCE 111 Mechanics Dynamics - Assignment 1Omar NabilNo ratings yet
- Physics Help Problems W SolutionsDocument11 pagesPhysics Help Problems W SolutionsbuffmomNo ratings yet
- Kinematicsschool 2009Document7 pagesKinematicsschool 2009EzhilarasiPazhanivelNo ratings yet
- Copperbelt University tutorial on kinematics problemsDocument4 pagesCopperbelt University tutorial on kinematics problemsDanny MutamboNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Fisica IDocument5 pagesTrabajo Fisica IMVAZ233No ratings yet
- Motion in 2 DDocument12 pagesMotion in 2 DVenesia Ayu Dewanti0% (1)
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionAlbert Ascher100% (34)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 8 MotionDocument22 pagesNCERT Solutions for Class 9 Physics Chapter 8 MotionRAJEEV MISHRANo ratings yet
- hwk12 PDFDocument24 pageshwk12 PDFRick PongiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Solved Examples ExplainedDocument6 pagesKinematics Solved Examples Explainedthiripura sundariNo ratings yet
- 02kinematics Practice Free Response W - AnswersDocument6 pages02kinematics Practice Free Response W - AnswersBrandonNo ratings yet
- G11 Revision Worksheet Sem - 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesG11 Revision Worksheet Sem - 1 SolutionsterabaapNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Rate of Change (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Amada Pega 357 With 04PC Programming LimitsDocument12 pagesAmada Pega 357 With 04PC Programming Limitsdtrnghia100% (1)
- General Physics 1 MOTION ALONG STRAIGHT LINEDocument28 pagesGeneral Physics 1 MOTION ALONG STRAIGHT LINEWarren SilvaNo ratings yet
- 1 Physics Previous (2009-2016) Questions Chapter WiseDocument44 pages1 Physics Previous (2009-2016) Questions Chapter WiseJulienJosephThomas89% (19)
- The Universe: Section 8 - AstrophysicsDocument3 pagesThe Universe: Section 8 - Astrophysicssweghswe asewgteswhyNo ratings yet
- TOLC-I Simulation 2024Document15 pagesTOLC-I Simulation 2024amayaamigo.gNo ratings yet
- m800 m80 E80 c80 Series Handbook Ib1501280engbDocument670 pagesm800 m80 E80 c80 Series Handbook Ib1501280engbsunhuynhNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Exercise PDFwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - General Physics 1Document14 pagesWeek 2 - General Physics 1do san namNo ratings yet
- Traffic Signals PuzzleDocument11 pagesTraffic Signals Puzzlesabir aliNo ratings yet
- Physics Intro & KinematicsDocument7 pagesPhysics Intro & KinematicsEnger AlingasaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Not For SaleDocument35 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Not For SaleRizafel Joy CuencaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 11 For Board Exam 2024pwdr720aiims.cardiologistNo ratings yet
- 2019 HSC Mathematics Extension 2 PDFDocument24 pages2019 HSC Mathematics Extension 2 PDFLOLNo ratings yet
- 9 Chapter-8Document16 pages9 Chapter-8dl9s6547100% (1)
- Radar Plotting TipsDocument6 pagesRadar Plotting TipsEugene Zenum100% (2)
- 16 Describing Motion - Chapter Resources For Differentiated InstructionDocument101 pages16 Describing Motion - Chapter Resources For Differentiated InstructionFernando Sorto70% (10)
- Velocity and AccelerationDocument15 pagesVelocity and Accelerationmohamad aliNo ratings yet
- Algebra 100 ItemsDocument5 pagesAlgebra 100 ItemsBensonNo ratings yet
- HPhys Unit 01 Packet PDFDocument14 pagesHPhys Unit 01 Packet PDFjbc929_billsNo ratings yet
- Youtube Channel Dixit Sir Android App LinkDocument4 pagesYoutube Channel Dixit Sir Android App LinkTanmoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Areas Related To CirclesDocument33 pagesAreas Related To CirclesDkuaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 19 April Test (2 HRS)Document4 pagesAP Physics 19 April Test (2 HRS)Dheeraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion PhysicsDocument4 pagesCircular Motion Physicsdhion13No ratings yet
- WiproDocument20 pagesWiproMuthu ManiNo ratings yet
- Science 7 MatrixDocument17 pagesScience 7 MatrixAlain Sayson PresillasNo ratings yet
- Driver 1330HDocument27 pagesDriver 1330HDede Zakaria AnwarNo ratings yet
- XI Physics CH 2 AssignmentDocument1 pageXI Physics CH 2 AssignmentFranknire IgNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Practice Problems SolvedDocument3 pagesKinematics Practice Problems SolvedAbhinandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Speed and distance word problemsDocument3 pagesSpeed and distance word problemsKarinaNo ratings yet
- PHYS 1120 Rotational Kinematics SolutionsDocument7 pagesPHYS 1120 Rotational Kinematics SolutionsEnger AlingasaNo ratings yet