Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Russia Russia
Uploaded by
WongHcCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Russia Russia
Uploaded by
WongHcCopyright:
Available Formats
Russia (Listeni/'r???/; Russian: ??????, tr. Rossija; IPA: [r?'s?ij?
]; from the G
reek: ??s?a
Rus'), also officially known as the Russian Federation[12] (Russian:
?????????? ?????????, tr. Rossijskaja Federacija; IPA: [r?'s?ijsk?j? f??d??'rats?
j?]), is a transcontinental country in Eurasia.[13] At 17,075,200 square kilomet
res (6,592,800 sq mi),[14] Russia is the largest country in the world, covering
more than one eighth of Earth's inhabited land area,[15][16][17] and the ninth m
ost populous, with over 146.6 million people at the end of March 2016.[6][7] Ext
ending across the entirety of northern Asia and much of Eastern Europe, Russia s
pans eleven time zones and incorporates a wide range of environments and landfor
ms. From northwest to southeast, Russia shares land borders with Norway, Finland
, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and Poland (both with Kaliningrad Oblast), Belarus,
Ukraine, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia, and North Korea. It
shares maritime borders with Japan by the Sea of Okhotsk and the U.S. state of A
laska across the Bering Strait.
The nation's history began with that of the East Slavs, who emerged as a recogni
zable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD.[18] Founded and rule
d by a Varangian warrior elite and their descendants, the medieval state of Rus
arose in the 9th century. In 988 it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the Byzan
tine Empire,[19] beginning the synthesis of Byzantine and Slavic cultures that d
efined Russian culture for the next millennium.[19] Rus' ultimately disintegrate
d into a number of smaller states; most of the Rus' lands were overrun by the Mo
ngol invasion and became tributaries of the nomadic Golden Horde in the 13th cen
tury.[20] The Grand Duchy of Moscow gradually reunified the surrounding Russian
principalities, achieved independence from the Golden Horde, and came to dominat
e the cultural and political legacy of Kievan Rus'. By the 18th century, the nat
ion had greatly expanded through conquest, annexation, and exploration to become
the Russian Empire, which was the third largest empire in history, stretching f
rom Poland on the west to Alaska on the east.[21][22]
Following the Russian Revolution, the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republ
ic became the largest and leading constituent of the Union of Soviet Socialist R
epublics, the world's first constitutionally socialist state.[23] The Soviet Uni
on played a decisive role in the Allied victory in World War II,[24][25] and eme
rged as a recognized superpower and rival to the United States during the Cold W
ar. The Soviet era saw some of the most significant technological achievements o
f the 20th century, including the world's first human-made satellite and the lau
nching of the first humans in space. By the end of 1990, the Soviet Union had th
e world's second largest economy, largest standing military in the world and the
largest stockpile of weapons of mass destruction.[26][27][28] Following the par
tition of the Soviet Union in 1991, fourteen independent republics emerged from
the USSR; as the largest, most populous, and most economically developed republi
c, the Russian SFSR reconstituted itself as the Russian Federation and is recogn
ized as the continuing legal personality and sole successor state of the Soviet
Union.[29] It is governed as a federal semi-presidential republic.
The Russian economy ranks as the twelfth largest by nominal GDP and sixth larges
t by purchasing power parity in 2015.[30] Russia's extensive mineral and energy
resources are the largest such reserves in the world,[31] making it one of the l
eading producers of oil and natural gas globally.[32][33] The country is one of
the five recognized nuclear weapons states and possesses the largest stockpile o
f weapons of mass destruction.[34] Russia is a great power and a permanent membe
r of the United Nations Security Council, as well as a member of the G20, the Co
uncil of Europe, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), the Shanghai Coop
eration Organisation (SCO), the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Eu
rope (OSCE), and the World Trade Organization (WTO), as well as being the leadin
g member of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the Collective Securit
y Treaty Organization (CSTO) and one of the five members of the Eurasian Economi
c Union (EEU), along with Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan.
You might also like
- Shaolin Chin NaDocument1 pageShaolin Chin NaWongHcNo ratings yet
- NeijiaDocument1 pageNeijiaWongHcNo ratings yet
- Pitman ShorthandDocument1 pagePitman ShorthandWongHcNo ratings yet
- TeelineDocument1 pageTeelineWongHcNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- +BBA - ZU Exam QuestionsDocument2 pages+BBA - ZU Exam Questionsblue nnn100% (1)
- Heritage and Deracination in Walker - EverydayUseDocument10 pagesHeritage and Deracination in Walker - EverydayUseIresha DeepthiNo ratings yet
- Payday 2 - Weapons GuideDocument28 pagesPayday 2 - Weapons GuideAleksander BielskiNo ratings yet
- Chris Pine: Germany?, A Short Film, and in The Princess Diaries 2: Royal Engagement. Pine PlayedDocument1 pageChris Pine: Germany?, A Short Film, and in The Princess Diaries 2: Royal Engagement. Pine Playedgabi_collaçoNo ratings yet
- John Brown's BodyDocument1 pageJohn Brown's BodyEmil BleiNo ratings yet
- CIE 2006 Paper 1Document8 pagesCIE 2006 Paper 1CH YueNo ratings yet
- Syria by Daniel MaesDocument7 pagesSyria by Daniel Maeskwintencirkel3715No ratings yet
- PRSSA Bateman Case Study CompetitionDocument63 pagesPRSSA Bateman Case Study CompetitionHannahNo ratings yet
- Battle of ImusDocument2 pagesBattle of ImusDarry Blancia100% (2)
- Risus Trek Starship RulesDocument2 pagesRisus Trek Starship Rulesdomingojs233710No ratings yet
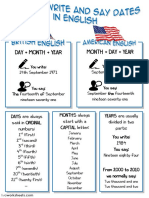
- How To Write and Say Dates in EnglishDocument2 pagesHow To Write and Say Dates in EnglishĆháŕáfŃéźhí33% (3)
- PM Letter To EU Council PresidentDocument6 pagesPM Letter To EU Council PresidentThe Guardian93% (14)
- CH2 Scarlet SorcererDocument177 pagesCH2 Scarlet Sorcererfury46No ratings yet
- 03 - Armies of Imperium v4.1Document87 pages03 - Armies of Imperium v4.1bruno260000% (1)
- Exalted 3E - Adversaries of The Righteous (COMPILED)Document77 pagesExalted 3E - Adversaries of The Righteous (COMPILED)241again71% (7)
- Lawsuit To Relocate Confederate MonumentDocument55 pagesLawsuit To Relocate Confederate MonumentGlennKesslerWPNo ratings yet
- Operation Benton AAR 28 Sep 1967Document48 pagesOperation Benton AAR 28 Sep 1967Robert Vale100% (1)
- MAP Work FOR CLASS 9Document16 pagesMAP Work FOR CLASS 9hkharshkumar2010No ratings yet
- Empire Army List by Border PrincesDocument26 pagesEmpire Army List by Border Princeskrychu1996100% (2)
- Anthem For Doomed Youth NotesDocument4 pagesAnthem For Doomed Youth NotesSnezhana Padeshka100% (1)
- 100 Demon WeaponsDocument31 pages100 Demon WeaponsSpencer KrigbaumNo ratings yet
- Megafortress (Early 90s PC Game) Radio CodesDocument51 pagesMegafortress (Early 90s PC Game) Radio CodesaccumulatorNo ratings yet
- Marcus Wallén, NAZI GOLD AND THE FIELD MARSHALL'S SECRETDocument1 pageMarcus Wallén, NAZI GOLD AND THE FIELD MARSHALL'S SECRETYasmin AlishenasNo ratings yet
- The Question of American Strategy in The Indo-PacificDocument21 pagesThe Question of American Strategy in The Indo-PacificHoover InstitutionNo ratings yet
- Leonhard 0403Document6 pagesLeonhard 0403jeetdokuneNo ratings yet
- Robert Clive: Assessing The "Conqueror of India"Document26 pagesRobert Clive: Assessing The "Conqueror of India"Nainil TripathiNo ratings yet
- IHL PrinciplesDocument41 pagesIHL PrinciplesD Del Sal0% (1)
- Read The Text and Do The ExercisesDocument5 pagesRead The Text and Do The Exercisesavicenna 27No ratings yet
- Fred Halliday... 1981... The Arc of Crisis and The New Cold WarDocument13 pagesFred Halliday... 1981... The Arc of Crisis and The New Cold WarBilgi SilinmistirNo ratings yet
- Michailidis AbecedarDocument10 pagesMichailidis Abecedarapi-235372025No ratings yet