Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Che 91165 Organicoutline PDF
Uploaded by
Mark Anthony CaroOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Che 91165 Organicoutline PDF
Uploaded by
Mark Anthony CaroCopyright:
Available Formats
No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY
AS91165
Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds
Level 2 4 Credits
This achievement standard involves demonstrating understanding of the properties of selected organic
compounds.
Achievement
Achievement with Merit
Achievement with Excellence
Demonstrate understanding of
the properties of selected
organic compounds.
Demonstrate in-depth
understanding of the properties
of selected organic compounds.
Demonstrate comprehensive
understanding of the properties of
selected organic compounds.
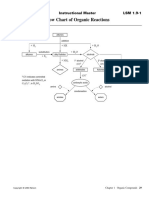
This AS involves selected organic compounds containing no more than eight carbons in the longest chain.
naming of organic molecules according to IUPAC convention.
formulae
o
empirical - stoichiometric proportions of atoms only e.g. CH2O
o
molecular - formula of the actual molecule e.g. C3H6O3
o
structural formulae - shows how atoms are connected. It may be drawn in different ways
condensed
e.g.
expanded
or
e.g.
selected organic compounds homologous series - their functional groups and reactions
o
alkanes
halogenation - substitution reactions of alkanes with halogens (limited to
monosubstitution)
o
alkenes
addition reactions of alkenes with
H2/Pt - hydrogenation (or H2/Ni)
Cl2, Br2 - halogenation
H2O/H+ (conc. H2SO4/H2O) hydration (including identification of major and minor
products on addition to asymmetric alkenes - Markovnikov's Rule)
hydrogen halides e.g. HCl & HBr hydrohalogenation (including identification of
major and minor products on addition to asymmetric alkenes - Markovnikov's Rule)
polymerisation
oxidation of alkenes with MnO4 and H+/ MnO4
o
alkynes
No Brain Too Small CHEMISTRY
haloalkanes
classification of haloalkanes as primary, secondary or tertiary
substitution reactions of haloalkanes with
ammonia
aqueous potassium hydroxide
elimination of hydrogen halides from haloalkanes with alcoholic potassium hydroxide
(including identification of major and minor products for asymmetric reactants - Saytzeff's
rule)
o
o
primary amines
acidbase reactions of amines
alcohols
classification of alcohols as primary, secondary or tertiary
substitution reactions of alcohols with hydrogen halides, PCl3, PCl5, SOCl2
oxidation of primary alcohols to form carboxylic acids with MnO4-/H+, heat or with Cr2O72/H+, heat
elimination of water from alcohols (including identification of major and minor products
for asymmetric reactants - Saytzeff's rule)
carboxylic acids
acidbase reactions of carboxylic acids
identification of unlabelled samples of the above through reaction with common reagents and
indicators
completion of flow charts/reaction schemes for simple organic conversions of the above
physical properties of the selected organic compounds
o
solubility in water
depending on functional group
depending on the size of the molecule
o
melting and boiling points
identification of types of reactions; addition, elimination, substitution, oxidation
isomerism
o
constitutional (structural - same molecular formula type and number of atoms - but different
connectivity)
different carbon skeleton
different position of functional group
different functional group e.g cycloalkane & alkene
o
geometric (cis and trans) isomers alkenes only
rotation of the atoms about the axis of the carbon to carbon double bond is restricted
requirement to have two different atoms/groups attached to each end of the double bond
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Alice in Wonderland - T. T. SutherlandDocument124 pagesAlice in Wonderland - T. T. SutherlandYago Martins Campos100% (1)
- Offerings in Gaelic PolytheismDocument10 pagesOfferings in Gaelic PolytheismGaolNaofa100% (7)
- E J Gello Winery Case AnalysisDocument29 pagesE J Gello Winery Case Analysismileva_lukicNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Implementation of The Integrated Work System in The Secondary Manufacturing Department of British American Tobacco BangladeshDocument49 pagesInternship Report On Implementation of The Integrated Work System in The Secondary Manufacturing Department of British American Tobacco BangladeshMark Anthony Caro0% (1)
- Diagnostic Study Report of Food Processing, Krishna District, Andhra PradeshDocument33 pagesDiagnostic Study Report of Food Processing, Krishna District, Andhra PradeshSudhir ImperfectNo ratings yet
- Vata Constitution AyurvedaDocument11 pagesVata Constitution AyurvedaElla Miu100% (1)
- Ricasoli Case StudyDocument21 pagesRicasoli Case StudyRodianneNo ratings yet
- DENR Rules for Implementing the Philippine Ecological Solid Waste Management ActDocument99 pagesDENR Rules for Implementing the Philippine Ecological Solid Waste Management ActPaolo Gonzales67% (3)
- Marketing Project On MaggieDocument28 pagesMarketing Project On MaggieSudipRanjanDas0% (1)
- (Cite If There Were Any Amendments) : Period CoveredDocument6 pages(Cite If There Were Any Amendments) : Period CoveredMark Anthony CaroNo ratings yet
- DAO 1992-29 - IRR of RA6969Document27 pagesDAO 1992-29 - IRR of RA6969Pacific Spectrum100% (1)
- (Cite If There Were Any Amendments) : Period CoveredDocument6 pages(Cite If There Were Any Amendments) : Period CoveredMark Anthony CaroNo ratings yet
- Ra 9003 PDFDocument44 pagesRa 9003 PDFMhare Oroceo Casanova100% (1)
- NPFCDocument1 pageNPFCMark Anthony CaroNo ratings yet
- Spring Mattresses Case StudyDocument5 pagesSpring Mattresses Case StudyMark Anthony CaroNo ratings yet
- Che2 Things To Remember OrganicDocument2 pagesChe2 Things To Remember OrganicMark Anthony CaroNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro PDFDocument56 pages1 Intro PDFMark Anthony CaroNo ratings yet
- 1-10 Organic Reactions Flowchart PDFDocument1 page1-10 Organic Reactions Flowchart PDFMark Anthony CaroNo ratings yet
- Organic ReactionsDocument1 pageOrganic ReactionsMasrulIsmailNo ratings yet
- AP Chem NotesDocument45 pagesAP Chem NotesSajiveSivalingamNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0268005X05000871 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0268005X05000871 MainMark Anthony CaroNo ratings yet
- Homework: I. Find The Word Which Has A Different Sound in The Underlined PartDocument7 pagesHomework: I. Find The Word Which Has A Different Sound in The Underlined PartTú QuyênNo ratings yet
- Pepsi MaxDocument17 pagesPepsi MaxWaqar Ali100% (1)
- Industri Media 2011Document8 pagesIndustri Media 2011Arinda Nur LNo ratings yet
- Travels With My Cats July 2009Document18 pagesTravels With My Cats July 2009Diego Shirley Medina ArandiaNo ratings yet
- Deniske product introduction: 一、 Dairy cultureDocument36 pagesDeniske product introduction: 一、 Dairy culturepengNo ratings yet
- Project Plan#3 (4th QTR)Document3 pagesProject Plan#3 (4th QTR)Rosann RosannNo ratings yet
- Matrix of Activities: Schools Division Office of Albay San Antonio National High SchoolDocument1 pageMatrix of Activities: Schools Division Office of Albay San Antonio National High SchoolJojie BurceNo ratings yet
- NagoriDocument27 pagesNagoriUmarchishtiNo ratings yet
- Committee MembersDocument6 pagesCommittee MembersAmman FinsNo ratings yet
- AGA User Manual - Companion ModelDocument48 pagesAGA User Manual - Companion ModelTamrspdNo ratings yet
- The Taste of Water in Japanese Garden Design by Wybe KuitertDocument2 pagesThe Taste of Water in Japanese Garden Design by Wybe Kuitertjtuylvanrilland100% (1)
- Personal SellingDocument8 pagesPersonal SellingAsim Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Nights in The Basement3Document14 pagesNights in The Basement3smithm12SNo ratings yet
- A Look at Your Child's NutritionDocument2 pagesA Look at Your Child's NutritionAslul KhitanNo ratings yet
- The Milk Teas Habits of 18 Year Onld Female Students in ISBADocument23 pagesThe Milk Teas Habits of 18 Year Onld Female Students in ISBAQuang HuyNo ratings yet
- Dark Obsessions A Dark Mafia Romance (McGowan Mafia Series Book 3) (Effie Campbell) (Z-Library)Document157 pagesDark Obsessions A Dark Mafia Romance (McGowan Mafia Series Book 3) (Effie Campbell) (Z-Library)AthroleetaNo ratings yet
- Wine MakingDocument13 pagesWine Makingper 11No ratings yet
- Syrups Are Concentrated Aqueous Preparations of A Sugar or Sugar Substitute With or Without Flavoring Agents and Medicinal SubstancesDocument2 pagesSyrups Are Concentrated Aqueous Preparations of A Sugar or Sugar Substitute With or Without Flavoring Agents and Medicinal SubstanceszuNo ratings yet
- SH0808Document16 pagesSH0808Anonymous 9eadjPSJNgNo ratings yet
- GV BrochureDocument4 pagesGV BrochureNatural Soy FoodsNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - The Farm LessonDocument3 pagesWeek 4 - The Farm LessonEccentricEdwardsNo ratings yet
- 52nd International Congress on Medieval Studies - May 2017Document259 pages52nd International Congress on Medieval Studies - May 2017jaredrodNo ratings yet
- Penns Restaurant Canton22 MenuDocument2 pagesPenns Restaurant Canton22 MenunuzunetNo ratings yet