Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computational Methods
Uploaded by
KarimMohamedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computational Methods
Uploaded by
KarimMohamedCopyright:
Available Formats
Numerical method for Improper Integrals
To solve an improper integral in the form of:
f ( x ) dx
We take the limit for the answer as the upper limit and the lower limit goes to
infinity
t
lim f ( x ) dx
t t
After that we should check if the integral converges or diverges, in case the
improper integral converges we get:
a
I = f ( x ) dx + f ( x ) dx+ f ( x ) dx
a
And we transform
1
A
f ( x ) dx= t12 f ( 1t ) dt AB> 0
A
1
B
I = f ( x ) dx+ f ( x ) dx+ f ( x ) dx
1/ A
A
1 / A
1/B
1 1
1 1
1 1
f
dt+ 2 f
dt+ 2 f
dt
2
t
t
t
t
1/B t
0 t
()
()
()
For Example:
sin ( x )
dx
x
3
let
I =
sin ( x )
sin ( x )
sin ( x )
dx+
dx +
dx
x
x
x
3
3
solve first term
sin ( x )
dx
x
1
3
sin
( 1t ) dt
Using extended midpoint rule, h=1/15
1
3
( 1t ) dt 1
sin
15
( )]
f ( t 0.3 ) + f t 7 + f t 1 + f ( t 0.1 ) +f t 1 =
( ) ( )
30
30
1
[0.63523.90151.67655.440229.6409 ] =
15
solve second term
sin ( x )
dx
x
3
Ignoring singularity at x = 0
Solving by (Abramowitz and Stegun 1972, p. 886) for Higher order rules n = 9, h =
2/3
3
sin ( x )
4h
dx=
989 f 7 +5888 f 5 928 f 1 +10496 f 1 4540 f 1 +10496 f 1928 f 5 +5888 f 7 + 989 f 3 =3.5
x
14175
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
Solve third term
1/ 3
sin ( x )
dx
x
0
sin
( 1t ) dt
Using extended midpoint rule, h=1/15
1/ 3
sin
( 1t ) dt 1
15
[( )
f t 1 + f ( t 0.1 ) + f t 1 +f t 7 + f ( t 0.3 ) =
30
( ) ( )
6
30
1
[ 29.64095.4402 ] =0.2 75295
15
First and third term are equal because function is odd function symmetric around xaxis
I =3.58142( 0.275295 )=3.03081
t =3.526
Error of Trapezoidal rule
Take a single interval and integrate by parts
x i+ 1
f ( x ) dx= f ( t + xi ) dt t=xx i
xi
f ( t+ x i ) dt=[ ( t+ a )f ( t+ xi ) ]0 ( t+ a ) f ' ( t+ x i ) dt
0
Integrate by parts one more time
h
[(
] (
h
( t+a )2
( t+ a )2
'
''
f
t
+
x
dt=
(
t+
a
)
f
t
+
x
+b
f
t+
x
+
( i) [
( i) ]0
( i ) 2 +b f ( t+ x i ) dt
2
0 0
0
h
[( ) ]
2
( h+ a )2
( t +a )2
f ( t + x i ) dt=( h+a ) f ( xi +1 )af ( x i ) 2 +b f ' ( x i+1 ) + a2 +b f ' ( x i ) + 2 +b f ' ' ( t + x i ) dt
0
0
[ ]
We choose the constants a, b so that they make the smallest error bound
2
h
h
a=
, b=
2
8
Thus
So, far
x i+ 1
f ( x ) dx=
xi
h
f ( x ) + f ( xi +1 ) ] +
2[ i
0
where this term
n1 h
E T =
i=0 0
f ' ' ( t + xi ) dt
h
f ( x ) + f ( x i+1 ) ] isthe area of trapezoid
2[ i
h 2
2
h2 ' '
f ( t + x i) dt
2
8
( )
t
h
2
( ) h
t
the error :
Assume f ' ' ( x ) has upper bound K
|(
|(
|ET|
0
|ET| nK
0
|
|
h 2
2
h2
(|f ' ' ( t + x 0 )|++|f ' ' ( t+ x n1 )|) dt
2
8
h 2
2
h2
nK h3
dt=
2
8
12
K ( ba )3
| ET|=
12 n2
h=
ba
n
Error of Simpsons rule
x2
f ( x ) dx
x0
We will expand the function around
x2
x2
f ( x ) dx=
x0
x0
x 1=
''
x0 + x2
2
using Taylor expansion
''
'' ' '
f ( x1 )
f ' ( x1 )
f ( )
4
f ( x 1) + f ( x1 ) ( xx 1 ) +
x x1 )2 +
xx 1) 3+
(
(
( xx 1 ) dx
2
6
24
'
x2
f ' ( x1 )
f '' ( x 1)
f ' ' ' ( x1 )
f '' ' ' ( )
2
3
f ( x ) dx= x f ( x 1 ) + 2 ( xx 1 ) + 6 ( xx 1 ) + 24 ( xx 1 )4 + 12 0 ( xx 1 )5
x
0
x2
x0
( x 2x 1 )
3
( x 2x 1 ) ( x0 x1 )
( x 2x 1 )
( x 2x 1 )
5
[ 5( x 0x 1 ) ]
f
'' ' '
( )
120
''
''
f ( x1 )
f ' ( x1 )
2
[ 2( x 0x 1 ) ]+
[ 3 ]+
6
24
f ' ( x1 )
f ( x 1 ) ( x 2x 0 ) +
[ 4( x 0x 1 ) ]+
x2
f ( x ) dx=
x0
x2
][
5 (4 )
h3 f ' ' ( x 1 ) h5 f ' ' ' ' ( )
h f () h
h3 f ( x 0 )2 f ( x1 ) + f ( x 2) h2 ( 4)
f
(
x
)
dx=
2
h
f
x
+
+
=
2
hf
x
+
f
(
)
+
= [ f ( x0 )+
( 1)
( 1) 3
3
60
12
60
3
h2
x
0
the error=
5 (4)
h f ( )
90
You might also like
- Problem Set 7 Solutions PDFDocument33 pagesProblem Set 7 Solutions PDFfrancis_tsk1No ratings yet
- MA1521 Solution3Document5 pagesMA1521 Solution3Ray TanNo ratings yet
- CaaaDocument2 pagesCaaaOrigamiNo ratings yet
- Chap1 IntroductionDocument54 pagesChap1 IntroductionSrivatsan SampathNo ratings yet
- 152 FormulasDocument1 page152 FormulasPrasanna RagunathanNo ratings yet
- Fall 2013 Math 647 Homework 5Document9 pagesFall 2013 Math 647 Homework 5gsmarasigan08No ratings yet
- Midterm Assignment2Document8 pagesMidterm Assignment2api-279116744No ratings yet
- Integrals FormulasDocument10 pagesIntegrals Formulas007phantomNo ratings yet
- Math 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsDocument3 pagesMath 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsexamkillerNo ratings yet
- Calculus: Differentiation RulesDocument17 pagesCalculus: Differentiation RulesAoSd' TikmanNo ratings yet
- Jawaban KalkulusDocument30 pagesJawaban KalkulusanitaNo ratings yet
- Math 31 Chapter 10 and 11 LessonsDocument26 pagesMath 31 Chapter 10 and 11 LessonsSam PanickerNo ratings yet
- Xy Xy y X: Solve Cauchy-Euler Type Differential Equation - Solution: Method 1: (A) LetDocument5 pagesXy Xy y X: Solve Cauchy-Euler Type Differential Equation - Solution: Method 1: (A) Letmasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Chapter 12-b: Integral Calculus - ExtraDocument24 pagesChapter 12-b: Integral Calculus - ExtraShahnaz GazalNo ratings yet
- Calculus Notes: 1 DifferentiationDocument6 pagesCalculus Notes: 1 DifferentiationsdrakosNo ratings yet
- Mth603 FormulaeDocument5 pagesMth603 FormulaeAmir Saleem33% (3)
- 101 - Full Derivative ReportDocument25 pages101 - Full Derivative ReportAmroKashtNo ratings yet
- C CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesDocument10 pagesC CN I N (n+1) : Critical ValuesFolk NarongritNo ratings yet
- HW #3Document3 pagesHW #3sshanbhagNo ratings yet
- Math 171 homework solutions for section 5.3 integralsDocument2 pagesMath 171 homework solutions for section 5.3 integralslusienopopNo ratings yet
- Knf1013 Week9 Differentiation Compatibility ModeDocument37 pagesKnf1013 Week9 Differentiation Compatibility ModeSyura PisyuNo ratings yet
- Product Quotient Rules DerivativesDocument9 pagesProduct Quotient Rules Derivativesmasyuki1979No ratings yet
- Numerical AnalysisDocument9 pagesNumerical AnalysisJoshua CookNo ratings yet
- Techniques of IntegrationDocument61 pagesTechniques of IntegrationAma PredaNo ratings yet
- Homework #2 Solutions Problems: Math 19: Calculus Summer 2010Document6 pagesHomework #2 Solutions Problems: Math 19: Calculus Summer 2010AnaMendezNo ratings yet
- Multivariable calculus exam with 7 problemsDocument5 pagesMultivariable calculus exam with 7 problemslieth-4No ratings yet
- Diferenciales Alvaro Mamamni Lanchipa 2011041679Document7 pagesDiferenciales Alvaro Mamamni Lanchipa 2011041679Adrian SalazarNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1000A, Section 007Document30 pagesCalculus 1000A, Section 007arrowroot1No ratings yet
- Xaliss Jamal Omer - NumericalDocument16 pagesXaliss Jamal Omer - NumericalBrikhov XNo ratings yet
- Math 113G1/114E1 Midterm Solutions (V1)Document15 pagesMath 113G1/114E1 Midterm Solutions (V1)examkillerNo ratings yet
- 2013Document10 pages2013Farid AliyevNo ratings yet
- Basic (1) MathDocument2 pagesBasic (1) MathIan KrebsNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 8Document3 pagesProblem Set 8Brian DunnNo ratings yet
- Exam - 2011 10 28Document5 pagesExam - 2011 10 28lieth-4No ratings yet
- Differentiation Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesDifferentiation Cheat SheetjieboNo ratings yet
- Problem SolutionDocument11 pagesProblem SolutionherringtsuNo ratings yet
- Formulario de calculo numericoDocument6 pagesFormulario de calculo numericoFabio Miguel RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (MAN 001)Document2 pagesAssignment 5 (MAN 001)Shrey AgarwalNo ratings yet
- N highest value wave parametersDocument31 pagesN highest value wave parametersGOWTHAMNo ratings yet
- What Is A FunctionDocument6 pagesWhat Is A FunctionRyan Kristoffer NuñezNo ratings yet
- Applied Math Paper 2 Marking by N.F. YangDocument12 pagesApplied Math Paper 2 Marking by N.F. Yang大頭邦No ratings yet
- Analisis Sistem Kendali #3Document57 pagesAnalisis Sistem Kendali #3AriNo ratings yet
- More Practice DerivativesDocument2 pagesMore Practice Derivativessriniyfa1No ratings yet
- Taylor Expansions in 2dDocument5 pagesTaylor Expansions in 2dpazrieNo ratings yet
- Limits & Derivatives Worksheet SOLUTIONS Math 1100-005 01/26/06Document4 pagesLimits & Derivatives Worksheet SOLUTIONS Math 1100-005 01/26/06vaibhav544No ratings yet
- Mth134 - Calculus II - Final Exam Formula Sheet: e e X e e XDocument3 pagesMth134 - Calculus II - Final Exam Formula Sheet: e e X e e Xafaflotfi_155696459No ratings yet
- Multivariable calculus practice problems and formulasDocument5 pagesMultivariable calculus practice problems and formulaslieth-4No ratings yet
- Maximum product of three partsDocument6 pagesMaximum product of three partssfluk2No ratings yet
- Interpolation and Approximation TheoryDocument15 pagesInterpolation and Approximation TheoryFaisal RahmanNo ratings yet
- D3NN1S 4Document52 pagesD3NN1S 4Molina Armas Hugo RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526Document5 pagesMultivariable Calculus, 2007-10-26. Per-Sverre Svendsen, Tel.035 - 167 615/0709 - 398 526lieth-4No ratings yet
- Math 462: HW3 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMath 462: HW3 SolutionssCoRPion_trNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument3 pagesFormulasYamer YusufNo ratings yet
- TABELA de Diretivas de Derivadas e IntegraisDocument1 pageTABELA de Diretivas de Derivadas e IntegraispablomuroNo ratings yet
- Math 150 Homework SolutionsDocument7 pagesMath 150 Homework SolutionsHa NoiNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1990 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument10 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1990 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Leep 207Document27 pagesLeep 207Koyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)From EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)No ratings yet
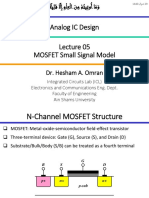
- MOSFET Small Signal ModelDocument19 pagesMOSFET Small Signal ModelKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Hazem Protocol V2Document5 pagesHazem Protocol V2KarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Lab#6 LNA Gain NF S11 IP3Document3 pagesLab#6 LNA Gain NF S11 IP3KarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- ControlDocument1 pageControlKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Project 3 Effect of changing λ from 1.55µm to 800nmDocument1 pageProject 3 Effect of changing λ from 1.55µm to 800nmKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Karim Mohamed Yossef's CVDocument2 pagesKarim Mohamed Yossef's CVKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Karim Yossef 2018Document3 pagesKarim Yossef 2018KarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Comparing Simulation Tools for OIC DesignDocument2 pagesComparing Simulation Tools for OIC DesignKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Trial 1Document2 pagesTrial 1KarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Quiz3 Model AnswerDocument3 pagesQuiz3 Model AnswerKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Types of Interconnect: Low Resistivity MetalsDocument3 pagesTypes of Interconnect: Low Resistivity MetalsKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Academic Calendar For AY 2016-2017Document3 pagesAcademic Calendar For AY 2016-2017KarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 (Ch4)Document2 pagesSheet 3 (Ch4)KarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Analyze Thin Films and Surfaces with LEISDocument2 pagesAnalyze Thin Films and Surfaces with LEISKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Relation between wavenumber & their order value p: F EC O Wavenumbers σ cm-1Document2 pagesRelation between wavenumber & their order value p: F EC O Wavenumbers σ cm-1KarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- App. QM Assigment 2 MatlabDocument3 pagesApp. QM Assigment 2 MatlabKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- QuantumDocument1 pageQuantumKarimMohamedNo ratings yet
- Biosensors, A Survey Report by Saraju P Mohanty (2001) 10.1.1.19.2093Document15 pagesBiosensors, A Survey Report by Saraju P Mohanty (2001) 10.1.1.19.2093IdeaTrackNo ratings yet
- Numerical Differentiation and IntegrationDocument84 pagesNumerical Differentiation and IntegrationRajaram KamathNo ratings yet
- Legendre PolynomialsDocument34 pagesLegendre Polynomialsyuj oNo ratings yet
- หนังสือ Math 3Document103 pagesหนังสือ Math 3Sarun SontikulNo ratings yet
- Review basic calculus concepts for business, biology & psychologyDocument4 pagesReview basic calculus concepts for business, biology & psychologySammar Ellahi100% (6)
- KT 14503 Mathematics For Computing Group Assignment 20 MarksDocument7 pagesKT 14503 Mathematics For Computing Group Assignment 20 MarksAnnie LeonhartNo ratings yet
- Lesson 31 Linear Differential Equation of Higher Order: Module 3: Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument6 pagesLesson 31 Linear Differential Equation of Higher Order: Module 3: Ordinary Differential EquationsJoseph NjugunaNo ratings yet
- MAT183 Scheme of Work - Sept Jan 2019Document4 pagesMAT183 Scheme of Work - Sept Jan 2019SyafiyatulMunawarahNo ratings yet
- CSS (Central Superior Service)Document14 pagesCSS (Central Superior Service)Asim ShehzadNo ratings yet
- Calculus and Liner AlgebraDocument10 pagesCalculus and Liner Algebrazambo godNo ratings yet
- Modeling A Composition PDF TransportDocument22 pagesModeling A Composition PDF TransportMohamad PoortoosiNo ratings yet
- ADS MathDocument2 pagesADS MathSaqib IbraheemNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics II Model Question Paper StudyhauntersDocument3 pagesEngineering Mathematics II Model Question Paper StudyhauntersSriram JNo ratings yet
- 03.1.2 - Solutions of Some Differential EquationsDocument11 pages03.1.2 - Solutions of Some Differential Equationswe_spidus_2006No ratings yet
- The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and The Poincaré LemmaDocument13 pagesThe Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and The Poincaré LemmasuperscriberNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics Project WorkDocument10 pagesAdditional Mathematics Project WorkQwin GanNo ratings yet
- M.SC MathDocument22 pagesM.SC MathSonu VermaNo ratings yet
- UPSC Previous Year Complex Analysis Question Paper Mathematics OptionalDocument10 pagesUPSC Previous Year Complex Analysis Question Paper Mathematics OptionalPrakash Narayan SinghNo ratings yet
- Gradeup Short Notes On Definite Integral and Area - pdf-54Document8 pagesGradeup Short Notes On Definite Integral and Area - pdf-54Tafazzul HazqueelNo ratings yet
- Using Fourier Transform To Detect Large Orders: Part 1Document4 pagesUsing Fourier Transform To Detect Large Orders: Part 1Nic LeeNo ratings yet
- Camarines Norte State CollegeDocument5 pagesCamarines Norte State CollegeRichelle Calandria VedadNo ratings yet
- Courses of Study - 2020 2021@IITDDocument373 pagesCourses of Study - 2020 2021@IITDunknownNo ratings yet
- 991Document3 pages991RACS ECETNo ratings yet
- Class XII - Part 2 PDFDocument546 pagesClass XII - Part 2 PDFSathish NirmalNo ratings yet
- 2400full Calculus PDFDocument354 pages2400full Calculus PDFvictorkrullNo ratings yet
- Westergaard Stress Functions For Displacement-Prescribed Crack - TadaDocument15 pagesWestergaard Stress Functions For Displacement-Prescribed Crack - TadaMarilene LobatoNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus Formula SheetDocument2 pagesIntegral Calculus Formula SheetAinaa MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Princeton MAT 104 Fall 2014 Assignment ListDocument3 pagesPrinceton MAT 104 Fall 2014 Assignment ListGokulIyerNo ratings yet
- Textile EngineeringDocument45 pagesTextile EngineeringSwati SakhareNo ratings yet
- Btech CSE 2nd YearDocument140 pagesBtech CSE 2nd YearDivyansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Syllabus IET - Biotechnology - NewDocument96 pagesSyllabus IET - Biotechnology - NewRanjeet SinghNo ratings yet