Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Costing Systems and Job Order Costing
Uploaded by
zikril94Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Costing Systems and Job Order Costing
Uploaded by
zikril94Copyright:
Available Formats
BKAM2013 Management Accounting I
Topic 3: Cost Assignment
Exercise 1
Differentiate between actual costing and normal costing.
Exercise 2
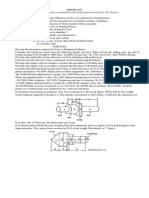
WoodPro Technology Sdn Bhd makes office furniture from quality woods. The
company uses a job-order costing system and predetermined overhead rates to
apply manufacturing overhead cost to jobs. The predetermined overhead rate in
the Preparation Department is based on machine hours, and the rate in the
Fabrication Department is based on direct materials cost. At the beginning of the
year, the companys management made the following estimates for the year:
Department
Preparation
Fabrication
80,000
21,000
35,000
65,000
RM190,000
RM400,000
RM280,000
RM530,000
RM416,000
RM720,000
Machine hours
Direct labor hours
Direct materials cost
Direct labor cost
Manufacturing overhead cost
Job 123 was started on 1 November 2006 and completed on 12 December 2006.
The companys cost records show the following information on the job:
Department
Preparation
Fabrication
350
70
80
130
RM940
RM1,200
RM710
RM980
Machine hours
Direct labor hours
Direct materials cost
Direct labor cost
REQUIRED:
(a)
Compute the predetermined overhead rate used during the year in the
Preparation Department and Fabrication Department.
(b)
Compute the total overhead cost applied to job 123.
BKAM2013 Management Accounting I
(c)
(d)
What would be the total cost recorded for job 123? If the job contained 25
units, what would be the unit product cost?
At the end of the year, the records of WoodPro Technology Sdn Bhd
revealed the following actual cost and operating data for all jobs worked
on during the year:
Department
Preparation
Fabrication
73,000
24,000
30,000
68,000
RM165,000
RM420,000
RM390,000
RM740,000
Machine hours
Direct labor hours
Direct materials cost
Manufacturing overhead cost
What was the amount of underapplied or overapplied overhead in each
department at the end of the year?
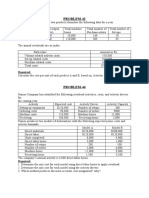
Exercise 3
Dont tell me we have lost another bid! exclaimed Roha, president of Rohami
Sdn Bhd. Im afraid so, replied Ramy, the operation vice president. One of our
competitors underbid us by about RM10,000 on the RR2 job. I just cant figure it
out, said Roha. It seems we are either too high to get the job or too low to make
any money on half the jobs we bid any more. Whats happened?
Roha Sdn Bhd manufactures specialized goods to customers specifications and
operates a job-order costing system. Manufacturing overhead cost is applied to
jobs on the basis of direct labor cost. The following estimates were made at the
beginning of the year:
Direct labor
Manufacturing overhead
Cutting
RM300,000
RM540,000
Department
Machining
Assembly
RM200,000 RM400,000
RM800,000 RM100,000
Total Plant
RM900,000
RM1,440,000
Jobs require varying amounts of work in the three departments. The RR2 job, for
example, would have required manufacturing costs in the three departments as
follows:
Direct materials
Direct labor
Manufacturing overhead
Department
Machining
Assembly
RM900
RM5,600
RM1,700
RM13,000
?
?
Cutting
RM12,000
RM6,500
?
Total Plant
RM18,500
RM21,200
?
BKAM2013 Management Accounting I
The company uses a plantwide overhead rate to apply manufacturing overhead
cost to jobs.
REQUIRED:
(a)
Assuming use of a plantwide overhead rate:
(i)
Compute the rate for the current year.
(ii)
Determine the amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would
have been applied to the RR2 job.
(b)
Suppose that instead of using a plantwide overhead rate, the company
had used a separate predetermined overhead rate in each department.
Under these conditions:
(i)
Compute the rate for each department for the current year.
(ii)
Determine the amount of manufacturing overhead cost that would
have been applied to the RR2 job.
(c)
Explain the difference between the manufacturing overhead that would
have been applied to RR2 job using the plantwide rate in part (a) (ii) above
and using the departmental rates in part (b) (ii).
(d)
Assume that it is necessary in the industry to bid jobs at 150% of total
manufacturing cost. What was the companys bid price on the RR2 job if a
plantwide overhead rate is used? What would the bid price have been if
departmental overhead rates had been used to apply overhead cost?
(e)
At the end of the year, the company assembled the following actual cost
data relating to all jobs worked on during the year:
Direct materials
Direct labor
Manufacturing overhead
Cutting
RM760,000
RM320,000
RM560,000
Department
Machining
Assembly
RM90,000
RM410,000
RM210,000 RM340,000
RM830,000
RM92,000
Compute the underapplied or overapplied overhead for the year:
(i)
Assuming that a plantwide overhead rate is used.
(ii)
Assuming that departmental overhead rates are used.
Total Plant
RM1,260,000
RM870,000
RM1,482,000
BKAM2013 Management Accounting I
Exercise 4
Ezy Furnish Sdn Bhd makes furniture using latest automated technology. The
company uses a job-order costing system and applies manufacturing overhead
cost to products on the basis of machine hours. The following estimates were
used in preparing the predetermined overhead rate at the beginning of the year:
Machine hours
Manufacturing overhead cost
75,000
RM900,000
During the year, a glut of furniture on the market resulted in cutting back
production and a buildup of furniture in the companys warehouse. The
companys cost records revealed the following actual cost and operating data for
the year:
60,000
Machine hours.....................................................................................
Manufacturing overhead cost.............................................................. RM850,000
Inventories at year end:
RM30,000
Raw materials......................................................................................
Work in process (includes overhead applied of RM36,000)............ RM100,000
Finished goods (includes overhead applied of RM180,000)........... RM500,000
Cost of goods sold (includes overhead applied of RM504,000)...... RM1,400,000
REQUIRED:
(a)
Compute the companys predetermined overhead rate.
(b)
Compute the underapplied or overapplied overhead.
(c)
Assume that the company closes any underapplied or overapplied
overhead directly to Cost of Goods Sold. Prepare the appropriate journal
entry.
(d)
Assume that the company allocates any underapplied or overapplied
overhead to Work in Process, Finished Goods, and Cost of Goods Sold on
the basis of the amount of overhead applied that remains in each account
at the end of the year. Prepare the journal entry to show the allocation for
the year.
BKAM2013 Management Accounting I
(e)
How much higher or lower will net operating income be if the underapplied
or overapplied overhead is allocated rather than closed directly to Cost of
Goods Sold?
You might also like
- SITXMGT001 Monitor Work Operations Assessment v.2019.1Document33 pagesSITXMGT001 Monitor Work Operations Assessment v.2019.1Ambika Suwal100% (7)
- Managing Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2009 EditionFrom EverandManaging Successful Projects with PRINCE2 2009 EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Case 2 (1-4)Document6 pagesCase 2 (1-4)zikril94No ratings yet
- Tutorial Pengekosan KeluaranDocument13 pagesTutorial Pengekosan KeluaranatehanaNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Assignment Questions 22Document12 pagesFINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Assignment Questions 22Natasha DavidsNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam - Business Planning & Cost AccountingDocument8 pagesMidterm Exam - Business Planning & Cost AccountingDan Ryan0% (1)
- Bmac 5203Document10 pagesBmac 5203ShaanySirajNo ratings yet
- Ma As2Document6 pagesMa As2Omar AbidNo ratings yet
- 3 Process and Job Order Costing System 2019Document8 pages3 Process and Job Order Costing System 2019Abdallah SadikiNo ratings yet
- Cost and Management Accounting AssignmentDocument8 pagesCost and Management Accounting AssignmentDinkar SuranglikarNo ratings yet
- Job, Batch and Service Costing Process Costing - F2Document24 pagesJob, Batch and Service Costing Process Costing - F2yikesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Job and Batch Costing: Ref: Cost & Management Accounting by K.S.AdigaDocument14 pagesChapter 1-Job and Batch Costing: Ref: Cost & Management Accounting by K.S.AdigaAR Ananth Rohith BhatNo ratings yet
- Factory OverheadDocument2 pagesFactory Overheadenchantadia0% (1)
- Assignment On ABCDocument5 pagesAssignment On ABCRaghav MehraNo ratings yet
- AA025 Chapter AT5Document2 pagesAA025 Chapter AT5norismah isaNo ratings yet
- Case Assignments Due 12 March 2016 JOC & Proc CostDocument8 pagesCase Assignments Due 12 March 2016 JOC & Proc Costsunny shopNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting ExercisesDocument1 pageCost Accounting ExercisesRaniel PamatmatNo ratings yet
- Tutorial JOCDocument5 pagesTutorial JOCainfarhanaNo ratings yet
- Brewer Chapter 2 Alt ProbDocument6 pagesBrewer Chapter 2 Alt ProbAtif RehmanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Activity Based Costing QDocument6 pagesTutorial 3 Activity Based Costing QnurathirahNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Introduction To Costing: DBS Management AccountingDocument9 pagesTopic 2 Introduction To Costing: DBS Management AccountingziehuiNo ratings yet
- Simple Problem On ABC: RequiredDocument3 pagesSimple Problem On ABC: RequiredShreshtha VermaNo ratings yet
- Title01_Job costing and Batch costingDocument72 pagesTitle01_Job costing and Batch costingPoonamNo ratings yet
- Revision Week 1. Questions. Question 1. Cost of Goods Manufactured, Cost of Goods Sold, Income Statement. (A)Document5 pagesRevision Week 1. Questions. Question 1. Cost of Goods Manufactured, Cost of Goods Sold, Income Statement. (A)Sujib BarmanNo ratings yet
- Cost-Management-Accounting-DEC-2023Document4 pagesCost-Management-Accounting-DEC-2023Aash RedmiNo ratings yet
- ABC TutotialDocument6 pagesABC TutotialChandran PachapanNo ratings yet
- Activity Based CostingproblemsDocument6 pagesActivity Based CostingproblemsDebarpan HaldarNo ratings yet
- WK5 - JOC Exercise 1Document5 pagesWK5 - JOC Exercise 1LIM YIN SHUAN KM-PelajarNo ratings yet
- Job Costing Calculations and Journal EntriesDocument5 pagesJob Costing Calculations and Journal EntriesYAHIA ADELNo ratings yet
- Accounting 203 Chapter 2 Practice TestDocument16 pagesAccounting 203 Chapter 2 Practice TestKing QasimNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - ABC - QDocument7 pagesTutorial 3 - ABC - QREDZUAN SHAH BIN HJ HASSANNo ratings yet
- Cost Assignment IDocument5 pagesCost Assignment Ifitsum100% (1)
- Paper - 4: Cost Accounting and Financial ManagementDocument20 pagesPaper - 4: Cost Accounting and Financial ManagementdhilonjimyNo ratings yet
- PMBA Cost Accounting Assignment AnalysisDocument8 pagesPMBA Cost Accounting Assignment AnalysisLabib SafeenNo ratings yet
- Prelim Cost AcctngDocument2 pagesPrelim Cost AcctngAnonymous JgyJLTqpNS0% (1)
- CSU-Andrews Cost Management Quiz 1Document4 pagesCSU-Andrews Cost Management Quiz 1Wynie AreolaNo ratings yet
- Paper - 3: Cost and Management Accounting Questions Material CostDocument33 pagesPaper - 3: Cost and Management Accounting Questions Material CostEFRETNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document7 pagesLecture 1HarusiNo ratings yet
- Factors Considered For The Tooling Decision On Derive The Process ParameterDocument2 pagesFactors Considered For The Tooling Decision On Derive The Process ParameterMithun RajNo ratings yet
- AFAR - 11.1-Cost Accounting (Job Order and Process Costing)Document3 pagesAFAR - 11.1-Cost Accounting (Job Order and Process Costing)Daniela AubreyNo ratings yet
- Job Costing Analysis for Furniture Manufacturing BusinessDocument4 pagesJob Costing Analysis for Furniture Manufacturing BusinessQudwah HasanahNo ratings yet
- (8)BATCH COSTING_0a298a02-916c-43a0-87ae-013083fd5c66Document8 pages(8)BATCH COSTING_0a298a02-916c-43a0-87ae-013083fd5c66Varun TiwariNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting RTP CAP-II June 2016Document31 pagesCost Accounting RTP CAP-II June 2016Artha sarokarNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of Commerce)Document4 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad (Department of Commerce)gulzar ahmadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - Costing For OverheadDocument5 pagesTutorial 4 - Costing For OverheadMuhammad Alif100% (1)
- Job and Batch CostingDocument3 pagesJob and Batch CostingbhngbjNo ratings yet
- May 2021 G1 Test2Document4 pagesMay 2021 G1 Test2Dipak UgaleNo ratings yet
- Midterm Question Strategic Management Accounting (11th Batch)Document5 pagesMidterm Question Strategic Management Accounting (11th Batch)Samir Raihan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 59 IpcccostingDocument5 pages59 Ipcccostingapi-206947225No ratings yet
- Cost Sheet - Pages 16Document16 pagesCost Sheet - Pages 16omikron omNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman Faculty of Accountancy and Management ACADEMIC YEAR 2020/2021 Bachelor of Accounting (Hons.)Document4 pagesUniversiti Tunku Abdul Rahman Faculty of Accountancy and Management ACADEMIC YEAR 2020/2021 Bachelor of Accounting (Hons.)Shi Yan LNo ratings yet
- 68957Document9 pages68957Mehar WaliaNo ratings yet
- Gregory Enterprises overhead cost allocationDocument2 pagesGregory Enterprises overhead cost allocationMandy KhouryNo ratings yet
- TutorialActivity 3Document7 pagesTutorialActivity 3Adarsh AchoyburNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting - Mid Term Exam PDFDocument4 pagesManagerial Accounting - Mid Term Exam PDFNavya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Cost ManagementDocument21 pagesStrategic Cost ManagementDeepak ShettyNo ratings yet
- Job Order Assignment PDFDocument3 pagesJob Order Assignment PDFAnne Marie100% (1)
- CA Course Work Take HomeDocument4 pagesCA Course Work Take HomeOgwang JoshuaNo ratings yet
- ABC Company manufacturing data problem-42 costing analysisDocument7 pagesABC Company manufacturing data problem-42 costing analysisRADHIKA V HNo ratings yet
- Korarai 18181881Document4 pagesKorarai 18181881KyraraNo ratings yet
- Case Studies of Cost and Works AccountingDocument17 pagesCase Studies of Cost and Works AccountingShalini Srivastav50% (2)
- Job CostingDocument3 pagesJob Costingshakibsahel0No ratings yet
- Menu With PriceDocument1 pageMenu With Pricezikril94No ratings yet
- (Journal 5) p462 5Document12 pages(Journal 5) p462 5zikril94No ratings yet
- (Journal 5) p462 5Document12 pages(Journal 5) p462 5zikril94No ratings yet
- Care PlusDocument1 pageCare Pluszikril94No ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Intro To ComputersDocument36 pagesChapter 01 Intro To Computerszikril94No ratings yet
- Issue 3Document1 pageIssue 3zikril94No ratings yet
- Topic 7 - BWFF3033 - FMI Capital Market DebtDocument36 pagesTopic 7 - BWFF3033 - FMI Capital Market Debtzikril94No ratings yet
- Academic Calendar 2015 For Undergraduate ProgrammesDocument1 pageAcademic Calendar 2015 For Undergraduate Programmesqaslun basheerNo ratings yet
- Astro Bill Summary and Payment DetailsDocument1 pageAstro Bill Summary and Payment Detailszikril94No ratings yet
- Beeb2033 Sow (1) A161Document11 pagesBeeb2033 Sow (1) A161zikril94No ratings yet
- Ma Po Tau Fu RiceDocument6 pagesMa Po Tau Fu Ricezikril94No ratings yet
- Hertland Tractor Club Magazine Ad RequestDocument1 pageHertland Tractor Club Magazine Ad Requestzikril94No ratings yet
- Hertland Tractor Club Magazine Ad RequestDocument1 pageHertland Tractor Club Magazine Ad Requestzikril94No ratings yet
- Swap of SharessDocument5 pagesSwap of Sharesszikril94No ratings yet
- RECEIPT Femina Fesatival A59 (Muz Asdstosadasdasre)Document1 pageRECEIPT Femina Fesatival A59 (Muz Asdstosadasdasre)zikril94No ratings yet
- RECEIPT Femina Fesatival A59 (Muz Asdstosadasdasre)Document1 pageRECEIPT Femina Fesatival A59 (Muz Asdstosadasdasre)zikril94No ratings yet
- Sales Receipt Muz StoresasasasasasDocument1 pageSales Receipt Muz Storesasasasasaszikril94No ratings yet
- Applying For JobssdsdDocument4 pagesApplying For Jobssdsdzikril94No ratings yet
- ONE PC SDN BHD Is An Enterprise Selling Computer Accescorries For Many Types and Also Good Branch A Laptopt Such As TOSHIBADocument1 pageONE PC SDN BHD Is An Enterprise Selling Computer Accescorries For Many Types and Also Good Branch A Laptopt Such As TOSHIBAzikril94No ratings yet
- Estate Complaint Letter AnswerDocument1 pageEstate Complaint Letter Answerzikril94No ratings yet
- ONE PC SDN BHD Is An Enterprise Selling Computer Accescorries For Many Types and Also Good Branch A Laptopt Such As TOSHIBADocument1 pageONE PC SDN BHD Is An Enterprise Selling Computer Accescorries For Many Types and Also Good Branch A Laptopt Such As TOSHIBAzikril94No ratings yet
- Bride Et Al., 2007 (Compassion Fatigue)Document9 pagesBride Et Al., 2007 (Compassion Fatigue)Filip Maciej SoszyńskiNo ratings yet
- Labour Compliance Checklist For Mumbai Per The New Shops ActDocument4 pagesLabour Compliance Checklist For Mumbai Per The New Shops ActwertyderryNo ratings yet
- Difference Between PM and HRMDocument3 pagesDifference Between PM and HRMBonny SebastianNo ratings yet
- Manpower Planning ProcessDocument38 pagesManpower Planning ProcessTuhin Subhra SamantaNo ratings yet
- Stonehill Corp Officers Cannot Challenge Search of Corporate OfficesDocument63 pagesStonehill Corp Officers Cannot Challenge Search of Corporate OfficesLexa ClarkeNo ratings yet
- KHCC Services:: (Click For PDF) Click For PDF) Click For PDF) Click For PDF) Click For PDFDocument27 pagesKHCC Services:: (Click For PDF) Click For PDF) Click For PDF) Click For PDF) Click For PDFOgy WinenriandhikaNo ratings yet
- IFC Invest in Women October 2017Document80 pagesIFC Invest in Women October 2017SophiaNo ratings yet
- JL HR Rasuna Said Kav.20 Tower 12A-E, Jakarta Selatan 12950Document2 pagesJL HR Rasuna Said Kav.20 Tower 12A-E, Jakarta Selatan 12950Hani ZeinNo ratings yet
- Job Search Cover Letter Example - Document #7Document2 pagesJob Search Cover Letter Example - Document #7Anthony V. HinesNo ratings yet
- Application For A Permanent Administrative or Professional PostDocument5 pagesApplication For A Permanent Administrative or Professional PostAmber ManacasNo ratings yet
- Justice Department's Memo of LawDocument19 pagesJustice Department's Memo of Lawjobrien1381No ratings yet
- Summer RoseDocument9 pagesSummer Rosesummer absolomNo ratings yet
- San Diego: A Premier Home For The NFLDocument41 pagesSan Diego: A Premier Home For The NFLapi-197535656No ratings yet
- Job Description - GenC Next - Data ScientistDocument4 pagesJob Description - GenC Next - Data ScientistThe HimanNo ratings yet
- Working Capital Project Report 2Document48 pagesWorking Capital Project Report 2Evelyn KeaneNo ratings yet
- NEBOSH International General Certificate in Occupational Safety and Health Igc1Document110 pagesNEBOSH International General Certificate in Occupational Safety and Health Igc1harikrishna100% (2)
- Lecture NO. 8: Labor Management RelationsDocument97 pagesLecture NO. 8: Labor Management RelationsAlviNo ratings yet
- Ethiopia's Industrial Parks: A Data Pack On Recent PerformanceDocument6 pagesEthiopia's Industrial Parks: A Data Pack On Recent PerformanceGeremew Kefale GobenaNo ratings yet
- Vendorregistrationform ACC PDFDocument5 pagesVendorregistrationform ACC PDFMarie EstesNo ratings yet
- Balwant Rai Saluja v. Air India LTD., (2014) 9 SCC 407: Eastern Book Company Generated: Friday, November 10, 2017Document2 pagesBalwant Rai Saluja v. Air India LTD., (2014) 9 SCC 407: Eastern Book Company Generated: Friday, November 10, 2017Teja Prakash chowdaryNo ratings yet
- EDC Fashion Manufacturing and Garment Center StrategyDocument23 pagesEDC Fashion Manufacturing and Garment Center Strategycrainsnewyork100% (1)
- ANC Manifesto 2019Document68 pagesANC Manifesto 2019Mail and GuardianNo ratings yet
- Acquiring Competent PersonnelDocument8 pagesAcquiring Competent PersonnelSam MoldesNo ratings yet
- Project BamulDocument74 pagesProject Bamulಜಯಂತ್ ಗೌಡNo ratings yet
- Employee Satisfaction To Financial PerformanceDocument99 pagesEmployee Satisfaction To Financial PerformanceMUHAMMAD SIDIKNo ratings yet
- HRM 221 NOTES pdf-1-2Document104 pagesHRM 221 NOTES pdf-1-2Kevin NdabambiNo ratings yet
- BX3051 Employment Relations: Chapters 2 & 3: Analytical Tools & Values - IR Versus HRM & Dominant Paradigms in ERDocument25 pagesBX3051 Employment Relations: Chapters 2 & 3: Analytical Tools & Values - IR Versus HRM & Dominant Paradigms in ERyahya weruNo ratings yet
- Presentation For Viva 2016Document65 pagesPresentation For Viva 2016rakeshkeniNo ratings yet
- Candidate Ref. No. Date: Position Code: Position:: HR Interview Form - DDocument1 pageCandidate Ref. No. Date: Position Code: Position:: HR Interview Form - DFadi BachirNo ratings yet