Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Cycle
Uploaded by
resolution8878Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cell Cycle
Uploaded by
resolution8878Copyright:
Available Formats
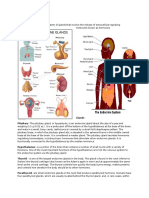
Cell cycle
Each turn
cell cycle divides the chromosomes in a cell nucleus.
of the
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in
a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication). In cells without a
nucleus (prokaryotes), the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary
fission. In cells with a nucleus (eukaryotes), the cell cycle can be divided in
two brief periods: interphaseduring which the cell grows, accumulating
nutrients needed for mitosis and duplicating its DNAand the mitosis (M)
phase, during which the cell splits itself into two distinct cells, often called
"daughter cells". The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a singlecelled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process
by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed.
Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter
cells from a single parent cell.
Meiosis is the type of cell division by which germ cells (eggs and sperm) are
produced.
You might also like
- Lesson Cell Division and Cell Cycle Lesson 4 and 5Document39 pagesLesson Cell Division and Cell Cycle Lesson 4 and 5silvajunjosephNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Division Lecture NotesDocument16 pagesCell Cycle Division Lecture NotesZachary HamidNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Note PDFDocument12 pagesCell Division Note PDFAishaizl100% (1)
- Cell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherDocument59 pagesCell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherTrisha Loise VillacampaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionHajie RosarioNo ratings yet
- Sourcing and ProcurementDocument50 pagesSourcing and Procurementresolution8878No ratings yet
- SOLIDMensuration Finals TopicsDocument25 pagesSOLIDMensuration Finals Topicsresolution8878100% (3)
- SOLIDMensuration Finals TopicsDocument25 pagesSOLIDMensuration Finals Topicsresolution8878100% (3)
- Cell CycleDocument1 pageCell CyclewilfNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and Cell Division ProcessesDocument7 pagesThe Cell Cycle and Cell Division ProcessesCatherine PagdonsolanNo ratings yet
- 4 Cell DivisionDocument43 pages4 Cell DivisionPrem ShuklaNo ratings yet
- mitosis-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesmitosis-WPS OfficeSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- 4 Cell DivisionDocument24 pages4 Cell DivisionAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- 4 Cell DivisionDocument24 pages4 Cell DivisionAbhinav AnandNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell DivisionAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and Cell Division ProcessesDocument1 pageThe Cell Cycle and Cell Division ProcessesMarko MarićNo ratings yet
- Pathology of CellDocument7 pagesPathology of CellamanuelNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Cellular Reproduction - NewDocument28 pages2.3 Cellular Reproduction - New23 JP NURFAEZZAH FAZRAHNI AKMADISNo ratings yet
- Bio SciDocument3 pagesBio ScilowdicakesNo ratings yet
- B.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesB.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionLAZY I LEoPARDNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsuckamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document14 pagesChapter 5ingridvirginia2006No ratings yet
- Division CelularDocument10 pagesDivision CelularCarla PeñaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and CycleDocument16 pagesCell Division and CycleAnaJeanJumawidMarananNo ratings yet
- Midterm Performance Task 1Document3 pagesMidterm Performance Task 1Mary Grace E. CerioNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument111 pagesCell Cyclepreyaaa pascuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell CyclesDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Cell CyclesKylie VillafloresNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDocument11 pagesWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzNo ratings yet
- SZL B206 Principles of GeneticsDocument28 pagesSZL B206 Principles of Geneticsawuors249No ratings yet
- Tri-Fold Template-1Document2 pagesTri-Fold Template-1api-260947636No ratings yet
- New Microsoft PowerPoint PresentationDocument22 pagesNew Microsoft PowerPoint Presentationsaramaktoof2No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Part 1 (Mitosis)Document25 pagesCell Cycle Part 1 (Mitosis)Awais GulNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument15 pagesMitosisJorge MurieteNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions Table: A Visual GuideDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Functions Table: A Visual GuideJade Mark CapiñanesNo ratings yet
- CELL DIVISION-MitosisDocument28 pagesCELL DIVISION-MitosisAVINASH VARMANo ratings yet
- Bio 001 Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesBio 001 Cell DivisionKnick KnackNo ratings yet
- Mitosis DefinitionDocument19 pagesMitosis DefinitionMar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Stages and Phases ExplainedDocument43 pagesCell Cycle Stages and Phases ExplainedMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell DivisionDocument5 pages1.6 Cell DivisionmariamNo ratings yet
- Biosciweek6 11Document43 pagesBiosciweek6 11Jesalyn AbrinicaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cell DivisionDocument1 pageWhat Is Cell Divisiongenemari gonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell DivisionAlusine Sheriff TommyNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationDocument12 pages1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationMo_Bash1No ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: TranscriptDocument2 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: TranscriptKareem AghaNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument24 pagesMitosisbrieNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: Not To Be Confused With, ,, orDocument6 pagesMitosis: Not To Be Confused With, ,, orWacek4444No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument23 pagesCell DivisionInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Gcse BiologyDocument1 pageMitosis Gcse BiologycrainerNo ratings yet
- 0 BooksDocument20 pages0 Bookslaraib zahidNo ratings yet
- 8.2 The Cell CycleDocument23 pages8.2 The Cell Cycleapi-520057338No ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle and Cell Division: Understanding How Cells Replicate Through Mitosis and MeiosisDocument17 pagesThe Cell Cycle and Cell Division: Understanding How Cells Replicate Through Mitosis and MeiosisMaricris GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Reproduction ExplainedDocument29 pagesCell Division and Reproduction ExplainedEdel John SivaNo ratings yet
- Bio-101 Cell DivisionDocument42 pagesBio-101 Cell DivisionGabriel NdandaniNo ratings yet
- GenbioDocument3 pagesGenbioMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & Meiosis: DR Michael Oku Department of Anatomy University of CalabarDocument18 pagesMitosis & Meiosis: DR Michael Oku Department of Anatomy University of CalabarchidimmaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle - Mitosis and Meiosis PDFDocument43 pagesCell Cycle - Mitosis and Meiosis PDFVEENA DEVINo ratings yet
- Mitosis & MeiosisDocument28 pagesMitosis & MeiosisEma ColleteNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument12 pagesMITOSISLarissa PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and ReplicationDocument29 pagesCell Cycle and ReplicationaustineNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesCell DivisionJohn AlexNo ratings yet
- Phases of The Cell CycleDocument9 pagesPhases of The Cell CycleZia PhotostateNo ratings yet
- Mitosis - WikipediaDocument107 pagesMitosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work English 3 Quarter 1Document5 pagesBudget of Work English 3 Quarter 1resolution8878No ratings yet
- Early Biotechnological PracticeDocument2 pagesEarly Biotechnological Practiceresolution8878No ratings yet
- SIM Animals & Their Basic NeedsDocument10 pagesSIM Animals & Their Basic Needsresolution8878No ratings yet
- Inventory Management (Grp. 1 Me-503)Document48 pagesInventory Management (Grp. 1 Me-503)resolution8878No ratings yet
- Division Memo No. 168 S. 2016 ; Reiteration of DepEd Order No. 8 S. 2007 on the Revised Implementing Guidelines on the Operation and Management of School Canteens in Public Elementary and Secondary Schools — DeDocument32 pagesDivision Memo No. 168 S. 2016 ; Reiteration of DepEd Order No. 8 S. 2007 on the Revised Implementing Guidelines on the Operation and Management of School Canteens in Public Elementary and Secondary Schools — Deresolution8878No ratings yet
- EUKARYOTICSDocument4 pagesEUKARYOTICSresolution8878No ratings yet
- w040001 PDFDocument31 pagesw040001 PDFresolution8878No ratings yet
- Family Planning: Birth Control MethodsDocument5 pagesFamily Planning: Birth Control Methodsresolution8878No ratings yet
- Classrooms FINAL PDFDocument12 pagesClassrooms FINAL PDFmutton moonswamiNo ratings yet
- Distribution Requirement PlanningDocument17 pagesDistribution Requirement Planningresolution8878No ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Living OrganismDocument1 pageCharacteristics of A Living Organismresolution8878No ratings yet
- ch01 FOROUZAN DATA COMMUNICATIONDocument18 pagesch01 FOROUZAN DATA COMMUNICATIONresolution8878No ratings yet
- The Sound Absorption of Occupied Auditorium Seating by J.S.Bradley 1996Document6 pagesThe Sound Absorption of Occupied Auditorium Seating by J.S.Bradley 1996resolution8878No ratings yet
- ForouzanDocument16 pagesForouzanresolution8878No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Introduction To ProgrammingDocument36 pagesChapter 2 Introduction To Programmingresolution8878No ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Living OrganismDocument1 pageCharacteristics of A Living Organismresolution8878No ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine Systemresolution8878No ratings yet
- Line Coding Techniques for Communications SystemsDocument27 pagesLine Coding Techniques for Communications Systemsars679100% (1)
- Spermatogenesis, Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesSpermatogenesis, Menstrual Cycleresolution8878No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: Mitosis Is A Process of Cell Division Which Results in The Production of Two DaughterDocument2 pagesCell Cycle: Mitosis Is A Process of Cell Division Which Results in The Production of Two Daughterresolution8878No ratings yet
- ADXL3 XXDocument7 pagesADXL3 XXresolution8878No ratings yet
- DICTDocument2 pagesDICTresolution8878No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document27 pagesChapter 1resolution8878No ratings yet
- BJT Amplifier Configurations ExplainedDocument9 pagesBJT Amplifier Configurations Explainedresolution8878No ratings yet
- Differential Equations Guide: Classical Methods for Solving DEsDocument45 pagesDifferential Equations Guide: Classical Methods for Solving DEsresolution8878No ratings yet
- Differential Equations Guide: Classical Methods for Solving DEsDocument45 pagesDifferential Equations Guide: Classical Methods for Solving DEsresolution8878No ratings yet