Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Temperature Limits and Applications of Low Carbon Alloys
Uploaded by
Mark Anthony Dacullo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesThe document discusses temperature limits, properties, and applications of different types of carbon alloy metals. It provides the melting points of various metals, with the temperature limit for low carbon alloy being 1464°C. It also explains that austenitic stainless steel is the most weldable, ferritic has good ductility but low strength, and martensitic can be hardened through heat treatment. Finally, it states that low carbon alloy is used for cold formed parts, medium carbon for gears and shafts, and high carbon for structural applications requiring strength.
Original Description:
material
Original Title
Materials
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses temperature limits, properties, and applications of different types of carbon alloy metals. It provides the melting points of various metals, with the temperature limit for low carbon alloy being 1464°C. It also explains that austenitic stainless steel is the most weldable, ferritic has good ductility but low strength, and martensitic can be hardened through heat treatment. Finally, it states that low carbon alloy is used for cold formed parts, medium carbon for gears and shafts, and high carbon for structural applications requiring strength.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views3 pagesTemperature Limits and Applications of Low Carbon Alloys
Uploaded by
Mark Anthony DaculloThe document discusses temperature limits, properties, and applications of different types of carbon alloy metals. It provides the melting points of various metals, with the temperature limit for low carbon alloy being 1464°C. It also explains that austenitic stainless steel is the most weldable, ferritic has good ductility but low strength, and martensitic can be hardened through heat treatment. Finally, it states that low carbon alloy is used for cold formed parts, medium carbon for gears and shafts, and high carbon for structural applications requiring strength.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Dacullo, Mark Anthony V.
BSME-4C
January 18, 2016
1) Temperature limit for Low Carbon Alloy
Metal
Melting Point Celsius
Stainless Steel
Steel-High Carbon
Medium Carbon
Low Carbon
1363
1353
1427
1464
Melting Point
Fahrenheit
2550
2500
2600
2700
http://ganoksin.com/blog/cgmfindings/2012/10/03/metal-melting-points-guide-to-melting-metals/
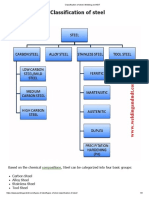
2) Difference between Martensitic, Austenitic and Ferritic
Austenitic
Austenitic stainless steels are the most weldable of the stainless. Austenitic is the most
popular stainless steel group. Austenitic stainless steels have a face-centered cubic structure.
Ferritic
Ferritic stainless steel consists of iron-chromium alloys with body-centered cubic crystal
structures. They can have good ductility and formability, but high-temperature strengths are
relatively poor when compared to austenitic grades. Other more highly alloyed steels low in C
and N are more costly, but are highly resistant to chlorides.
Martensitic
Martensitic stainless steels are similar in composition to the ferrite group, but contain a
balance of C and Ni vs. Cr and Mo; hence, austenite at high temperatures transforms to
martensite at low temperatures. Like ferrite, they also have a body-centered cubic crystal
structure in the hardened condition..
https://app.aws.org/wj/1998/11/kotecki/
3) Application for Low, High and Medium Carbon Alloy
Low Carbon Alloy Steel
Used for simple structural applications such as cold formed fasteners and bolts. It is often used
in the case hardened condition. Often employed in high volume screw machine parts
applications, such as shafts, spindles, pins, rods, and sprocket assemblies.
Medium Carbon Alloy Steel
Used in gears, shafts, axles, bolts, studs, and machine parts. Used for hand tools such as
screwdrivers, pliers, and similar items.
High Carbon Alloy Steel
Used in applications that require a good combination of strength and impact resistance, such as
gears, aircraft landing gear axles, and shafts for power transmissions. Typically used for aircraft
landing gear, power transmission gears and shafts, and other structural parts.
http://www.coburnmyers.com/materials-carbon-steel/
Orosco, Krista Nia P.
January 18, 2016
BSME-4C
1) What Is Temperature Limit For Low Carbon Alloy
Metal
Melting Point Celsius
Silver (pure)
Silver (sterling)
Stainless Steel
Steel-High Carbon
Medium Carbon
Low Carbon
961
893
1363
1353
1427
1464
Melting Point
Fahrenheit
1762
1640
2550
2500
2600
2700
http://ganoksin.com/blog/cgmfindings/2012/10/03/metal-melting-points-guide-to-melting-metals/
2) What is the difference between austenitic, ferritic and martensitic?
Ferritic These steels contain less than 0.10% carbon and are magnetic. The fact that
they cant be hardened via heat treatment and dont weld to a high standard limits the
use of these metals somewhat, but they are still suitable for a wide range of applications.
Austenitic This is the most common type of stainless steel, accounting for up to 70%
of all stainless steel production. Its versatility is in large part down to the fact that it can
be formed and welded with successful results.
Martensitic This type of steel shares some characteristics with ferritic, but boasts
higher levels of carbon, up to a full 1%. This means that they can be tempered and
hardened and are thus highly useful in situations where the strength of the steel is more
important than its resistance to corrosion.
http://www.brownmac.com/blog/what-is-stainless-steel
3) What are the application for Low, Medium, High Carbon
Low Carbon Alloy Steel - Used for applications such as cold headed fasteners and bolts.
Often employed in high volume screw machine parts applications, such as shafts,
spindles, pins, rods, sprocket assemblies, and an incredibly wide variety of component
parts.
Medium Carbon Alloy Steel - Used for crankshafts, couplings, and cold headed parts.
Used in gears, shafts, axles, bolts, studs, and machine parts.
High Carbon Alloy Steel - Used in structural applications such as aircraft engine mounts
and welded tubing applications. Typically used for aircraft landing gear, power
transmission gears and shafts, and other structural parts.
http://www.coburnmyers.com/materials-carbon-steel/
You might also like
- Ferrous Alloys GuideDocument16 pagesFerrous Alloys GuideGhaith MdljNo ratings yet
- Irjet V7i8884Document9 pagesIrjet V7i8884Mastram HatheshNo ratings yet
- Classification of Materials NotesDocument9 pagesClassification of Materials NotesJohn K KikwaiNo ratings yet
- Wrought Alloys for Orthodontic ApplicationsDocument33 pagesWrought Alloys for Orthodontic ApplicationsKanjiMasroorNo ratings yet
- Classification of Steel - Welding and NDTDocument3 pagesClassification of Steel - Welding and NDTAshif Iqubal100% (1)
- Technical Update How To Weld Maintain Stainless SteelDocument16 pagesTechnical Update How To Weld Maintain Stainless Steeloquintero99No ratings yet
- Ferrous Metals and Alloys: (26 Marks)Document10 pagesFerrous Metals and Alloys: (26 Marks)Abhinav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stain Less SteelDocument4 pagesStain Less Steelkihal zohirNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Austenitic and Ferritic Stainless Steels - The FabricatorDocument7 pagesAn Overview of Austenitic and Ferritic Stainless Steels - The FabricatorAhmadiBinAhmadNo ratings yet
- Stamping 101: Material Guidelines: Properties and Characteristics That Affect FormabilityDocument5 pagesStamping 101: Material Guidelines: Properties and Characteristics That Affect FormabilityDavid RodriguezNo ratings yet
- C-MN SteelsDocument48 pagesC-MN SteelsEri Dya FadliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Alloys (Ferrous)Document103 pagesEngineering Alloys (Ferrous)Sukhwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- 211 2aDocument33 pages211 2aMada ChohNo ratings yet
- Welding Martensitic Stainless SteelsDocument4 pagesWelding Martensitic Stainless SteelsBabar Manzoor GhauriNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument81 pagesStainless SteelRockey ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Engineering MaterialsDocument32 pagesEngineering MaterialsAdhanom G.No ratings yet
- Workshop ReportDocument8 pagesWorkshop ReportAloshNo ratings yet
- Stainles SteelDocument66 pagesStainles SteelHarshita DabasNo ratings yet
- Comsats University Islamabad, Lahore CampusDocument4 pagesComsats University Islamabad, Lahore CampusMaryam FatimaNo ratings yet
- Carbon steelDocument9 pagesCarbon steelArfanAliNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Manufacturing ProcessesDocument27 pagesStainless Steel Manufacturing Processesmaadhesh100% (1)
- Alloy CarbidesDocument2 pagesAlloy Carbidesmp87_ing100% (1)
- DESIGN 1 NotesDocument7 pagesDESIGN 1 NoteslordyNo ratings yet
- Ss Wire Properties / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument79 pagesSs Wire Properties / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Welding: A Subramanian/Lecturer/AWTI/ICFDocument62 pagesStainless Steel Welding: A Subramanian/Lecturer/AWTI/ICFaravindanNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Metals Phase DiagramDocument28 pagesFerrous Metals Phase DiagramDiyar NezarNo ratings yet
- Classifying Carbon Steels by Composition & Heat TreatmentDocument19 pagesClassifying Carbon Steels by Composition & Heat TreatmentManoj BallaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Steel Welding and NDTDocument4 pagesClassification of Steel Welding and NDTALFA ENGINEERING0% (1)
- Ferrous Alloys Classification and Types GuideDocument36 pagesFerrous Alloys Classification and Types GuideNipun HarshaNo ratings yet
- Lec 25Document32 pagesLec 25Sergio zihadNo ratings yet
- Alloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaDocument25 pagesAlloy Steels: Dr. Indika de SilvaChandima K PriyamalNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument24 pagesStainless SteelsmrutiNo ratings yet
- Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Alloys GuideDocument22 pagesFerrous and Non-Ferrous Alloys GuideHarsh V Ashok0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Finalok Ok PDFDocument63 pagesChapter 1 Finalok Ok PDFYasser RezkNo ratings yet
- Metals and Alloys & Heat Treatment of Steels 2,4Document82 pagesMetals and Alloys & Heat Treatment of Steels 2,4Vimukthi KumaraNo ratings yet
- Microstructure Differences Between Base Metal, Weld Metal and HAZDocument3 pagesMicrostructure Differences Between Base Metal, Weld Metal and HAZShaikhan Nadzemi100% (1)
- Carbon in SteelDocument8 pagesCarbon in SteelJanice FernandezNo ratings yet
- Identification of Basic Engineering Materials ExperimentDocument9 pagesIdentification of Basic Engineering Materials ExperimentSeth Aboagye JnrNo ratings yet
- ADI - A Perfect Engineering MaterialDocument12 pagesADI - A Perfect Engineering MaterialVS SaravananNo ratings yet
- MZ FS Unit - 1Document27 pagesMZ FS Unit - 1Jai KumarNo ratings yet
- Duplex & Super Duplex InformationDocument7 pagesDuplex & Super Duplex InformationrajeshNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument2 pagesStainless Steeltablo1234No ratings yet
- Anirudha Samant REG NO.-16BME1044 Slot - C1 Alloy SteelsDocument12 pagesAnirudha Samant REG NO.-16BME1044 Slot - C1 Alloy SteelsAnirudhaNo ratings yet
- INSDAG - Institute for Steel Development and GrowthDocument3 pagesINSDAG - Institute for Steel Development and GrowthJeeva Z FedricoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Stainless SteelsDocument5 pagesAn Introduction To Stainless SteelsMELVIN MAGBANUANo ratings yet
- Material Science: Prof. Satish V. KailasDocument12 pagesMaterial Science: Prof. Satish V. KailasAlvin SmithNo ratings yet
- Properties and applications of carbon and alloy steelsDocument12 pagesProperties and applications of carbon and alloy steelsananda narayananNo ratings yet
- AlloysDocument91 pagesAlloysNiccoloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Ferrous AlloysDocument31 pagesLecture 9 - Ferrous Alloysmahmoud foudaNo ratings yet
- Chap-10 Materials and Fabrication SelectionDocument51 pagesChap-10 Materials and Fabrication SelectionSuprio KamalNo ratings yet
- Sandvik Steel Hardening GuideDocument25 pagesSandvik Steel Hardening GuidejasonsivertsenNo ratings yet
- Stainless SteelDocument4 pagesStainless SteelByronNo ratings yet
- Steel ClassificationDocument3 pagesSteel Classificationasfarjee100% (1)
- Alloys in FPDDocument6 pagesAlloys in FPDharshita parasharNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel MaterialDocument9 pagesStainless Steel MaterialdeliNo ratings yet
- Materials 022312Document68 pagesMaterials 022312randz8No ratings yet
- SS COCrDocument101 pagesSS COCrsoujanyaNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Alloys GuideDocument56 pagesFerrous Alloys Guidejayakrishnan psNo ratings yet
- A Very Old Man With Enormous WingsDocument4 pagesA Very Old Man With Enormous WingsMark Anthony DaculloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1Document4 pagesChapter 1.1Mark Anthony DaculloNo ratings yet
- Interchangeable and Simultaneous Utilization of Peltier Module For Portable Heating and Cooling of Drinking WaterDocument5 pagesInterchangeable and Simultaneous Utilization of Peltier Module For Portable Heating and Cooling of Drinking WaterMark Anthony DaculloNo ratings yet
- Hi The TitleDocument1 pageHi The TitleMark Anthony DaculloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3Document5 pagesChapter 1.3Mark Anthony DaculloNo ratings yet
- Engineering FormulasDocument52 pagesEngineering FormulasMark Anthony DaculloNo ratings yet
- US Army Basic Electricity Part 1Document120 pagesUS Army Basic Electricity Part 1Space_Hulker100% (1)
- Plates & Coils - Jindal Steel & Power LTDDocument12 pagesPlates & Coils - Jindal Steel & Power LTDjindalsteelsNo ratings yet
- Friction Stir Welding and Processing IX PDFDocument315 pagesFriction Stir Welding and Processing IX PDFjaimin777No ratings yet
- Special Requirements For Hydrogen ServiceDocument5 pagesSpecial Requirements For Hydrogen ServiceMastram HatheshNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Specification GuideDocument29 pagesHeat Treatment Specification Guidefordsho95No ratings yet
- ASME B31.3 CalculatorDocument144 pagesASME B31.3 CalculatorLeoNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 - Annealing Test 2017Document4 pagesPractical 1 - Annealing Test 2017Yu HuiNo ratings yet
- BS 970 Chemical Composition TableDocument18 pagesBS 970 Chemical Composition Tablepm Starkeon100% (1)
- FULLTEXT01Document73 pagesFULLTEXT01hengkiirawan2008No ratings yet
- Coatings 11 00053Document15 pagesCoatings 11 00053Radu CristianNo ratings yet
- 08MAT1.5 Nickel and Nickel AlloysDocument9 pages08MAT1.5 Nickel and Nickel AlloysNdomaduNo ratings yet
- Technical Information No. 8 Datasheet ADIDocument2 pagesTechnical Information No. 8 Datasheet ADIAnonymous T02GVGzBNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Structural MaterialDocument30 pagesAircraft Structural MaterialRiggs Marasigan100% (2)
- EPMA Proceedings 2009 Sintering PDFDocument200 pagesEPMA Proceedings 2009 Sintering PDFEugene PaiNo ratings yet
- ASTM A213-A213M-05cDocument12 pagesASTM A213-A213M-05cNadhiraNo ratings yet
- Carbon SteelsDocument7 pagesCarbon SteelsRickle Vincent PilongoNo ratings yet
- Design and MFG of Hydraulic PressesDocument54 pagesDesign and MFG of Hydraulic Pressesraghumn100% (3)
- Basic Steel Selection Based On BS 970 en SeriesDocument8 pagesBasic Steel Selection Based On BS 970 en SeriesAmarendra Pendse100% (1)
- Summary of Intensive Quenching Processes Theory and Applications 17pDocument17 pagesSummary of Intensive Quenching Processes Theory and Applications 17pLi HojunNo ratings yet
- Hardenability: Amal C AbrahamDocument51 pagesHardenability: Amal C AbrahamAditya UNo ratings yet
- Review On Jominy Test and Determination of Effect of Alloying On Hardenability of Steel Using Jominy End Quench Test Copyright Ijaet1Document8 pagesReview On Jominy Test and Determination of Effect of Alloying On Hardenability of Steel Using Jominy End Quench Test Copyright Ijaet1enrico susantoNo ratings yet
- Astm A781 PDFDocument13 pagesAstm A781 PDFIslam Fawzy100% (6)
- Carbon steel impact test materialsDocument4 pagesCarbon steel impact test materialsnike_y2kNo ratings yet
- Pipes. Pressure and Wall Thickness Equations and Data For A Straight Pipe. ASME B31.1 and B31.3.odsDocument100 pagesPipes. Pressure and Wall Thickness Equations and Data For A Straight Pipe. ASME B31.1 and B31.3.odsNaufal FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Flexural Response of SS Reinforced Concrete BeamDocument15 pagesFlexural Response of SS Reinforced Concrete BeamShakil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7 - Heat TreatmentDocument4 pagesAssignment 7 - Heat TreatmentALaa YahiaNo ratings yet
- Certifica To Ac Credit Amen ToDocument12 pagesCertifica To Ac Credit Amen ToValerio RussoNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel Pipe and Tube SpecificationsDocument10 pagesStainless Steel Pipe and Tube SpecificationsDIBYENDU MONDALNo ratings yet
- Thyssen Krup Stainlesssteel - BrochurenewDocument23 pagesThyssen Krup Stainlesssteel - BrochurenewthomasNo ratings yet
- Astm e 407Document22 pagesAstm e 407Rafael ScatolinNo ratings yet
- Alloy 318Document2 pagesAlloy 318Branko FerenčakNo ratings yet